Self-Care in People with Pre-existing Cardiovascular and/or Respiratory Conditions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Overall AIM
Identify
minor ailments
worsening of existing medical conditions
ADR’s
Decide to
test and/or refer
give self care advice, treat with OTC?
how urgent is the referral?
Pharmacists role in self - care
•Help patients and the public by assessing their conditions and making decisions about which medicines they should or shouldn’t take.
•Offer advice and practical help on keeping healthy and managing their conditions
•Medicines reviews
Pharmacists are always available and members of the public will often see pharmacists first as they are more accessible
Any existing medical conditions?
Any existing medication?
Their new symptom may be related to their existing medical condition
their new symptom may be an ADR of medication - new doses, change in medication
their medical condition could interact with GSL and P medicines
What are the CV conditions
HT
Heart failure
Arrhythmia
Peripheral vascular disease
coronary heart disease or ischaemic heart disease e.g. angina
previous myocardial infarction
previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack
previous deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary thrombosis
congenital heart or heart valve defects
Be familiar with patients using different simple terminology to describe their medical condition
Hypertension - high Blood pressure
Often discovered during routine health checks as its asymptomatic
Symptoms are usually rare
Headache or blurred vision
Referrals often made by opticians
Increases risk of other, often more serious cardiovascular conditions such as HF, MI, CKD, increased risk of vascular dementia
Pharmacists can:
Measure blood pressure
Advise on lifestyle changes to decrease risk
Advise on medication side effects
requires referral to GP
If patient is already diagnosed with HT, and has headache, need to find out of its other things causing the headache
patients may have severe HT - consistently have systolic of greater than 160 and diastolic more than 100 then GP referral within 2 days
patients with chronic HT - systolic greater than 180 and diastolic ore than 110 then needs A and E or G.P straight away
Heart Failure
The heart not pumping blood as effectively. Caused by other CV conditions
Symptoms are caused by accumulation of fluid in the lungs or legs and ankles: accumulation in the abdomen in more serious cases
Breathlessness and fatigue causing decreased exercise tolerance
Cough or shortness of breath at night
Unable to lie flat
Swollen ankles legs
Weight increase - more than 2kg over a short period of time
is it a respiratory related symptoms? cough associated with sputum
give practical advice such as prepping themselves up and using two pillows to help with breathlessness
Attend A&E if there are sudden and worsening changes in the patient’s usual symptoms
Arrhythmias
Irregular heart rate or rhythm e.g. atrial fibrillation/flutter, or ventricular tachycardia
Normal resting heart rate for adults is 60 to 100 bpm
Sensation of “fluttering” in chest
Racing heart (tachycardia) - HR over 100, can be post exertion which is normal or when patients are unwell
Light-headed or fainting episodes … “funny turn” - ask patient to expand if you don’t understand, refer to A and E, if occasionally then refer to GP
Patients who are treated for arrythmias may also be prescribed anticoagulant therapy to prevent stroke
Be aware of the common side effects for anticoagulants e.g. unusual bleeding
Attend A & E if:
Involved in an accident
Experience a blow to the head or fall
Are unable to stop the bleeding
Coronary artery disease
Angina
Tight and pressing pain in the chest, neck or jaw.
If exercise induced likely stable angina
If not exercise induced or happens at rest suspect unstable angina
If not previously diagnosed, suspect MI
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Pain (tight, pressing) chest
Also, can spread to jaw, neck, arm (tingling)
Sweating, nausea, breathless and can come on suddenly
300mg aspirin and GTN spray - can administer this and let ambulance know so they don’t administer again.
If GTN spray doesn’t work then likely high levels of occlusion - call a and e
Peripheral vascular disease
Narrowing or occlusion of the peripheral arteries, reducing the blood supply to the lower limbs
Intermittent claudication - pain in lower limbs which is relieved by rest
Shiny skin, hair loss on calves, discolouration
Temperature differences between legs
Numbness or tingling (may be intermittent)
Poor wound healing or ulceration due to decreased blood supply - common in diabetic patients
Leg or hip cramps
Ischaemia in the limbs can lead to the need for amputation
The main risk factors are smoking and diabetes
Stroke or TIA
Face – the face may drop on 1 side, the person may not be able to smile, or their mouth or eye may have drooped.
Arms – the person may not be able to lift both arms and keep them there due to weakness or numbness in 1 arm.
Speech – speech may be slurred or garbled, or the person may not be able to talk at all despite appearing awake; they may have problems understanding what you say.
