Practical #3 Study Guide Bio 105 Lab
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
One parent producing offspring that are identical to the parent
Pros of Asexual Reproduction
simple procedure
does not need as much energy, mobility, time, or a mate like sexual reproduction
Cons of Asexual Reproduction
makes identical offspring
identical offspring decreases diversity, chances of adaptation and evolution, passes on mutations, and can lead to overcrowding
Asexual Reproduction Example: Budding
A parent makes copes of its genetic material within new cells and grows small “buds” from its body
These “buds” enlarge little by little until a new organism is fully formed
What are examples of Budding?
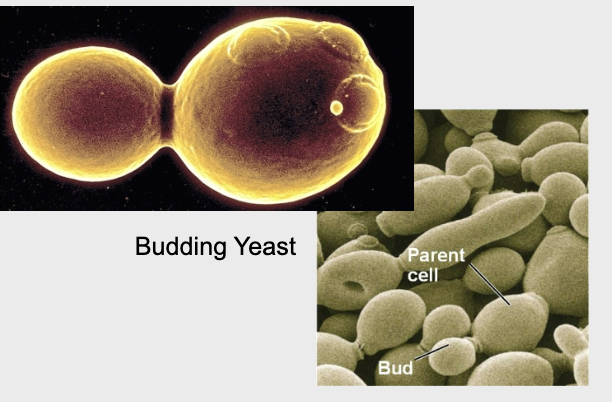
Unicellular yeast
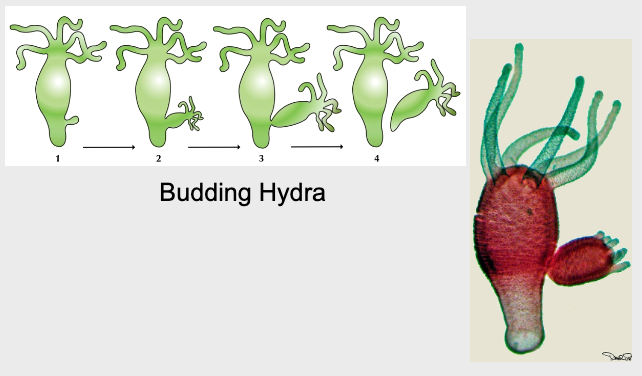
Multicellular hydra
Budding in Yeast
Budding in Hydra
Asexual Reproduction Example: Spore Formation
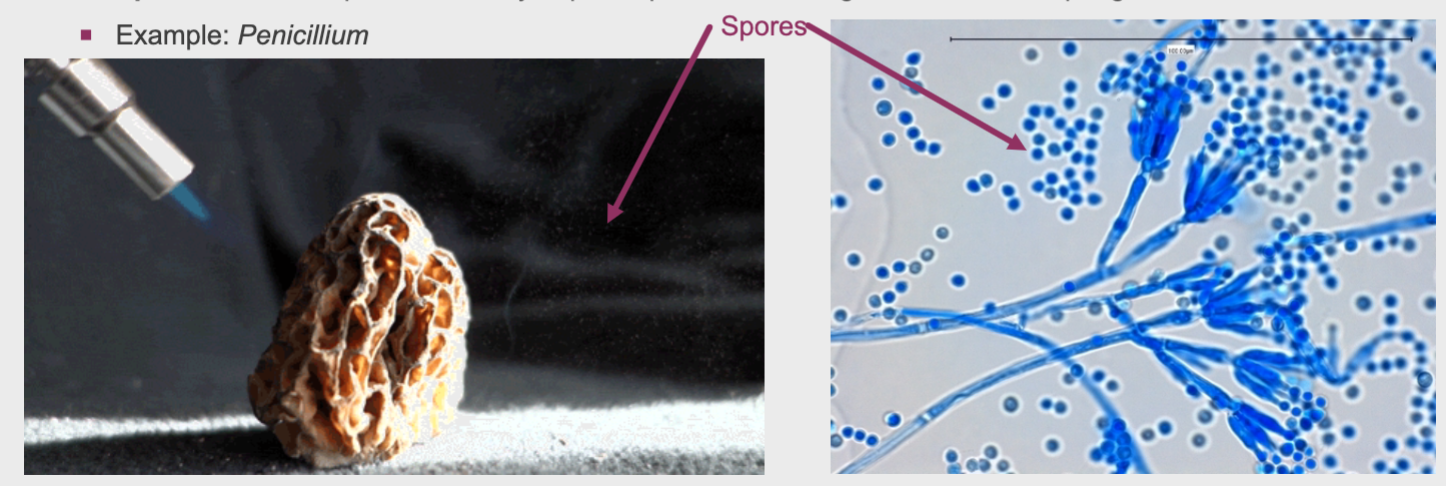
Produces many haploid spores that germinate into offspring
What is an example of spore formation
Penicillium
Spore formation in Penicillium
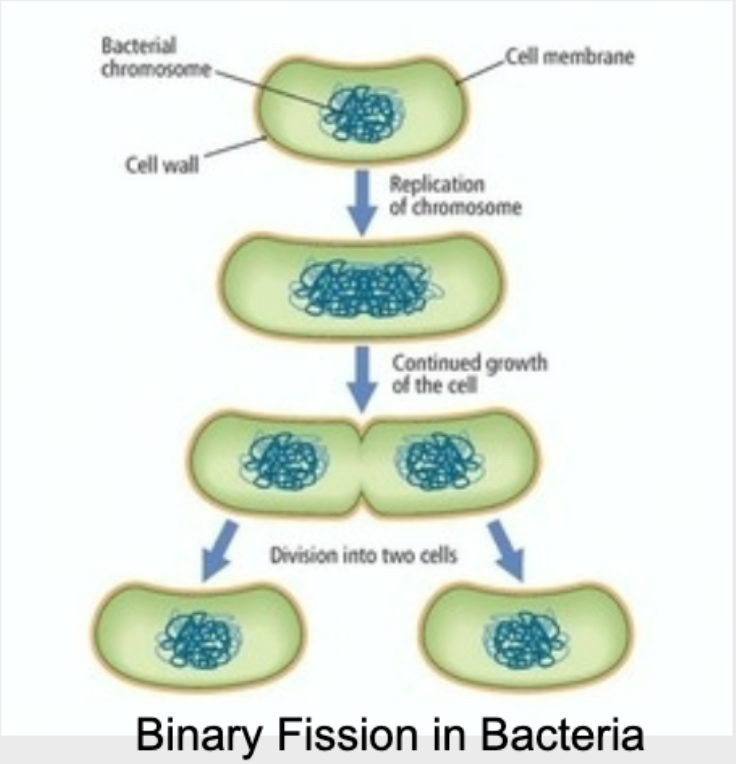
Asexual Reproduction Example: Binary Fission
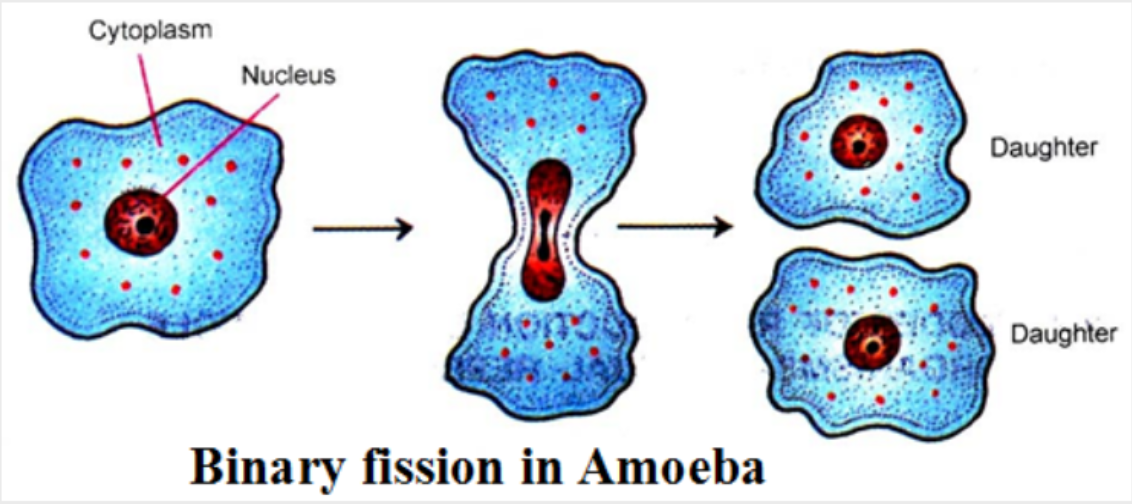
The parent cell copies its chromosome, elongates, and then divides into two equal parts, creating two offspring
Examples of Binary Fission
Bacteria (such as E. coli)
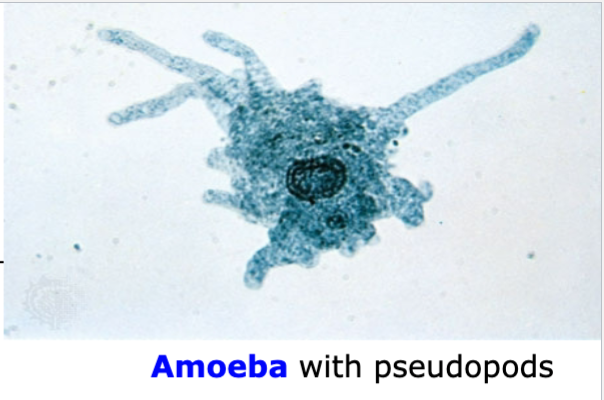
Amoeba
Binary Fission in Amoeba
Binary Fission in Bacteria
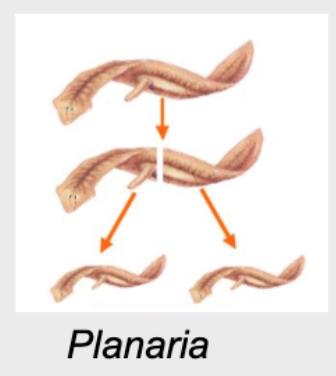
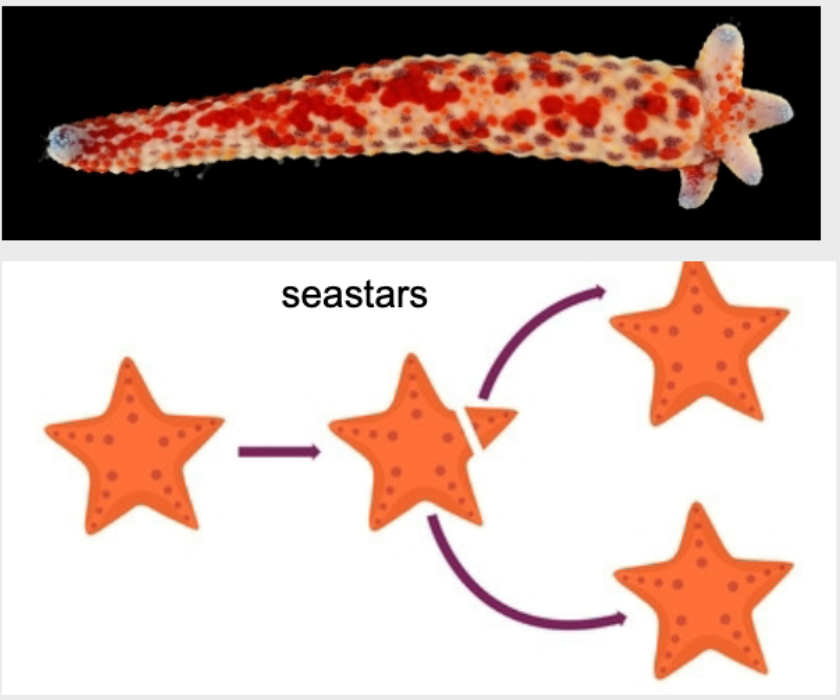
Asexual Reproduction Example: Fragmentation
The breaking off of a piece of a multicellular organism
