Immunology Lecture 18: Lymphocyte development and antigen receptor gene rearrangement
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What does the maturation of B and T cells involve? Where does it occur?
a series of events that occur in the primary lymphoid organs
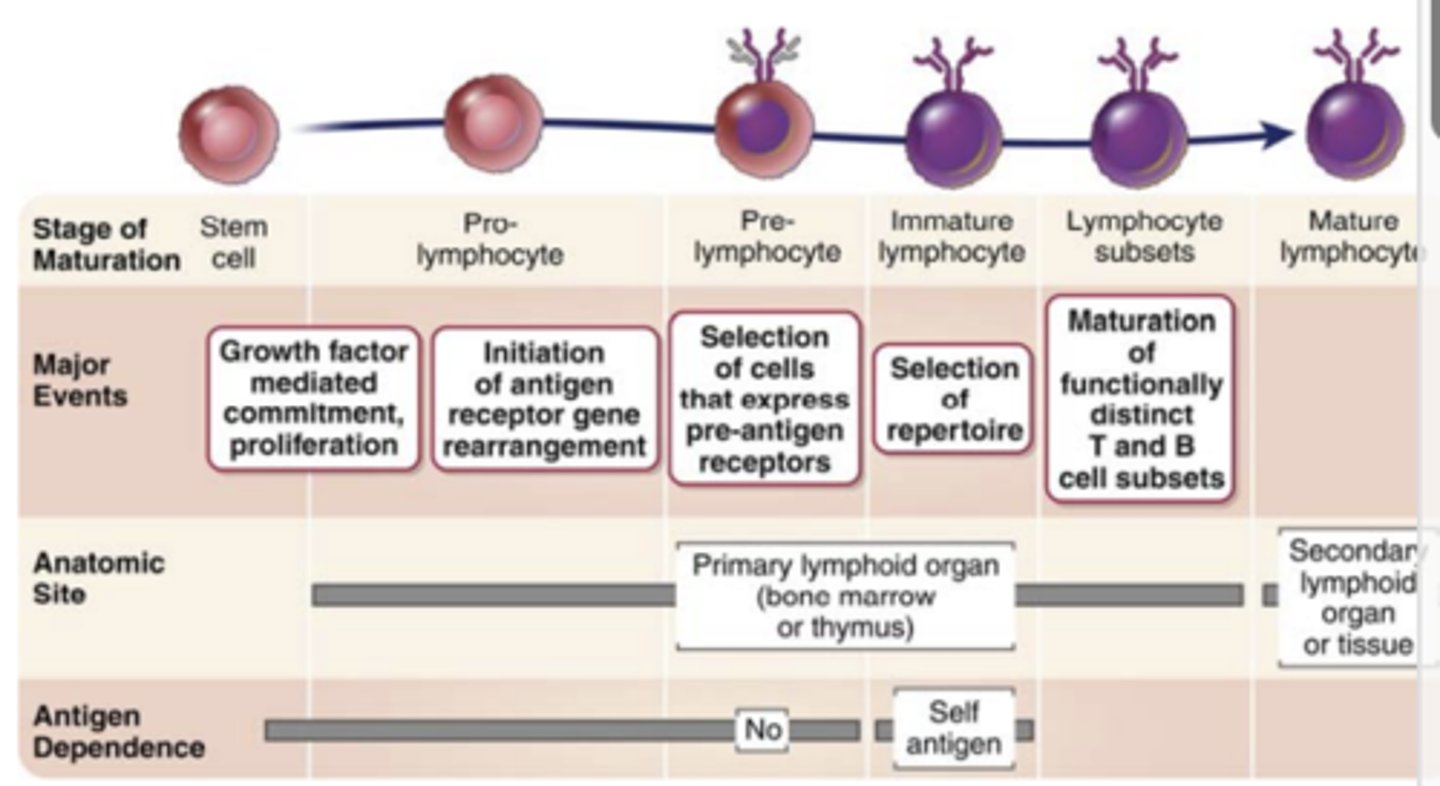
maturation of B and T cells:
Step 1: commitment of _______________ to the ___ or ____________________ lineage
Commitment of progenitor cells to the B lymphoid or T lymphoid lineage
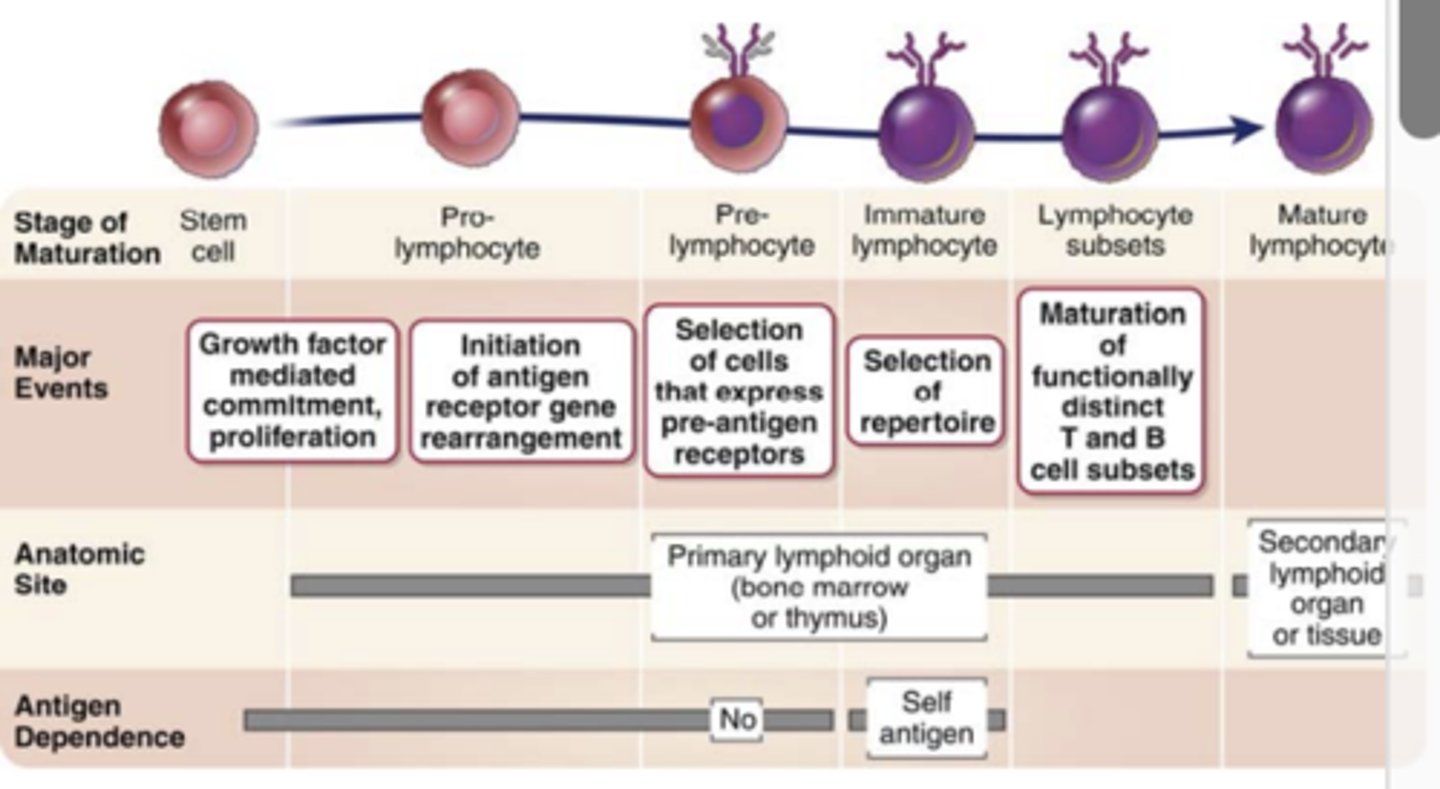
maturation of B and T cells:
Step 2: Proliferation of progenitors and immune committed cells at specific early stages of development provides......
- Proliferation
- provides large pool of cells that can generate useful lymphocytes
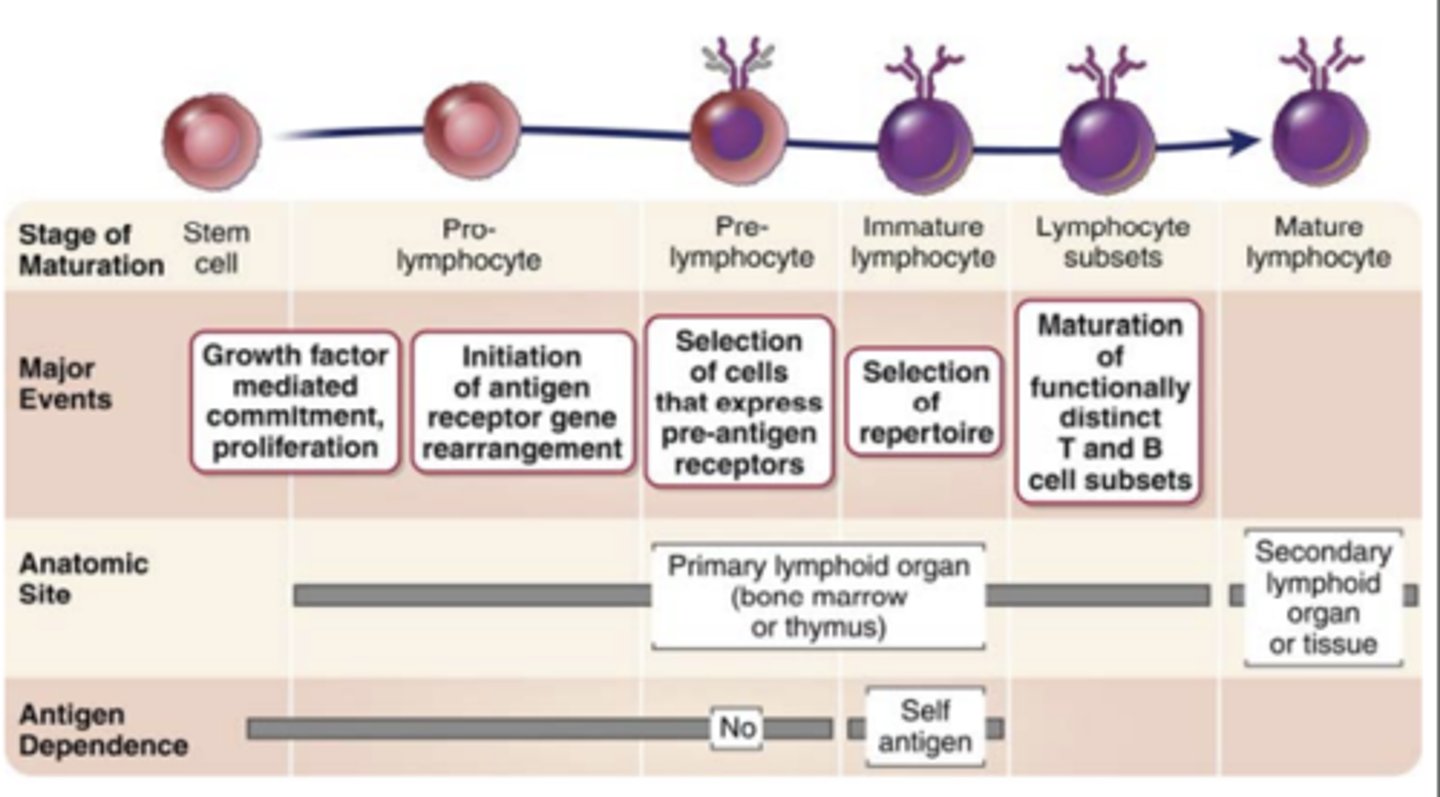
maturation of B and T cells:
Step 3: The sequential and ordered rearrangement of ___________________ genes and the expression of ________________ proteins
- antigen receptor genes
- the expression of antigen receptor proteins
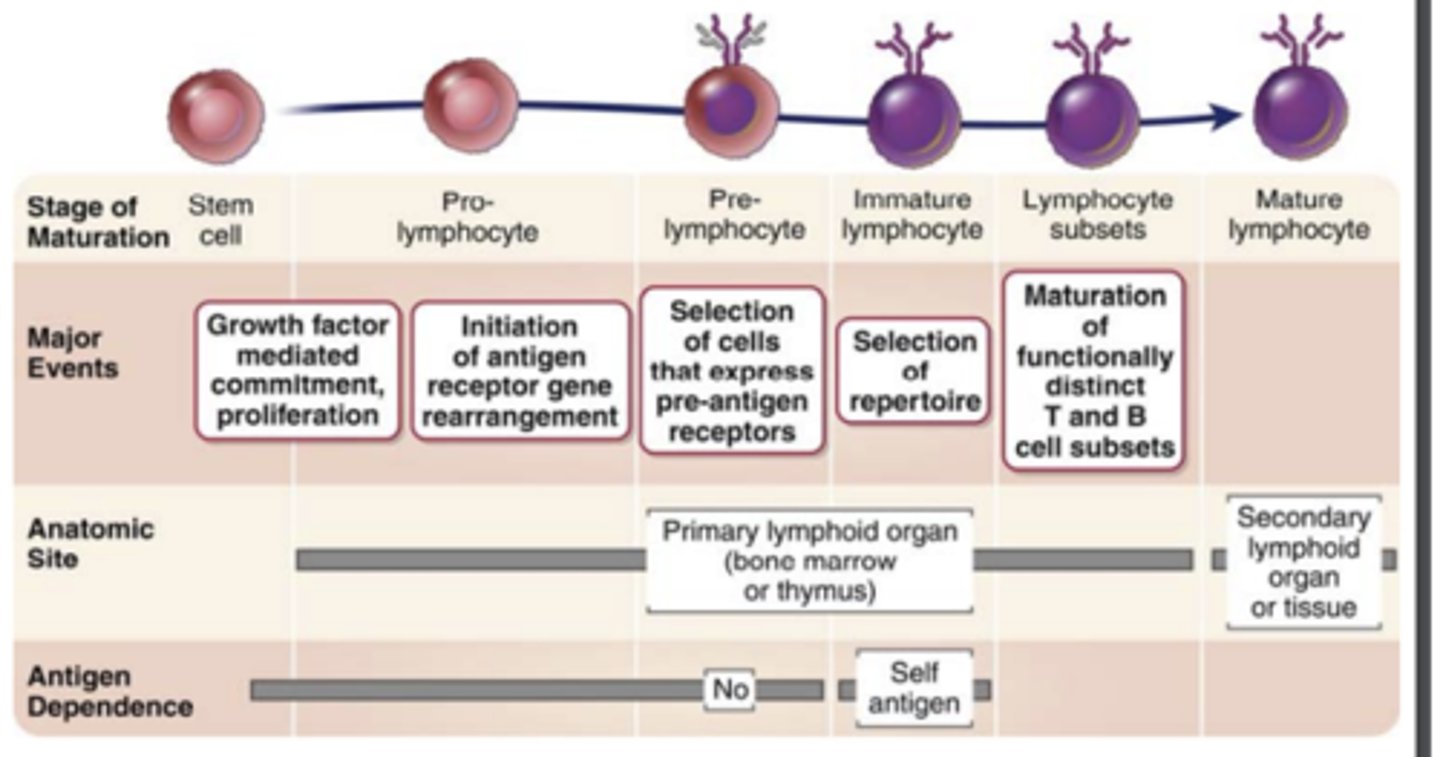
maturation of B and T cells:
Step 4: Selection events: What cells are preserved? which are eliminated?