Time – to dial 999 immediately if you notice any of these signs or symptoms, AS TREATMENT IS TIME DEPENDENT
Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Pain, swelling and tenderness in one leg (usually calf)
A heavy ache in the affected area
Warm skin around the area of the clot
Red skin, particularly at the back of a leg below the knee
Sometimes there are no symptoms
Pulmonary embolism (PE)
Breathlessness which may come on gradually or suddenly
Chest pain which may become worse when breathing in
Sudden collapse
Signs of DVT
Call 999 if patients are experiencing symptoms of…
MI, sudden chest pain that
Spreads to the arms, back, neck or jaw
Makes their chest feel tight or heavy
Accompanied with shortness of breath, sweating and nausea and/or vomiting
Last more than 15 minutes
Overwhelming feeling of anxiety
Cardia arrest, collapse or unconsciousness
Stroke symptoms - F.A.S.T
Common adverse effects to CVS medication...
Drug Group | Common adverse effects |
Beta blockers [e.g. atenolol, bisoprolol] | Fatigue, cold hands, slow heart beat, insomnia, impotence |
ACE inhibitors [e.g. ramipril, lisinopril] | Dry cough, light-headedness, angioedema |
Calcium channel blockers [e.g. amlodipine, nercidipine] | Headache, swollen ankles, flushing- |
Diuretics [e.g. indapamide, bendroflumethiazide] | Dehydration (?), thirst, Gout, impotence, hypoglycaemia |
Statins [e.g. simvastatin, atorvastatin] | Muscle pain and weakness, raised blood sugar (diabetes) |
Anticoagulants [e.g. warfarin apixaban, rivaroxaban] | Easy to bruise, short nose bleeds Blood in urine, unexplained bruises, severe headaches, bleeding that doesn’t stop 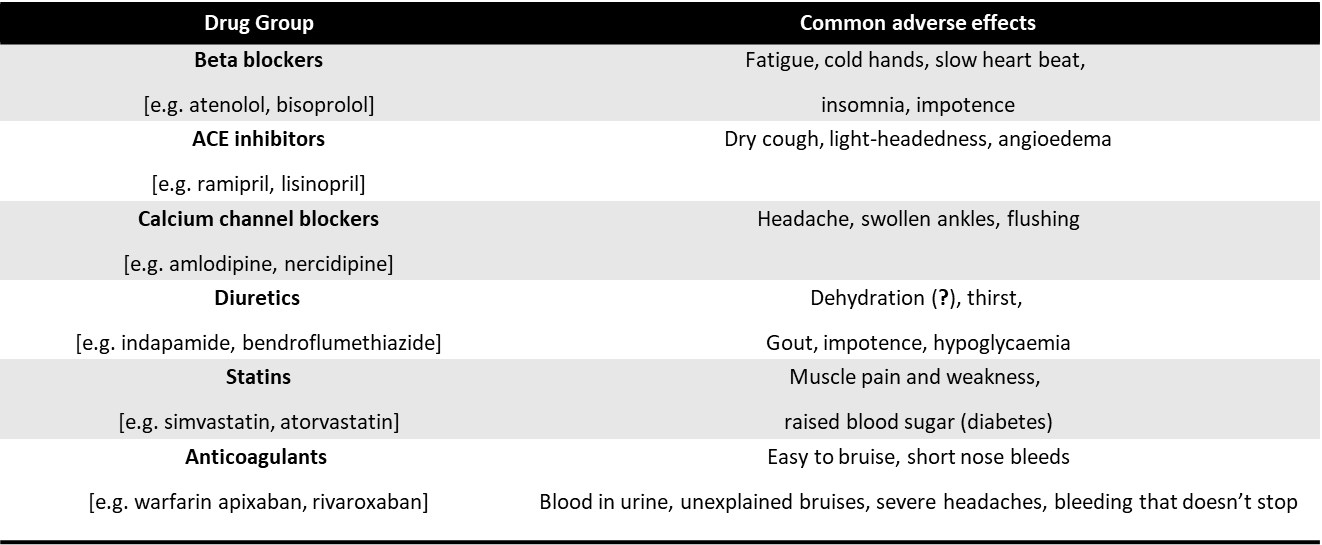 |
THIS LIST IS NOT EXHAUSTIVE
MAKE NOTES ON COMMON SIDE EFFECTS ON ALL CLASSES OF DRUGS YOU LEARN
Current medications
Many people experience adverse drug reactions (ADRs)
Always consider the possibility of a symptom being related to prescribed or OTC medication … so always ask the question
The reaction/s may be mild or severe
reaction may be individual
It may occur immediately or after some time of taking
Find out how long a medicine/s has been taken for
Any recent changes to medication - e.g. dose, frequency etc
If you don’t know the common side-effects for a drug/drug group a person is taking – look it up (especially if the symptom coincides with starting the new drug)
If person stops amiodarone - still stays in system for months - check when they last stopped taking it so can still interact with other medications
What P/GSL medicines should be avoided in cardiovascular disease?
