Housing Design and Considerations 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Rubber Flooring
Comfortable for cattle, reduces mechanical foot stress.
Cubicle Occupancy Rates
Rubber mattress 89%, deep bedding sand 79%.
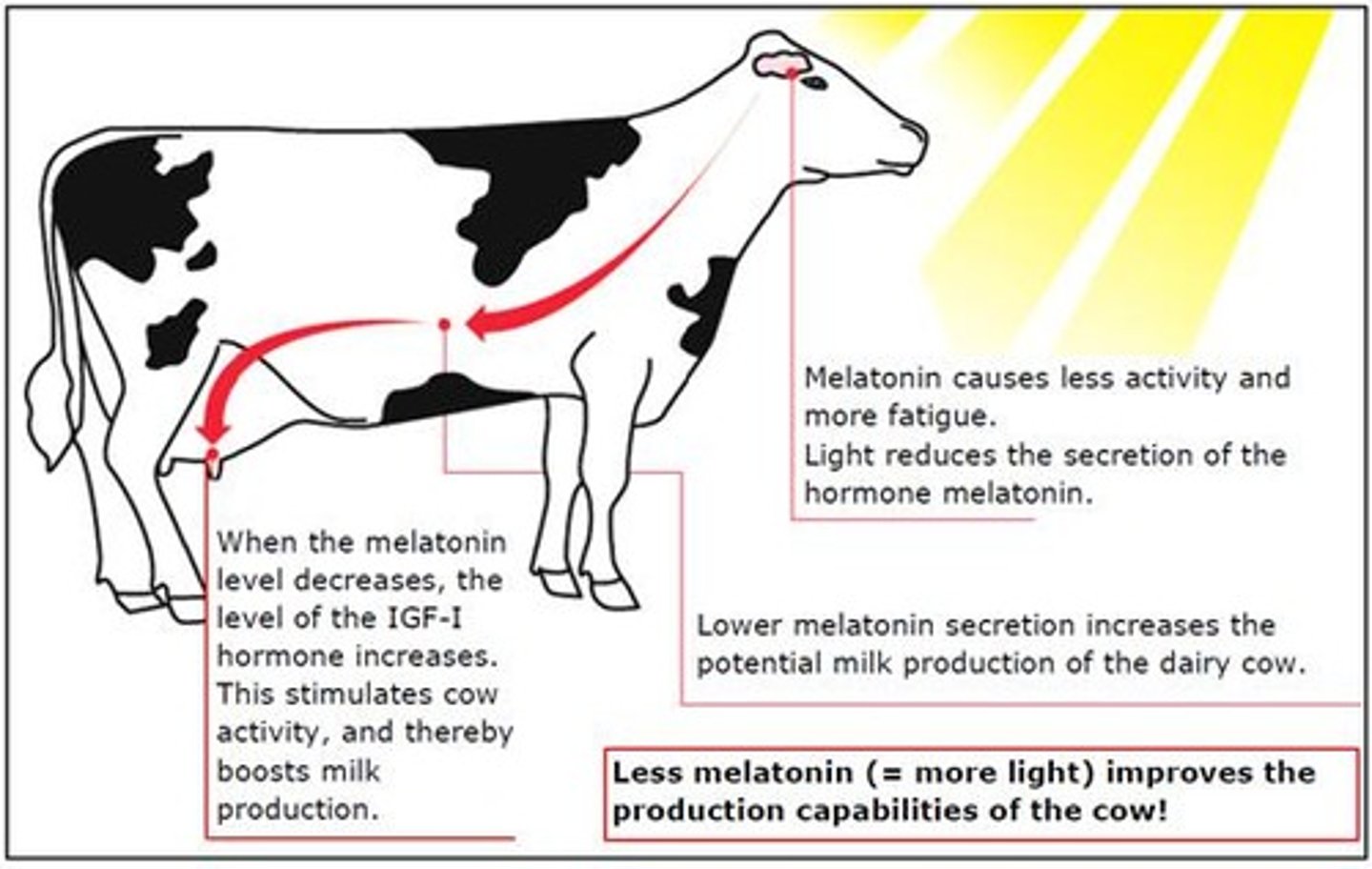
Lighting Lux for Cattle
Recommended range is 160-200 lux for visibility.