Preserved: functional antigen receptor proteins
Eliminated: potentially dangerous cells that strongly recognize self-antigens
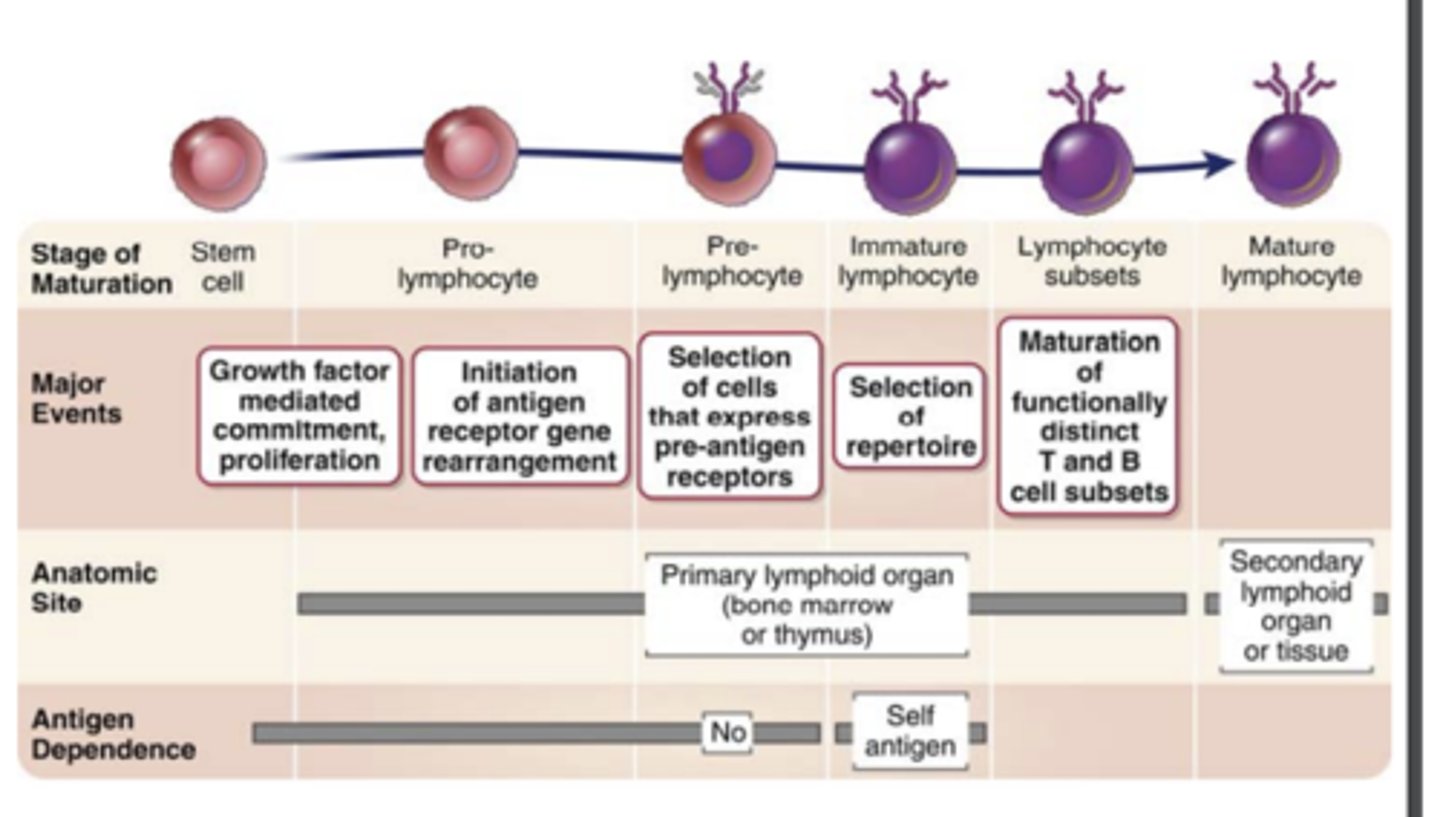
maturation of B and T cells:
Step 5: Differentiation of B and T cells into.....
functionally and phenotypically distinct subpopulations
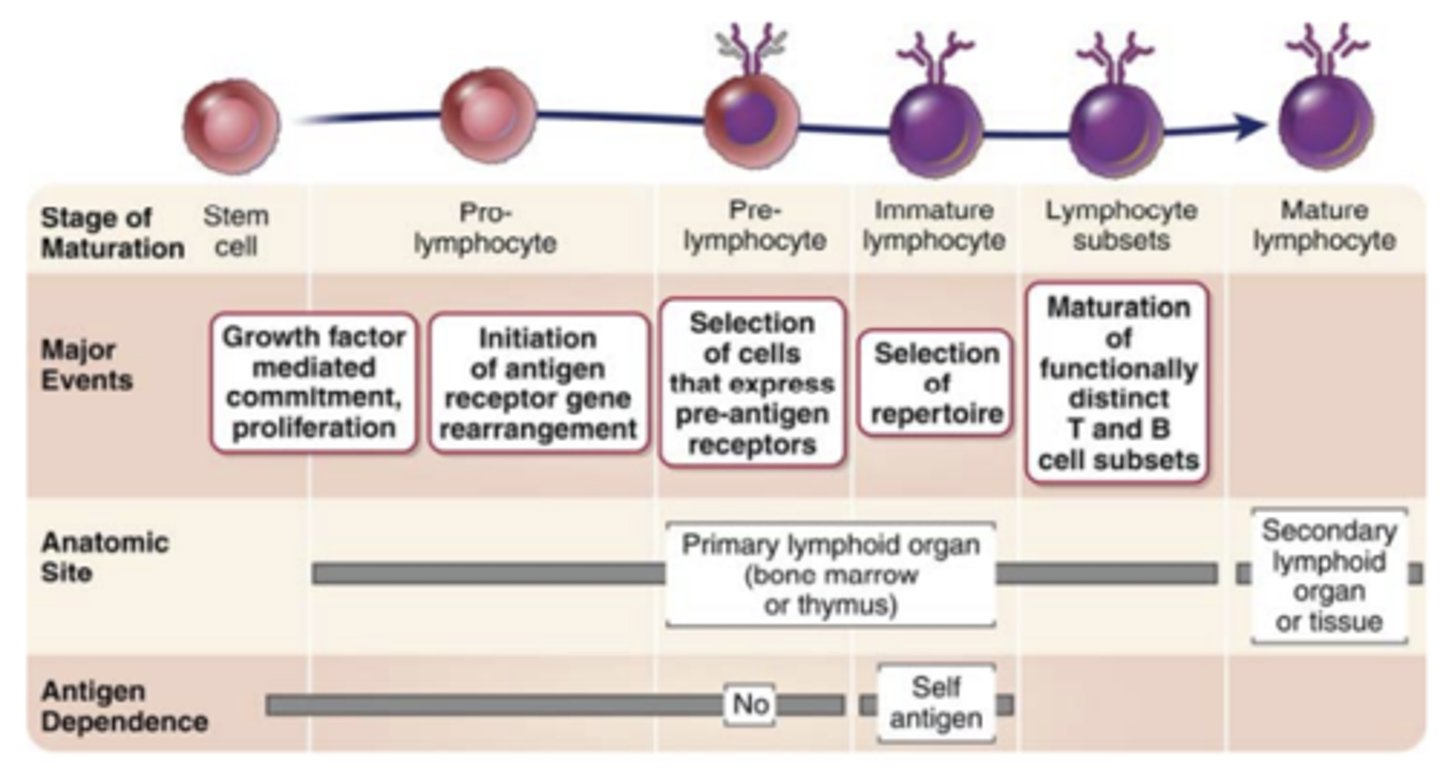
Lymphocyte development: Step 1: Commitment to the....
1. Commitment to the B and T cell lineages
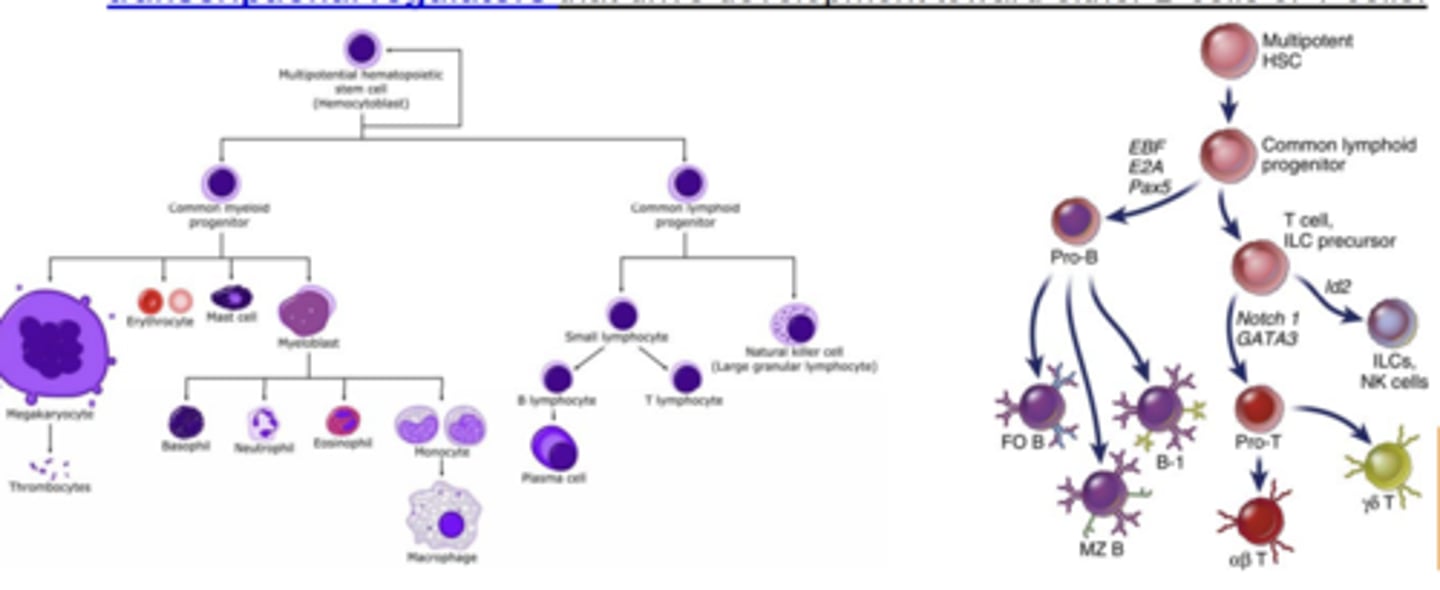
Lymphocyte development: 2. Proliferation of progenitors
- Hematopoietic stem cells and what they give rise to
- Commitment of common lymphoid progenitors to the B or T cell lineage depends on....
