topic 4- bioenergetics photosynthesis + respiration
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
jan-mar
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
photosynthesis word equation
photosynthesis equation
Carbon dioxide + Water →(light) Glucose + Oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O→(light) C6H12O6+6O2
what are the 6 ways plants use glucose
convert it to sucrose (type of sugar found in fruit)
convert it to starch, food store found in fruit
convert it to cellulose to make plant cell walls
combine it with nitrate ions to make AA used to make protein for growth and repair
convert it to fats and oils, food stores found in plant seeds
used in respiration to release energy for plant cells
defining limiting factor
any factor that slows the rate of photosynthesis if there isnt enough of it
called a limiting factor as it ‘limits‘ the reaction from taking place-even if the other reactants are in plentiful supply
what are the 3 factors that affect the rate of photosyntheseis
carbon dioxide concentrstion
light intensity
temperature
how is co2 concentration a limiting factor of photosynthesis
-as CO2 concentration increases so does photosynthesis initially
-at a certain point the rate of photosynthesis remains constant- so the CO2 concentration doesnt increase the rate of photosynthesis
-so the rate of photosynthesis stays the same
how is light intesnsity a limiting factor of photosynthesis
-as light intensity increases so does photosynthesis initially
-at a certain point the rate of photosyntehsis stays the same- so light intensity doesnt increase the rate of photosynthesis
-so the rate of photosynthesis stays the same
how is temperature a limiting factor of photosynthesis
at a lower the rate of photosynthesis is slower as particles doesnt have as much kinetic energy- so less collisions between particles
-when temperature incfreases beyond the optimum temp the rate of photosynothis decreases- as enzymes denature and the active site has chasnged shape- so the substrates/reactants needed for photosynthesis no longer bind to the enzymes as they arent complimentary
what happened at the required practicle for investigating the effect of light intesnsity on photosynthesis in pondweed
as lamp is moved away from mondweed the light intyesnisty decreases and the number of oxygen bubbles produced will decrease so the rate of pohotosynthesis has decraesed
what was the purpose of the sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and the beaker of water for the required practicle investigating the effect of light intensitry on photosynthesis in ponweed
sodium hydrogen carbonate solution= source of CO2 for pondweed
the beaker of water= keeps temp of pond weed the same/regulated
why is counting the bubbles per min not the most accurate method to measure the rate of photosynthesis
how could we improve this
-the bubbles arent the same size
-collect the oxygen gas from the photosynthesizing pondweed
-measure the volume of gas with a syringe
inverse square law
light intensity ∝ (proportional to) 1/distance2
what equiptment do we need to artificially grow plants (6)
and purpose
AFHIPTev ACTIVE
artificial lighting- supplies planty with light-can photosynthesize at night
fertiliser-gives mineral ions to plants
heater-so the plant can have its optimum temp through winter
irrigation system- provides plants with water for photosyntgsis-cells remain turgid and well supported
propane burner- provides heat and makes CO2 as a by-product
thermostatically controlled vents- controls temp of greenhouse- so in summer the greenhouse will stay cool as the vents can be opened
what do younneed to consiv=der with a greenhouse ()3
-cost of equiptment
-cost to increase crop yield
-how much extra ioncome generated
lable the lungs
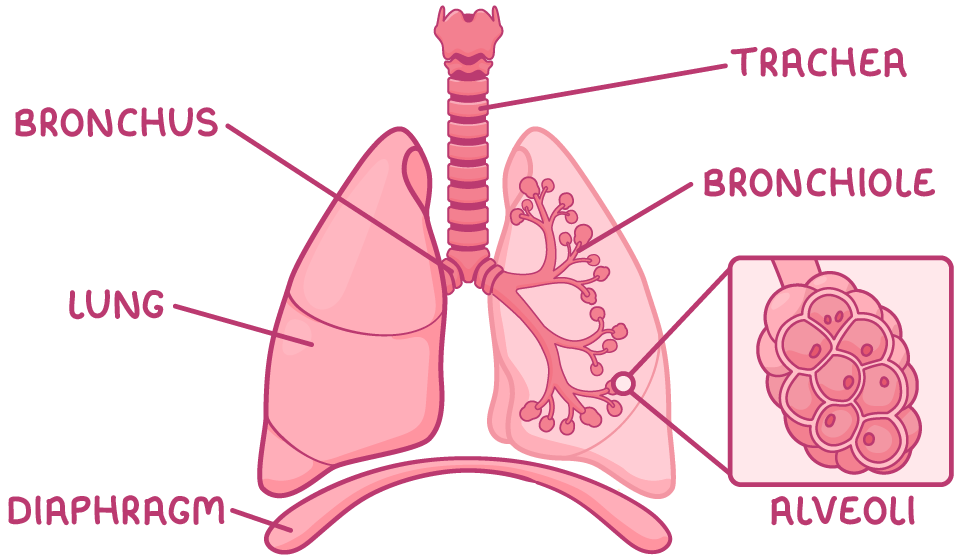
bronchus-bronchi
alveoli- where gas exchange occurs
aerobic respiration word equation
aerobic respiration symble equation
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+energy)
C6 H12O6+ 6CO2→ 6CO2 + 6H2O
define aerobic respiration
using glucose and oxygen to release energy for cells. Occurs in individual cells
breathing
-breathing=process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling CO2- occurs in lungs (alvioli)
-oxygen inhaled diffuses into the blood stream and binds to the haemoglobin inside red blood cells- oxygen gets transported to cells and tissues around the body
-once at the bodys cells oxygen diffuses from the red blood cells→body cells so cells use that oxygen in respiration.
