Neuro Lecture 8: CN III, IV, VI
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is "OS"?
Ocular sinister (left eye)
What is "OD"?
Ocular dexterous (right eye)
What does visual acuity refer to?
- Sharpness of vision
- Normal is 20/20
When do your eyes converge?
Seeing close objects
When do your eyes diverge?
Seeing distant objects
What does accommodation refer to?
Lens adjustment for refraction
What is conjugate gaze?
All 6 muscles in both eyes act together to allow for smooth movement
What is a dysconjugate gaze?
Eyes do not look at same place at same time when a muscle is affected
What does depth perception refer to?
Binocular vision
What does dissociation refer to?
Eye movements with the head fixed
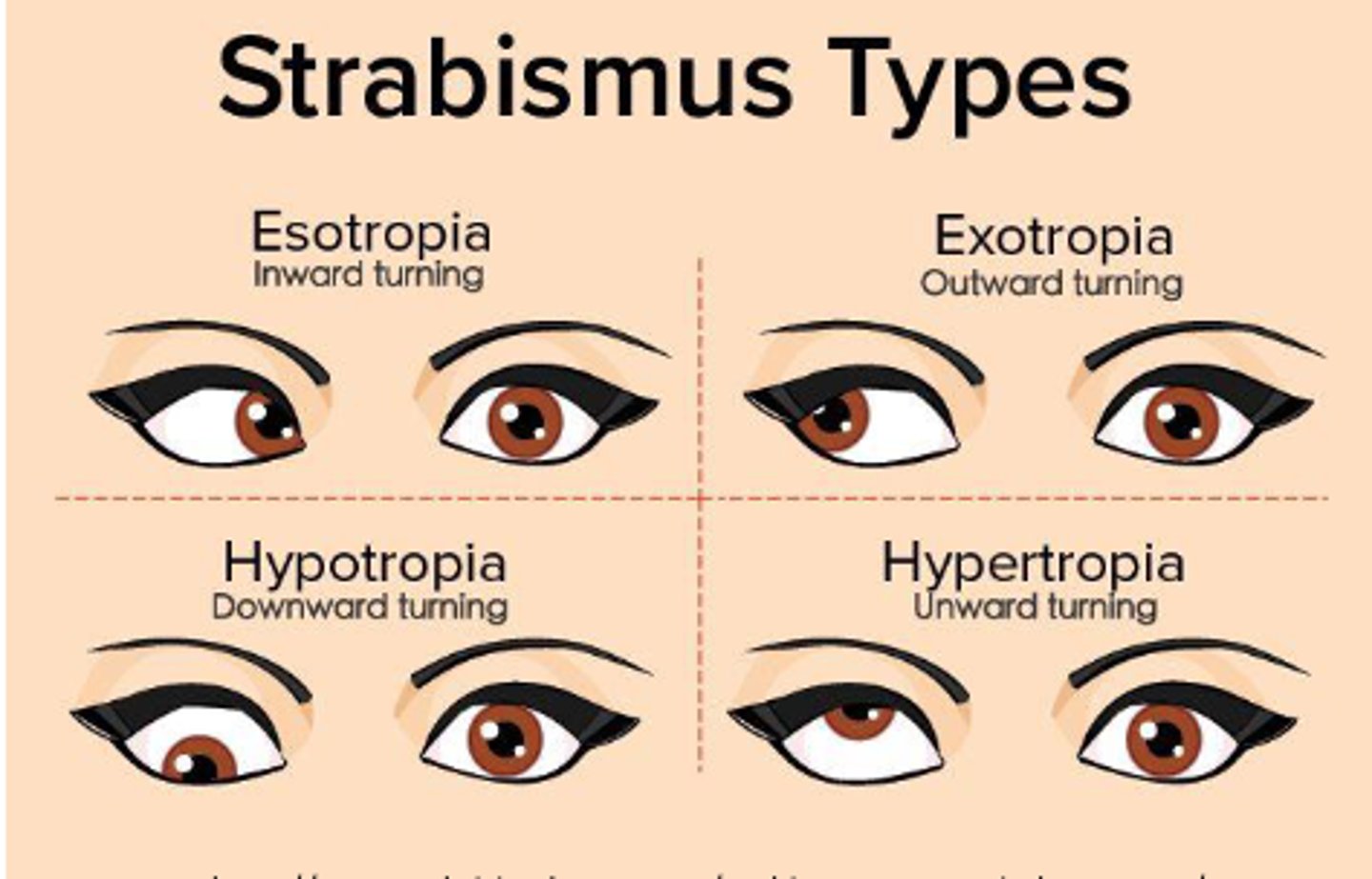
What does strabismus refer to?