Decongestants e.g. pseudoephedrine - constricts blood vessels
Anti-inflammatories e.g. aspirin, ibuprofen
Products containing excess sodium – antacids, effervescent/soluble tablets, cystitis sachets
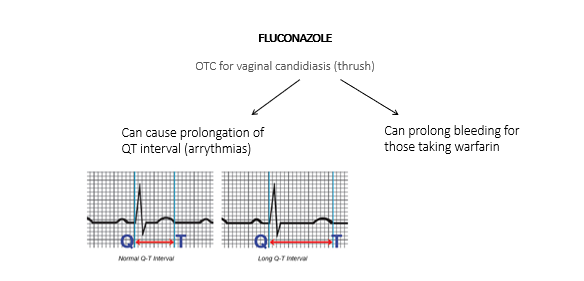
Oral antifungals – fluconazole can interact and cause arrythmias
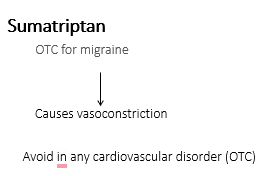
5-HT agonists - Sumatriptan causes vasoconstriction
*Don’t sell OTC, as not licensed for it
Decongestants
Ephedrine and pseudoephedrine has direct or indirect sympathomimetic activity
Pseudoephedrine is less potent but can still produce elevation in systolic blood pressure by causing vasoconstriction, and can also cause tachycardia.
Aspirin and NSAID’S
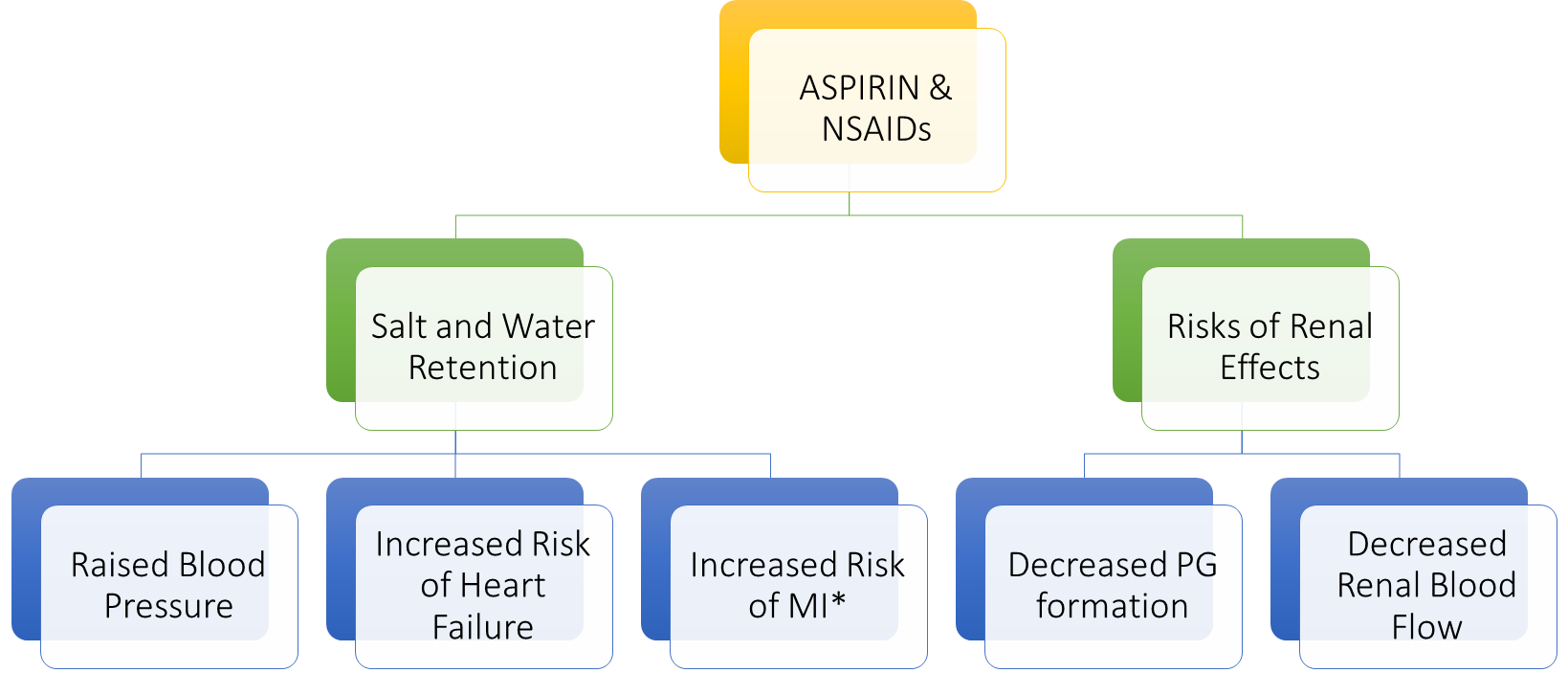
Anti-inflammatories inhibit COX enzyme so lower synthesis of prostaglandins which act on kidney as a vasodilator, so reduced blood flow to kidneys, indirect effect on CV system - can lead to heart failure and high blood pressure
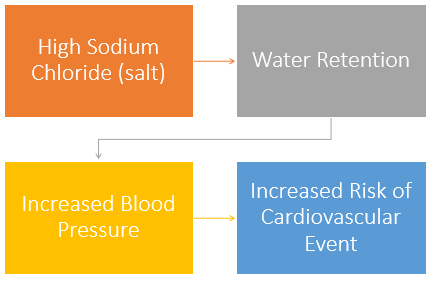
High sodium
Recommended sodium intake:
Not more than 2.4g/day
check for sodium content in tablets - paracetamol and Solpadine
Oral antifungal
Has many interactions so better to double check
Sumatriptan
Vasoconstriction to relieve symptoms of migraines caused by vasodilation.
