Cariology
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
243 Terms
____ is the name of the disease, a result of imbalance in the resident bacterial flora (biofilm) of the oral cavity (shift towards the cariogenic types) and an associated intra-oral low pH condition
dental caries
____ is a detectable change in tooth structure, the consequence and manifestation of the disease (signs and symptoms)
caries lesion
The caries process is ___
dynamic (demineralization and remineralization)
Caries lesion ____ is a process involving the recognition and recording, traditionally by optical or physical means, of changes in enamel, dentin, or cementum, which are consistent with having been causes by the caries process.
detection
T/F diagnosis and detection can be used synonymously
false
caries ___ is the human professional summation of all signs and symptoms of disease to identify the past or present occurrence of the disease caries
diagnosis
What process uses various sources of information and is deductive?
diagnosis
what ICDAS codes are early carious lesions and are considered non cavitated?
Code 1 and 2
Some non carious non cavitated lesions include?
fluorosis and developmental defects
causes of decalcification?
active caries lesions (early stage)
causes of fluorosis?
excess fluoride
causes of hypo calcification?
ameloblasts affected, caused by trauma, fever, malnutrition, or hypocalcemia during teeth formation
often due to deciduous tooth being accessed or physically forced into enamel organ of permanent tooth
causes of hypoplasia?
developmental enamel defect
caused by genetic disorders, malnutrition, low birthweight, prematurity, maternal illness, smoking, drug abuse, liver disease
results in caries due to difficulty in oral hygiene
what condition makes it hard to maintain oral hygiene?
hypoplasia
location of decalcification?
plaque stagnation areas along gingiva and gingival to interproximal areas
location of fluorosis?
incisal edges and cusp tips
location of hypo calcification?
centered in smooth surface, may affect entire crown
front teeth and six-year molars ---> occurred first year of life
bicuspids and second molars ---> occurred around age 3
location of hypoplasia?
defect can be small pit or so widespread that whole tooth is mis-shaped
often results in subsequent caries
shape of decalcification?
well defined borders, follows contour of gingival tissues
shape of fluorosis?
lines correspond to perikymata to lattice pattern
borders blend into adjacent normal enamel
shape of hypo calcification?
often oval or round, well defined borders and differentiated from normal enamel
shape of hypoplasia?
rough pitted area in enamel, not well defined or complete loss of enamel
color of decalcification?
light white to dark brown
not present at eruption
color of fluorosis?
light white to dark brown
cusp tips may appear frosted
may not show stain at time of eruption
color of hypo calcification?
creamy yellow to dark reddish orange
can be white or brown spots as well
usually pigmented at eruption
what lesion is pigmented at eruption?
hypocalcification
color of hypoplasia?
white, yellow or brown pitted and rough spot lesions
what teeth are usually affected by decalcification?
canines, pre-molars, and molars
what teeth are usually affected by fluorosis?
teeth that calcify slowly (canines, premolars, molars)
often in same spot on contralateral tooth
what teeth are usually affected by hypocalcification?
any tooth, frequently on labial surface of incisors
often occurs singly
what lesions occur contralaterally? singular?
contra: fluorosis and hypoplasia
singly: hypocalcification
what teeth are affected by hypoplasia?
contralateral tooth and opposite arch
ex: all central incisors or all first molars
excess fluoride causes what in terms of enamel proteins? how does the color form?
excessive retention of enamel proteins and disrupts mineralization
in porous enamel, proteins pick up color
most likely combination of non-cavitated lesions?
decalcification and fluorosis
examples of cavitated non carious lesions?
tooth wear (erosion, abrasion, attrition, abfraction)
enamel and dentin dysplasias
trauma
examples of cavitated carious lesions?
cavitation of enamel or dentin and rampant caries
ICDAS code for cavitation of enamel?
3 and 4
ICDAS code for cavitation of dentin?
5 and 6
what three things lead to abfraction?
bruxism, parafunction, and occlusal function
abfraction causes what type of lesion?
wedge-shaped cervical lesion
what is evidence of attrition? (where, shape, due to what, affects)
occlusal and incisal surfaces
shiny, well defined facets
patient may have myofacial pain disfunction and stiff jaw
often due to bruxism (grinding teeth)
what is evidence of erosion? (where, shape, due to what, affects)
glazed, smooth and round edged surfaces
looks scooped out
no well defined facets
patient has sensitivity
often due to bulimia and GERD
what is evidence of abrasion? (where, shape, due to what, affects)
pitted, scratched out surface
facet or scooped out dentin if extreme
no sensitivity
often due to toothbrush and abrasives in tooth paste
T/F abfraction usually occurs in multiple teeth
false --> single tooth
abfraction is most common where?
buccal of canines and posterior teeth
important clinical factors to consider for differential diagnosis?
age of patient, diet and lifestyle, oral hygiene techniques, occlusion, habits, bruxism and parafunction
three requirements for formation of caries?
susceptible host, microbes, and substrate
what percentage of plaque is bacteria?