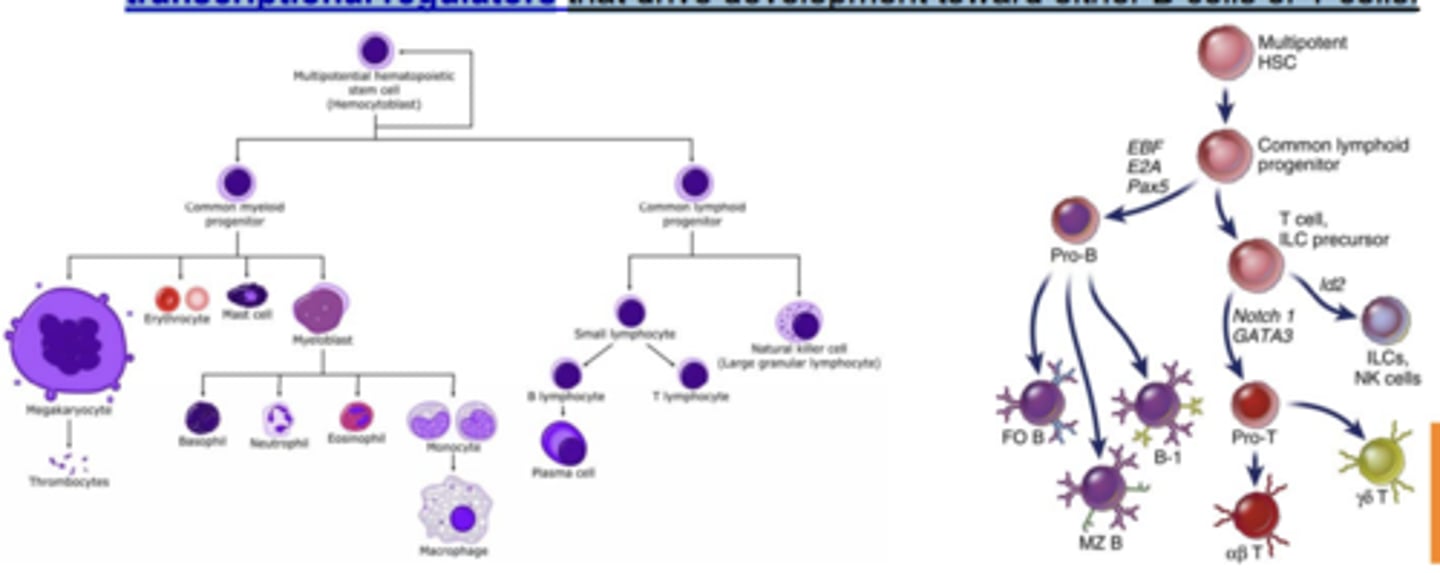
- multipotent stem cells in the fetal liver (before birth) and bone marrow (after birth) known as hematopoietic stem cells give rise to all lineages of blood cells, including lymphocytes
- transcriptional regulators that drive development toward either B cells or T cells.
Lymphocyte development: 3. Antigen receptor gene rearrangement and expression is responsible for the....
generation of a diverse adaptive immune repertoire
3. Antigen receptor gene rearrangement and expression:
Each clone of B or T lymphocytes produces an _______________ with a unique _____________ structure. In any individual, there may be 10 7 to 10 9 different B and T lymphocyte clones, each with a unique __________
- antigen receptor with a unique antigen-binding structure
- unique receptor
Where are functional antigen receptor genes produced?*****
- immature B cells are produce in the bone marrow
- immature T cells are produced in the thymus by gene rearrangement
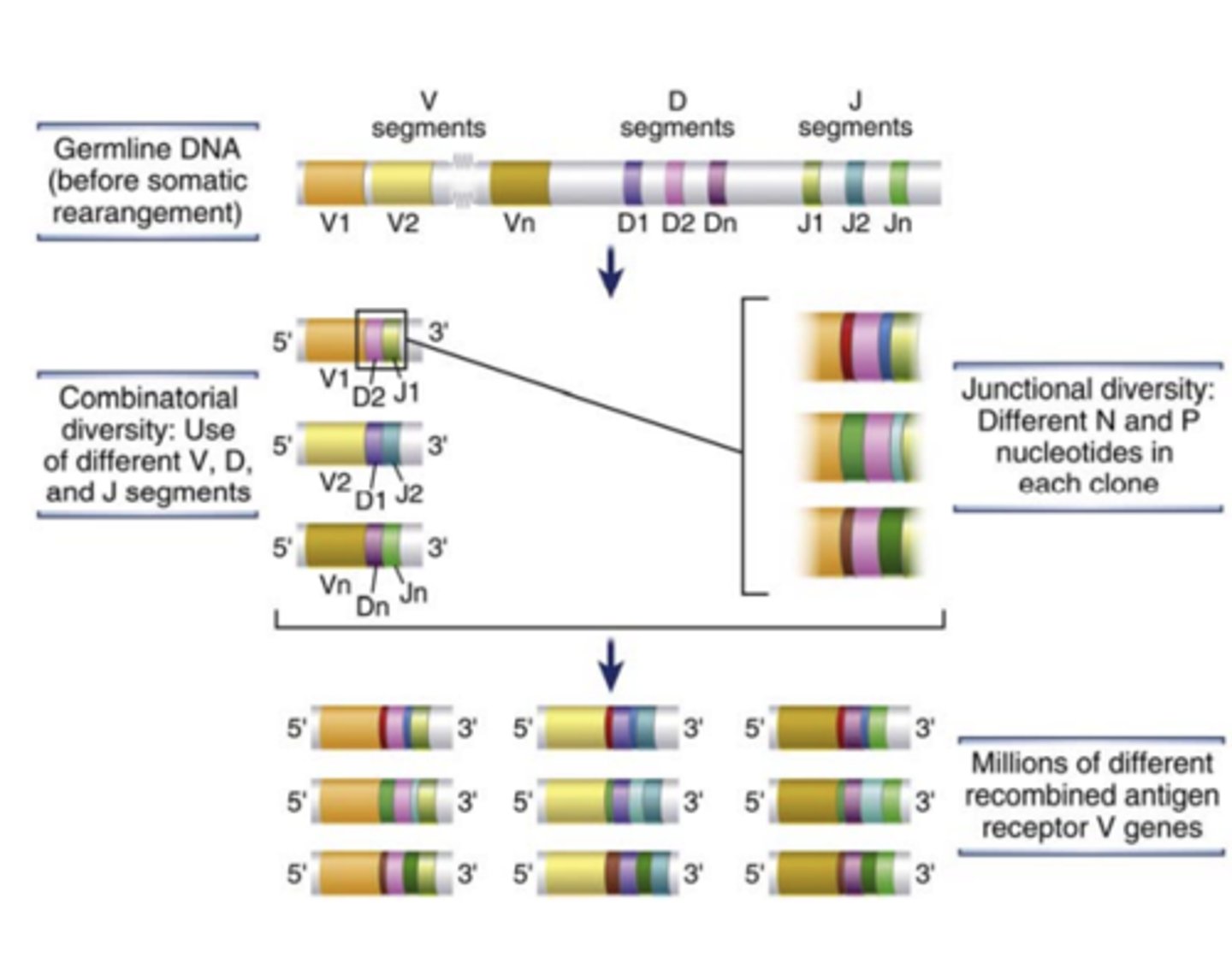
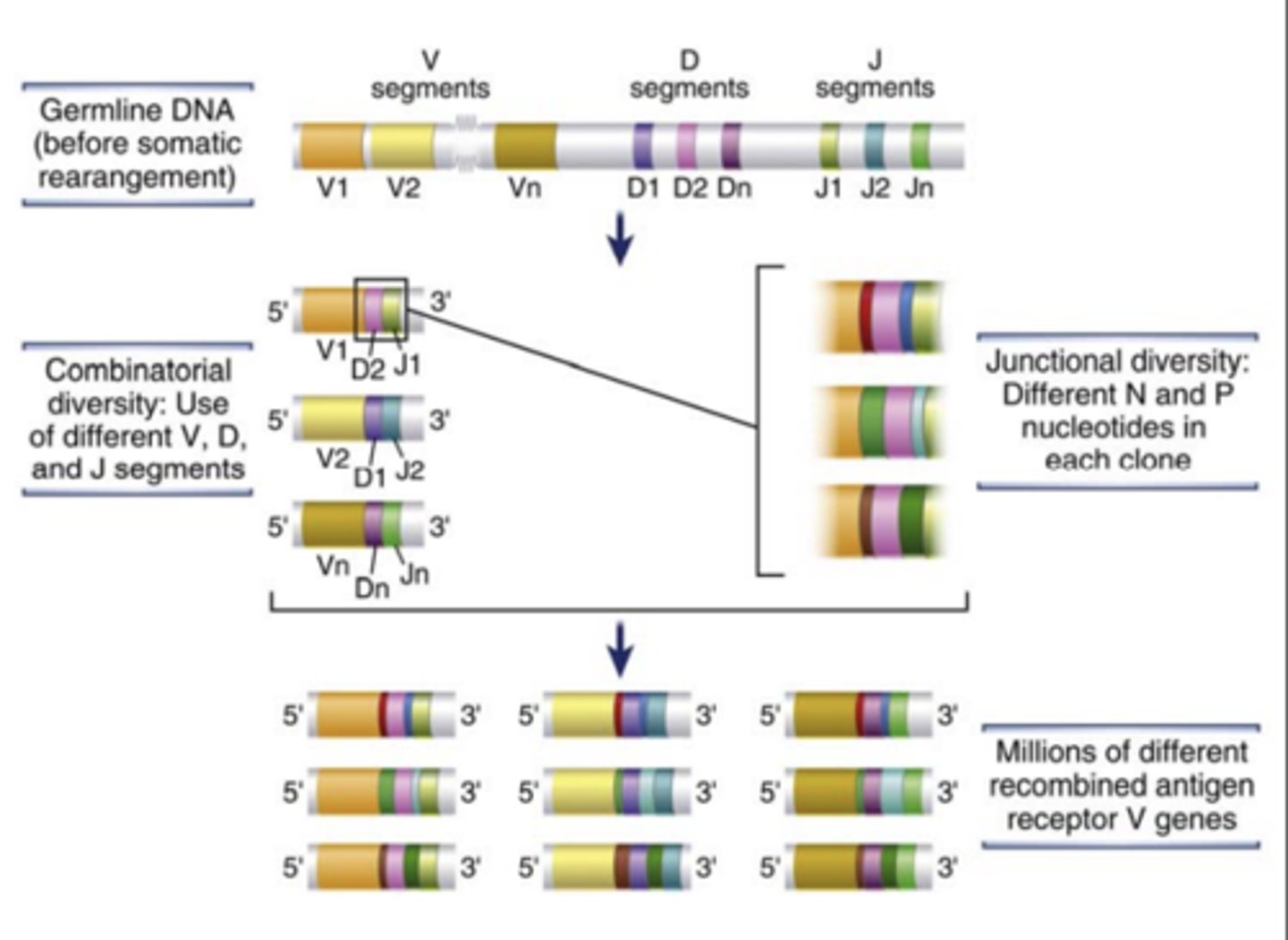
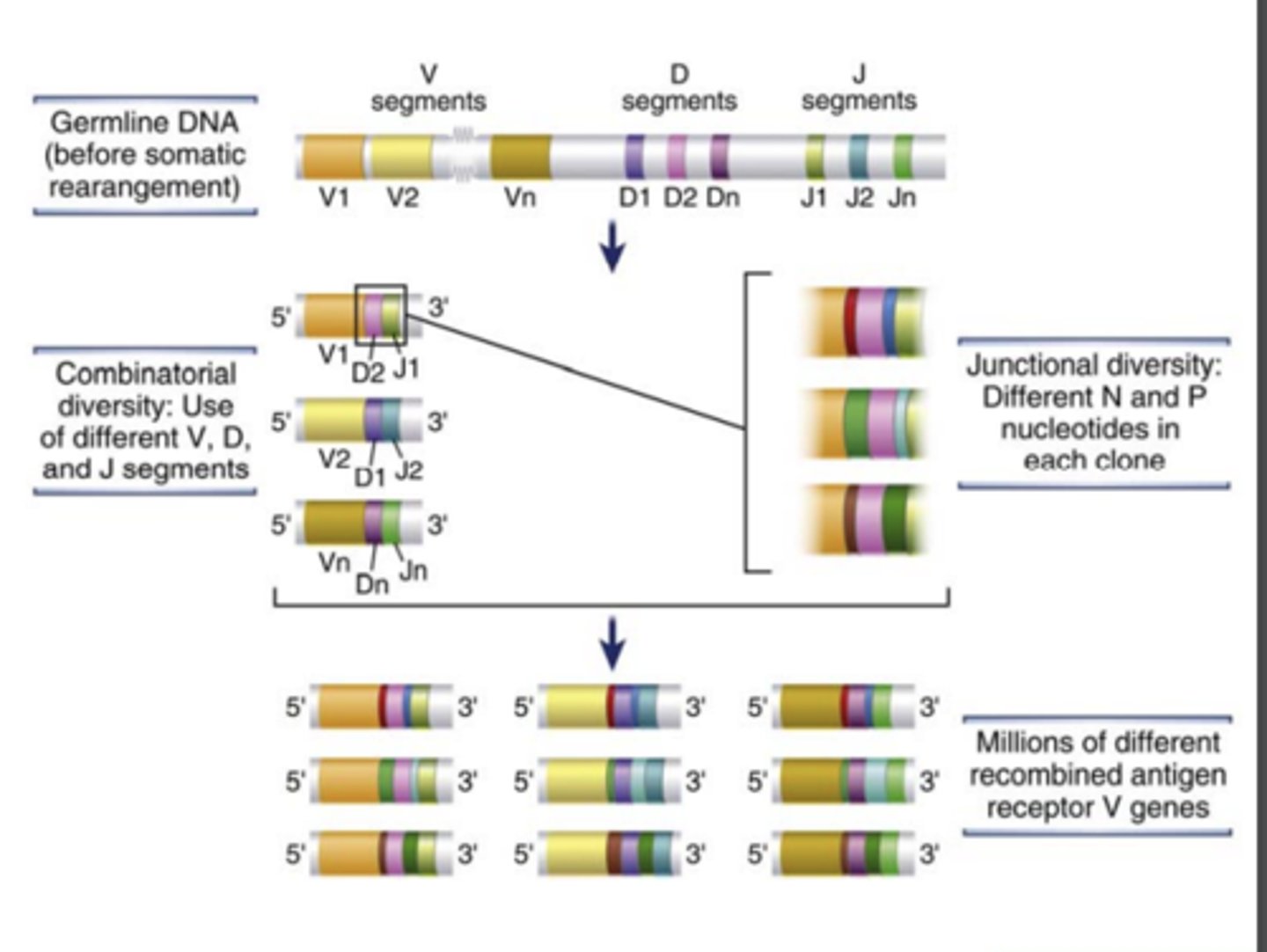
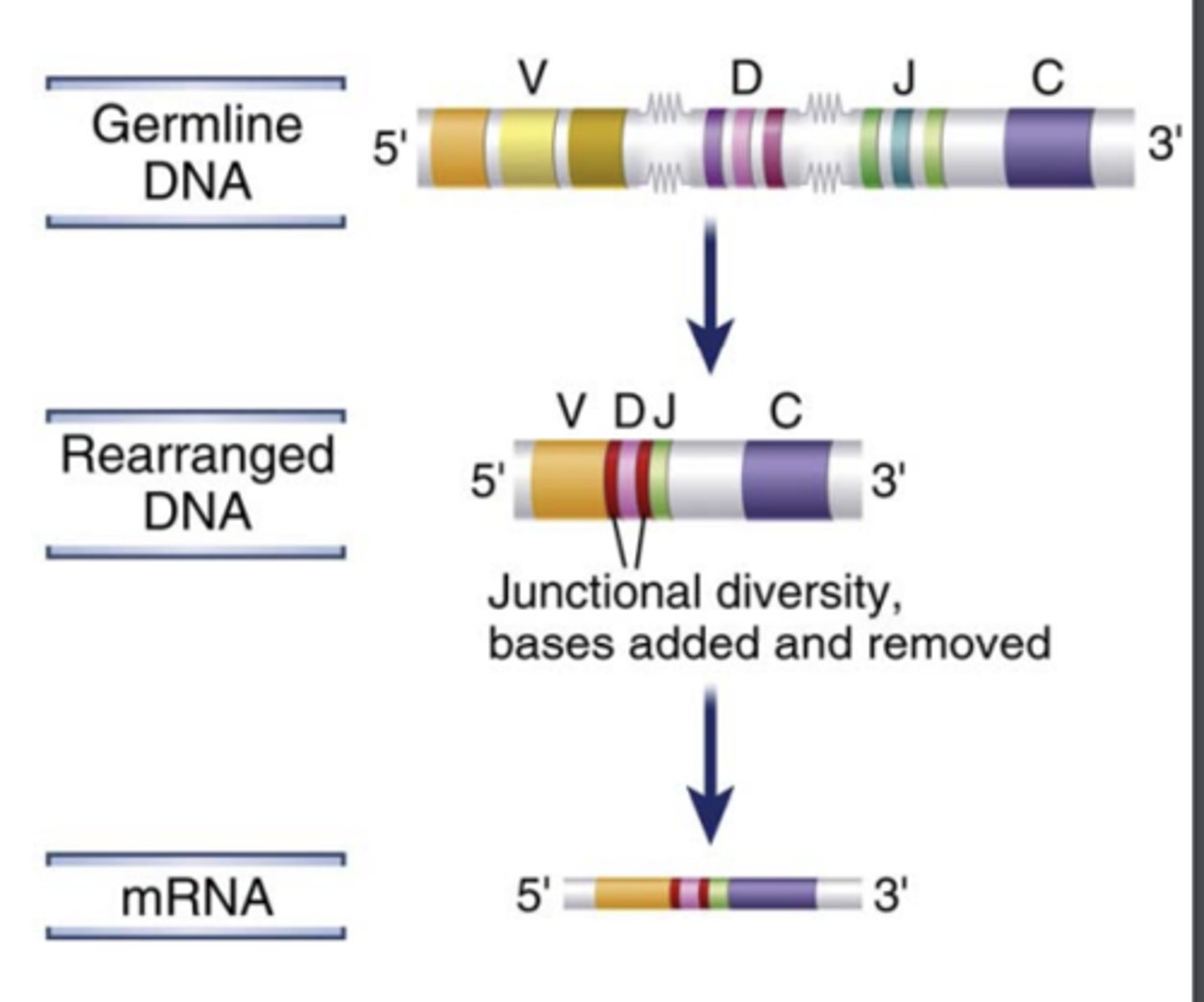
What are genes that encode diverse antigen receptors of B and T lymphocytes generated by?