- Eyes not aligned
- Lacking a coordinated gaze
- Constant
- Tropia
What does tropia refer to?
Constant or intermittent visible misalignment when both eyes are focusing on an object
What are the types of tropia? (4)
- Esotropia
- Exotropia
- Hypertropia
- Hypotropia
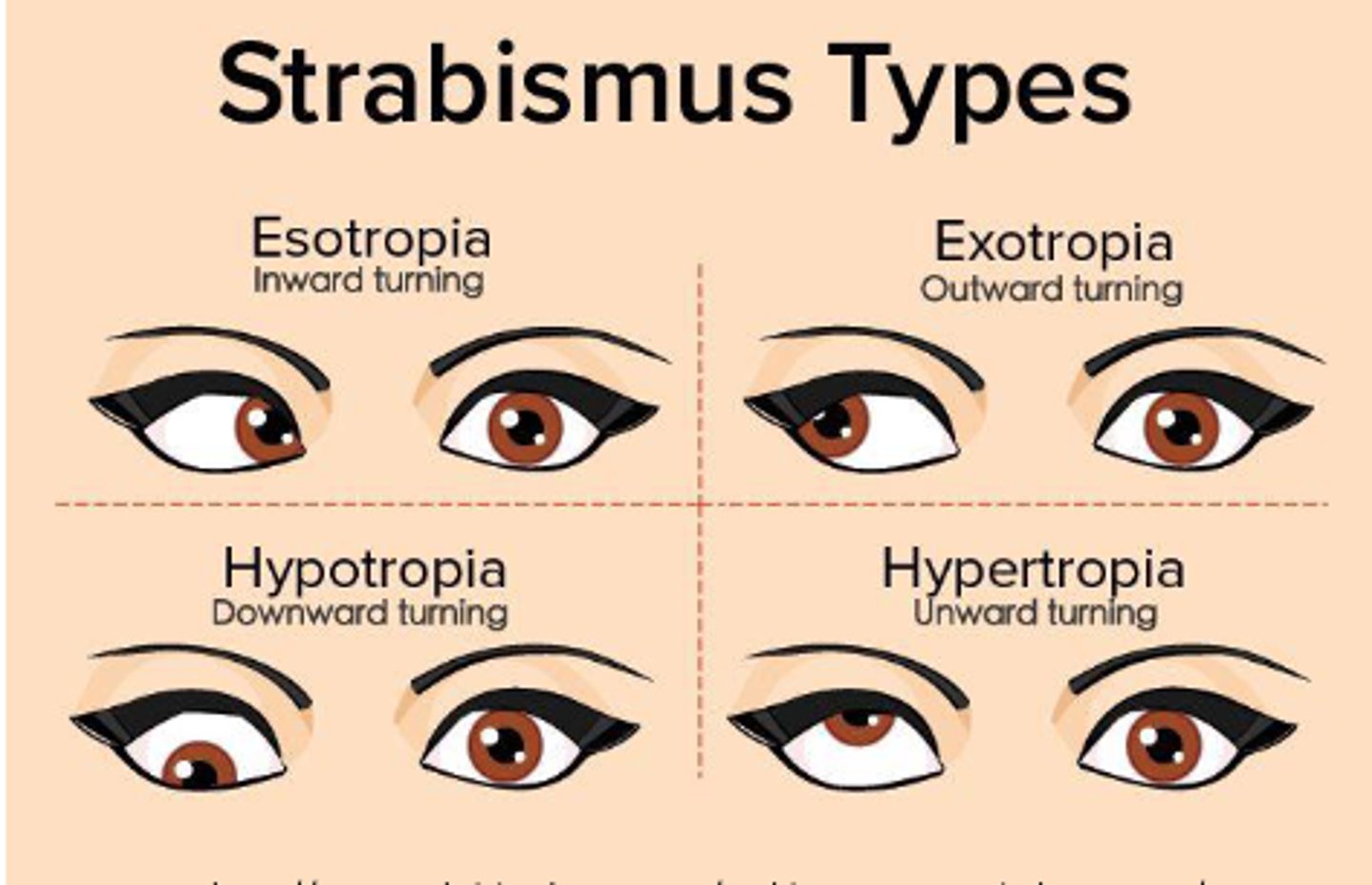
Is esotropia inward or outward?