60-70%
bacterial product that causes demineralization?
acid in plaque matrix
time periods for the peak incidence of caries?
6-8 years, 11-19 years, and 56-65 years
early childhood, teenage, and cemental
what three things have decreased the caries incidence?
fluoridated water, fluoridated dentrifices, and improved oral hygiene
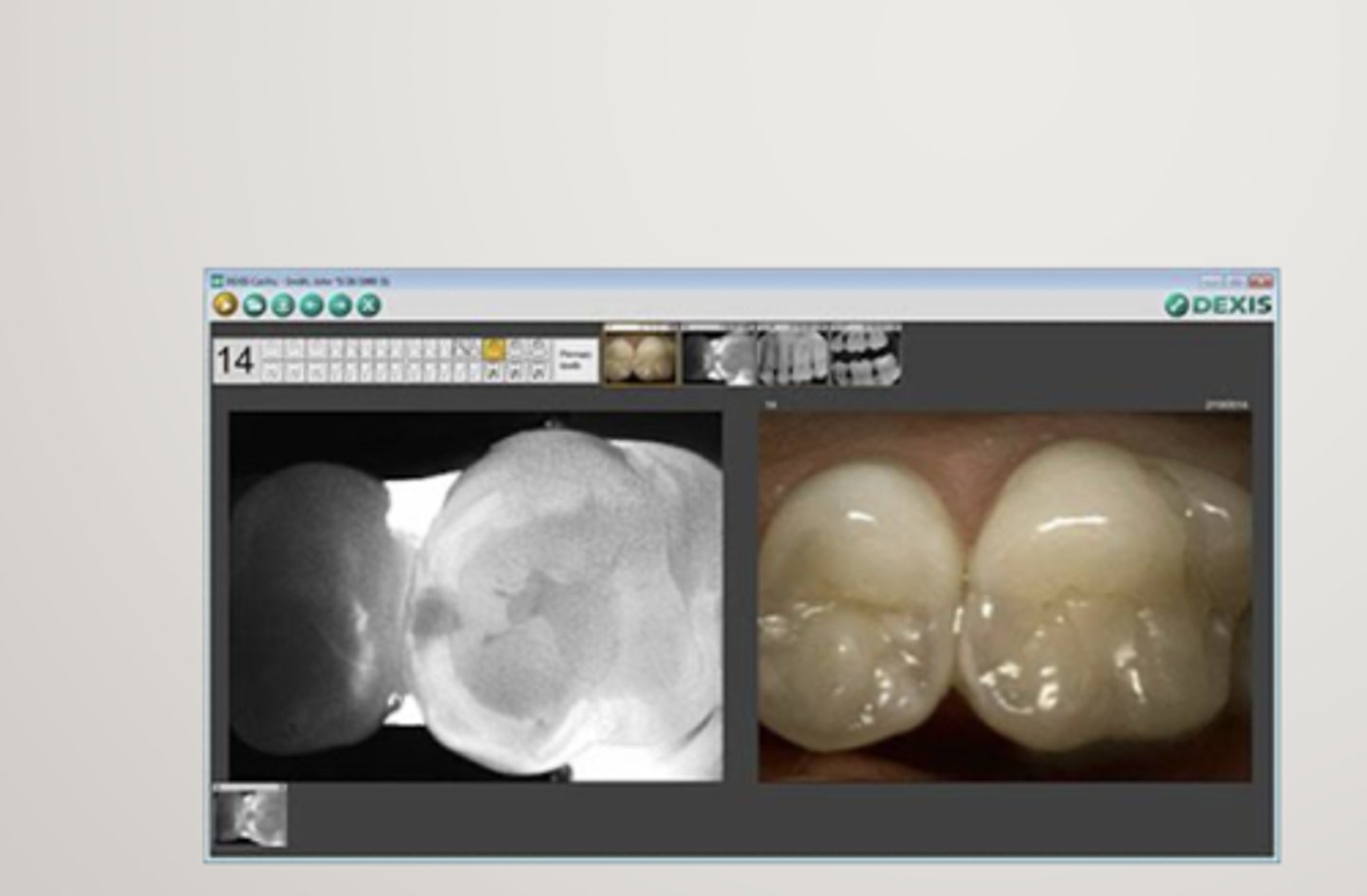
what is the radiograph of choice for interproximal posterior caries?