the recombination of different variable (V) region gene segments with diversity (D) and joining (J) gene segments.
- This specialized process of site-specific gene arrangement is V(D)J recombination
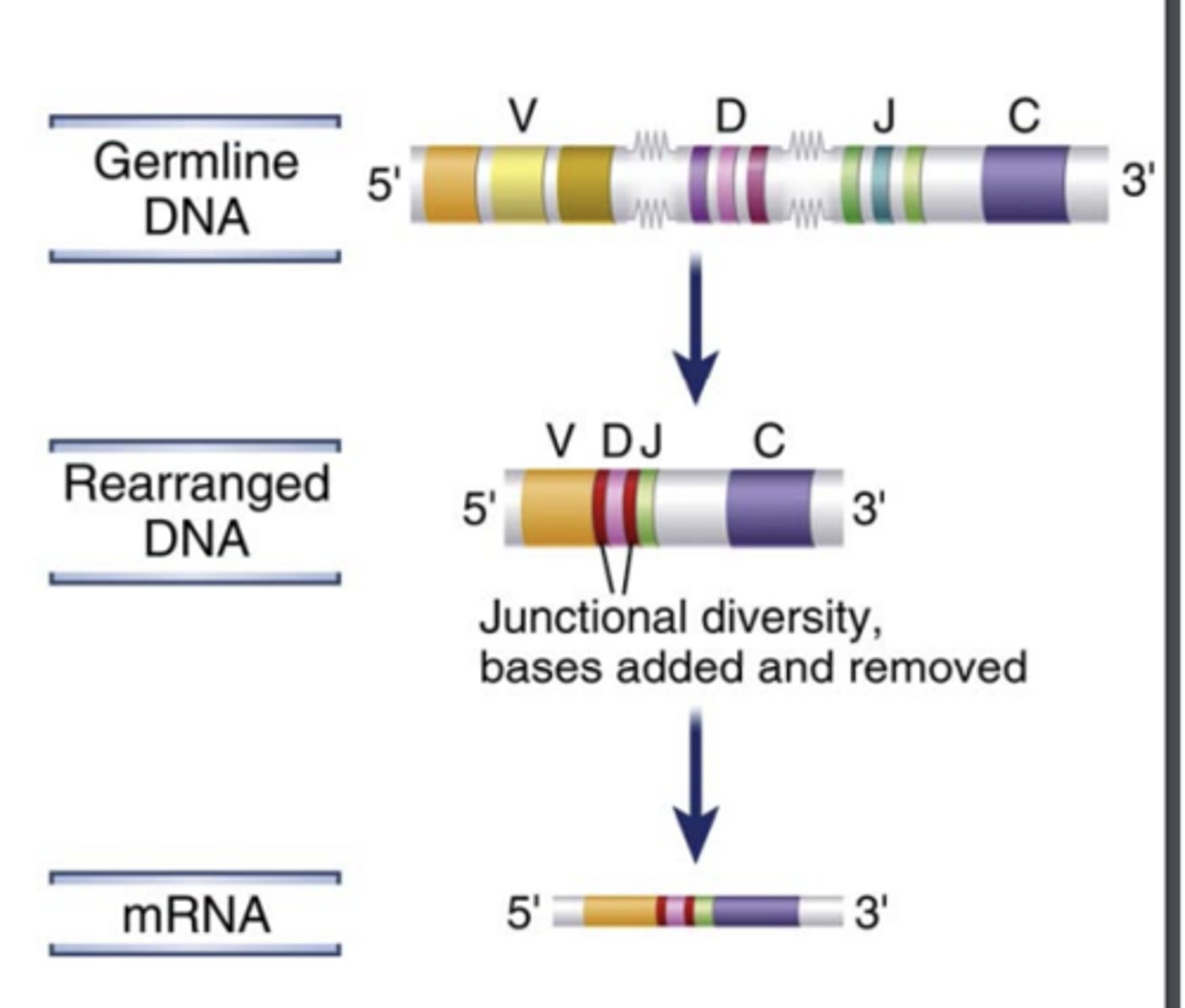
The process of V(D)J recombination at any Ig or TCR locus involves the rearrangement of.....
- one V gene segment
- one D segment (only in Ig heavy chain and TCR β and δ chain loci)
- one J segment in each lymphocyte to form a single V(D)J exon that will code for the variable region of an antigen receptor protein
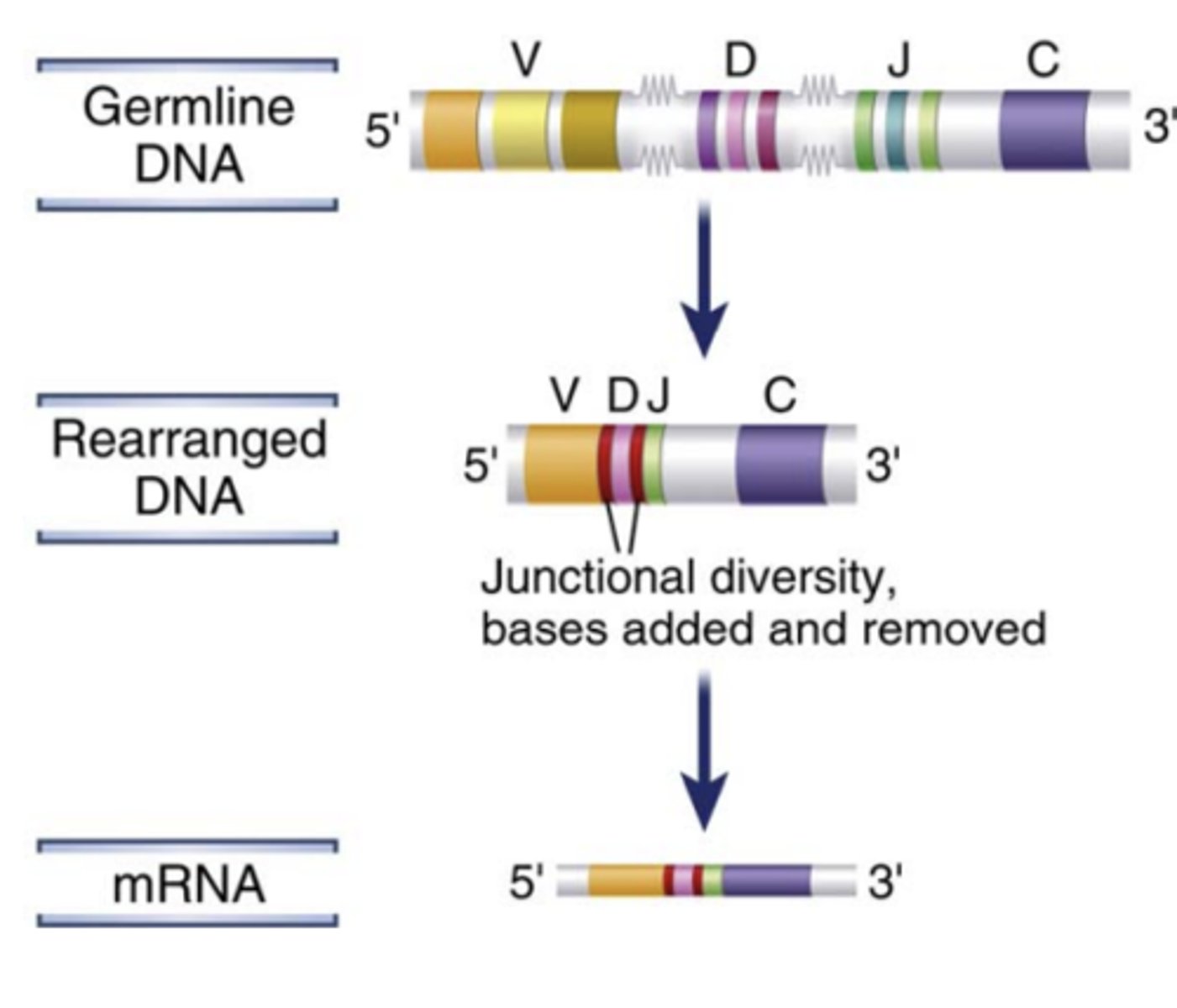
the diversity of antigen receptors is also made by the addition or removal of.....