Each broken piece will generate enough new cells to make an entirely new organism
Examples of Fragmentation
Starfish (seastars)
Planaria
Fragmentation in Planaria
Fragmentation in Starfish/Seastars
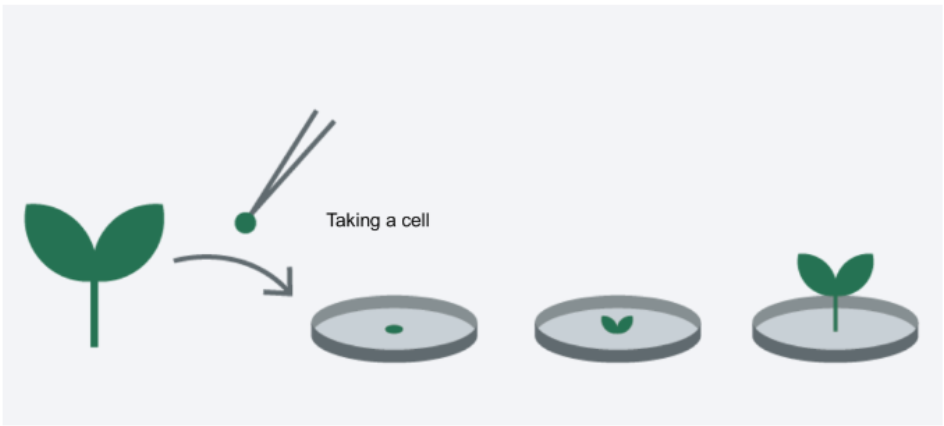
Asexual Reproduction Example: Plant Tissue Culture (laboratory technique)
Scientists are able produce multiple offspring from a small portion of the parent plant
Pros/Uses of Plant Tissue Culture
Increase the food supply
Duplicate new varieties of plants
Duplicate disease-free or pest-resistant plants
Preserve endangered plants
Preserve crops that are seedless
Make plant metabolites for use in medicine
Lumber
Plant Tissue Culture in Test Tubes (Asexual Reproduction)

Plant Tissue Culture Process (Asexual Reproduction)
Sexual Reproduction
Involves two parents contributing genetic material to produce unique offspring
Major steps of sexual reproduction
Fertilization
Meiosis
Fertilization in Sexual Reproduction
fusion of 2 haploid (n) individuals resulting in a diploid (2n) zygote
Meiosis in Sexual Reproduction
chromosomal division of diploid (2n) zygote resulting in haploid (n)
Pro of Sexual Reproduction
This form of reproduction produces genetically unique individuals which promotes survival of a population by increasing genetic diversity
Cons of Sexual Reproduction
Process requires two parents
A lot of time and energy
Does not produce as much offspring as asexual reproduction
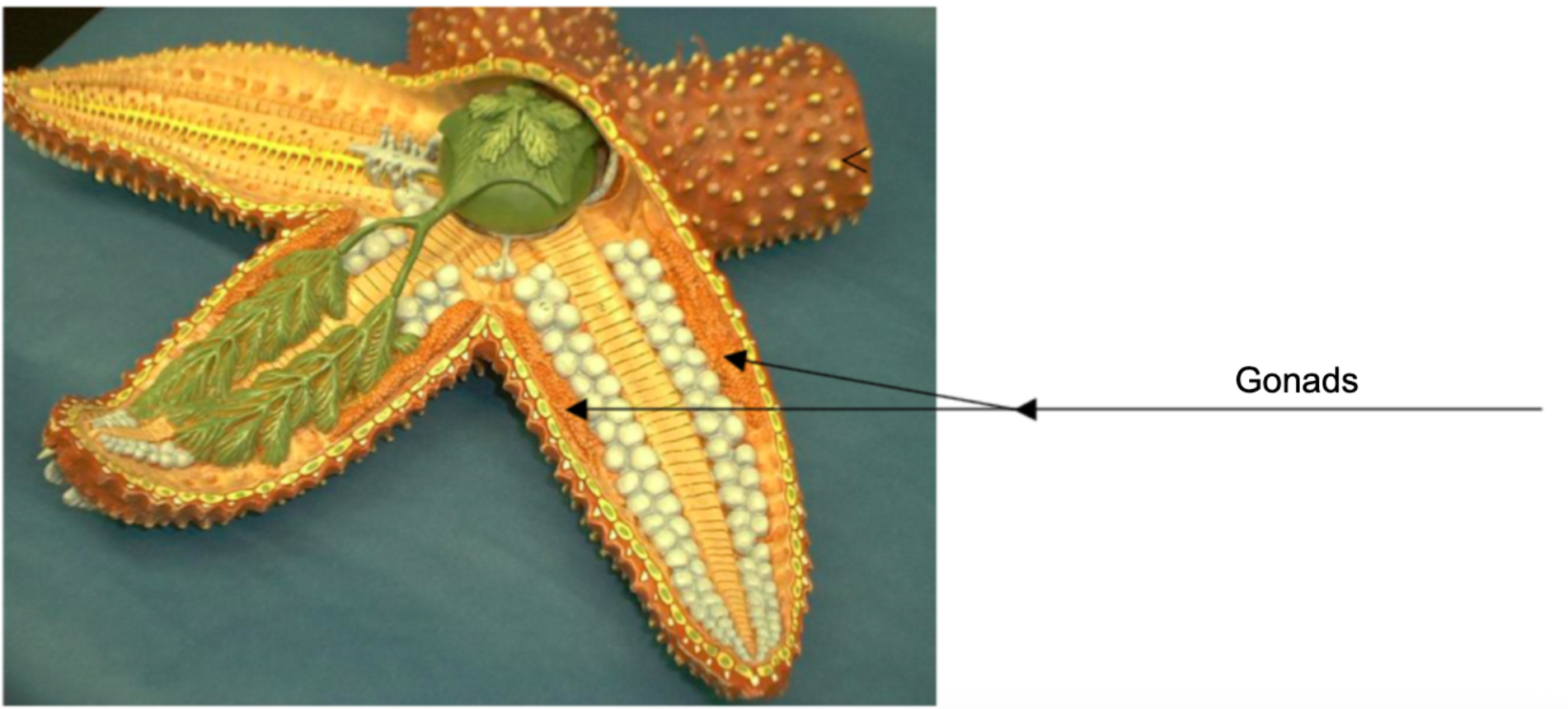
Gonads on Sea Star Model (Sexual Reproductive Structure)
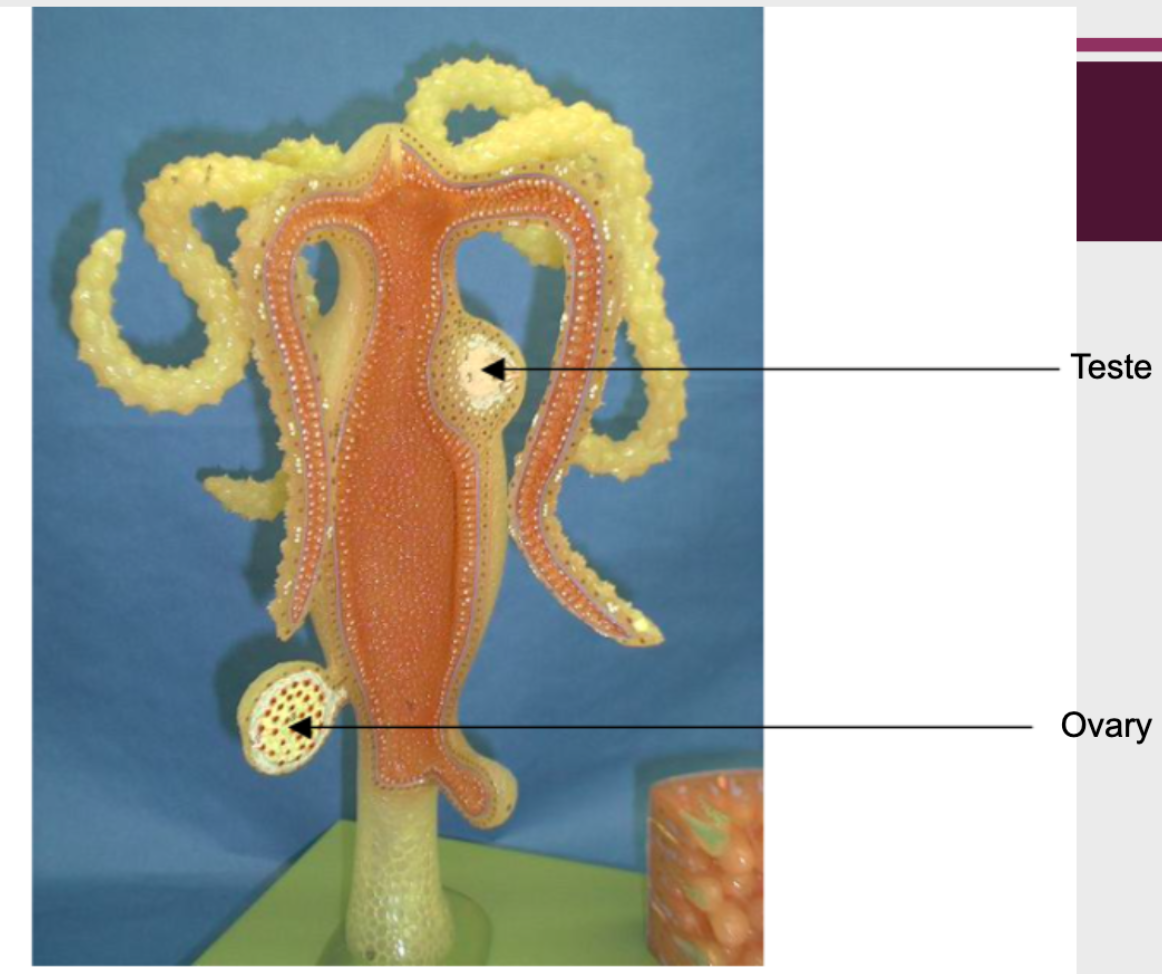
Teste and Ovary on Hydra Model (Sexual Reproductive Structure)
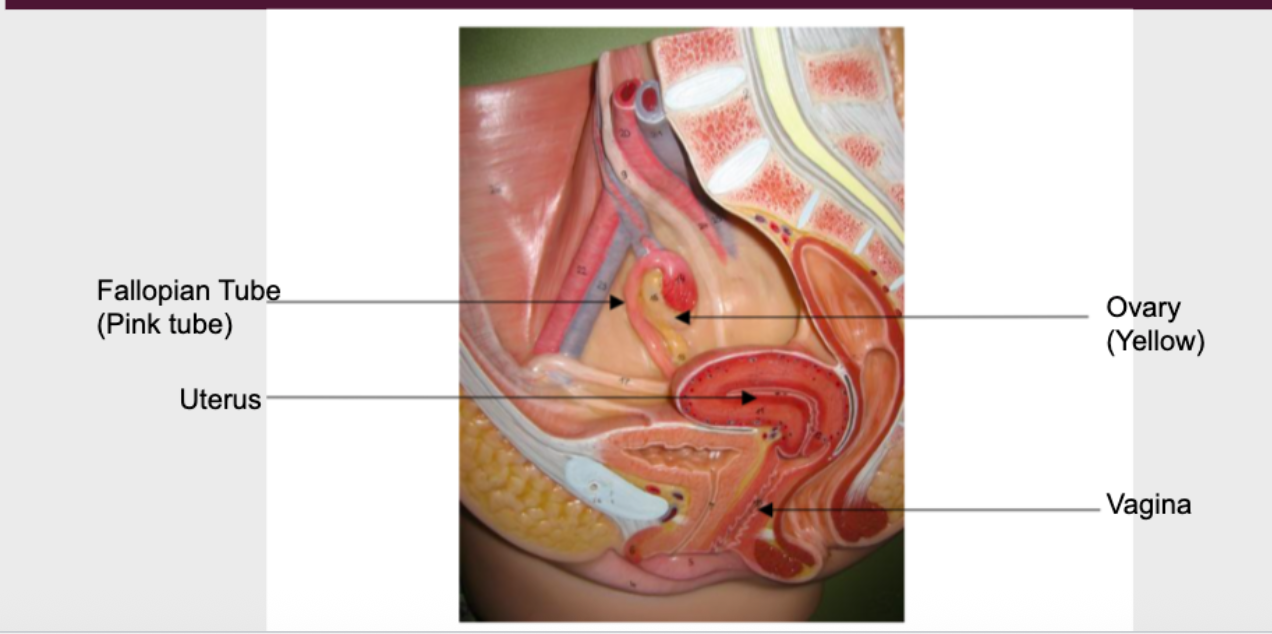