BW
50% of caries would be missed without BW
full mouth radiographic series includes?
14 PA and 4 BW
optimal viewing conditions for radiographs?
view box or monitor, darkened room, and magnifying glass or magnification tools
what are acute caries?
caries in deciduous teeth
caries proceed faster in deciduous teeth than in permanent teeth
what are chronic caries?
usually in adults
slower progression with larger surface lesion
what are arrested caries?
caries become static
seen in large occlusal carious lesions that have become self-cleaning
dentin has polished blackened appearance
occasionally seen in proximal surfaces where tooth has been extracted
primary caries are?
caries originating on a non-restored surface
secondary caries are?
caries in an immediate vicinity of a restoration
hard to detect radiographically due to superimposition of restoration
what are incipient proximal caries?
less than 1/2 way through enamel
white spot clinically
cone or V shape with broad base at surface of enamel
what are moderate proximal caries?
caries extending more than 1/2 way through enamel but not involving DEJ
what are advanced proximal caries?
at or through the DEJ and extend no more than 1/2 way through the dentin to pulp
spreads along DEJ
dentinal tubules act as a tract along which microbes travel
second radiolucent triangle in dentin with base at DEJ
what are severe proximal caries?
caries of enamel and dentin extending more than 1/2 way through dentin towards pulp
when are occlusal caries evident radiographically?
once lesion has entered the dentin
occlusal caries are what shape?
diamond with base towards dentin
buccal/lingual caries look like what?
like looking into a "hole"
well-demarcated
easily detected by lineal examination
cemental/root surface caries look like?
cementum is soft and thin at CEJ
"scooped out" or
"saucer-shaped" appearance
does not involve enamel except by extension
seen in elderly
why are root surface caries seen mostly in elderly?
gingival recession, loose contacts, xerostomia
cervical burnout vs cervical caries?
burnout: radiolucent artifact caused by change in density at cervical margin, extend below level of bone
caries: scooped out or saucer shaped below CEJ, Above level of bone
what are radiation caries?
looks similar to cervical caries, does not directly affect permanent teeth
caused by xerostomia as direct result of radiation on salivary glands
extremely rapid
what does reduced saliva lead to?
rampant decay --> usually cervical
What percentage of decalcification is needed before a lesion becomes evident radiographically?
40%
the clinical lesion is (bigger/smaller) than the radiographic lesion
bigger
clinical is always in advance of radiographic lesion
what are some technical errors for radiographs?
overlapping, poor contrast, and too light
too much kVp causes what to a radiograph?
over-penetration and "peripheral burnout"
appears as open contacts
will miss incipient proximal caries
T/F an increase in density may make caries easier to see
true
what do restorations look like on radiographs?
some materials are radiolucent
"c" shaped (class III)
defined margins of restorations
recurrent caries hard to detect
what is turner's tooth?
hypoplastic incisor
dots, irregular tooth surface, infection
T/F hypoplasia makes teeth susceptible to caries but does not mimic caries radiographically
false
hypoplasia makes teeth susceptible to caries AND mimics caries radiographically
Attrition is ___ wear
physiologic
What is the mach band effect?
overlapping teeth that exaggerates the contrast between edges
what is sensitivity?
the ability of a test to detect disease when lesion is present
true pos/(true pos + false neg)
what is specificity?
ability of a test to exclude caries lesion when there is truly none present
true neg/(true neg + false pos)
what is fiber-optic-trans-illumination (FOTI)?
intense light beam transmitted through a fiber optic cable to a specially designed probe
mainly used for interproximal caries

what is digital imaging fiber-optic-trans-illumination (DIFOTI)?
uses visible light to create high resolution digital images
not quantitative, clinician must evaluate images
sensitivity high/lower than radiographs
specificity is approximately the same

what is Denis cariVu?