Inward
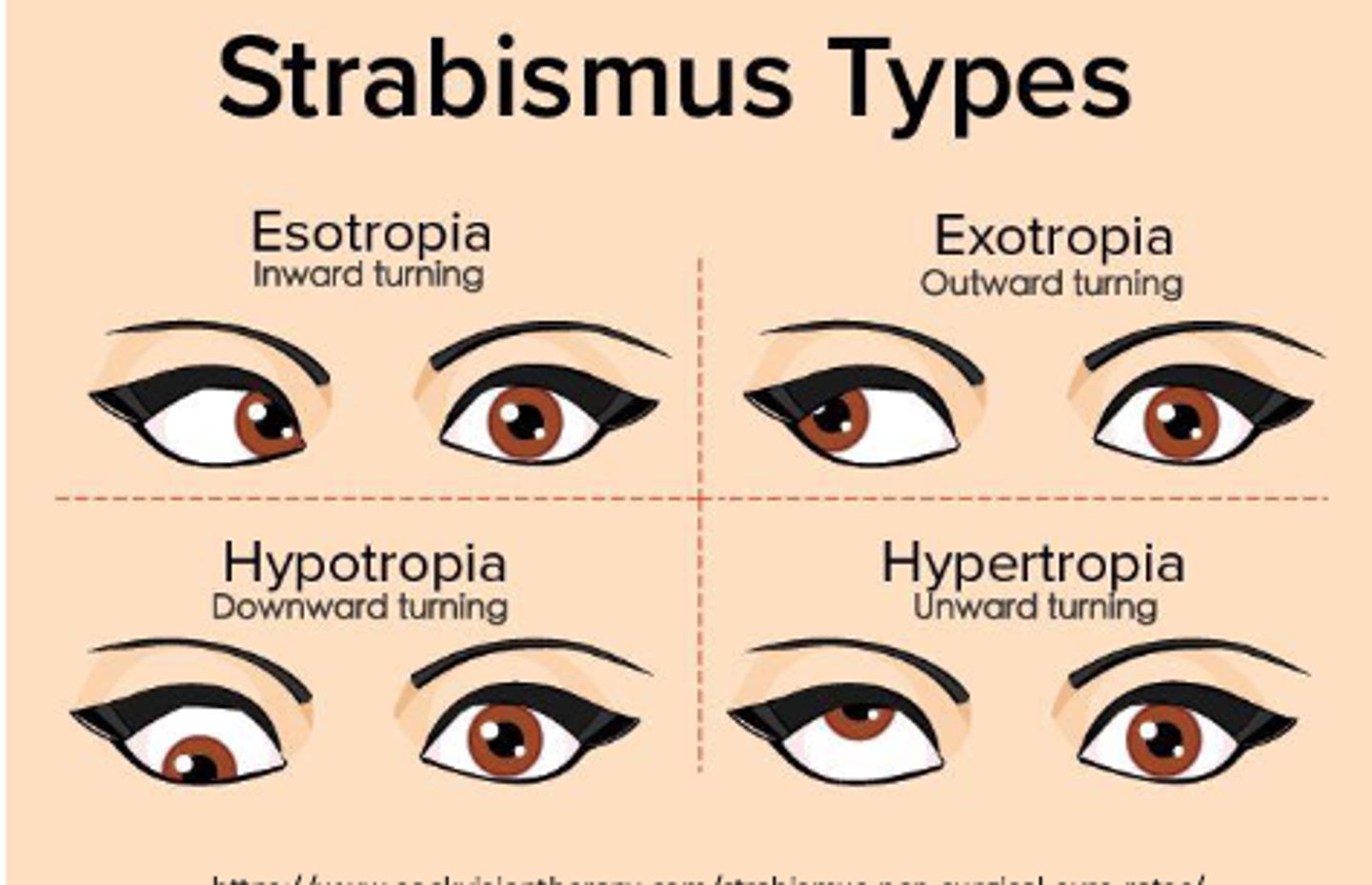
Is exotropia inward or outward?