Female Reproductive System (Sexual Reproductive Structure)
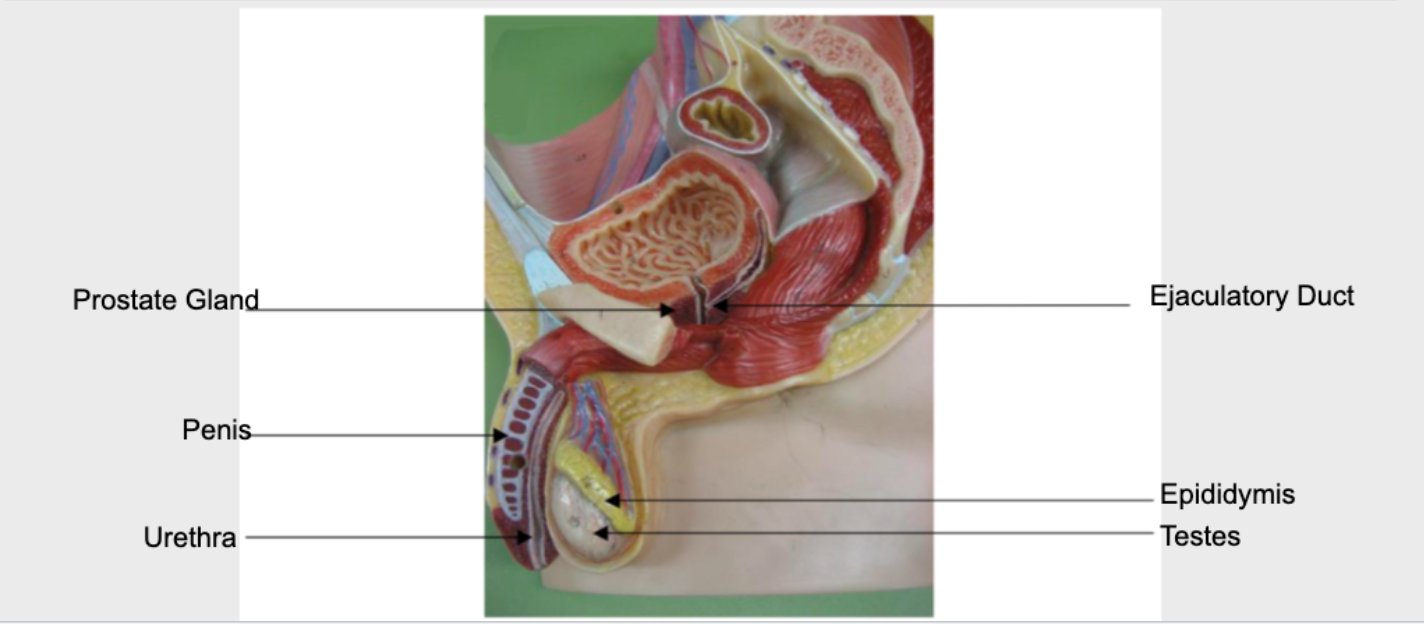
Male Reproductive System (Sexual Reproductive Structure)
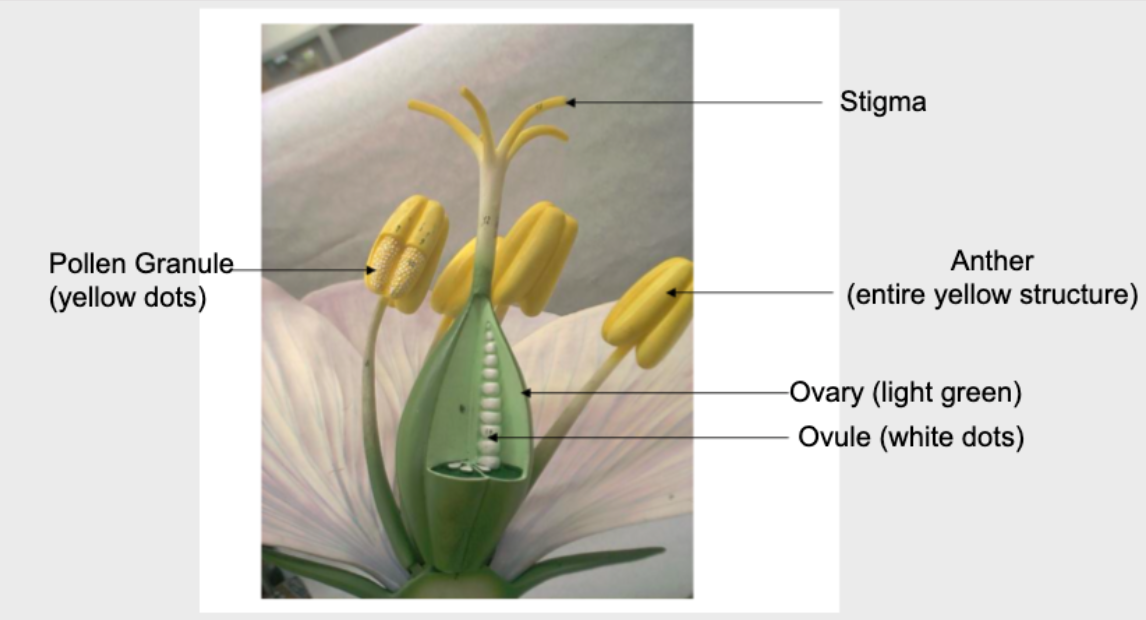
Flower, Fruits, and Seeds Model of Parts (Sexual Reproductive Structure)
Tapeworm Hermaphrodite Model of Parts (Sexual Reproductive Structure)

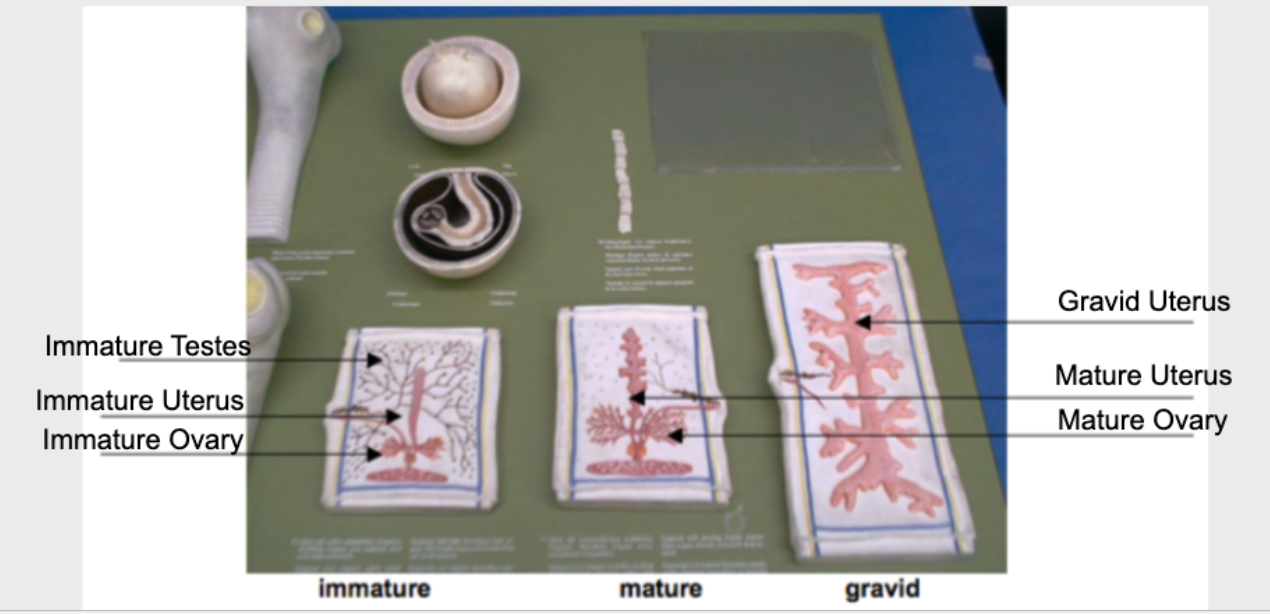
Premature Hermaphrodite Models and Parts (Sexual Reproductive Structures)

Cloning (Reproductive Technology)
somatic cell nucleus implantation into an anucleate egg
Result: identical offfspring
Pros of Cloning
Making antibiotics
Making insulin
Improving recovery time
Cons of Cloning
Reduced lifespan
Unethical to some — eugenics
Time-consuming
low success rate in complex organisms
In-Vitro Fertilization (Reproductive Technology)
egg and sperm combined on a Petri dish
Result: Unique offspring
Pros of In-Vitro Fertilization
Genetic diversity
Treat infertility
People in a high risk profession can have children if they pass away prematurely (ex: soldiers, policemen, etc.)
Cons of In-Vitro Fertilization
Multiple pregnancy
Expensive
Human Genome Project Benefits
The Human Genome Project mapped all human genes, helping scientists understand how DNA controls traits
It allows easier identification of Mendelian genetic disorders and improves DNA analysis in labs, making genetic studies more accurate and faster
Gene Testing in Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project enabled precise gene testing by identifying locations of genes linked to Mendelian traits.
This helps detect genetic mutations causing inherited disorders and supports DNA analysis in the lab to study how traits are passed down