nucleotides at the junctions of the V and D, D and J, or V and J segments (junctional diversity)
(C represents the constant region)
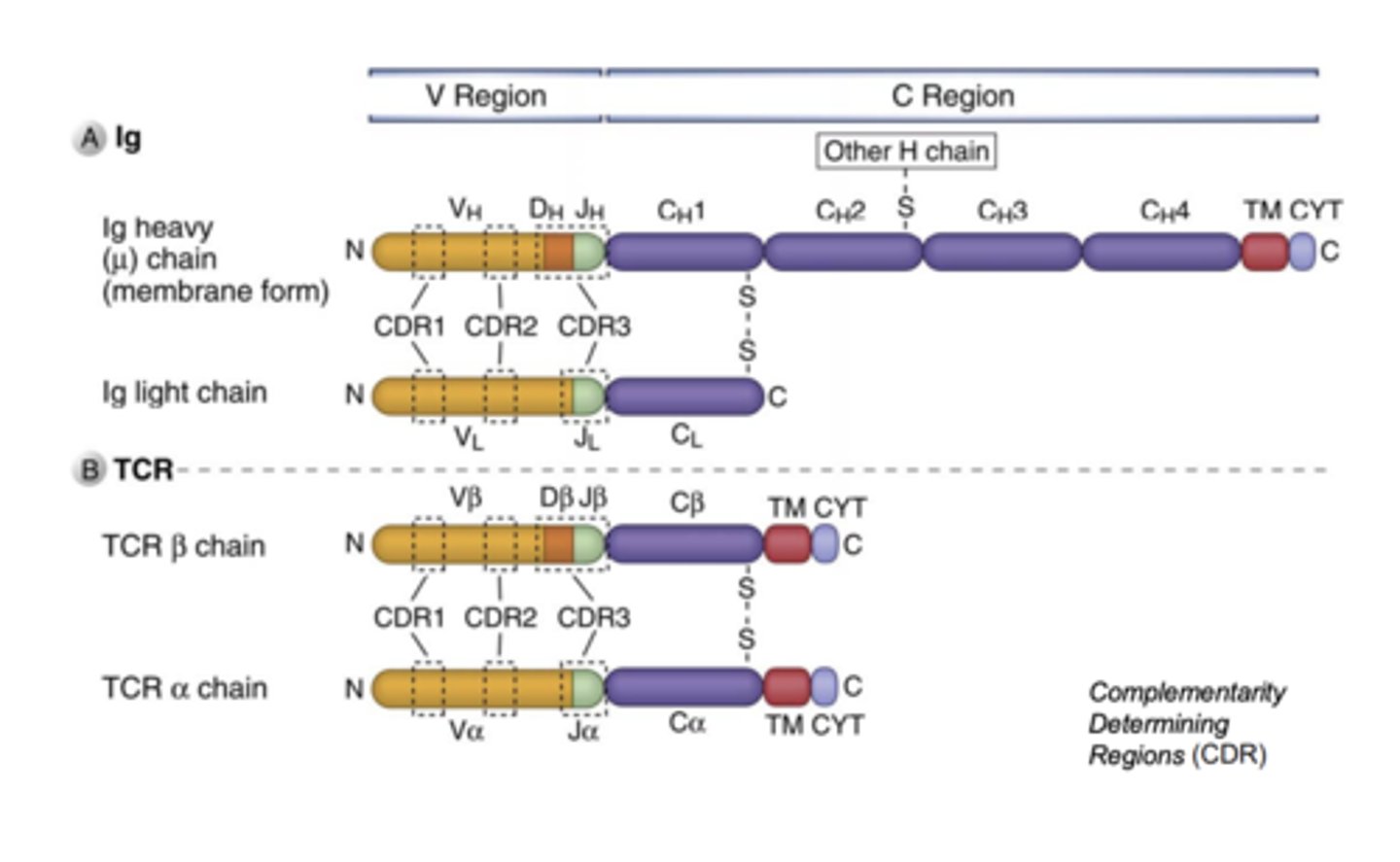
Domains of immunoglobulin and T cell receptor proteins
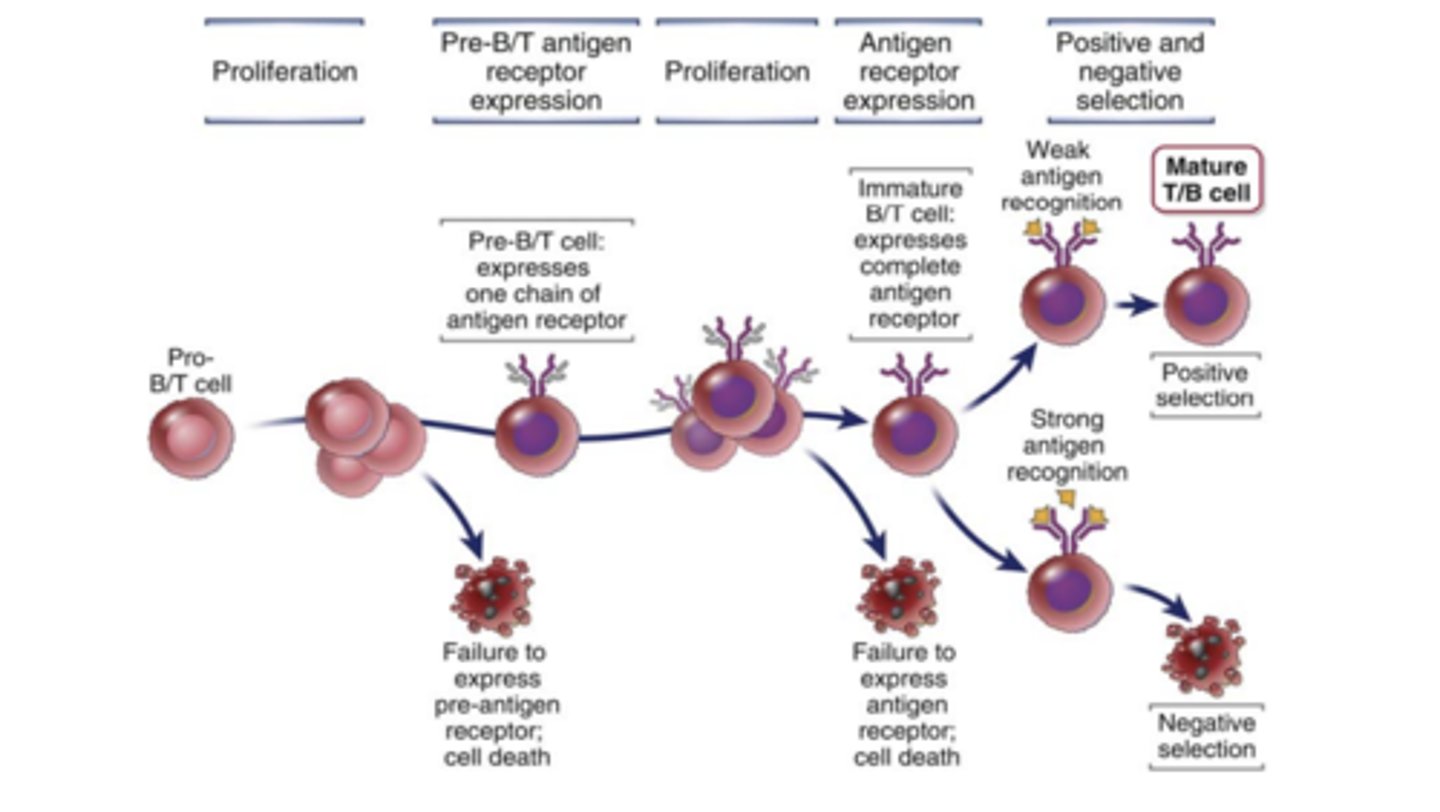
Lymphocyte development: 4. Selection processes that shape the B and T lymphocyte repertoires:
process of lymphocyte development contains numerous steps, called checkpoints, at which the developing cells are....
tested and continue to mature only if a preceding step in the process has been successfully completed