Impact of Shadows
Cattle panic in shadows, affecting feeding and hydration.
Red Lights
Aid in cattle management and access to resources.
Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)
Toxic gas from slurry, can cause death if inhaled.
Symptoms of H2S Exposure
Smells like rotten eggs, can cause loss of smell.
Slurry Storage Risks
Agitation releases H2S, posing health hazards.
Sheep Housing Guidelines
Access to dry bedding and ventilation is essential.
Liver Fluke Risk
Concern for sheep grazing in damp conditions.
Environmental Impact on Sheep
Weather affects sheep housing decisions and welfare.
Red Tractor Guidelines
Standards for sheep housing in barns or pens.
Multi-functional Environments
Sheep often housed during extreme weather or lambing.
Pig Housing Considerations
Group dynamics and space allocation are crucial.
Flooring in Pig Housing
Slat flooring and gap widths affect animal welfare.
Cattle Thermal Comfort
Rubber flooring enhances thermal comfort when lying down.
Preference Testing in Cattle
Evaluates material preferences for cubicle comfort.
Cow Confidence
Improved by comfortable flooring, aids movement.
Health Risks in Close Housing
Increased disease spread and welfare concerns.
Access to Resources
Water, feed, and lying areas are essential for livestock.
Pen Shape and Layout
Affects ease of management in pig housing.
Cattle Resting Needs
Constant light exposure can stress cattle.
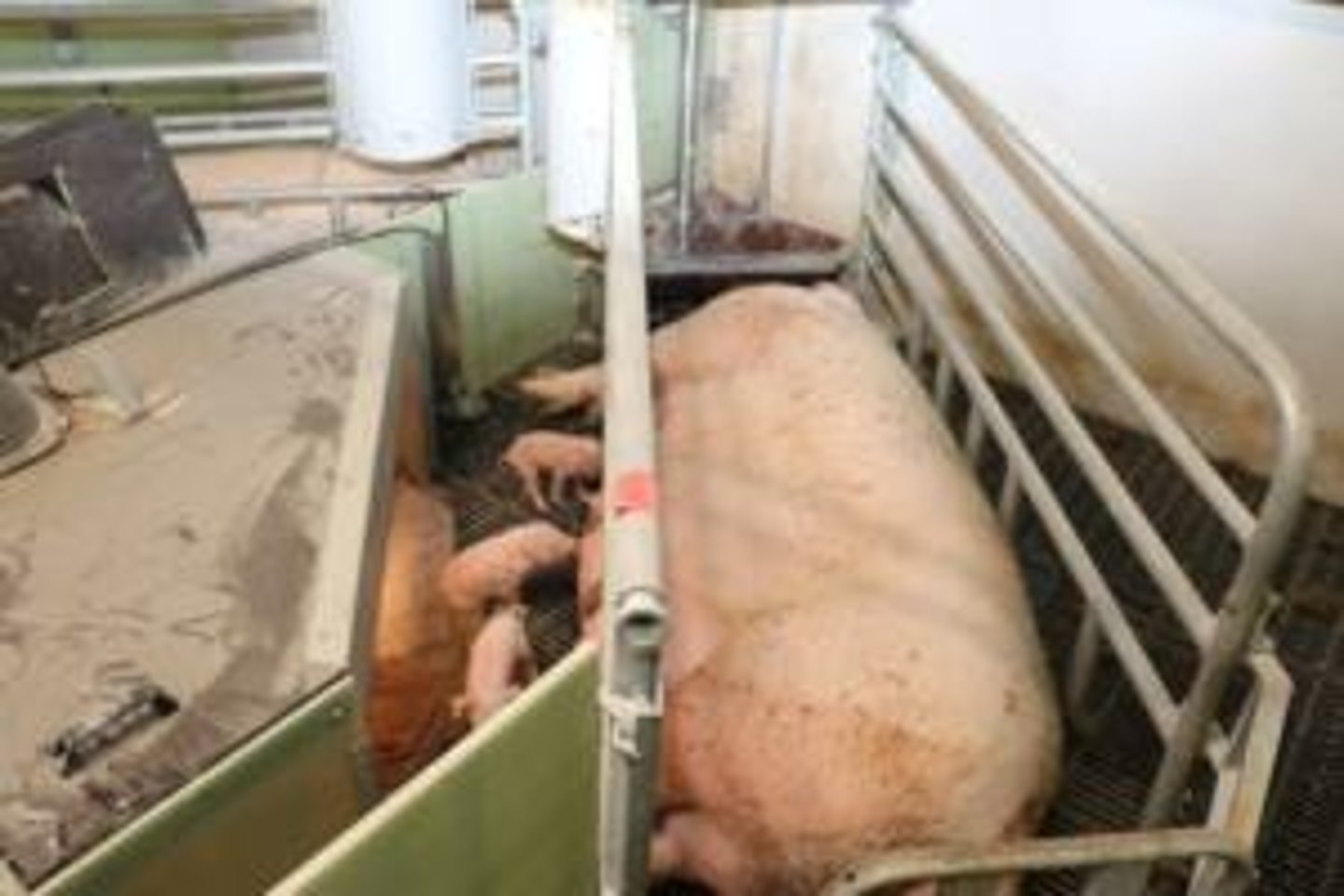
Social Hierarchy
Space divisions facilitate social stability among pigs.
Farrowing Crates
Reduce piglet mortality by preventing crushing.

Temperature Regulation
Limited ability to control body temperature in pigs.
Weaner Housing
Housing options vary for pigs at different life stages.
Environmental Enrichment
Varies across housing types, affects pig welfare.
