Chemistry Unit 3 Test Flashcards
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
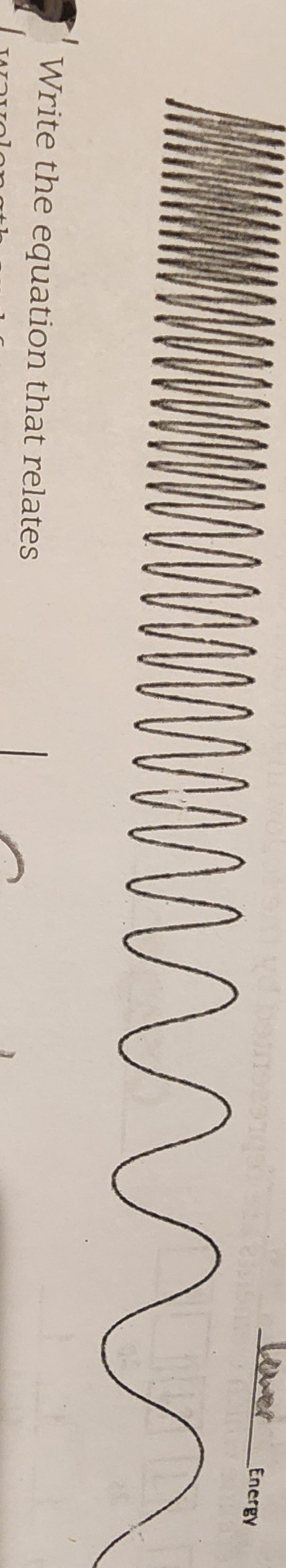
What happens in the left part of the spectrum?
Shorter wavelength
Higher frequency
Higher energy
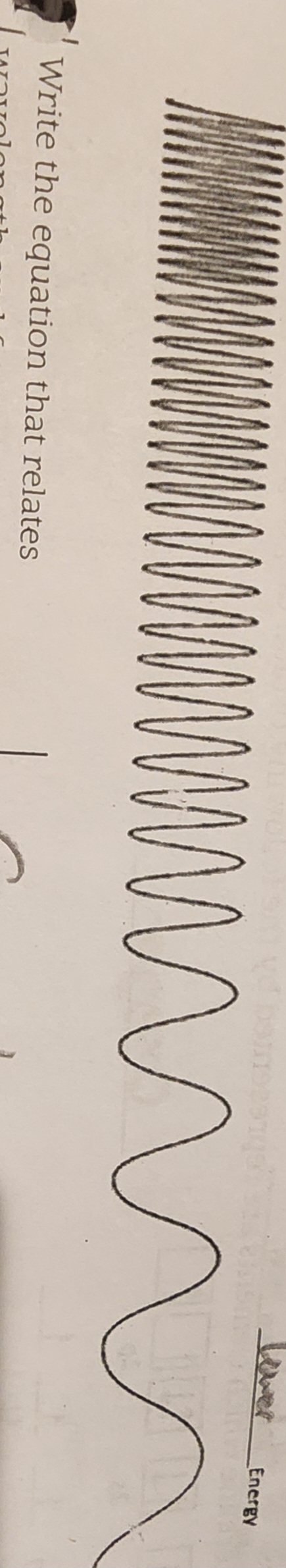
What happens towards the right of the spectrum?
Longer wavelength
Lower frequency
Lower energy
What do the symbols mean in the equation of wavelength and frequency?
C=ƴv
C= Speed of light
ƴ= Wavelength
V= Frequency
What electromagentic radiation has high/medium/low frequency?
High= Gamma
Medium= Visible
Low= Radio
How can atoms emit light?
Atoms emit light when an electron jumps from a higher energy level to lower.
The color depends on distance change which determines frequency.
What is an atomic emission spectra?
The pattern of lines that form when light passes through a prism to separate it into its component wavelengths.
Why are the atomic emission spectrums of every element different?
Because all elements have a unique number and arrangement of electrons.
What is the pattern with valence electrons for the main 8 groups of elements?
Main group number = number of valence electrons (except Helium)
What are valence electrons?
The number of electrons located in an element’s outermost shell.
Atomic radius:
The size of a neutral atom
Ionic radius:
The size of an ion
Electronegativity:
The ability of an atom to attract electrons
Ionization Energy:
The energy required to remove an electron
Melting and Boiling Point:
The temperature at which an element changes state
Why does atomic radius decrease as you move to the right of a period?
Across a period more protons are located in the nucleus as you move from left to right, which pulls electrons in closer towards it
Another name for full outer shell of an element’s atom?
Full valence shell
Most reactive metal group in the P.T
Alkali Metals
Most reactive nonmetal group in the P.T
Halogens
Properties of Transitional Metals:
Called the d-block (center of P.T)
Can have 1-4 valence electrons
Not part of the main group
Where does reactivity increase with metals on the Periodic Table?
Periods: ←
Groups: ↓
Where does reactivity increase with nonmetals on the Periodic Table?
Periods: →
Groups: ↑
Elements in the same group:
Have similiar physical and chemical properties
The periodic table is designed to:
Group elements with similar properties together
Periodic Law:
When elements are arranged in increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties
Metals and properties:
Form allays; mixed with other metals
Malleable
Good conductors of heat and electricity
Ductile
Lustrous
Nonmetals and properties:
Not malleable or ductile
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Solid, liquid, or gas at room temp
Brittle