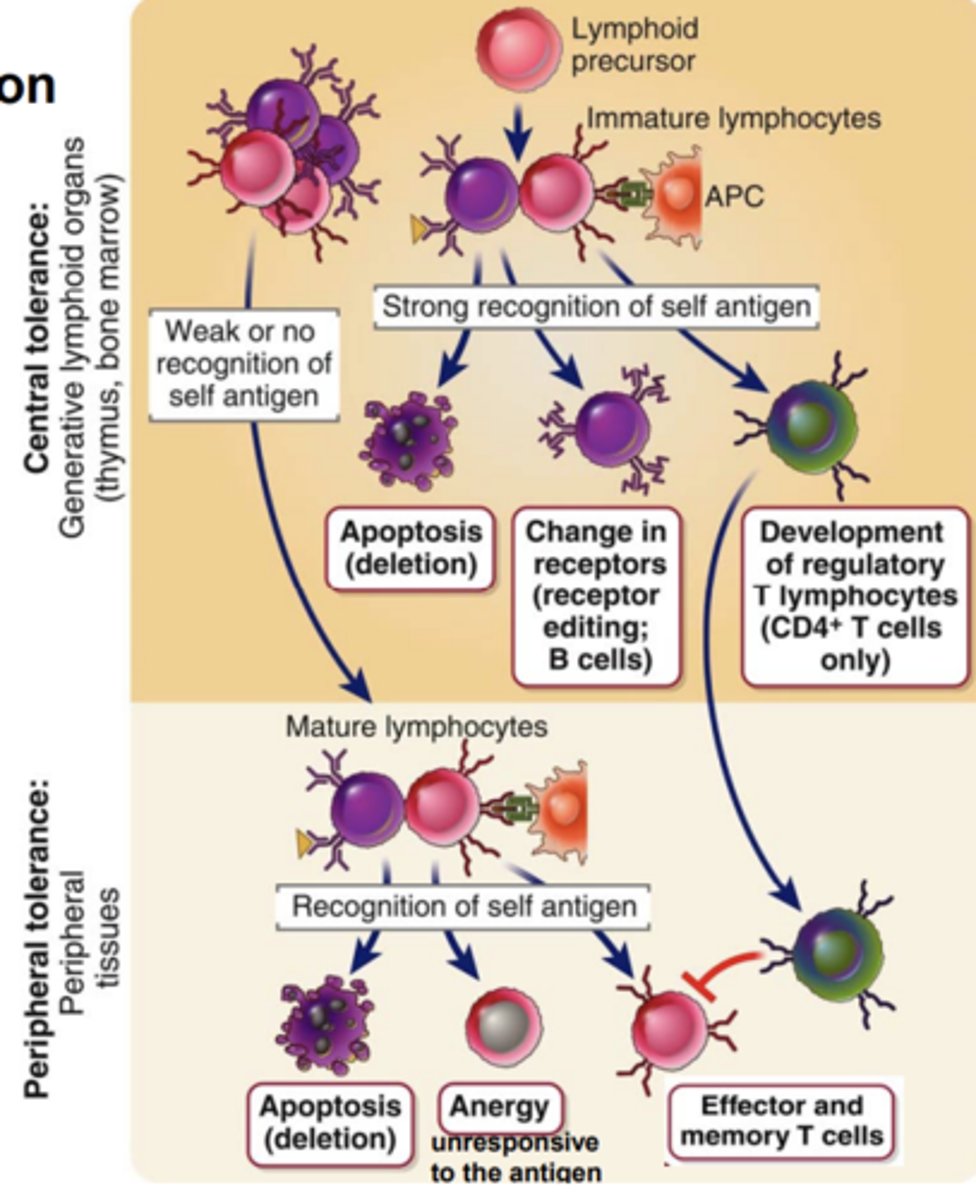
****Where does central tolerance (negative selection) develop?
it develops in the primary (central) lymphoid organs
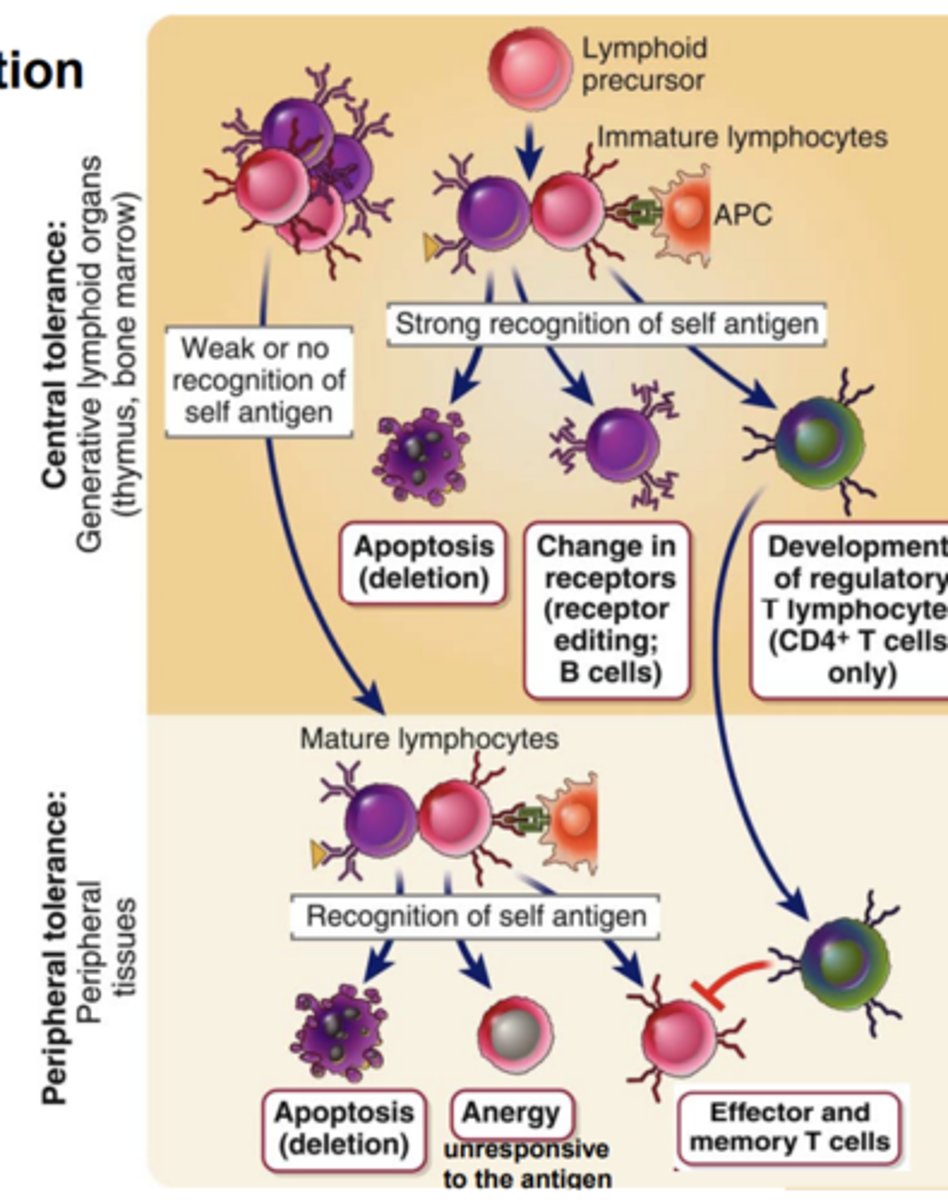
****Central tolerance (negative selection) is the process that...
eliminates or alters developing lymphocytes whose antigen receptors bind strongly to self antigens
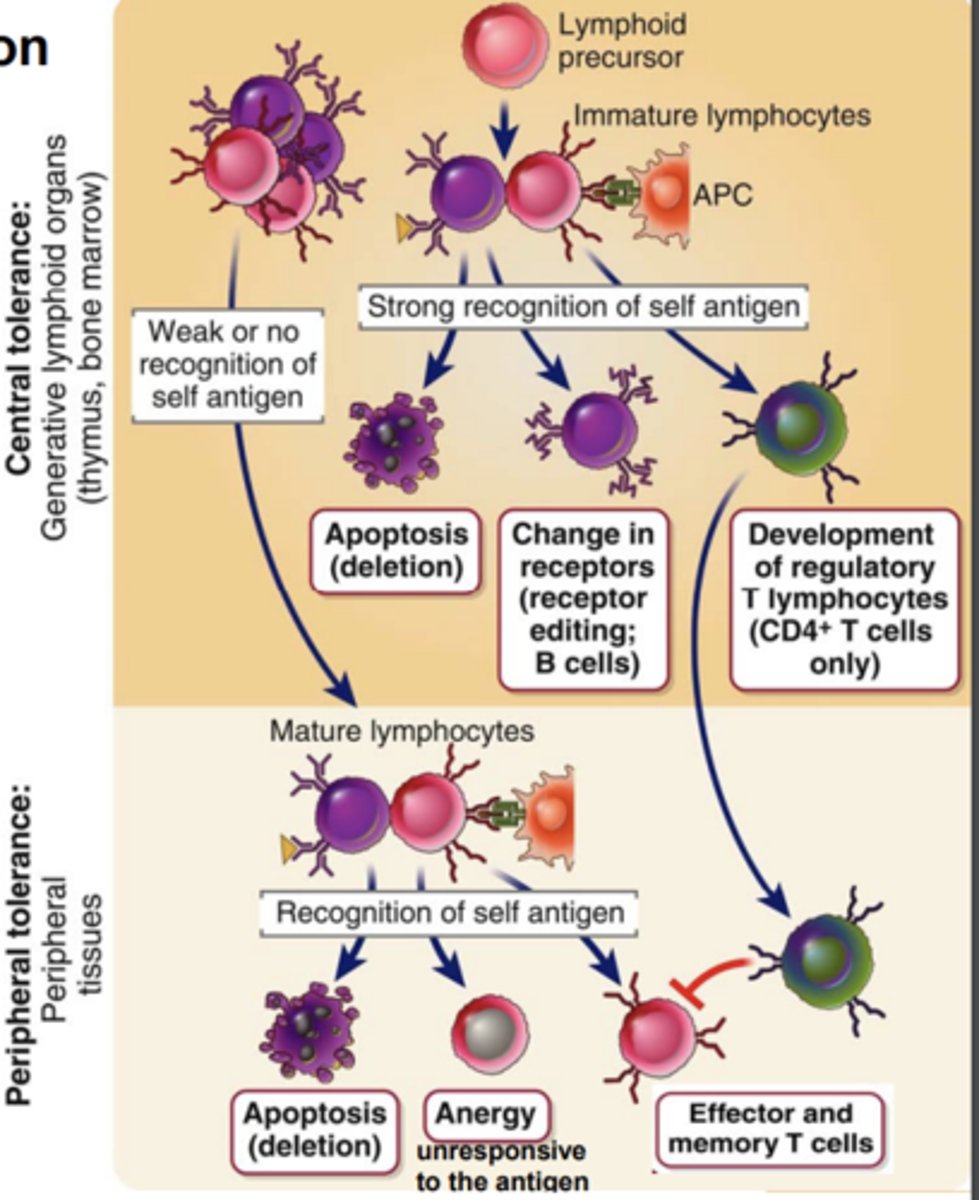
Central tolerance (negative selection) develops T cells with a.....
or form....***
- high affinity for self antigens eliminated by apoptosis (colonel deletion)
- or form regulatory T cells (Tregs)
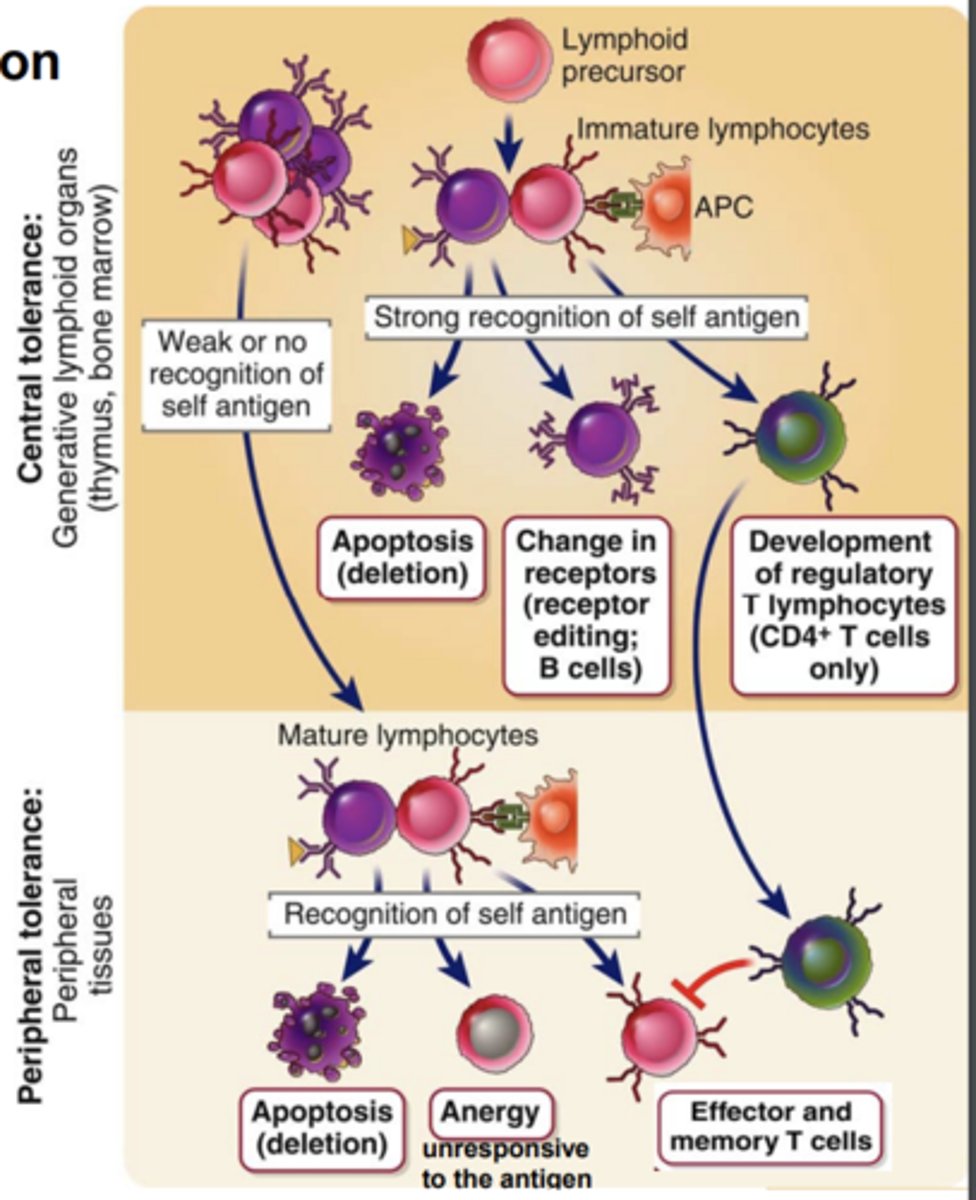
Central tolerance (negative selection) has strongly self-reactive immature B cells forced to make further Ig ______________________ and avoids ______________.
This phenomenon is called _____________. If editing fails, the self-reactive B cells ________, also called ______________.*****
- Ig gene rearrangements
- self reactivity
- receptor editing
- dies, clonal deletion (apoptosis)
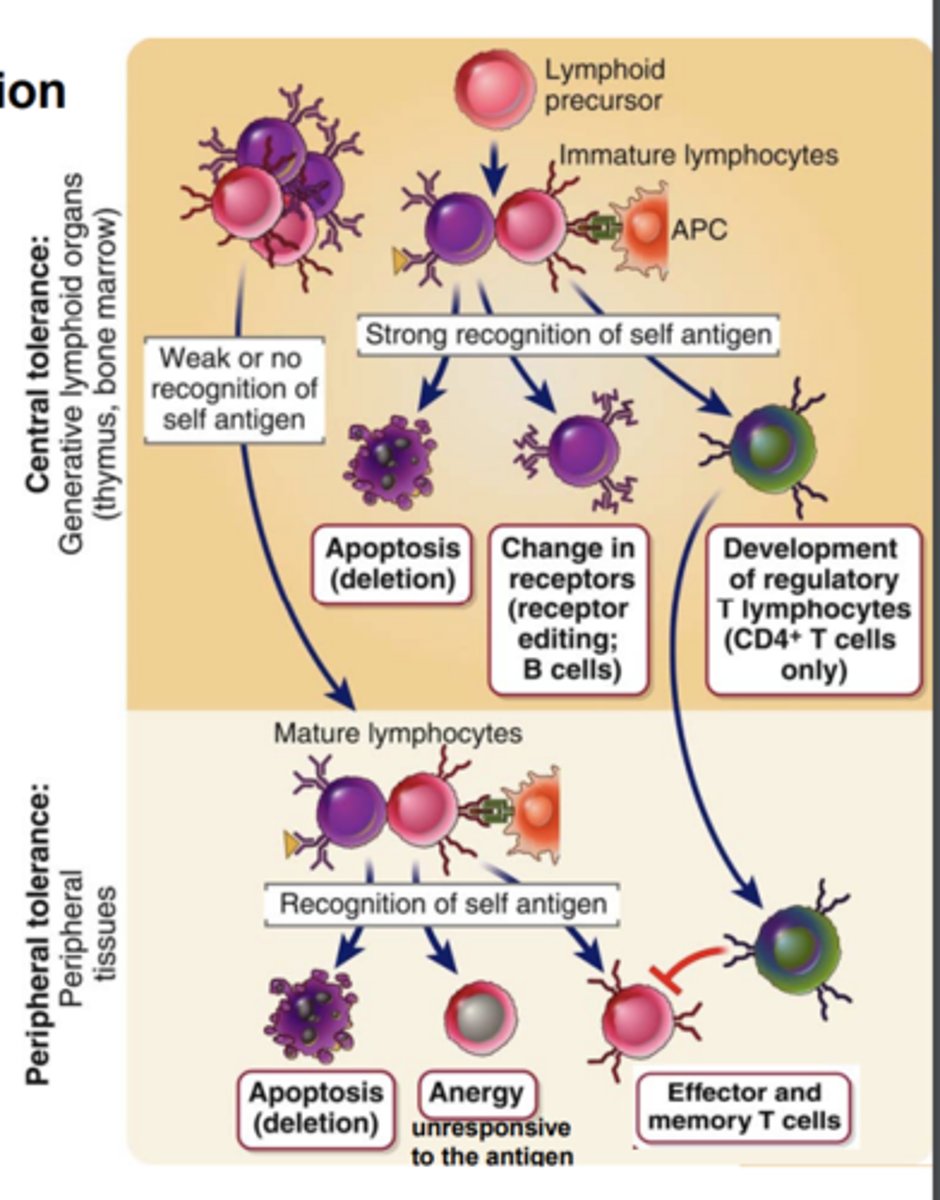
*****Where does Peripheral tolerance (Positive selection) take place?
it takes place in peripheral tissues****
In the T cell lineage, positive selection ensures....
the maturation of T cells whose receptors recognize self MHC molecules
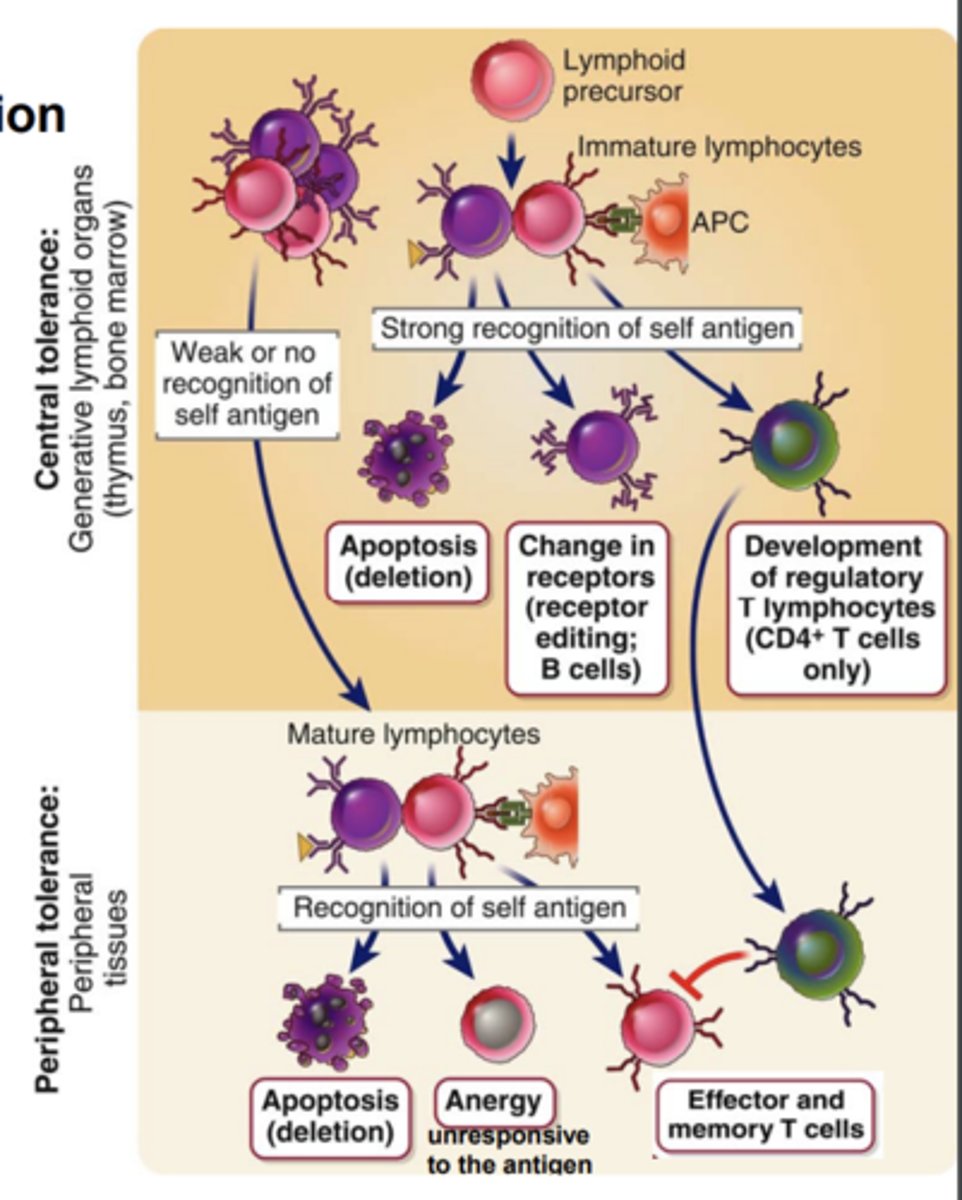
The expression of the coreceptor on a T cell (CD8 or CD4) is matched to the recognition of....