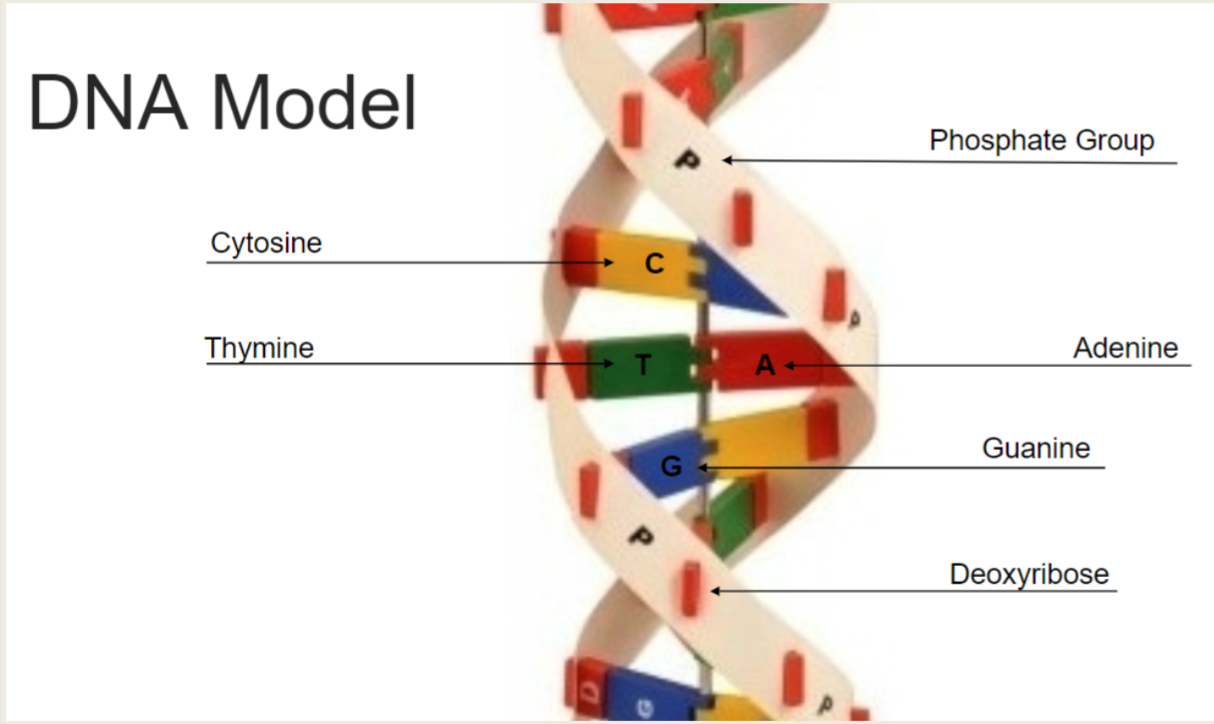
Complementary Nitrogenous Base Pairing in DNA (Pairs)
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G)
Complementary Nitrogenous Base Pairing Definition
The specific way that nitrogenous bases in DNA pair up with each other to form the rungs of the DNA ladder
Complementary Nitrogenous Base Pairing Explanation in relation to bonds
The pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds, ensuring accurate DNA replication and proper genetic information transfer
DNA Model
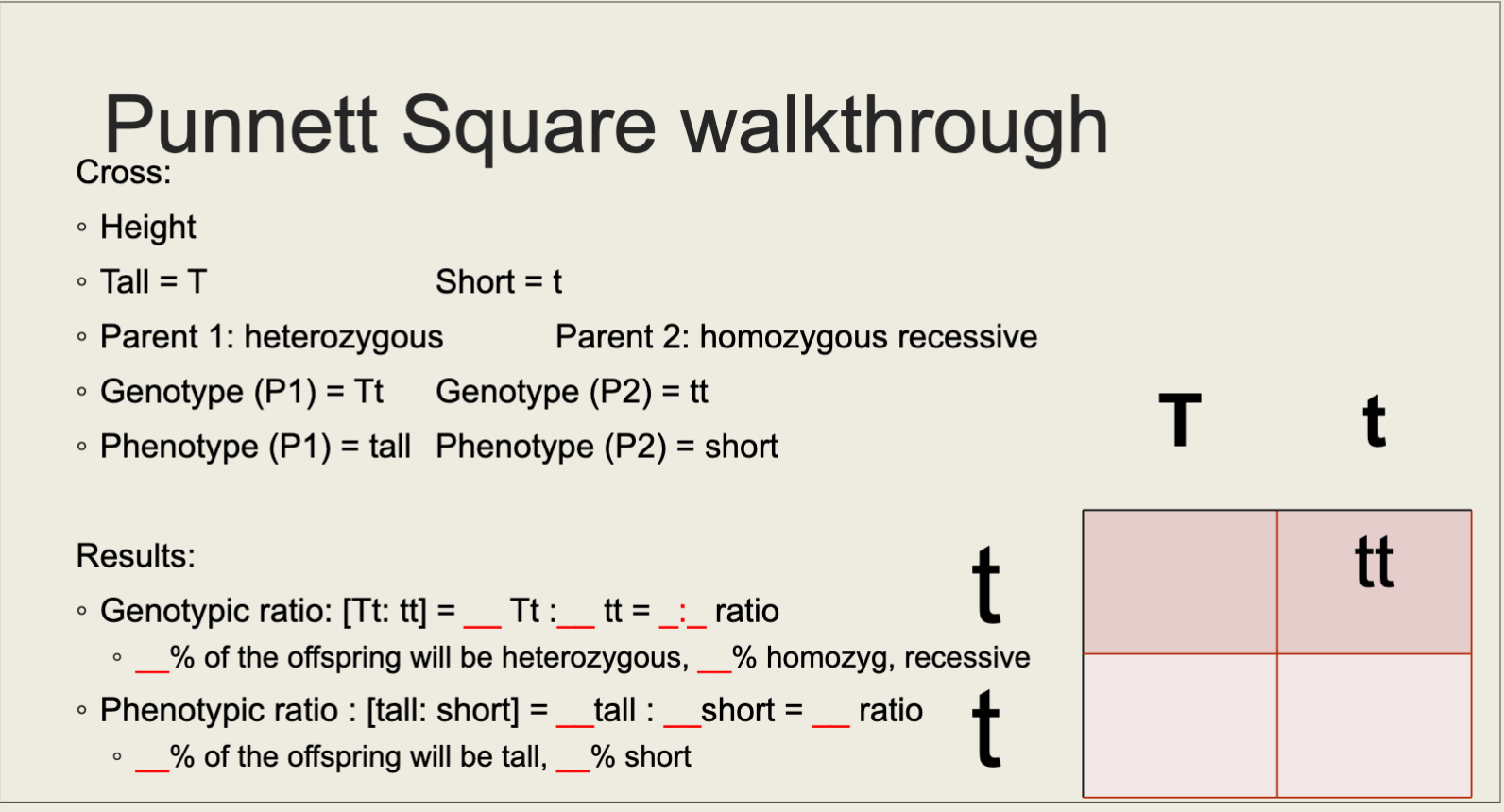
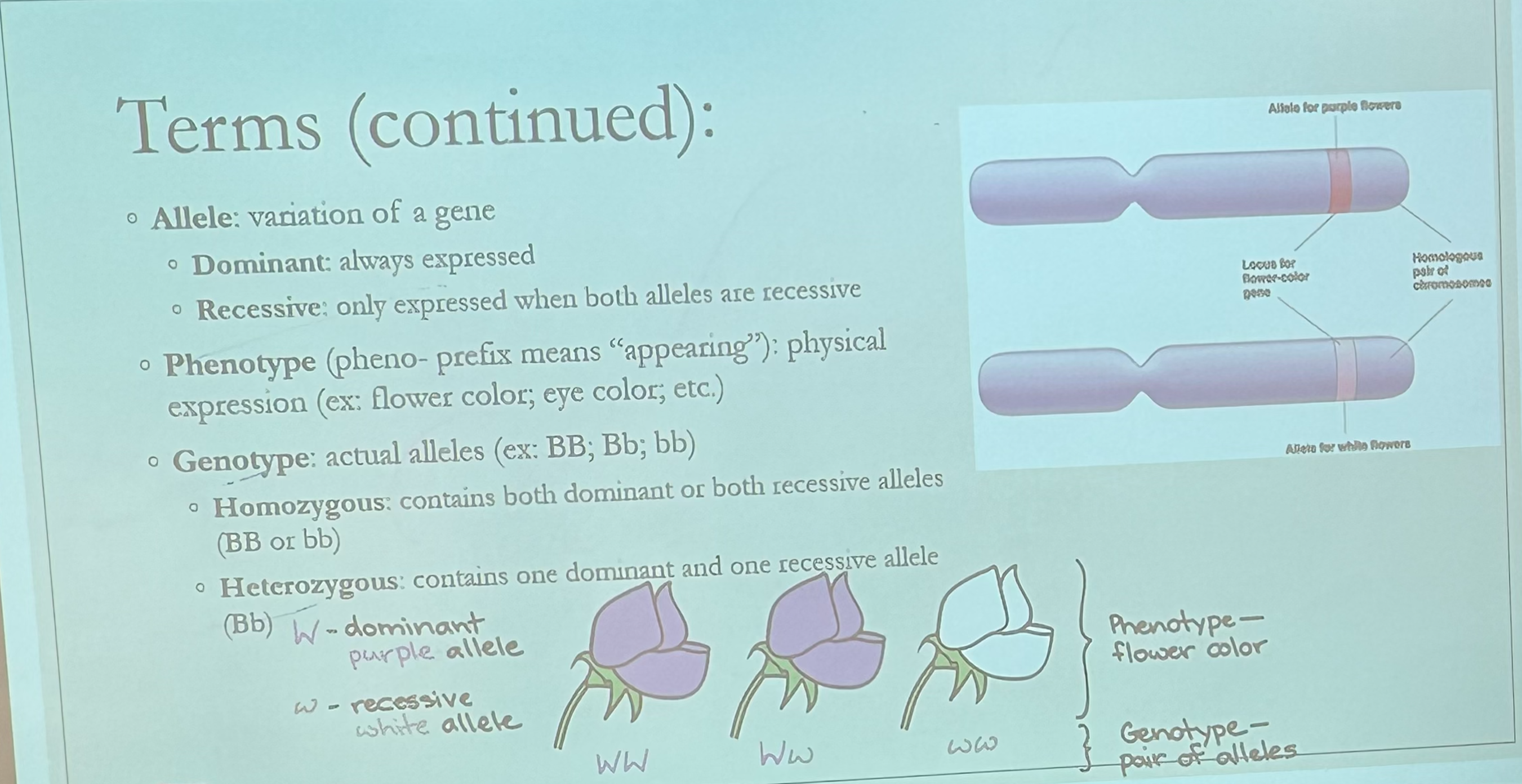
Homozygous
Contains both dominant or both recessive alleles (BB or bb)
Heterozygous
Contains one dominant and one recessive allele (Bb)
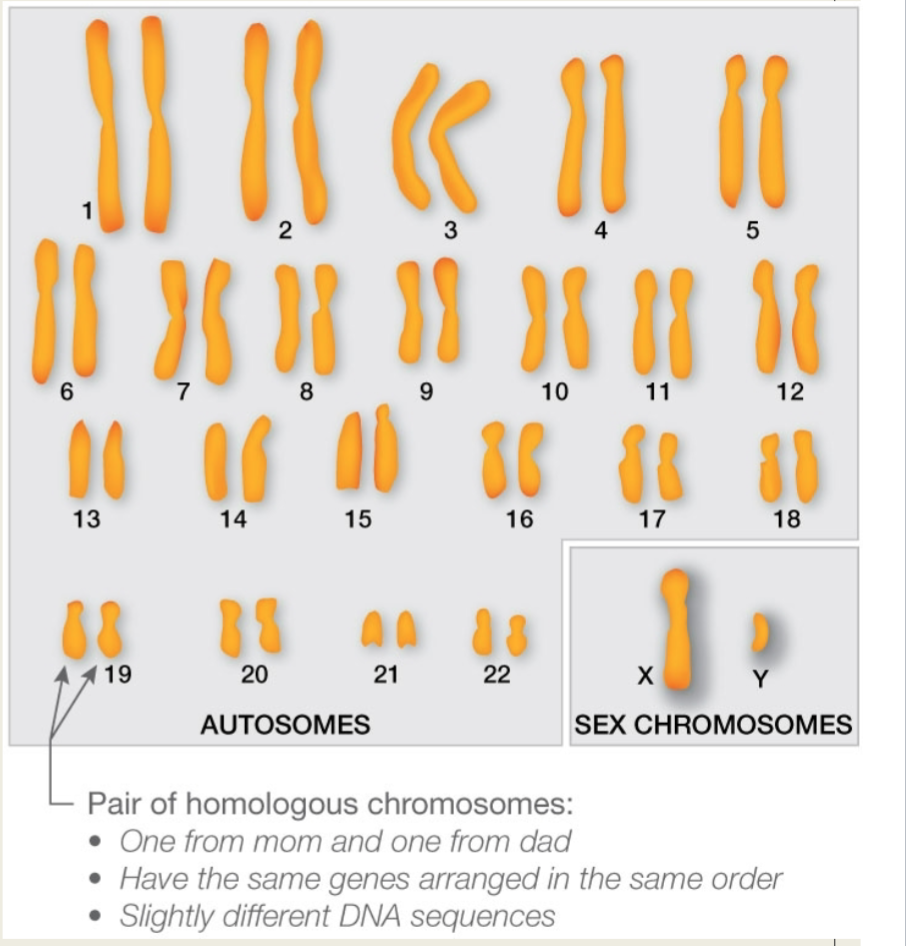
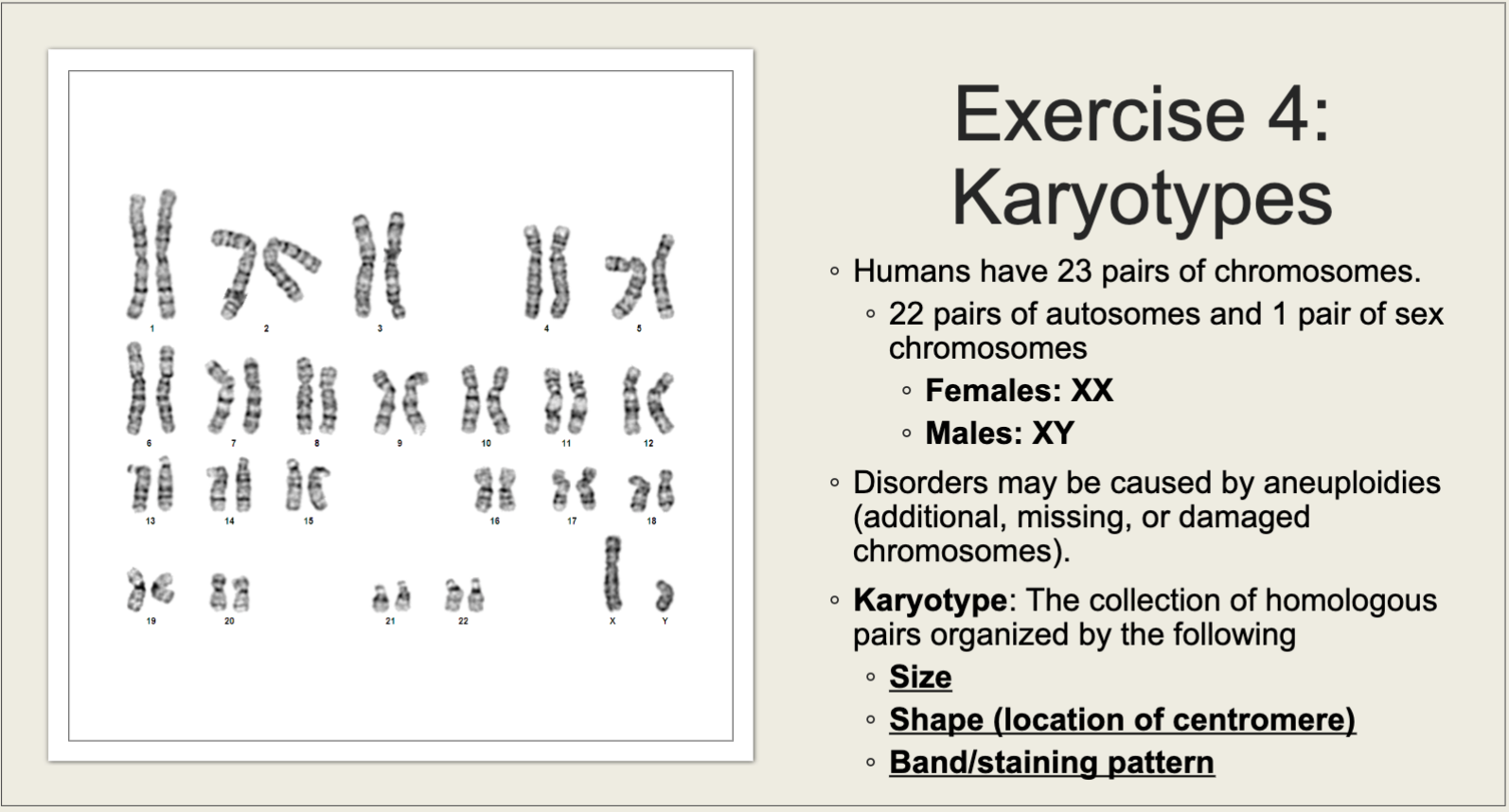
Karyotype
homologous chromosomes matched by size, shape, and banding pattern; used to determine genetic diseases by aneuploidy (abnormal number of chromosomes, ex: Down syndrome, which is caused by having an extra copy of chromosome 21)
Homologous Chromosomes
Structurally identical pair of chromosomes containing alleles of the same genes at corresponding locations; one received from each parent
Karyotyping visual
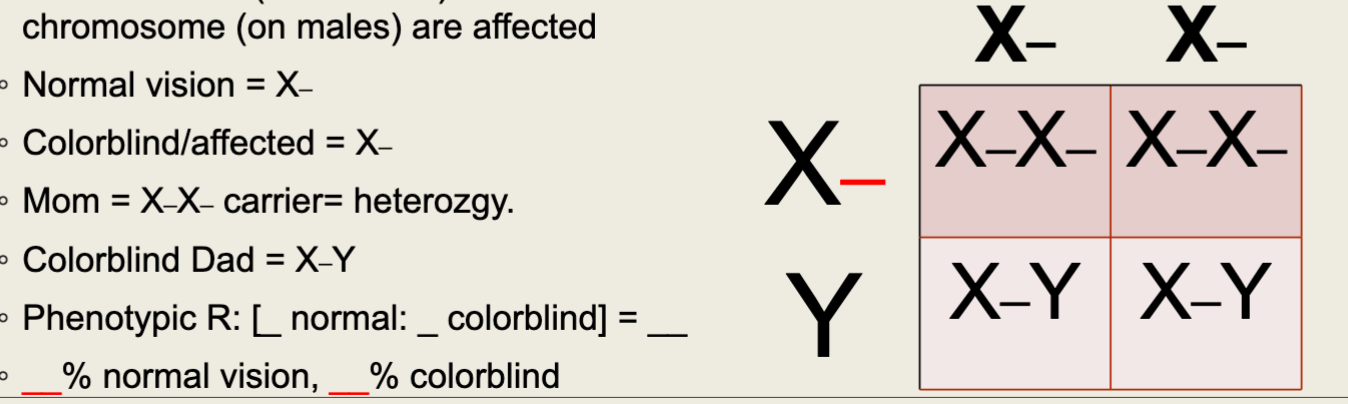
Sex-Linked Punnett Squares
These Punnett Squares ALWAYS include the sex chromosomes
Female: XX
Male: XY
Colorblindness (a sex-linked trait) will never be found on the ____
“Y” chromosome
Sex-linked traits are only found on the ___ , or the ____ pair
sex chromosome, 23rd
Traits like ___ , ____, or ____ can be found on both males and females in equal rates. These traits are not sex-linked.