transillumination
for occlusal, interproximal and recurrent carious lesions and cracks
near-infrared light
-enamel appears transparent, porous lesions traps and absorb light, similar to radiographic images
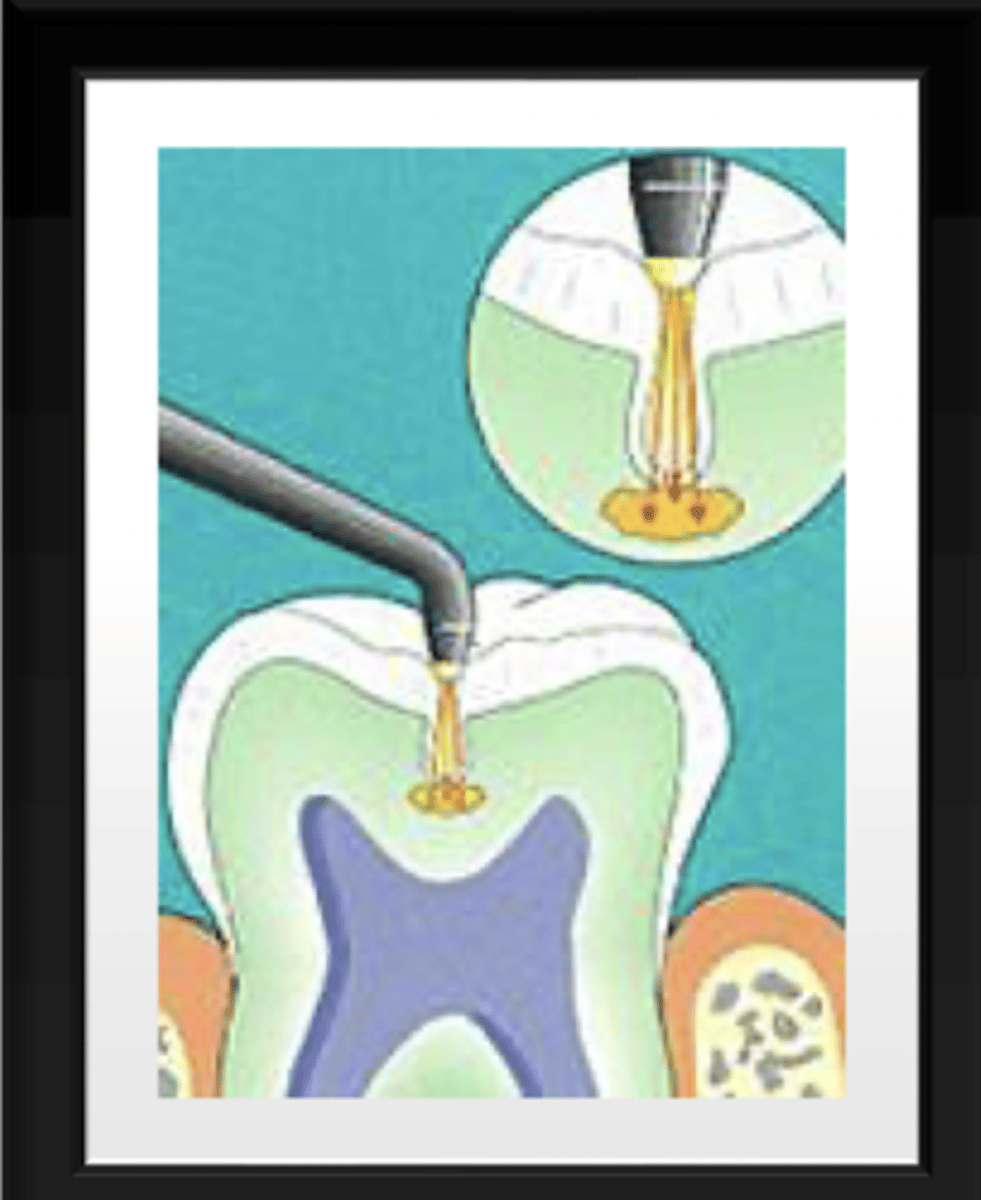
what is laser fluorescence?
pyrphyrins (bacterial byproducts) reside in porous carious lesions
laser fluorescence transmits through the tooth reflecting on the porphyrins
reflected light has a longer wavelength, indicating a carious lesion
what is diagnodent?
more sensitive than visual
less specific (false-pos)
better on occlusal than interproximal
beneficial in longitudinally monitoring lesions
is diagnodent qualitative or quantitative?