What can be used instead
Aspirin & NSAIDs
For pain & fever recommend paracetamol insteadDecongestants - ephedrine and pseudoephedrine, including nasal sprays – for blocked nose, recommend eucalyptus vapour rub, steam inhalation
Regular use of high sodium products
e.g. effervescent/soluble preparations, certain antacids, cystitis relief sachetsFluconazole – antifungal cream for thrush. Or refer to GP for further investigation if cream already tried. Check for diabetes
Sumatriptan – paracetamol, codeine & antiemetic (where necessary) preparations, licensed to treat migraines
Warfarin interactions
take care when recommending medicines to anyone taking warfarin and other anticoagulants such as rivaroxaban
Read SmPC or PIL
Significance consequence of getting this wrong
common interactions - St John’s Wort, PPI’s, glucosamine, fluconazole, NSAID's, ASPRIN
paracetamol can cause bleeding if patients INR is not stable
Also think about medications increasing bleeding
Natural products
St John’s Wort
Ginseng
Gingko biloba
Echinacea
Liquorice - a lot of products contain this for flavour
Consider:
Blood pressure effects
Effect on bleeding (warfarin)
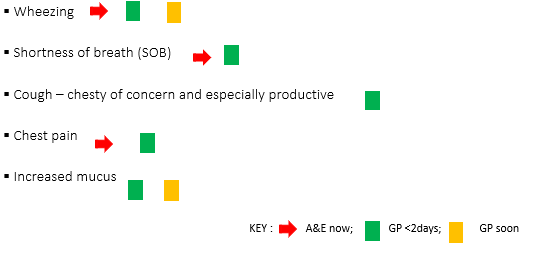
People with RT conditions
What are the RT conditions?
