Lecture 18 - atomic physics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what is the theory of relativity
replacing newtonian mechanics when dealing with particle speeds comparable to the speed of light - Einstein
what is the quantum theory
understanding behaviour of atoms in absorption and emission of radiation
all objects emit radiation whose total intensity is proportional to the … of their kelvin temperature
fourth power
a body that emits all radiation when hot is called a
blackbody
a blackbody … all radiation that are incident on it and will … none, thus it appears …
absorb
reflect
black
examples of blackbodies
sun
hot oven or glowing filament of a light globe may be considered as a blackbody radiator
what is a plot of intensity and wavelength
spectrum of black body radiation
total power of the emitted radiation increases as T increases
Stefan Boltzmann law :
P = omega A e T^4
peak of the spectra shifts towards shorter wavelength as T increases
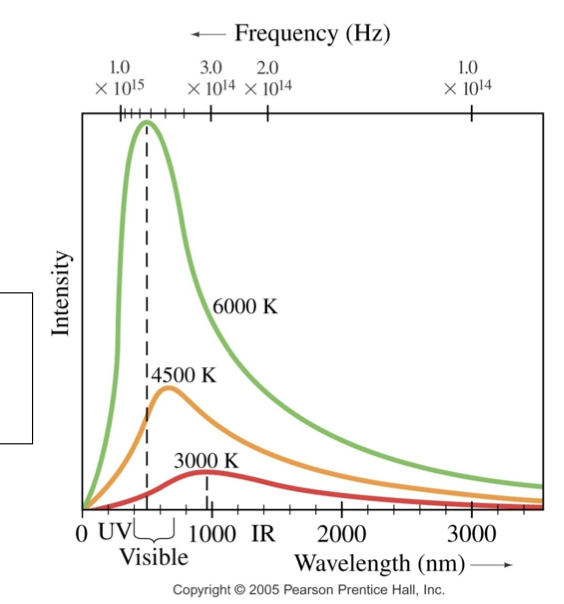
Wien’s Law Equation
wavelength(MAX) x T = (2.9 × 10^-3)
how does an ear thermometer work
measures the amount of infrared radiation emitted by the ear drum, then it converts the amount of radiation into a temperature reading.
increase from 37-38 degrees c is
(273+38/(273+37) = 1.0032 → 0.32% increase
ear thermometer is given by the fourth power of temperature
((273+38/(273+37))^4 =5,564,554,869.945 1.013 → 1.3% increase in radiated power
Planck’s Quantum Hypothesis (1900)
the energy of an atomic oscillator can have only certain discrete values (En), that is, energy of oscillator is quantized
E(n) = nhf
n = quantum number
h = planck constant = 6.63 × 10^-34 J.s
f = frequency
oscillator emit and absorb energy when making a transition from one quantum state to another in the form of a single quantum energy, energy of radiation is quantised
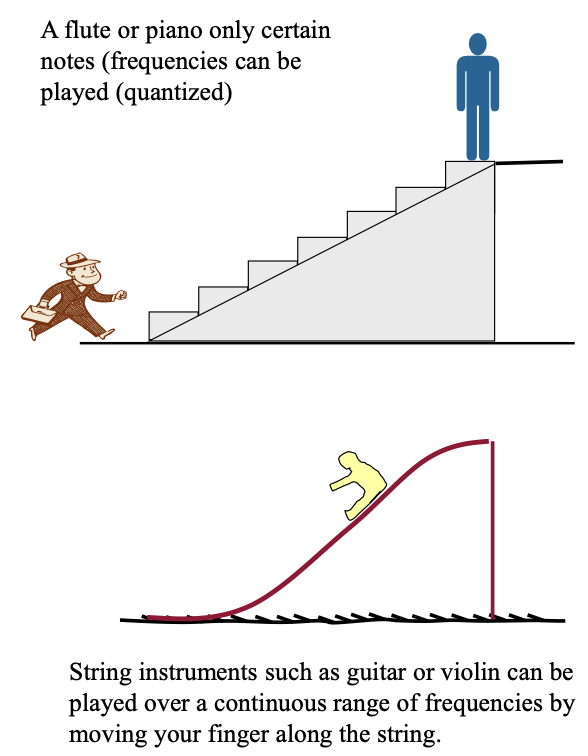
quantised vs NOT quantised examples
quantised = energy of a staircase
the person can have only certain discrete values of PE when climbing steps
not quantised = energy of a slide
the child can have any value of PE when sliding
observations of the photoelectric effect
electrons are ejected when light strikes a metal surface
photocurrent is proportional to light intensity
an increase in intensity of the light beam means more photons are incident, so more electrons will be ejected but energy of each photon is not changed
emission is instantaneous
max KE of electron is proportional to frequency
max KE is not proportional to intensity of light
no electron emission below frequency fc
max KE can be measured by reversing the terminals of the battery
max KE = eVs
Vs = stopping potential
work function (Wo)
minimum energy required to eject an electron from a material measured in eV
stopping voltage Vs
voltage at which no electron reaches the collector
photons
light ought to be emitted in packets or quanta, since all energy ultimately comes from a radiating source, this suggests that light is transmitted as tiny particles, or photons, in addition to waves
Einstein’s Photon Theory
quantum theory can explain photoelectric effects
hf = (energy needed to release an e) + (KE of e)
hf = Wo + max KE \
NOTE: one photon ejects one electron only
E = hf = hc/wavelength
E = energy of photon
h = Planks constant
c = speed of light
f = frequency
E = energy of photon / …
energy of an electron
number of photons emitted
total energy emitted by light global / energy of one photon
Find the maximum KE and speed of electrons ejected from
a sodium surface, when illuminated by light of λ = 410 nm.