Outward
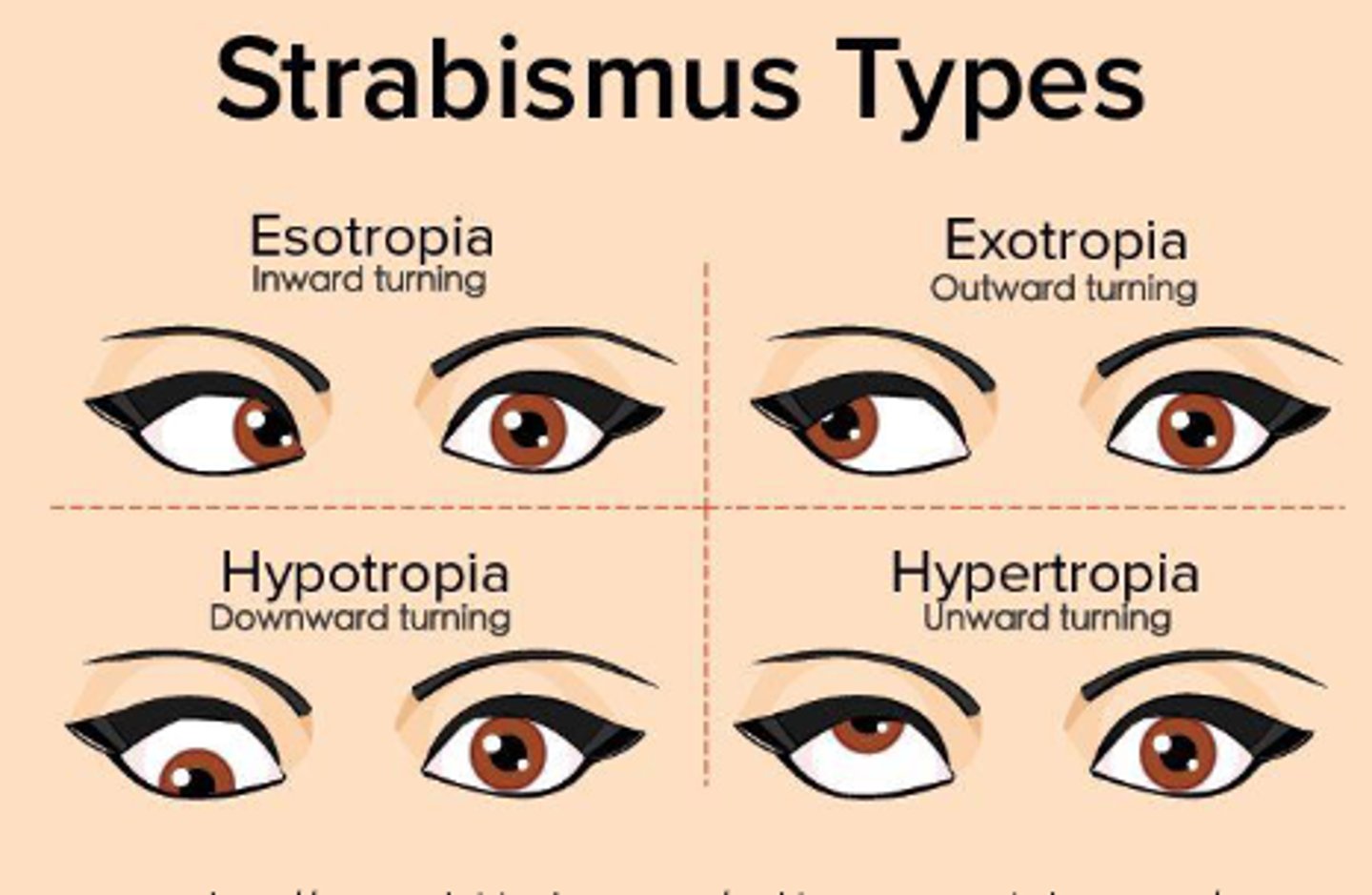
Is hypertropia upward or downward?
