2.3 HIV AND AIDS.
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
WHAT DOES HIV STAND FOR?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
LABEL A DIAGRAM OF HIV?
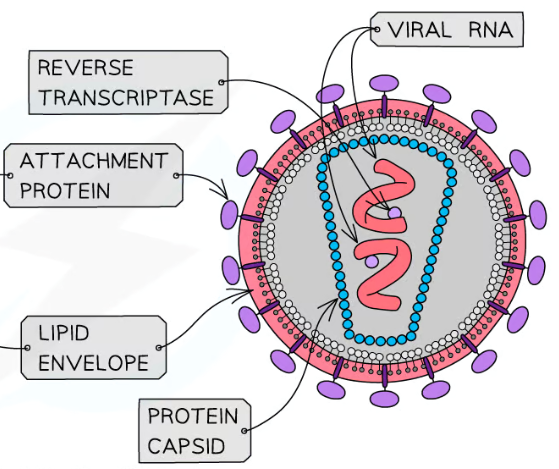
WHY IS HIV A RETROVIRUS?
It has RNA and reverse transcriptase.
HOW DOES HIV REPLICATE?
Attachment protein binds to complementary THcells
Capsid containing genetic material and reverse transcriptase is released into THcells.
RNA is used as a template to form a complementary double-stranded DNA strand.
This DNA is incorporated into the THcells’ own DNA.
Viral DNA is used to make new viral proteins.
These are assembled into new viruses inside the cells.
These now bud from the THcell.
They then infect other THcells.
Bilal ran to India per Ali’s bequest immediately.
WHAT DOES AIDS STAND FOR?
Acquired.
Immune.
Deficiency.
Syndrome.
WHAT IS AIDS?
The replication and release of HIV from THcells leads to destruction of cells and THcell numbers decrease :: less B cells and TCcells are activated.
:: immune system is reduced :: more susceptible to infections and cancer.
WHAT ARE AIDS SYMPTOMS?
Fever.
Tiredness.
Diarrhea.
Headache.
Rash,
Swollen lymph nodes.
Weight loss.
Infection of lungs/intestines/brain/eyes.
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT FOR HIV/AIDS?
High mutation rate.
Combination of antiretroviral drugs.
WHY CAN’T ANTIBIOTICS BE USED TO TREAT HIV?
Viruses don’t have the structure that antibodies target e.g. cell wall, ribosomes.
Different metabolism.
Viruses infect inside cells, ab cannot get in without damaging cells.