height, hair color, or eye color
Colorblindness is sex-linked and carried on the ____ chromosome.
“X”
_____ trait codes for colorblindness (Dominant is normal vision)
Recessive
Phenotype and Genotype Chart for Colorblindness
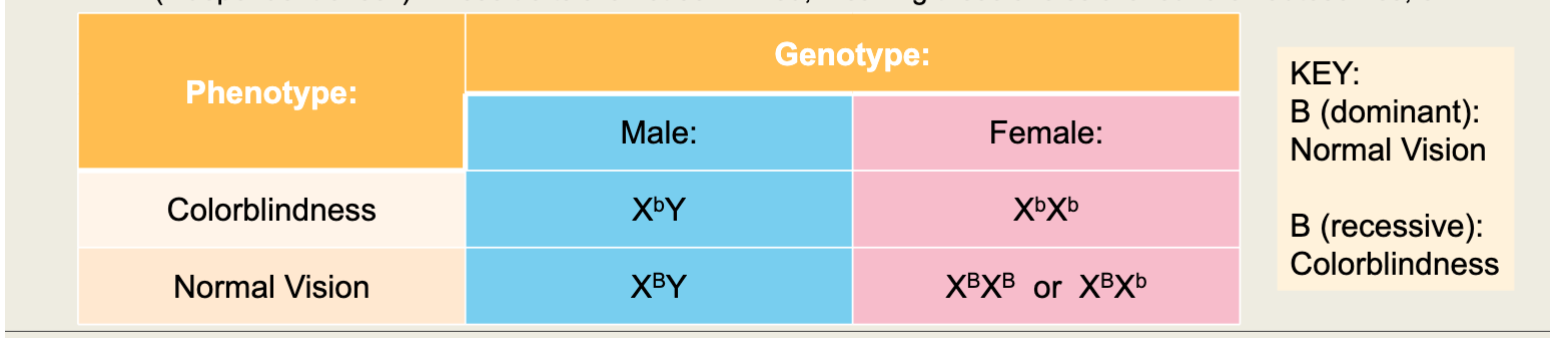
The phenotype of colorblindness is present when both ___ chromosomes (on females) or one ____ chromosome (on males) are affected.
“X” , “X”
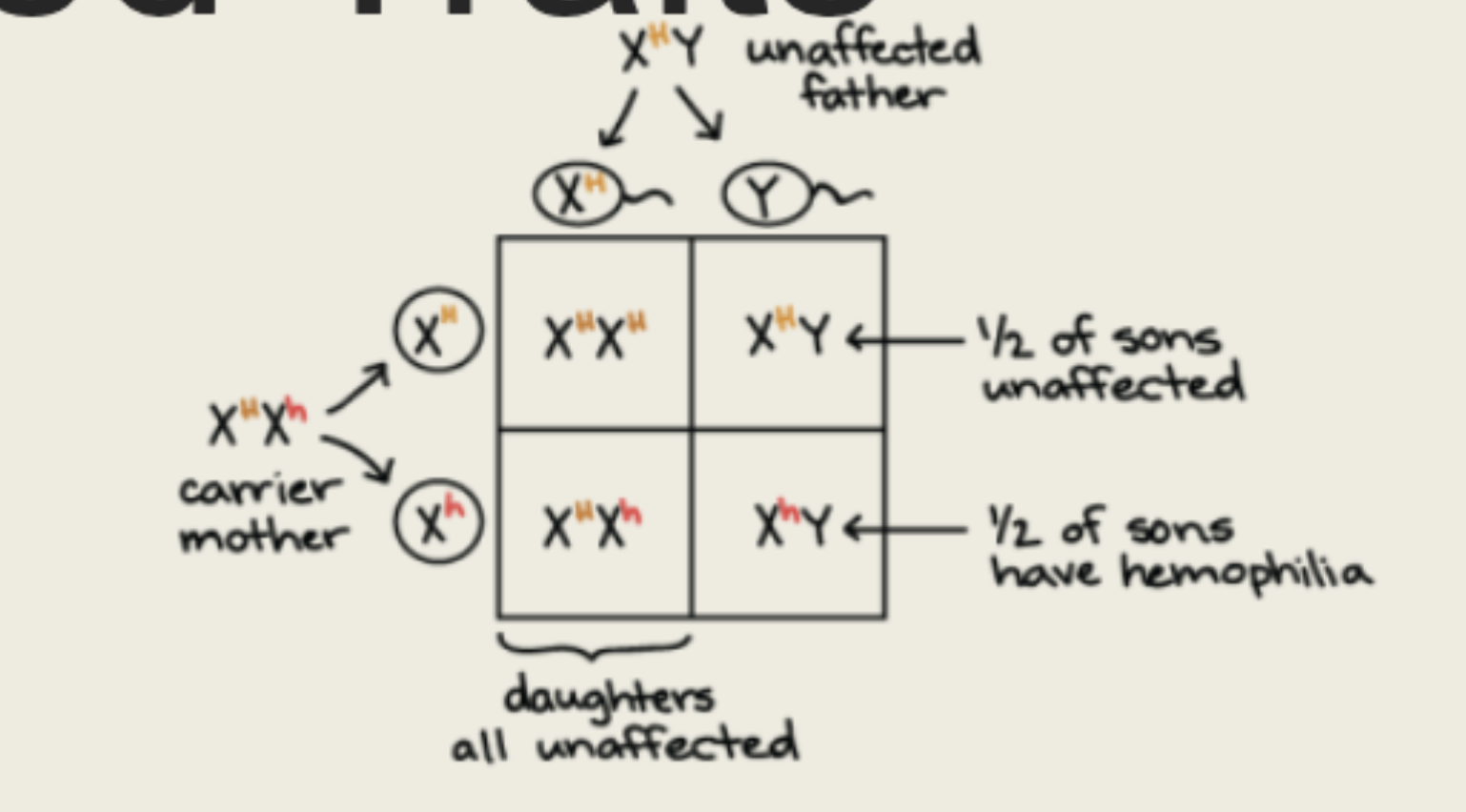
Hemophilia Punnett Square Example
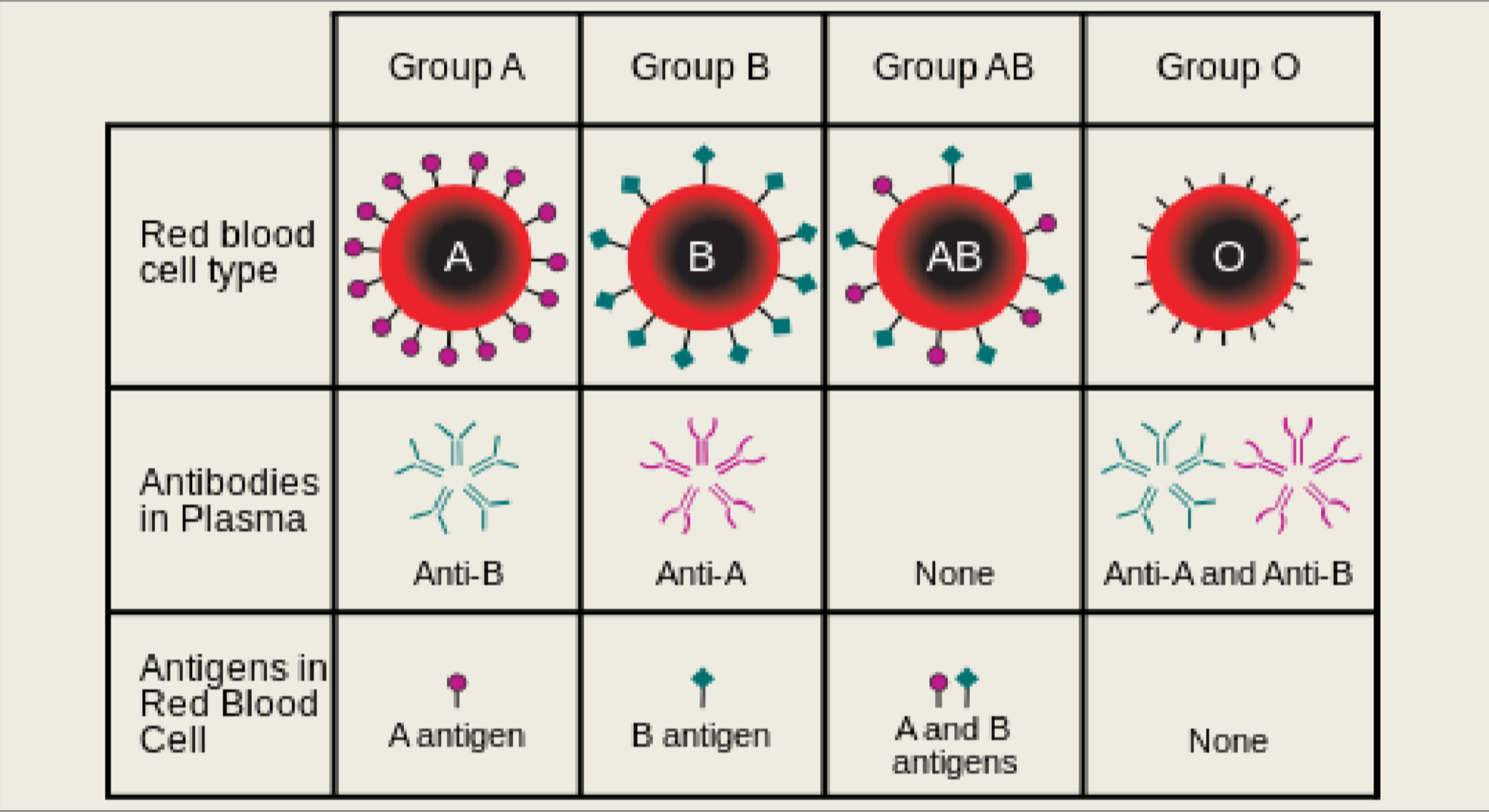
Blood Type Chart
Agglutination/Clumping with Blood Typing Slide

Blood typing is NOT _____ — do not include sex chromosomes
sex-linked
Blood Typing Punnett Square Example
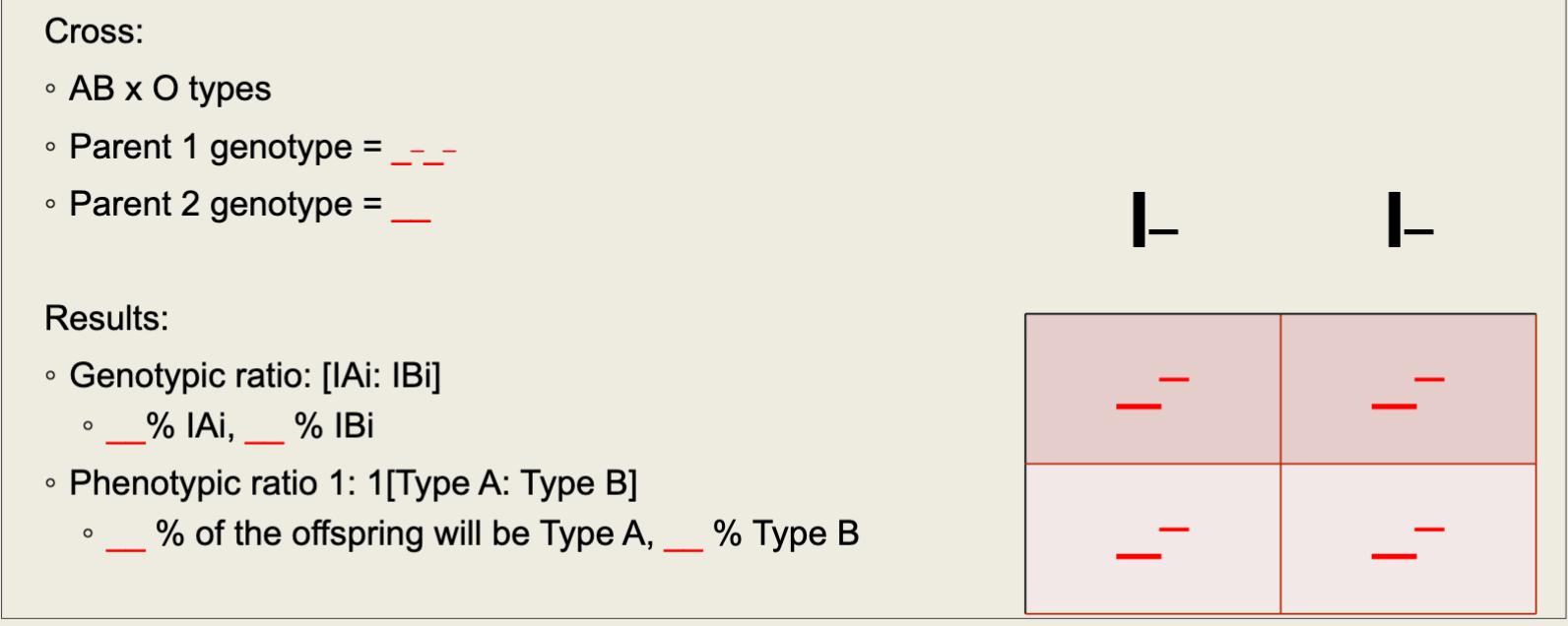
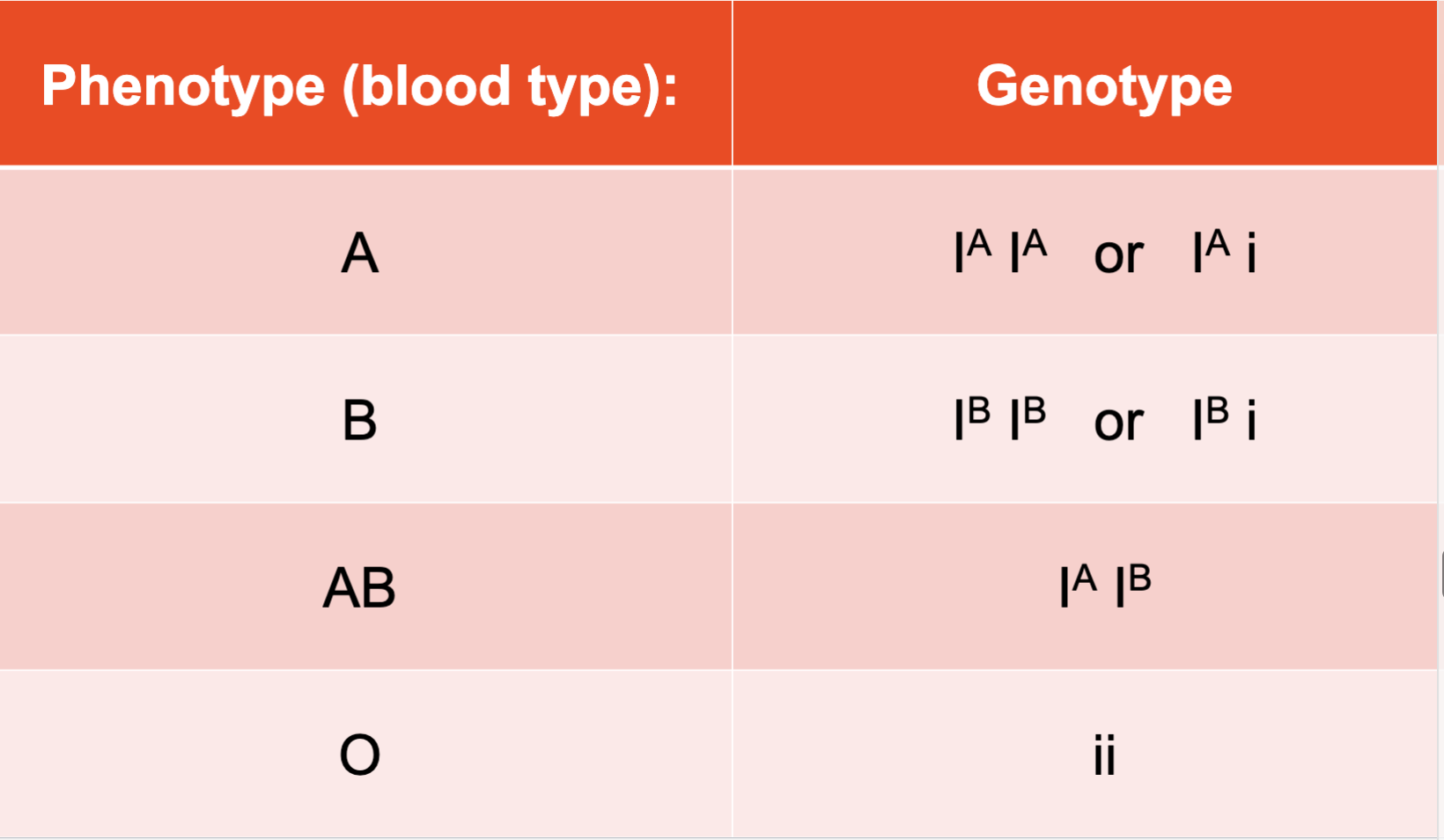
Phenotypes and Genotypes with Blood Types Chart
Anitgens vs. Antibodies in Blood Types

Colorblindness Sex-Linked Punnett Square Example
Karyotypes Review
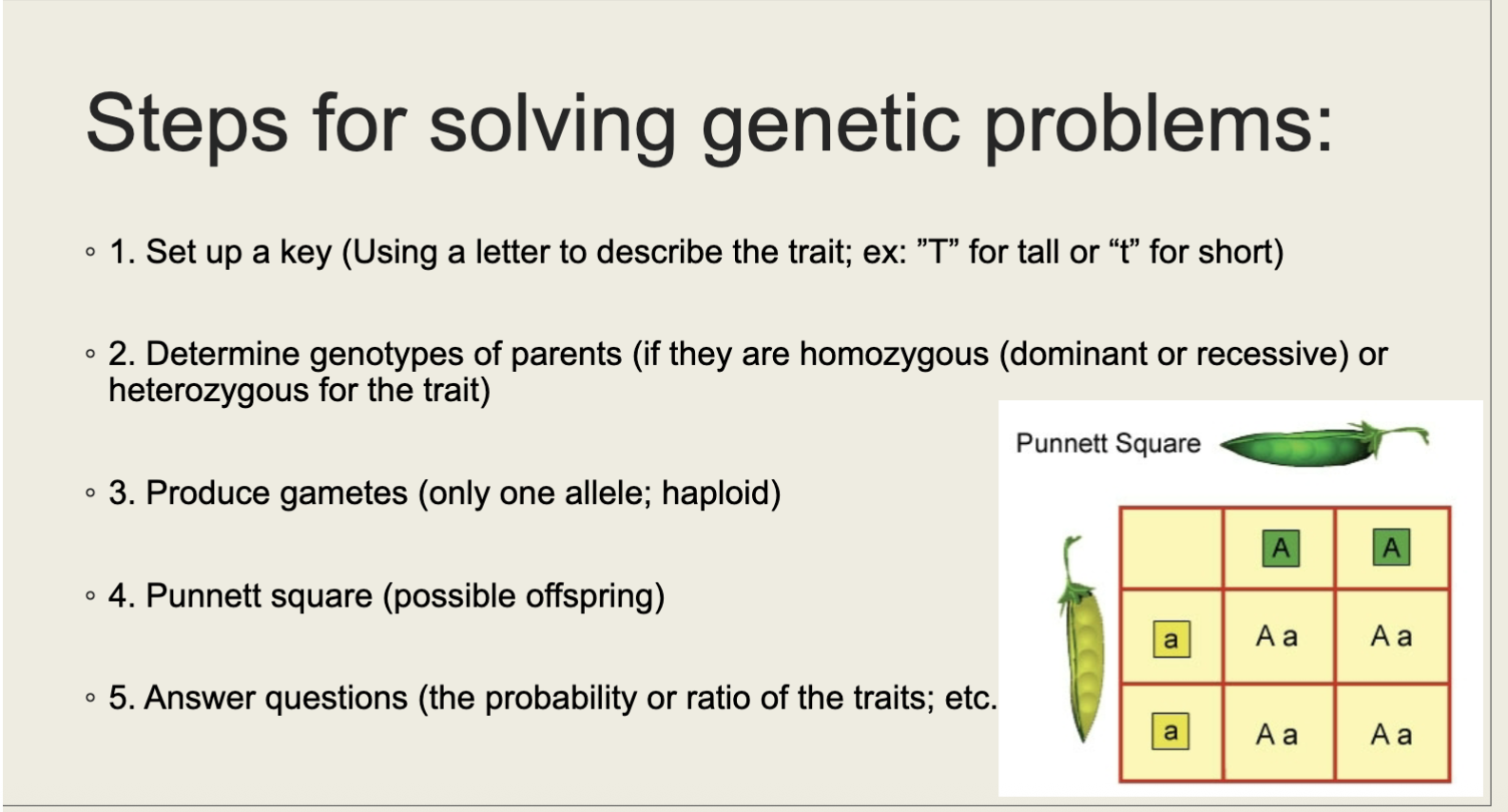
Punnett Square Walkthrough
Simple Mendelian Cross/Terms
Steps for solving genetic problems
Kingdom Monera
Unicellular
Prokaryotic
Some are autotrophs, but most are heterotrophs