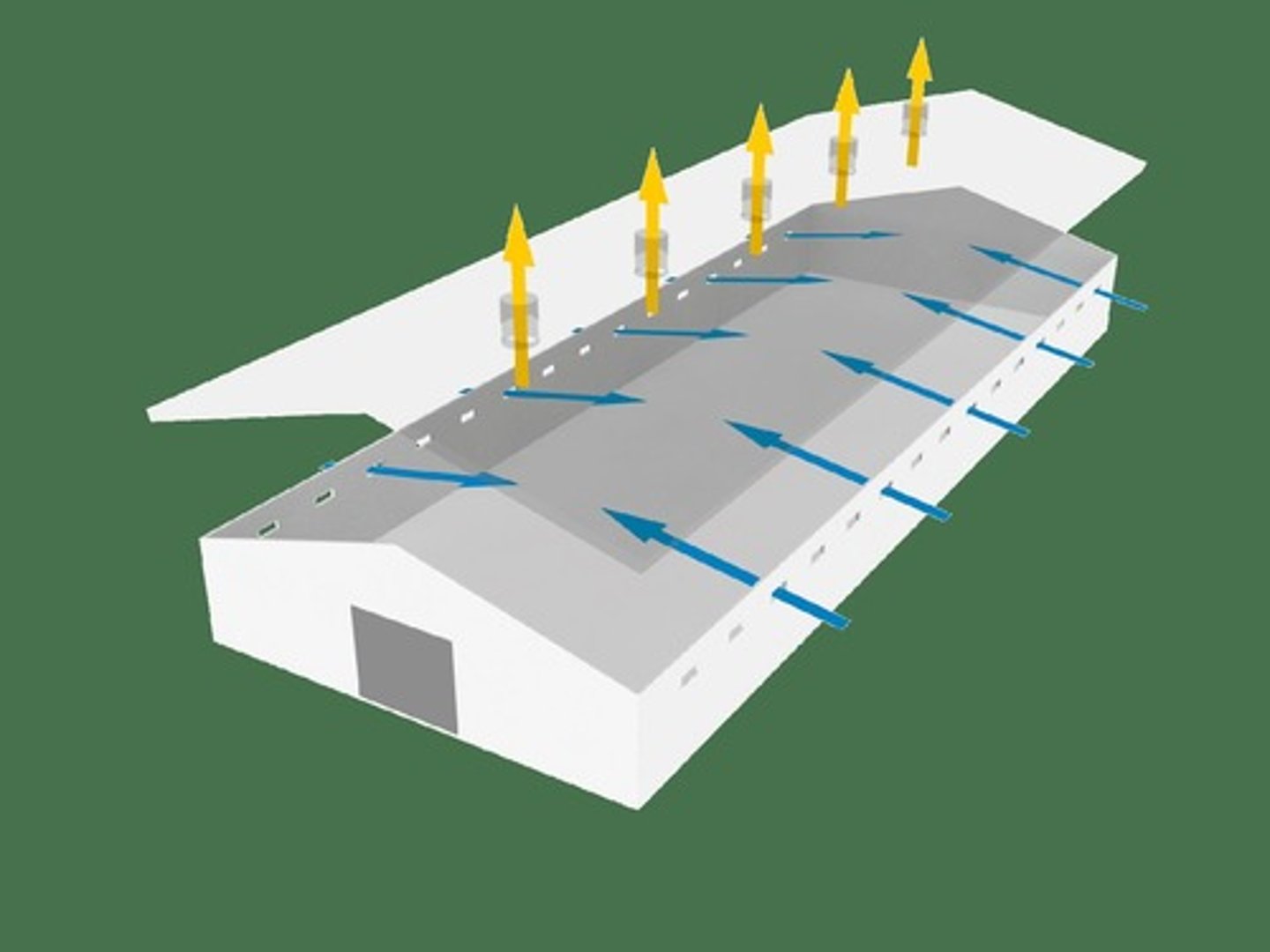
Ventilation Importance
Removes stale air, reduces respiratory disease risks.
Nutrient Requirements
Increase during lactation, influenced by temperature.
Voluntary Feed Intake
Declines by 170g/day per 1°C rise above 16°C.
Outdoor Housing Considerations
Climatic conditions affect pig welfare outdoors.
Farrowing Paddocks
Avoid sloping ground for better piglet safety.
Water Access
Clean water must be available, not in wallows.
Sow Density
10 sows per acre for gestation, 6-10 for farrowing.
Crop Rotations
Pigs integrate well into crop rotation systems.
Heat Loss Prevention
Critical for piglets due to large surface area.
Housing Comfort
Solid floors offer comfort; slatted floors are hygienic.
Consumer Views
Public perception of farrowing crates is generally negative.
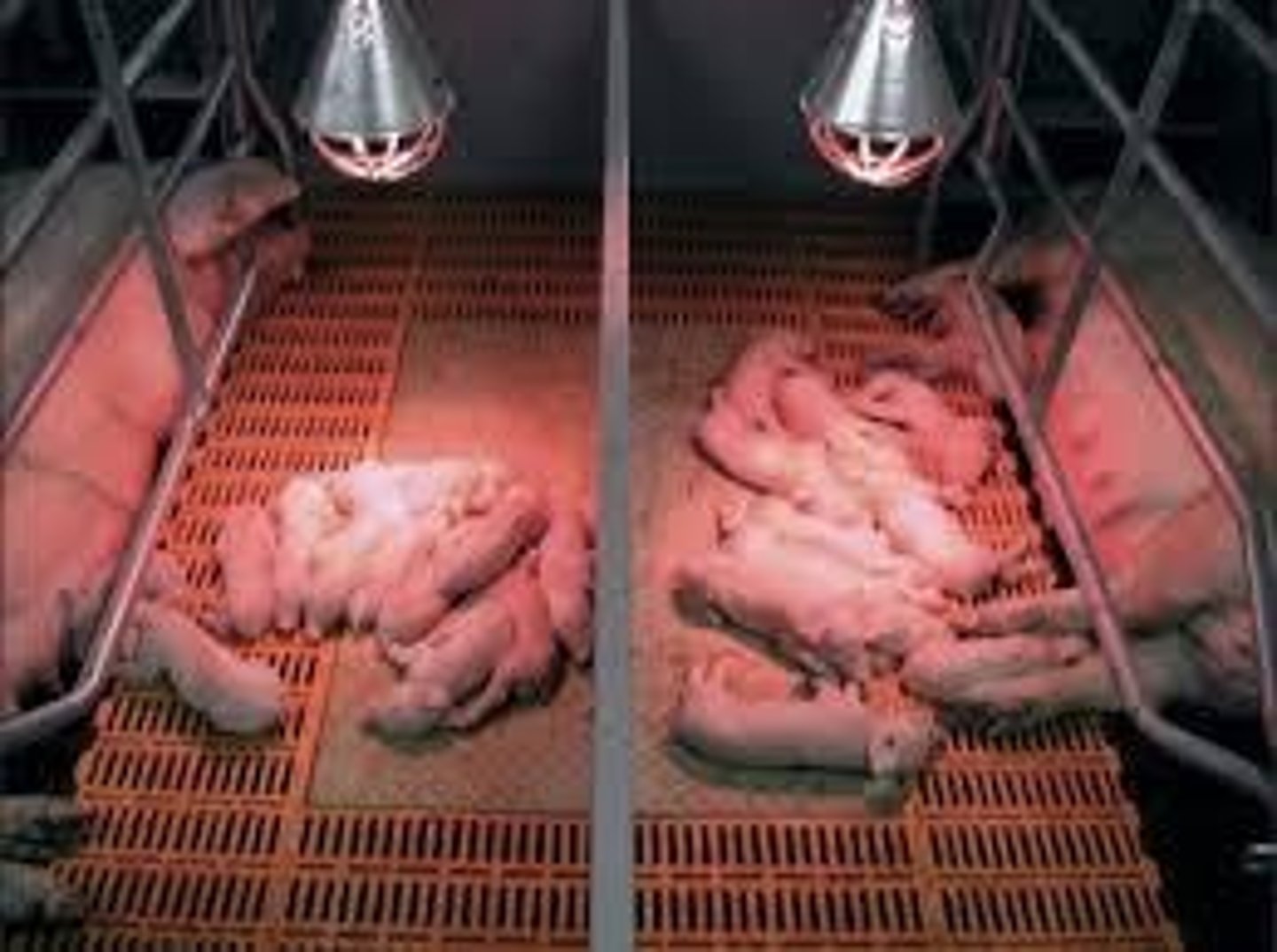
Creep Area
Covered area for piglets to maintain warmth.