asthma
COPD
C.F
a RT symptoms may be new or related to an existing condition
Common adverse effects
Drug Group | Common adverse effects |
Beta₂ agonists | Palpitations, arrhythmias, headache, tremor, hypokalaemia |
Antimuscarinics | Dry mouth, arrhythmias, headache |
Corticosteroids e.g. beclometasone, budesonide, fluticasone, | Oral candidiasis, throat irritation, hoarseness, visual disturbance |
Leukotriene antagonists (oral) e.g. montelukast, | Gastrointestinal, headache, upper RTI |
Cromoglycate e.g. sodium cromoglycate, nedocromil sodium | Cough, bronchospasm, headache, throat irritation 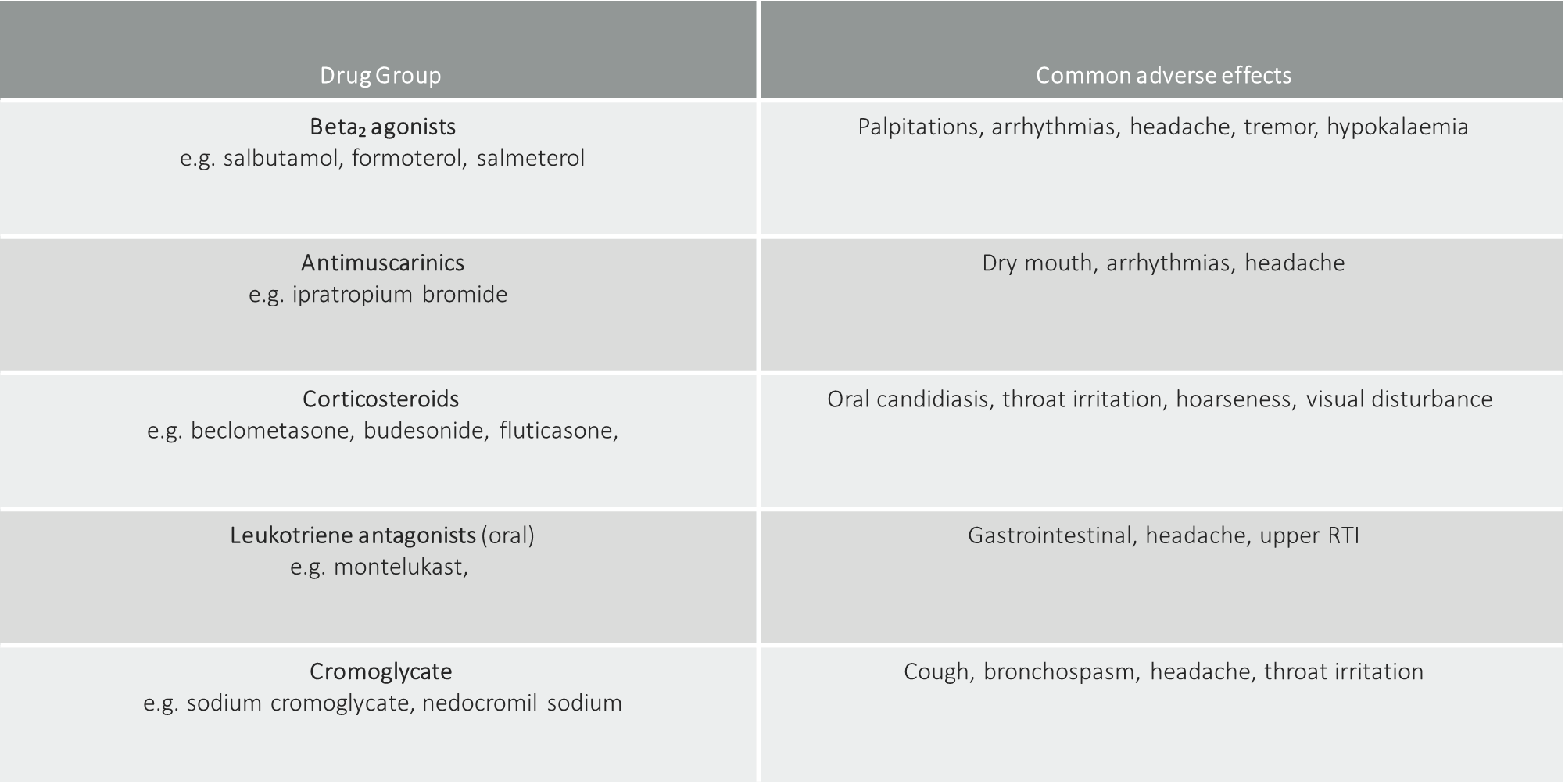 |
Asthma - Aspirin and NSAID’s
Aspirin and NSAID’S may precipitate bronchospasm in 8 to 20 percent of patients with asthma
can we ever sell aspirin and NSADI’s to people with asthma
if taken before without detriment then yes, otherwise no
However paracetomal as a wiser option even if they have taken befoe. Some people might not have noticed worsening symptoms with use of NSAID’s
People with respiratory conditions
OPIOIDs:
Codeine, pholcodine, dihydrocodeine, dextromethorphan
Codeine (co-codamol) & dihydrocodeine (codydramol) in compound pain relief preparations OTC
Pholcodine & dextromethorphan (and codeine) in cough suppressants
and compound cough/cold products
Opiates cause respiratory depression (and sputum retention) and so should be avoided in people with respiratory conditions such as
Asthma
COPD
Cystic fibrosis
Summary
•Aspirin and NSAIDs, e.g. ibuprofen
- avoid these drugs in people with asthma
- they can cause or worsen bronchospasm
- look out for them in compound pain, & cold/flu products
•Codeine, pholcodeine, dihydrocodeine, dextromethorphan
- avoid in asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis
- they are respiratory suppressants
- they can cause sputum retention
- look out for them in compound pain & cold/flu/cough products
•Alcohol containing products for nit treatment