Asexual reproduction — mostly binary fission
Size
Shape (cocci (spherical) , bacilli, (rod-shaped), and (spirilla) spiral))
have cell walls composed of peptidoglycan
Ex: Bacteria, Cyanobacteria
Microscopic in size
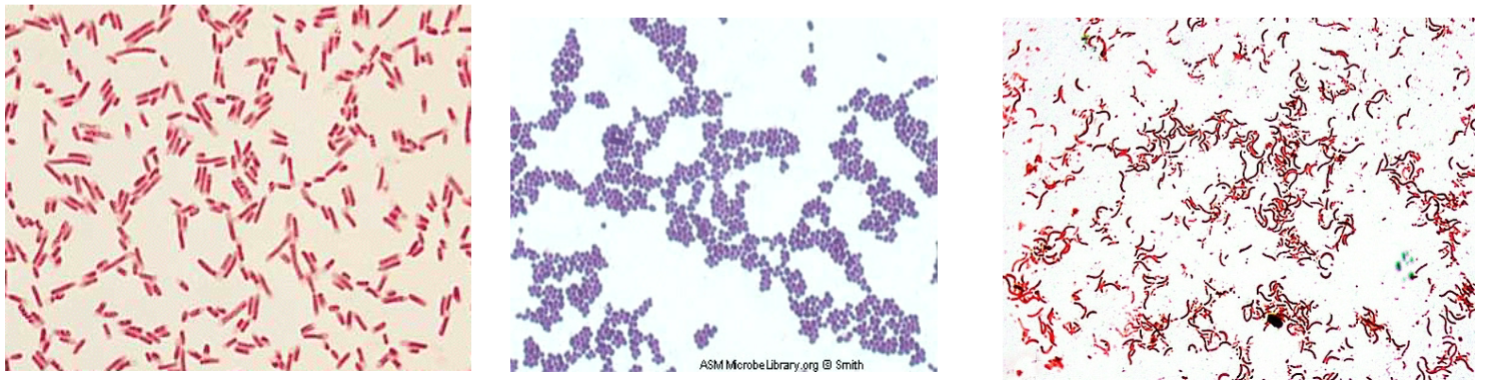
Kingdom Monera Gram Stain
Gram positive - purple
Gram negative - red
Examples of Microscopic Kingdom Monera
going left to right: gram negative bacilli, gram positive cocci, gram negative spirilla
Kingdom Protista
Eukaryotic
Mostly unicellular
Some are autotrophs and some are heterotrophs
Can be divided into three groups:
Algae — autotrophs
Slime molds —- heterotrophs (absorb nutrients)
Protozoans —- heterotrophs (ingest nutrients)
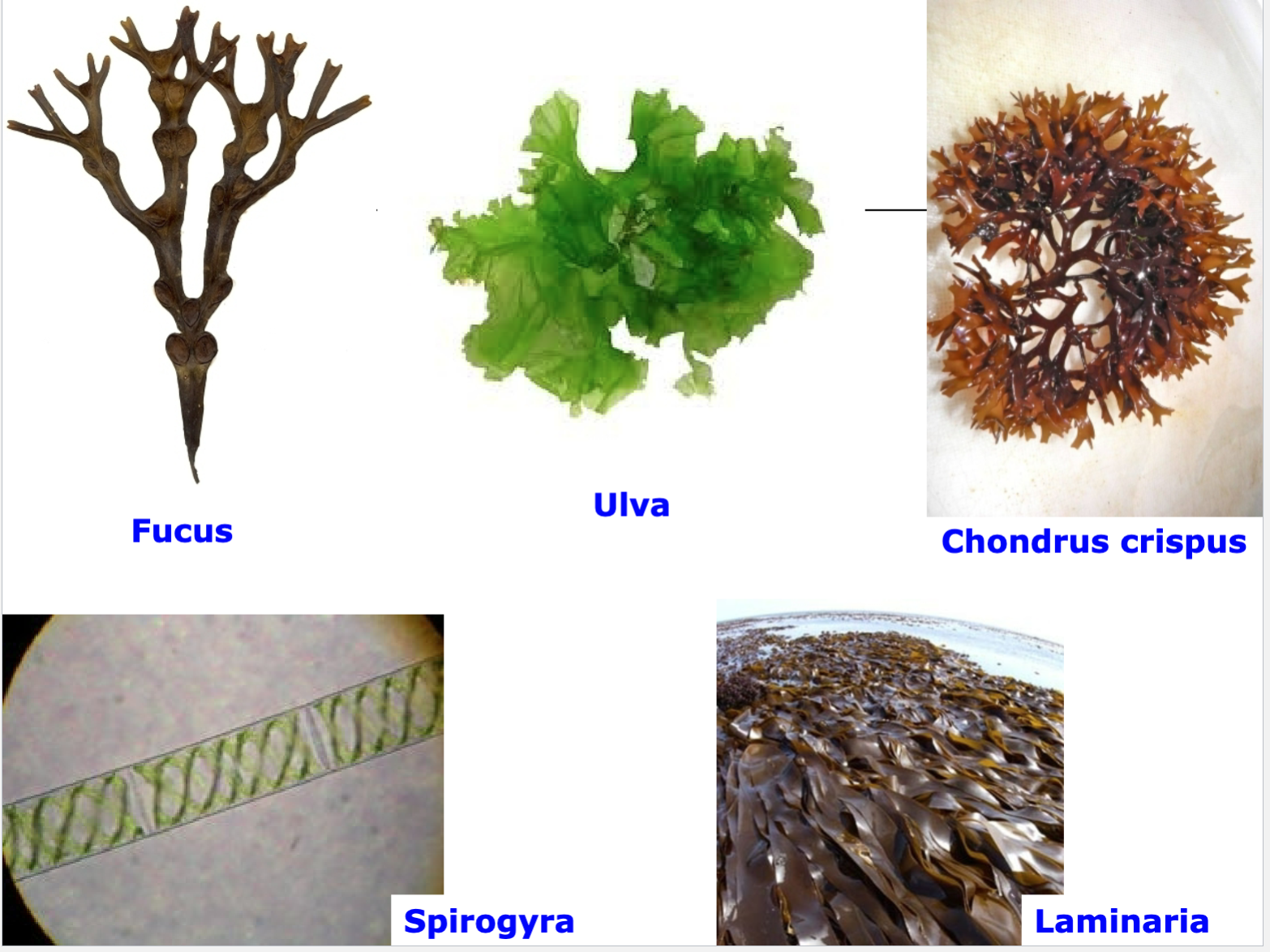
Algae
Cell wall made of cellulose
Unicellular/multicellular
Microscopic/macroscopic
Found in freshwater/marine environments
Pictures of Algae

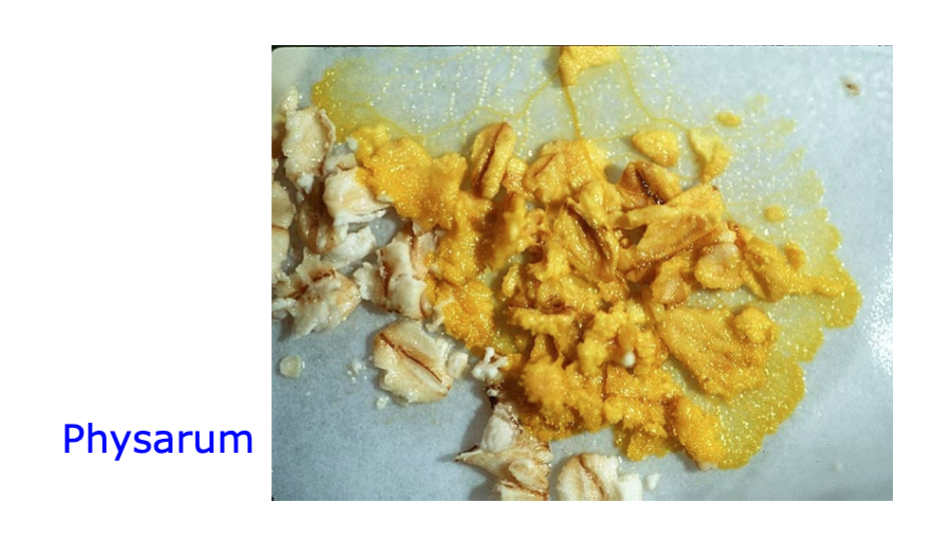
Slime molds
no chitin cell wall like that of fungi
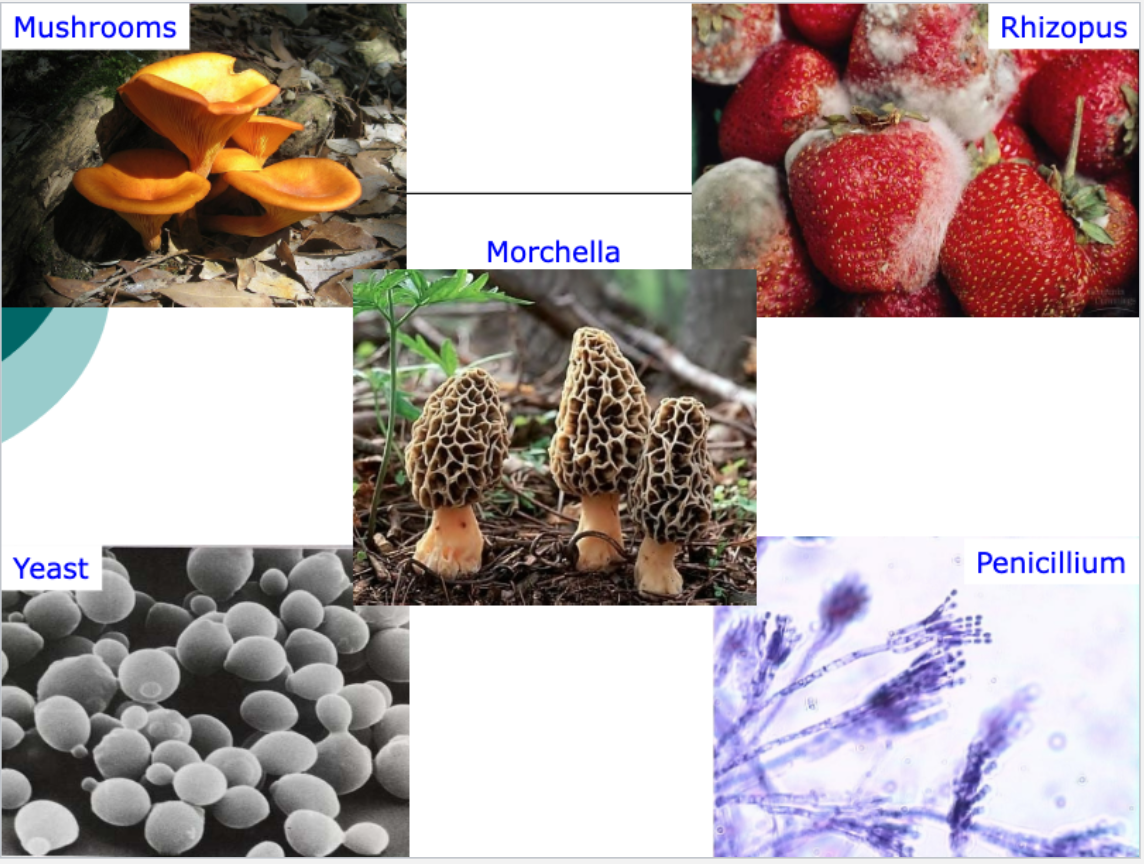
Kingdom Fungi
Eukaryotic
Mostly multicellular (yeast are unicellular)