Wo= 2.28 eV.
E = hf = hc/wavelength = (6.63 × 10^-34)(3×10^8)/(410×10^9)(1.6×10^-19)
= 3.02 eV;
hf = Wo + max KE
max KE = hf - Wo
3.03 - 2.28 = 0.75 eV
max KE = ½ mv²
v = sqrt((2 * max KE) / m)
v = sqrt((2 × 0.75(1.6 × 10^-19))/9.1×10^-31)
= 5.1 × 10^5 m/s
will brighter light eject more electrons from a surface than dimmer light of the same frequency?
yes, because brighter light means more intensity - which means more photon/m².s
will high frequency light eject more electrons than low frequency light? assume f > fc and both sources are of the same brightness
no, only the KE of electrons will increase with increasing frequency
when you are at the beach which radiation is more likely to cause sunburn, UV or infrared?
f(uv)>f(ir)
therefore E(uv)>E(ir)
therefore, UV is more likely to cause sunburn
applications of the photoelectric effect
burglar alarms
smoke detectors
automatic door opener
light meters
movie sound track reader
gas heated in a discharge tube emits light only at…
characteristic frequencies, called line spectrum
line spectrum works as a fingerprint for identification of the gas
when electron makes upward jump (transition it absorbs … When electron makes downward jump it …. energy
energy
emits
A photon is emitted as a hydrogen atom undergoes a
transition from the n = 6 state to n = 2 state.
Calculate the:
a. energy
b. wavelength
c. frequency of the emitted photon.
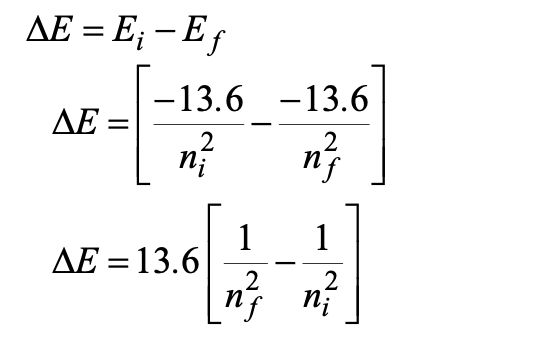
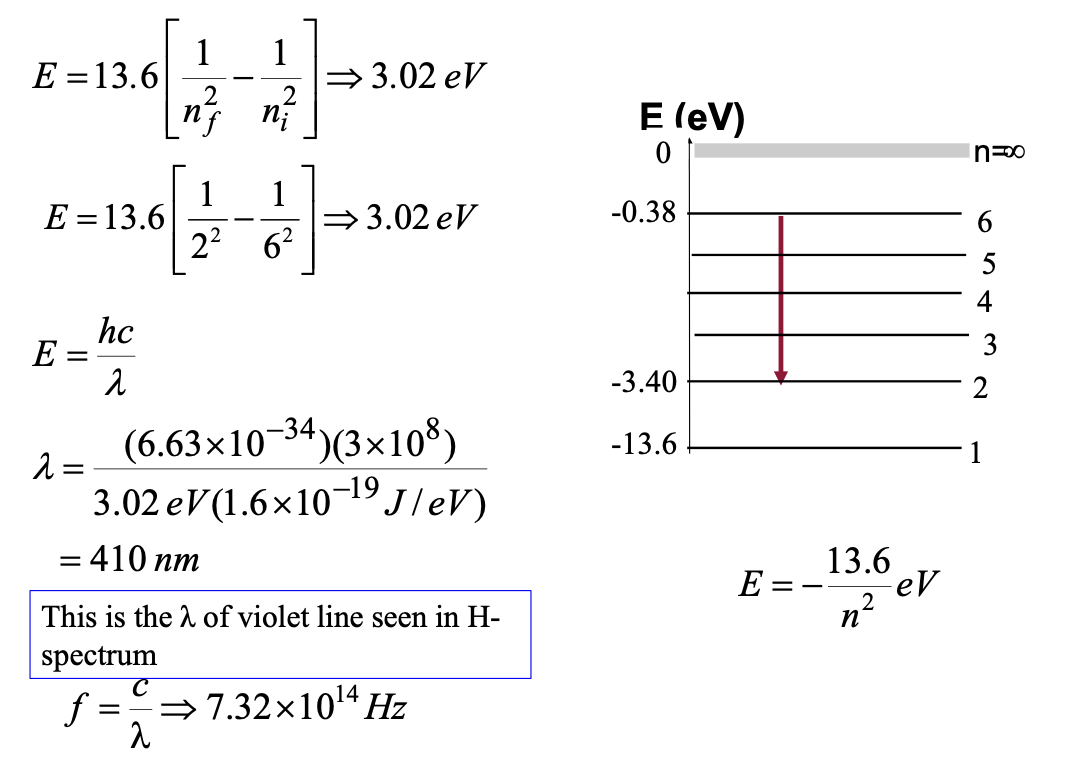
Ionisation Energy
minimum energy required to ionise the atom at ground state
hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV
negative sign means that the energy is to be supplied to the electron to make it an upward transition
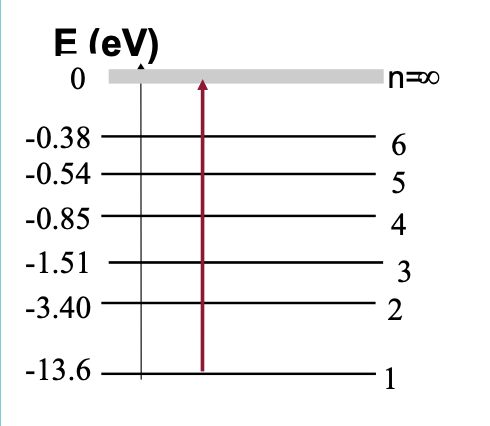
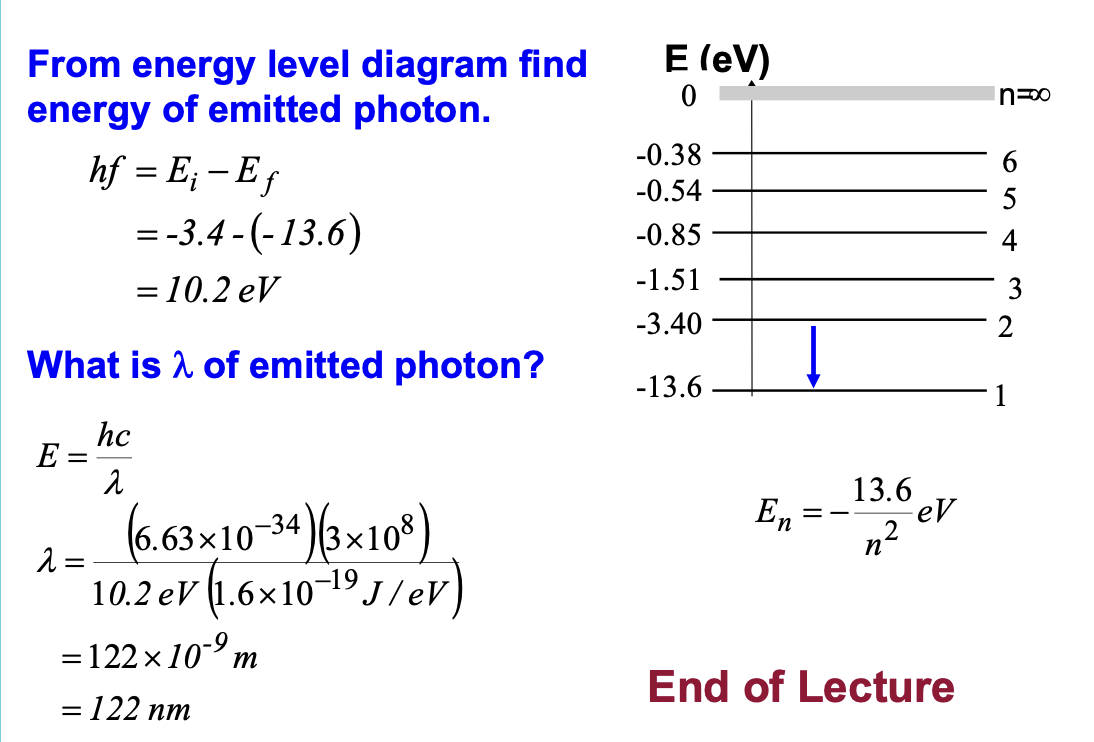
From the energy level diagram calculate the energy
and wavelength of the photon emitted when an
electron makes a transition from n = 2 to n = 1?