Upward
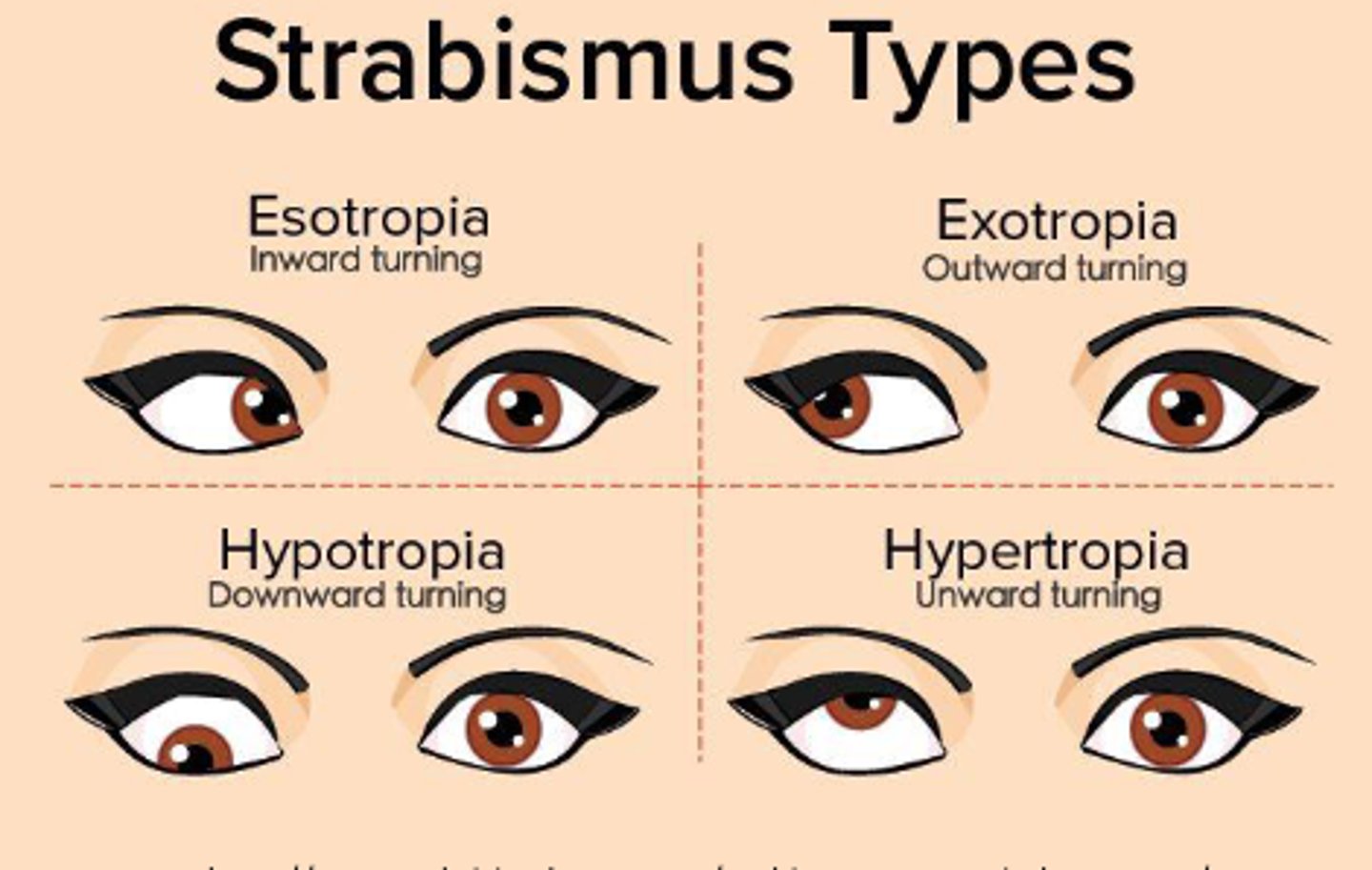
Is hyportropia upward or downward?