Health Checks
Individual sows may need segregation for health monitoring.
Mixing Pens
Facilitates movement and social interactions among pigs.
Piglet Exploration
Heat mats allow piglets to explore safely.
Climatic Variation
Soil type and topography affect outdoor housing.
Crop Rotation
Systematic planting of different crops sequentially.
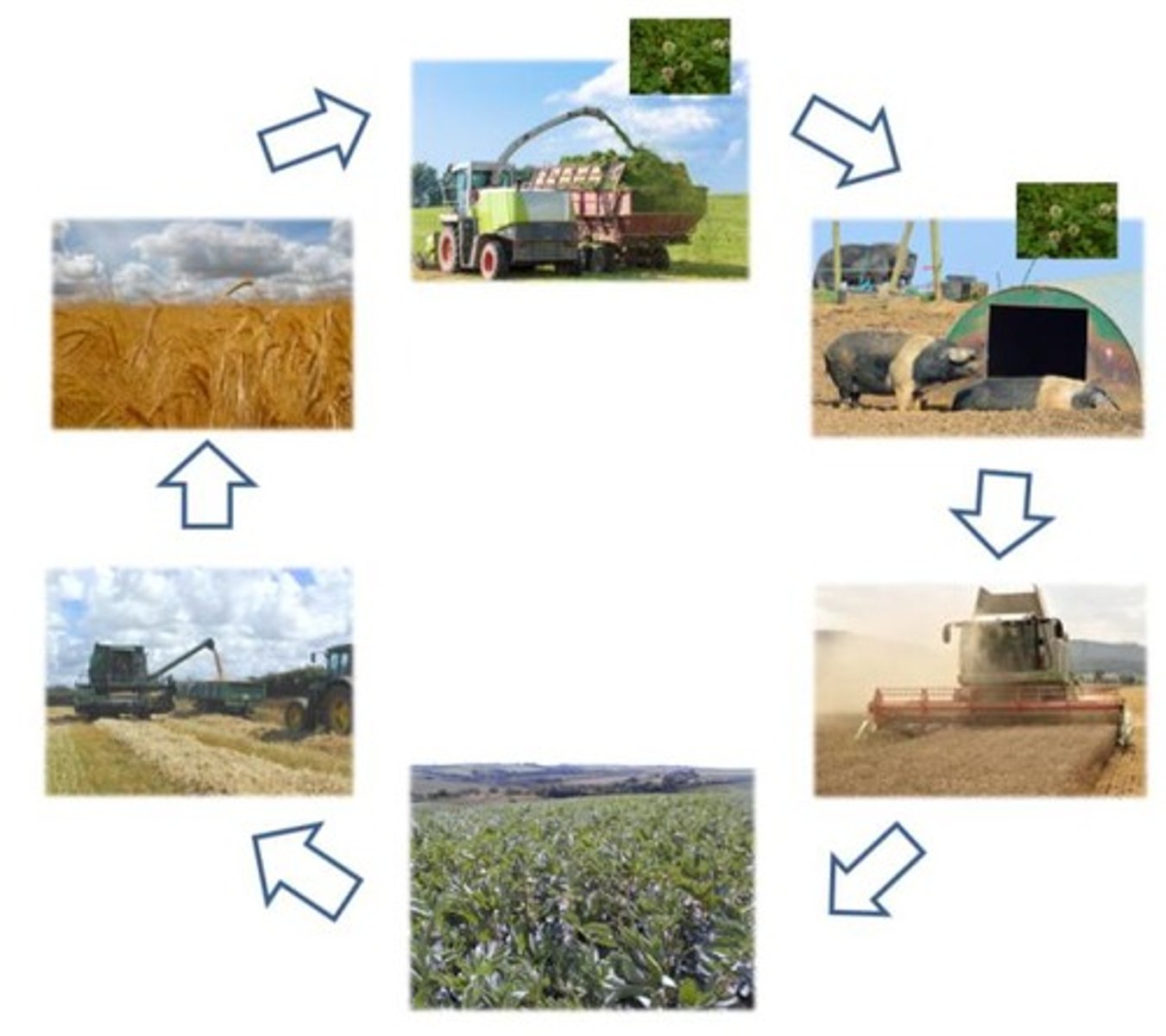

Grass-Clover Pasture
Pasture mix for pigs, enhances soil fertility.

Cereal Crop
Grain-producing plants, e.g., wheat, barley.
Legume Crop
Plants like beans, enrich soil nitrogen.
Loose Housing Systems
Housing allowing pigs to move freely.
Colostrum Intake
Initial milk intake critical for piglet immunity.
Space Allowance
Minimum space of 2.25 sq/m per sow.
Lameness Prevalence
Higher in group-housed sows than individual stalls.
Nose-to-Nose Contact
Social interaction in group housing, potential pathogen spread.
Poultry Housing
Structures designed to protect birds from elements.
Vermin Concerns
Pests that threaten poultry health and food.
Water and Food Accessibility
Birds should access essentials within 3m.

Dark Areas
Should be limited to nesting boxes only.
Free Range Housing
Chickens have outdoor access, perceived as humane.

Enriched Cages
Cages providing more space and stimulation for birds.
Ammonia Release
From litter, causes respiratory and skin issues.
Lighting Importance
Stimulates egg production and growth in poultry.
Pecking Order
Social hierarchy in poultry flocks, influences behavior.
Feather Pecking
Aggressive behavior linked to housing and stress.
Air Quality Deterioration
Ammonia from litter reduces bird productivity.
Welfare-friendly Systems
Housing types that improve animal welfare despite challenges.
Health Impacts
Conditions affecting poultry welfare and productivity.