the appropriate type of MHC molecule (class I or II)
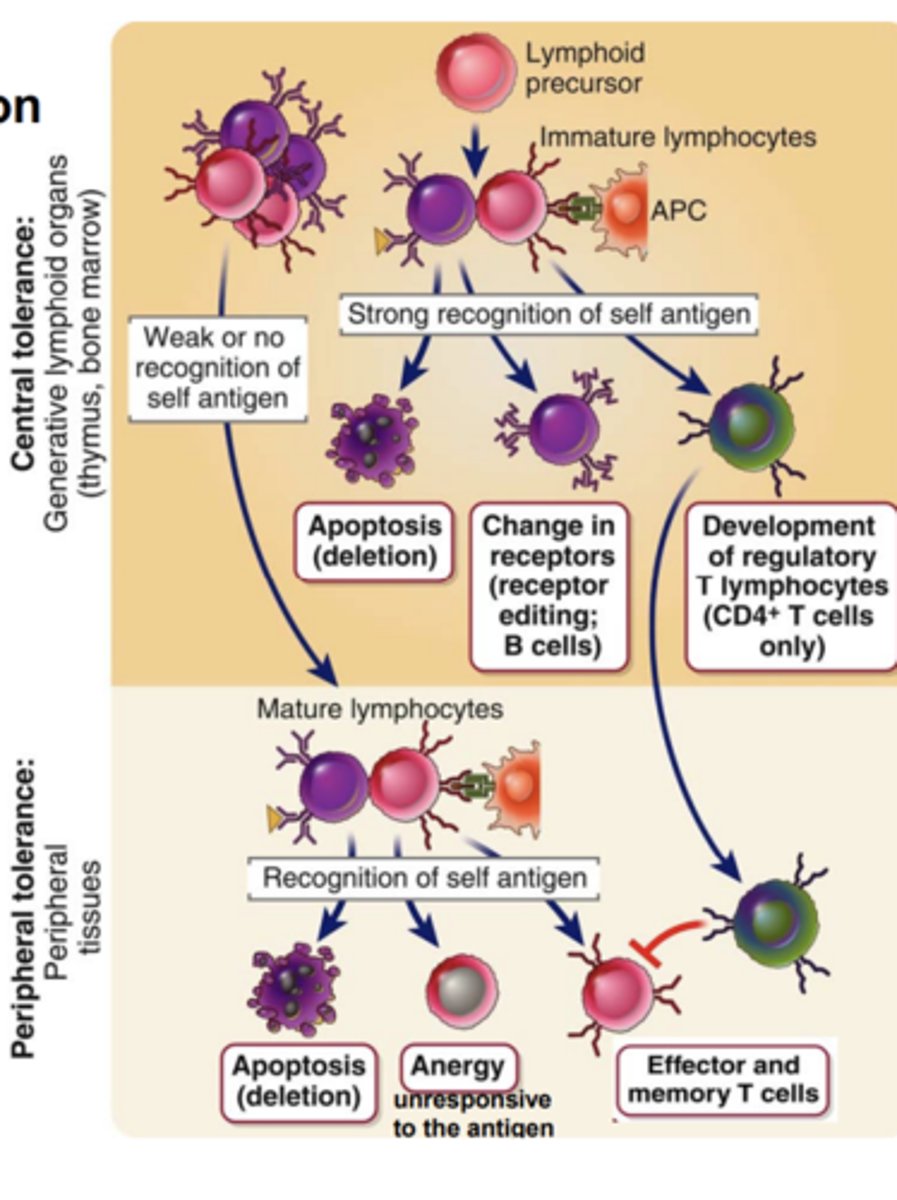
Mature T cells whose precursors are positively selected by self _____________________ in the thymus are able to recognize ________________________ antigens displayed by the same self MHC molecules on APCs in ____________________ tissues
- self MHC molecules
- foreign peptide antigens
- peripheral tissues
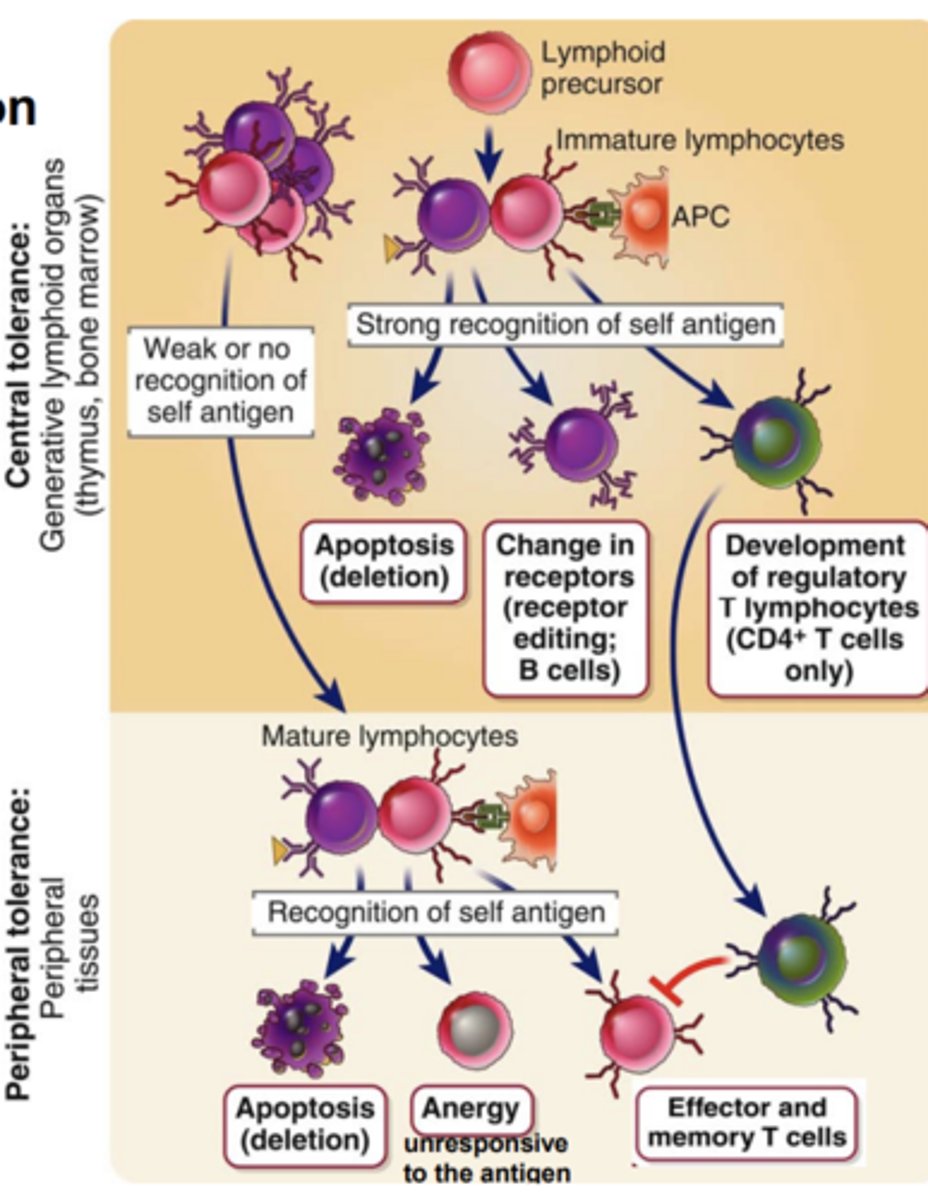
In the B cell lineage, positive selection, preserves.....
all the B cells that don’t recognize the self-antigens from periphery
Mature T lymphocyte development from committed progenitors involves the....
sequential rearrangement and expression of TCR genes, cell proliferation, antigen-induced selection, and commitment to phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets
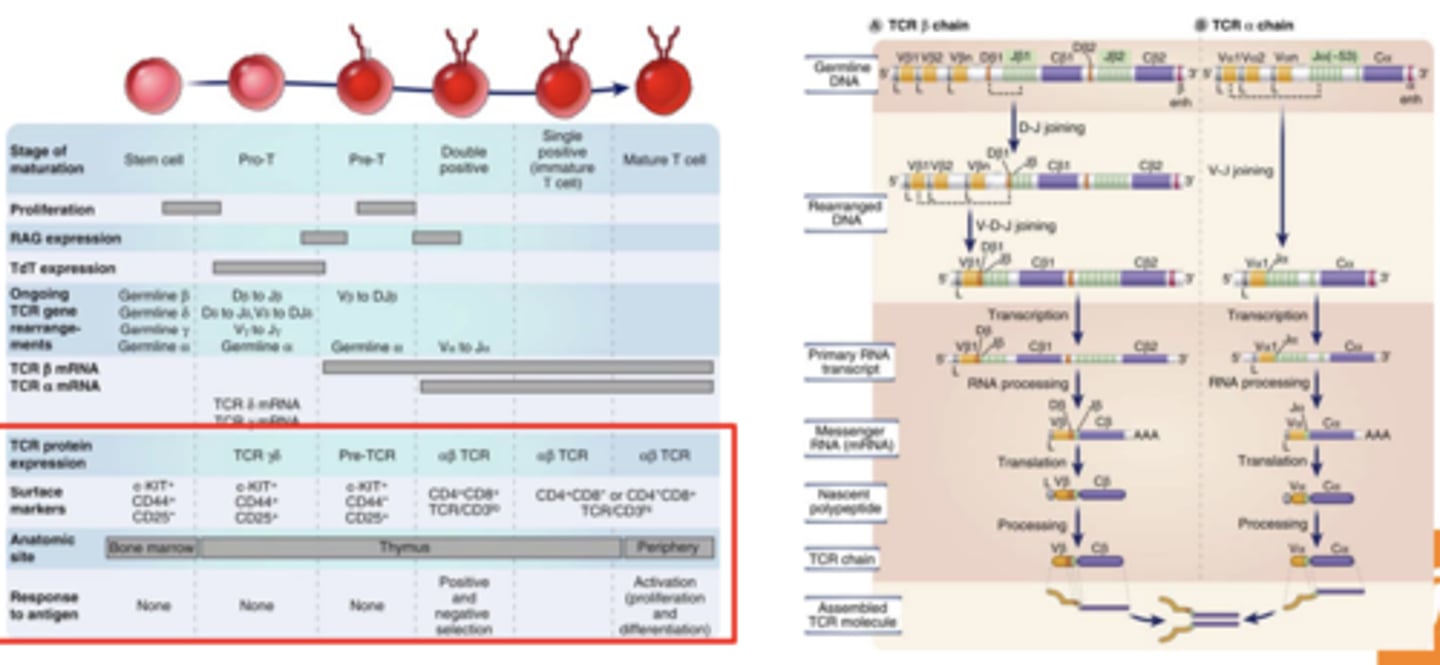
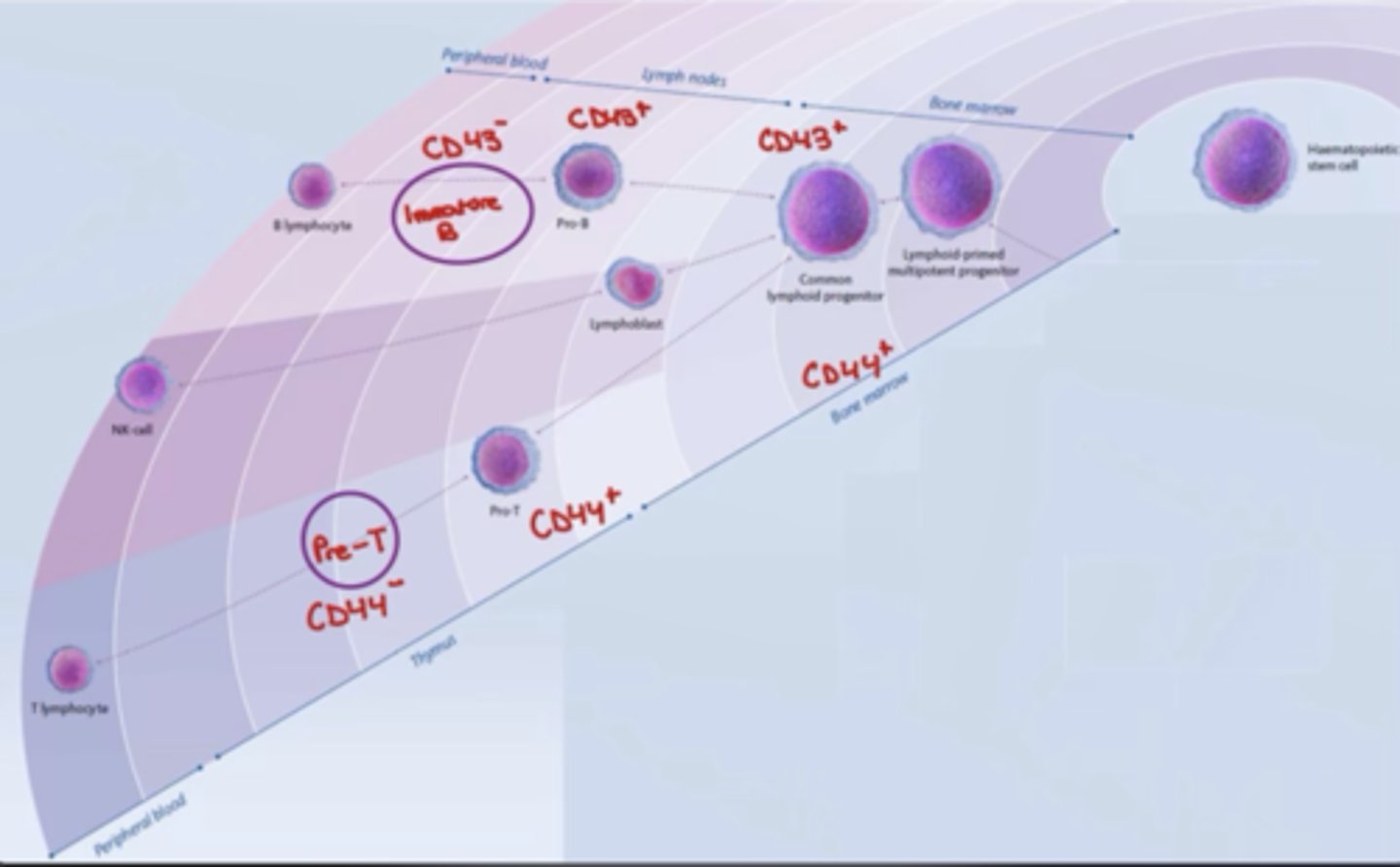
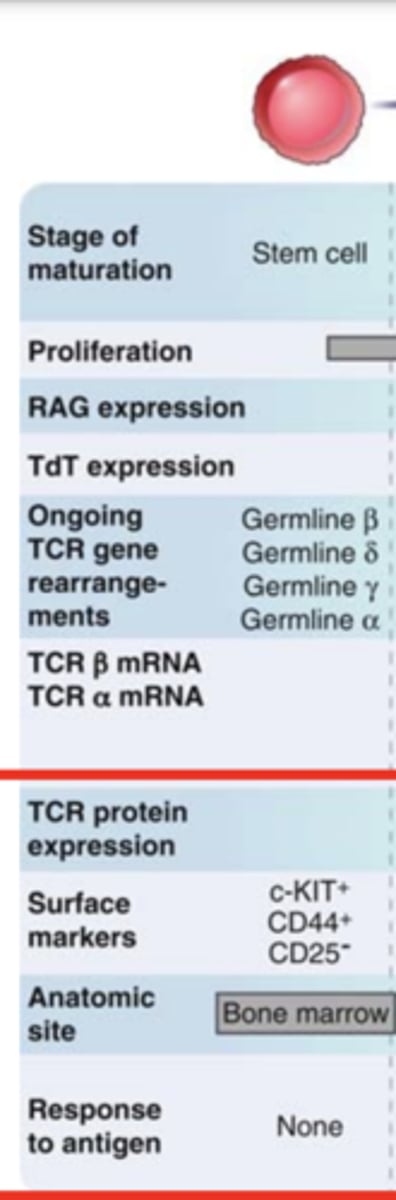
T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Stem cell stage
- C-KIT+
- CD44+
- CD25-
T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Pro-T stage
- C-KIT+
- CD44+
- CD25+

T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Pre-T stage
- C-KIT+
- CD44-
- CD25+

T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Double Positive stage
- CD4+, CD8+
- TCR/CD3lo

T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of stages Single positive (immature T cell) and Mature T cell
- CD4+, CD8- OR CD4-, CD8+
- TCR/CD3hi

B lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Stem cell stage
- CD43+

B lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Pro-B stage
- CD43+
- CD19+
- CD10+

B lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Large Pre-B stage
- B220lo
- CD43+

B lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Small Pre-B stage
- B220lo
- CD43+

B lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Immature B stage
- IgM+
- CD43-
(CD43 becomes negative)

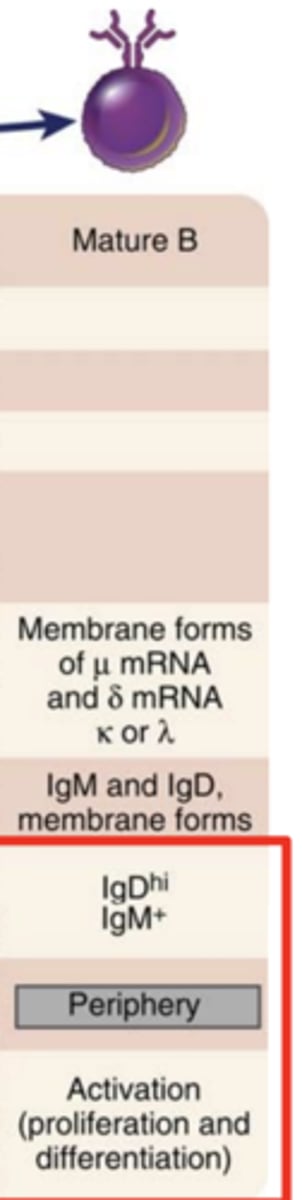
B lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Mature B stage
- IgDhi
- IgM+