Downward
What does phoria refer to?
- One eye goes out of alignment when tired
- Not constant
- Daydreaming

When does phoria become visible?
- When binocular vision is disrupted (one eye covered)
- Brain compensates for misalignment
- Cover/cover test

How much of the visual field is covered horizontally?
180-200º
How much of the visual field is covered vertically?
120-135º
What occurs during binocular vision?
- Image falls on same point and same time on bilateral retina
- Brain sees 1 image
How much overlap occurs with binocular vision?
120º
What is the function of binocular vision?
- Depth perception
- 3D vision
What does peripheral vision allow for?
Detection of movement and objects without focus on them
What is higher with central vision?
Visual acuity
What is CN III responsible for generally?
Oculomotor
What is the functional category of CN III?
- Somatic motor
- Parasympathetic
What muscles is the somatic motor aspect of CN III responsible for?
- Levator palpebrae superior
- Superior/inferior/medial rectus
- Inferior oblique
- (Rest of oculomotor muscles except those under CN IV and VI)
What muscles is the parasympathetic aspect of CN III responsible for?
- Parasympathetics to pupil constrictor and ciliary muscles
- Near vision
What is CN IV responsible for generally?
Trochlear
What is the functional category of CN IV?
Somatic motor
What muscles is CN IV responsible for?
- Superior oblique muscle
- Depression (motor) of eye
- Intorsion
What is CN VI responsible for generally?
Abducens
What is the functional category of CN VI?
Somatic motor
What muscles is CN VI responsible for?
- Lateral rectus muscle
- Abduction of eye
What mnemonic can help you remember the muscles of the eye and their corresponding nerve?
LN6SO4R3
What can a CN III injury result in?
- Third nerve (oculomotor) palsy
- Diplopia
- Ptosis
- Blown pupil
What does third nerve (oculomotor) palsy lead to?
- Lateral deviation of eye
- Medial rectus impaired
What does diplopia lead to?
- Double vision
- Dysconjugate gaze
What does ptosis lead to?
- Drooping of upper eyelid
- Levator palpebrae is impaired
What does blown pupil lead to?
- Pupil dilated
- Pupillary constrictors are impaired
What is the function of pupillary light reflex?
- Controls the light reaching the retina and photoreceptors (protective)
- Direct response
- Consensual response
What is a direct response (pupillary light reflex)?
Constriction of pupil that you can shine light onto
What is a consensual response (pupillary light reflex)?
- Constriction of contralateral pupil
- Due to crossing at posterior commissure
What pathway is CN II part of?
Extra geniculate
What is step 1 of the pathway of the pupillary light reflex (CN II and CN III)?
CN II detects stimulus
What is step 2 of the pathway of the pupillary light reflex (CN II and CN III)?
Message sent to bilateral pretectal nucleus
What is step 3 of the pathway of the pupillary light reflex (CN II and CN III)?
- Pretectal nucleus sends bilateral signals to Edinger Westphal nucleus
- Crossing via posterior commissure
What is step 4 of the pathway of the pupillary light reflex (CN II and CN III)?
Edinger Westphal nucleus sends bilateral signals through CN III
What is step 5 of the pathway of the pupillary light reflex (CN II and CN III)?
Pupillary sphincters in iris and ciliary body/muscles receive signals
What happens if light is shown in left eye and left CN II is impaired?