respiration
respiration =process where cells use oxygen to break down glucose to release energy for the cells
- waste gas (carbon dioxide) diffuses from body cells into the blood. The plasma of the blood transports CO2 back to the lungs to be exhaled
adaptions of the lungs (4)
-the wall of the alveoli is 1 cell thick→ decreases the distance for oxygen to diffuse- speeds up the rate of gas exchange
-the alveoli have many capillaries surrounding it.→ maintains the concentration gradient of oxygen and carbon dioxide so more gas exchange occurs
-many alveoli in lungs→increases surface area so the rate of gas exchange is faster
-each aveoli is right next to a capillary→decreases the distance for oxygen to diffuse which speeds up the rate of gas exchange
what do cells need energy for (4)
-building larger molecules from smaller ones (e.g using AA to make protein)
-muscle contraction
-active transport
-mitosis
where does aerobic respiration occur
mitochondria
where does anaerobic respiration occur
cytoplasm
Anaerobic respiration in animals word equation
Glucose→lactic acid (energy)
Anaerobic respiration in plant cells, yeast cells, and other microorganisms word equation
glucose→ carbon dioxide + ethonal (energy)
does aerobic respiration reaction use oxygen
does anaerobic respiration in animal cells use oxygen
does anareobic respiration in P,Y, + OM use oxygen
yes
no
no
which type of respiration uses more energy
aerobic respiration uses more energy (released over a longer period of time)
anaerobic respiration (in animal cells) uses less energy released more immediatly
when might cells carry out aerobic respiration
-when oxygen is available
-endurance activities (e.g marathons)
when might cells carry out anaerobic respiration in animal cells
plant,yeast cells and other microorganisms
-oxygen isnt available
-short, high intnsity activities (e.g sprint)
oxygen isnt availbale
whats the body’s response to exercise
muscles start contracting at a quicker rate
heart rate inc
the lumen of the arteries start supplying blood to your muscles - inc in diameter vaso dialation)
this inc the flow of blood to the muscles ehich brings oxygen gas and glucose to cells.
Therefore the rate of respiration can increase in muscle cells which release more energy so that muscle cells can do more muscle contraction
breathing rate inc + you breathe more deeply.
inc amount of oxygen in blood delivered to muscle cells.
Allows carbon dioxide to be removed more quickly from the blood
body temp inc- as more energy is released when cells do respiration + some of that energy is thermal energy which warms up the body
sweat glands start making swear.Thermal energy causes the sweat to evaporate- cools down the body
muscle cells break down glycogen into glucose. More glucose is then available for muscle cells to do more respiration
at a certain point not enough oxygen will be delivered to muscle cells and so cells will need to start doing anaerobic respiration
when this happens, lactic acid builds up in your muscles which makes your muscles fatigue.
As a result they may stop contracting efficiently.
At the end of oxygen, your body willl be in a state of oxygen debt. You breathe more deeply so that more oxygen can be delivered to your muscle cells.
This extra oxygen is used to react with the build up of lactic acid and to remove it from the cells
lactic acid transported from muscles cells to the liver through the blood/stream. In this organ, the lactic acid is converted back to water
difference between fit vs unfit individuals during exercise (4)
-fit have lower resting heart rate
-fit individuals heart rate increases slower (as on the graph the slope line is less steep compared)
-fir have a lower peak heart rate
-fit individuals have a shorter recovery tijme- meaning it takes less gtime for them to reat there resting heart rate
metabolism
all the chemical reactions that occur within a cell or the body
metabolic rate
the speed at which chemical reactions take place
factors affecting metabolism (5)
age
sex (gender)
genetic makeup
pregency
amount of exercuse (proportion of muscle to body fat)
anabolic reaction
enerfy is used to make larger molecules from smaller molecules
catabolic reaction
larger molecules are broken down to make smaller molecules and energy is released
exothermic reaction
reaction where heat is released to the surroundings
endothermic reaction
reaction where heat/energy is absorbed from the surroundings
examples of anabolic reactions
-photosynthesis
-synthesis of protein
(when were building up)
examples of catabolic reactions
aerobic respiration
anarobic respiration
digestion of:
-fats/lipids
-protein
-starch
examples of endothermic reactions
photosynthesis
synthesis of protein
(building up)
examples of exothermic reactions
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
digestion of:
-fats/lipids
-protein
-starch
What makes starch a useful long term storage molecule?
It can easily be broken down when needed
It is insoluble in water
It is compact
examples of how cells use the energy from respiration.
To combine small molecules to make larger molecuels
to break large molecules into smaller ones
muscle contraction
maintain body temp
to move substances around the celll
how excersise affects the body (5)
In order to move during exercise, we have to contract and relax our muscles.
Muscular contraction requires energy though, which has to be released by cellular respiration.
Most of the time cells carry out aerobic respiration, which is far more efficient but requires oxygen.
This means that we have to pump oxygen around the body faster when we exercise.
As a result we increase both our heart rate and our breathing rate.
what type of respiration is more efficient why
AEROBIC RESPIRATION
doesnt produce lactic acid-toxic to animals and liver has to remove it from blood
-produces oxygen debt
breaks more glucose molecule down completely so releases more energy
(requies oxygen)