Heterotrophic (parasitic (feeds off of a live host) or saprophytic (feeds off of a dead host) )
cell wall composed of chitin
Ex: Mold, Mildew, Yeast
Slime mold photo
Protozoans
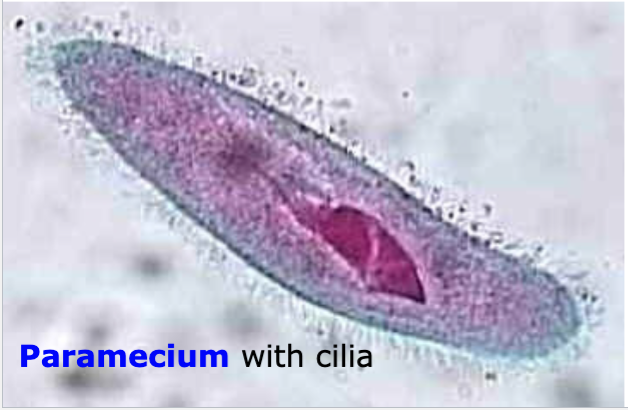
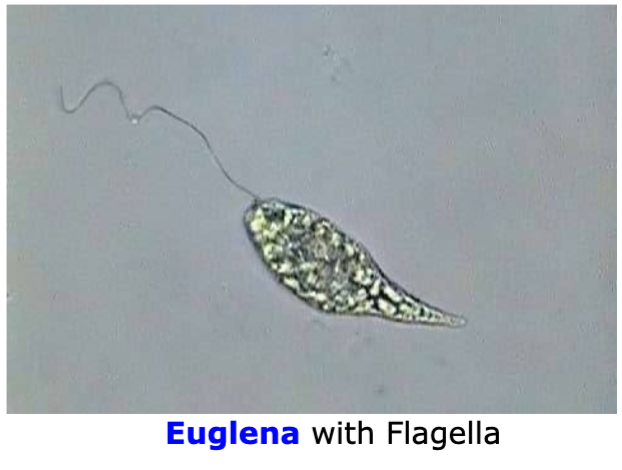
Form of locomotion
Cilia, pseudopods, flagella
Can include human pathogens
Ex: giardia
Protozoan Paramecium
Protozoan Euglena
Protozoan Amoeba
Kingdom Fungi continued…

Pictures of Fungi

Kingdom Plantae
Multicellular
Eukaryotic
Autotrophic: cells contain chloroplast, the site of photosynthesis
Cell walls composed of cellulose
Store food as starch
May be vascular or non-vascular
Some produce seeds during reproduction
* Exceptions: moss and fern
Vascular vs. Non Vascular
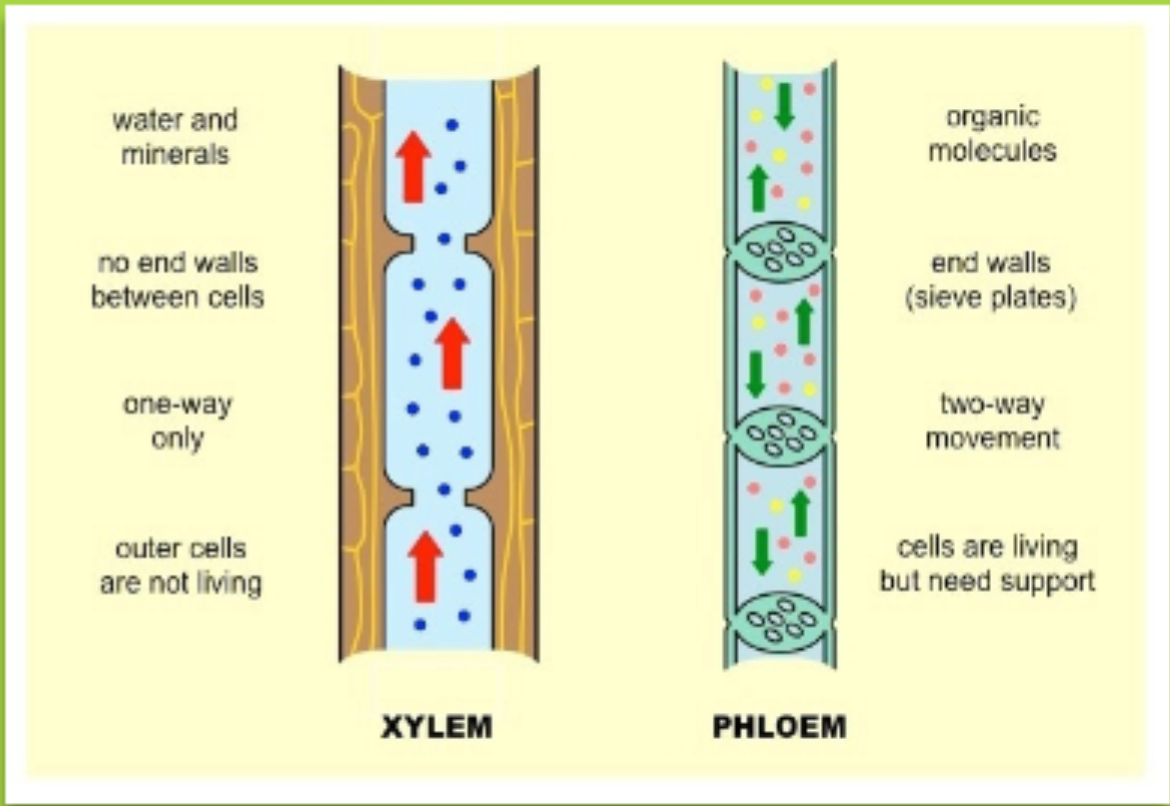
Possess specialized tissue for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic materials throughout the plant body
Vascular - anything generally w/ true roots and the system of xylem and phloem
Xylem — water transport
Phloem — “food” / organic molecules transport
Nonvascular — no true roots, no xylem or phloem
Xylem and Phloem Diagram
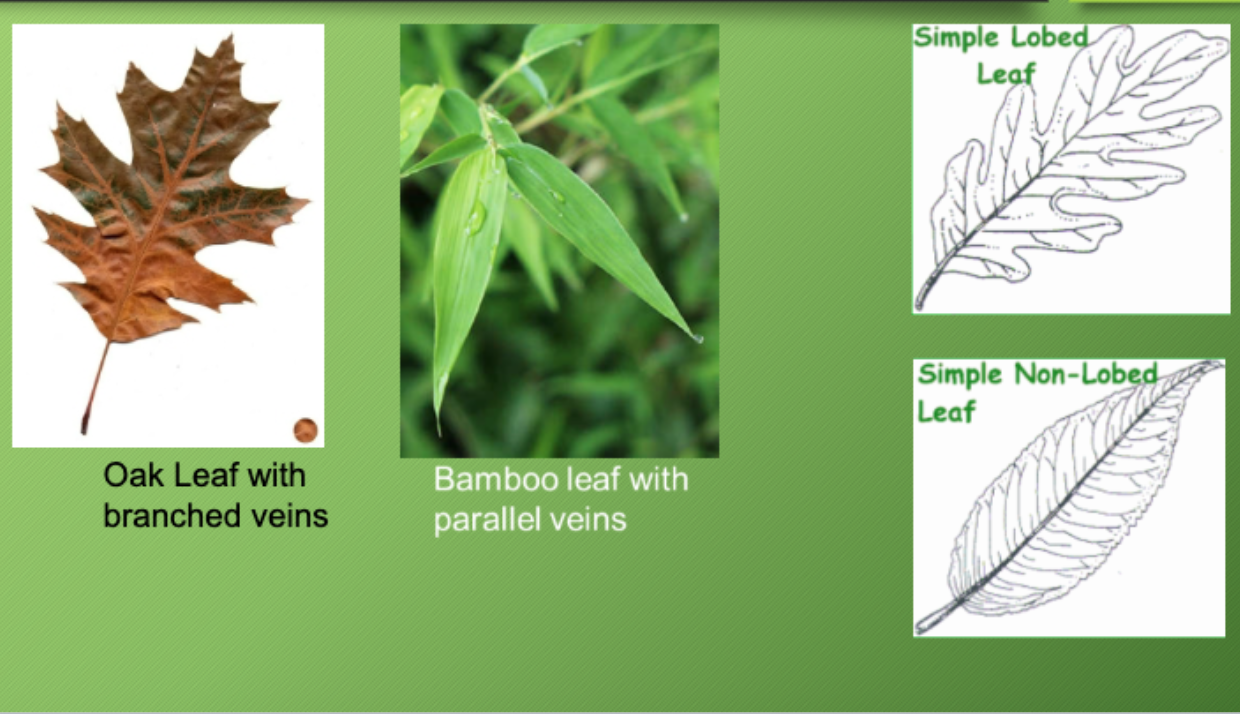