quantitative
values are given
what is QLF (quantitative laser fluorescence)
laser is used to measure induced tooth fluorescence
measures changes in fluorescence that result from carious lesions scattering light
contrast between sound and pathogenic tissue
potential for longitudinal evaluation of lesions, ability to measure remineralization protocols
expensive
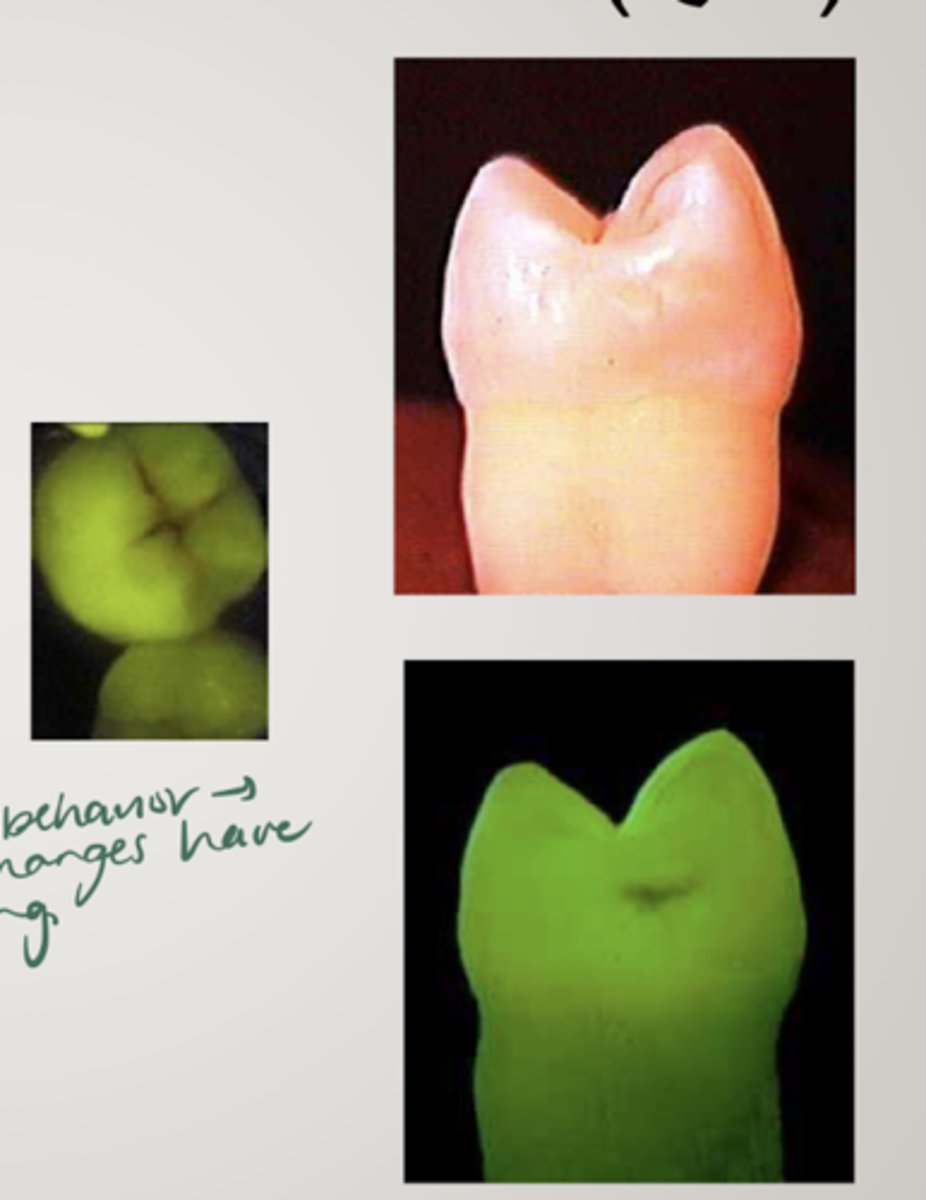
what diagnostic tool has the highest reproducibility?
QLF
what is the spectra caries detection aid?
uses change of frequency in fluorescence to detect caries in fissures and smooth surfaces
capture image and extent of decay is displayed as:
-color either blue, red, orange or yellow
-0-5
405 nm
green = ___ in spectra device
healthy
red = ___ in spectra device
caries lesions
what is the canary system?
PTR-LUM
low-power, pulsating laser light absorbed in tooth results in:
-laser light converted into luminescence and release of heat
-measure reflected heat
-97% sensitivity
-measures crystalline structure
higher canary number = advanced decay
what does a higher canary number mean?
more advanced decay
What is the light emitting diode?
LED
occlusal and proximal, different optics for sound and demineralized
analyzes reflectance and refraction of LEF, triggering audible electrical signal
tooth must be wet
LED is quantitative or qualitative?
qualitative
what is soprolife?
light induced fluorescence evaluator
visual = subjective
450 nm
demineralized area looks opaque
differentiate between infected and affected tissue
daylight (magnifies) and blue light (indicates demineralized tissue and signals tissue to be removed)
is soprolife superior to ICDAS?
no but better than other caries detection devices