When specific lymphocytes encounter antigens, the lymphocytes may be _____________, leading to ___________________, or the cells may be _____________, leading to _______________
- activated
- immune responses
- inactivated
- tolerance
Antigens that induce tolerance are called ________________ to distinguish them from immunogens, which generate immunity
- tolerogens (or tolerogenic antigens)
Self-tolerance
tolerance to self antigens
- fundamental property of the normal immune system
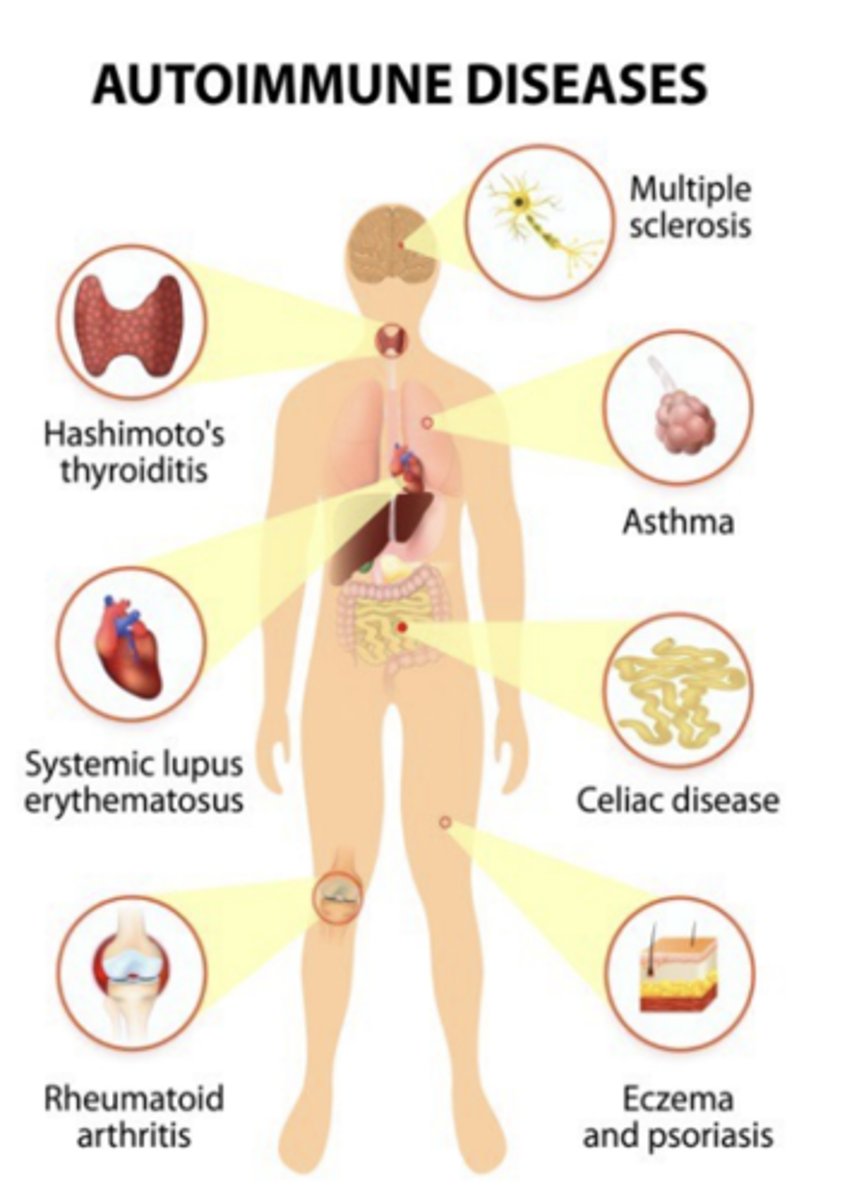
What does failure of self-tolerance result in?
- immune reactions against self (autologous) antigens, called autoimmunity. Diseases they cause are called autoimmune diseases
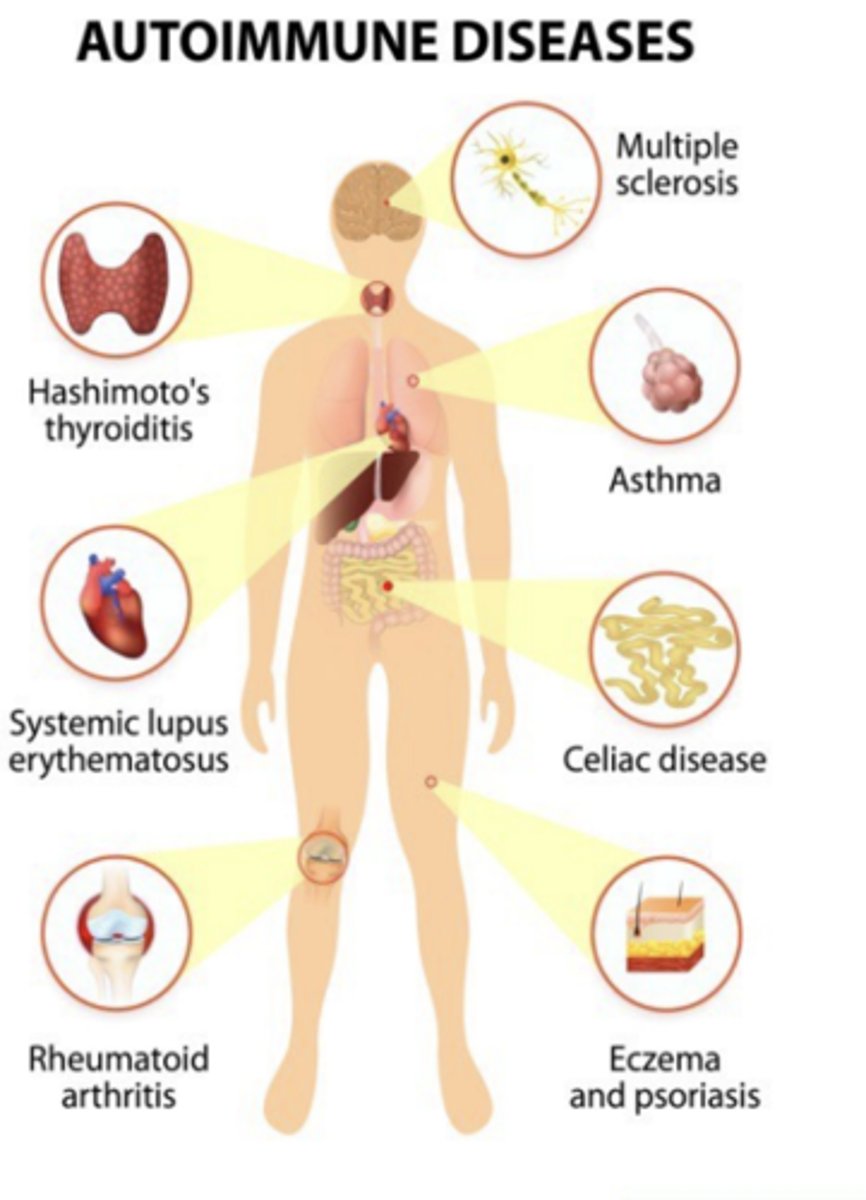
What are immunologic abnormalities leading to autoimmunity?
- Defective self-tolerance
- Abnormal display of self antigens
- Inflammation or an initial innate immune response
Defective self-tolerance
inadequate elimination/regulation of T or B cells, leading to an imbalance between lymphocyte activation and control
- underlying cause of all autoimmune diseases
Abnormal display of self antigens
structural changes in self antigens resulting from enzymatic modifications or from cellular stress or injury (neoantigens)
Inflammation or an initial innate immune response
activate APCs to express increased levels of costimulators, which overcome regulatory mechanisms and result in excessive T cell activation & in the breakdown of T cell tolerance
The 4 steps of therapeutic tolerance induction
1. Repeated administration of small doses of immunodominant peptides
2. Administration of peptides derived from self antigens coupled to nonimmunogenic substrates (such as nanoparticles and erythrocyte membranes)
3. Transfer or activation of Tregs.
4. Costimulatory blockade
therapeutic tolerance induction: Repeated administration of small doses of immunodominant peptides derived from the....
self antigen in aqueous form without adjuvants
- expected that the antigen will be recognized in the absence of costimulation and will induce peripheral T cell anergy or deletion
therapeutic tolerance induction: costimulatory blockade refers to...
blocking B7 molecules using the drug CTLA4-Ig
T and B lymphocyte Chart