Branched vs. Parallel Veins (Examine the veins on the underside of their leaves)
Branched veins: branched/separate veins on leaf
Parallel veins: parallel lines on leaf
Some scientists believe plants evolved from _____.
algae
Plants and algae both:
Starch storage
Cellulose call wall
Photosynthetic
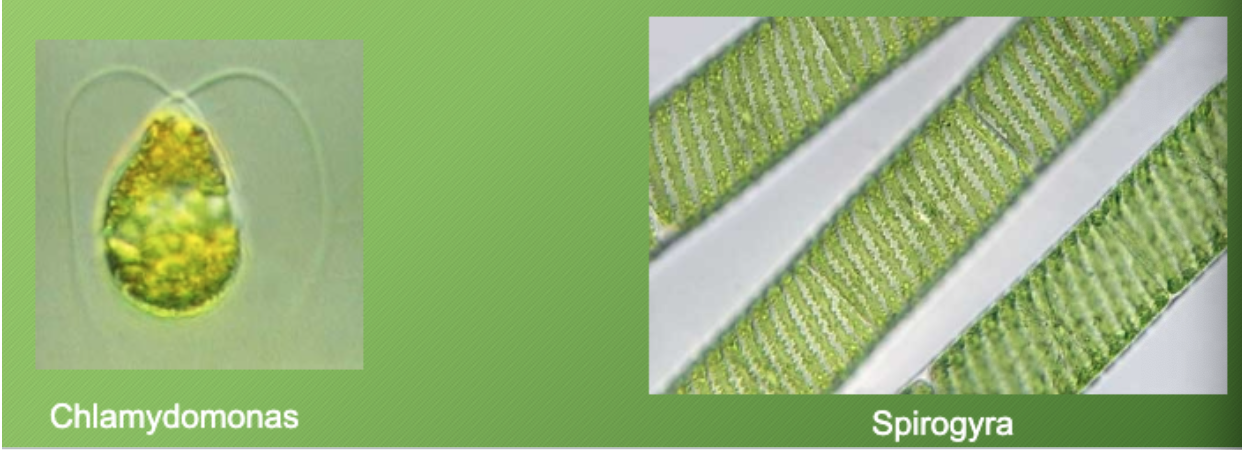

Moss (Representative Species)
non-vascular, produces spores
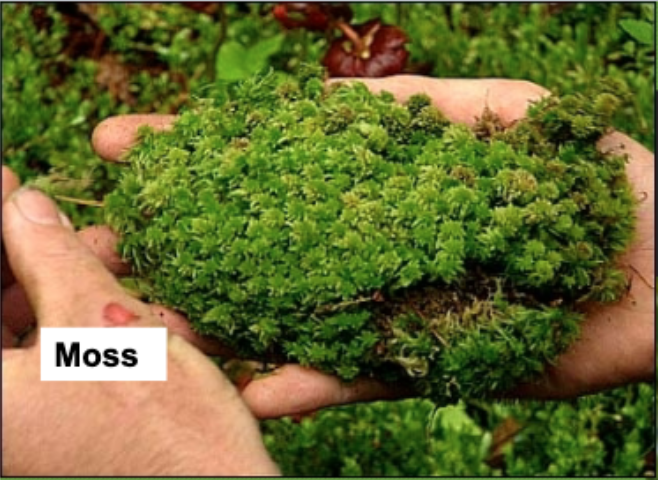

Ferns (Representative Species)
produces spores, vascular
brown dots on underside of leaf
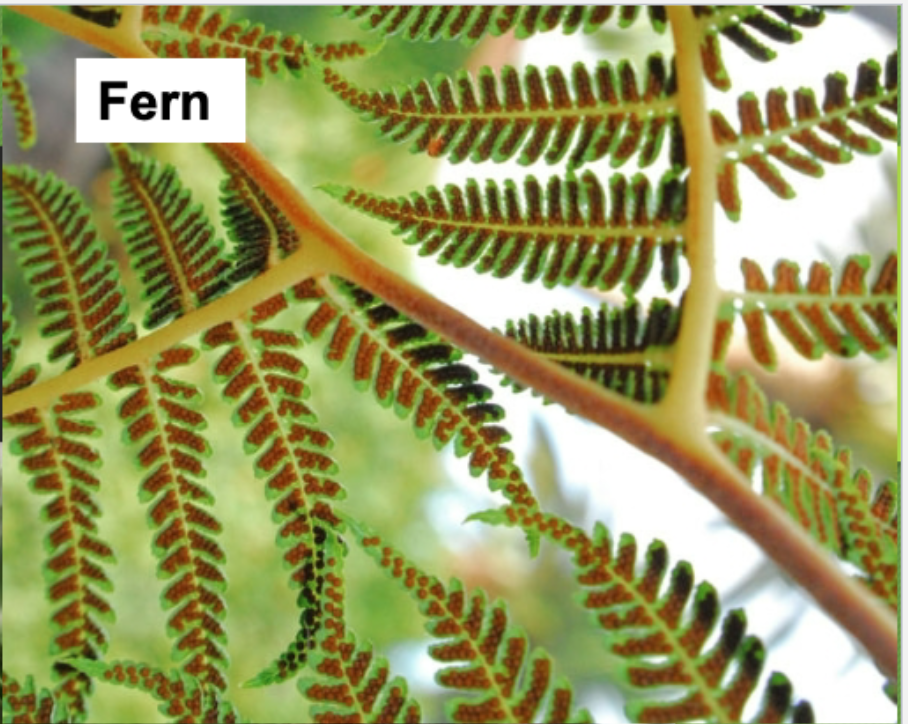

Conifers/Gymnosperms (Representative Species)
plants that use cones for seed dispersal, vascular

Flowering plants/Angiosperms (Representative Species)
flower ensures fertilization of the ovule and development of fruit for seed dispersal, vascular

Leaf characteristics

Lobed vs. non-lobed leaves
simple lobed leaf: clusters for each vein
non-lobed leaf: parallel pattern, lack distinct indentations or lobes along leaf margin
Kingdom Animalia
Multicellular
Eukaryotic
Heterotrophic
No cell wall or chloroplasts
Motile
Primarily sexual reproduction
Period of embryonic development