- Pupillary light reflex dysfunction
- No detection of visual stimulation
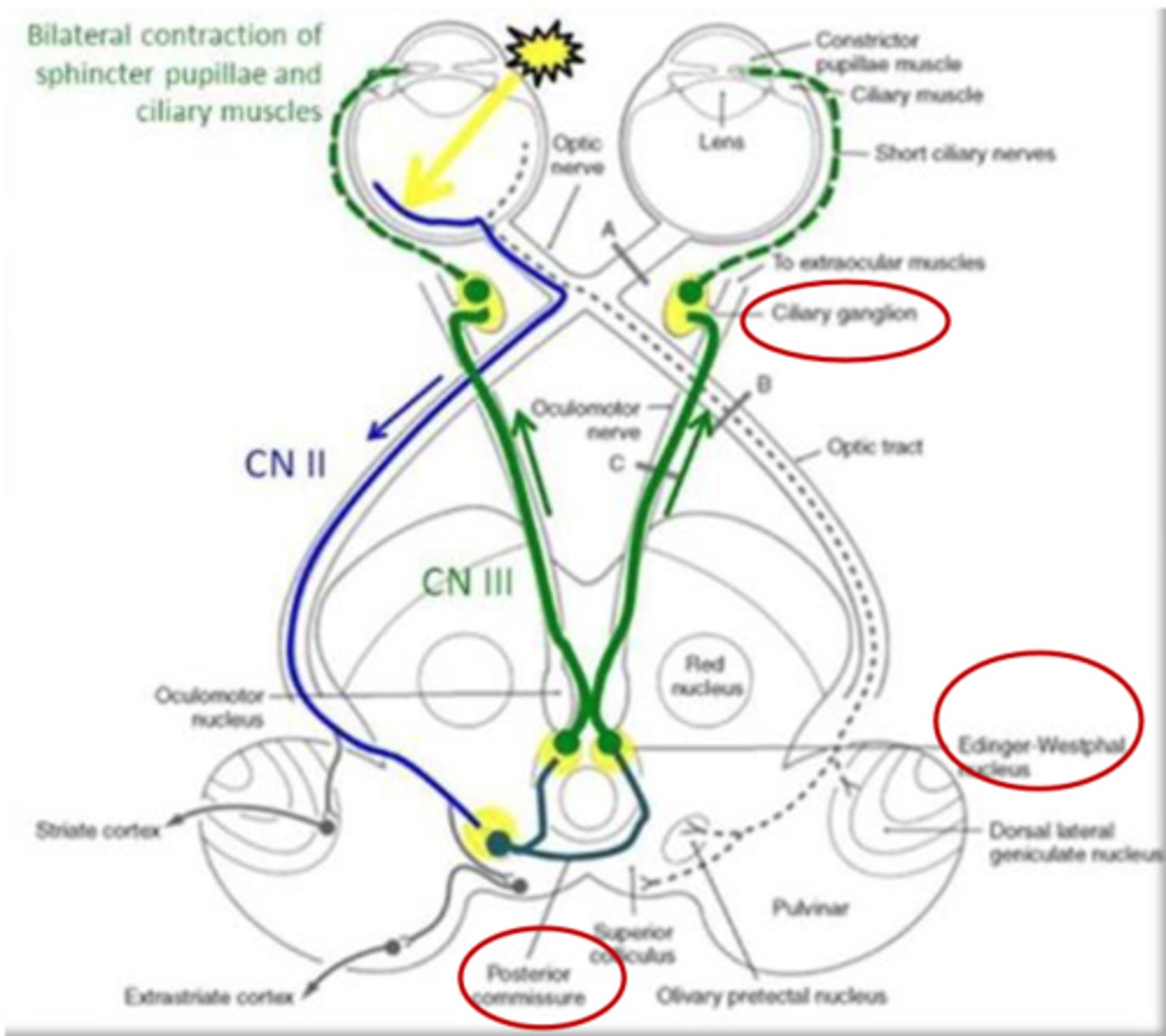
What happens if light is shown in left eye and left CN III is impaired?
- Pupillary light reflex dysfunction
- No reflex in left eye
- Reflex in right eye
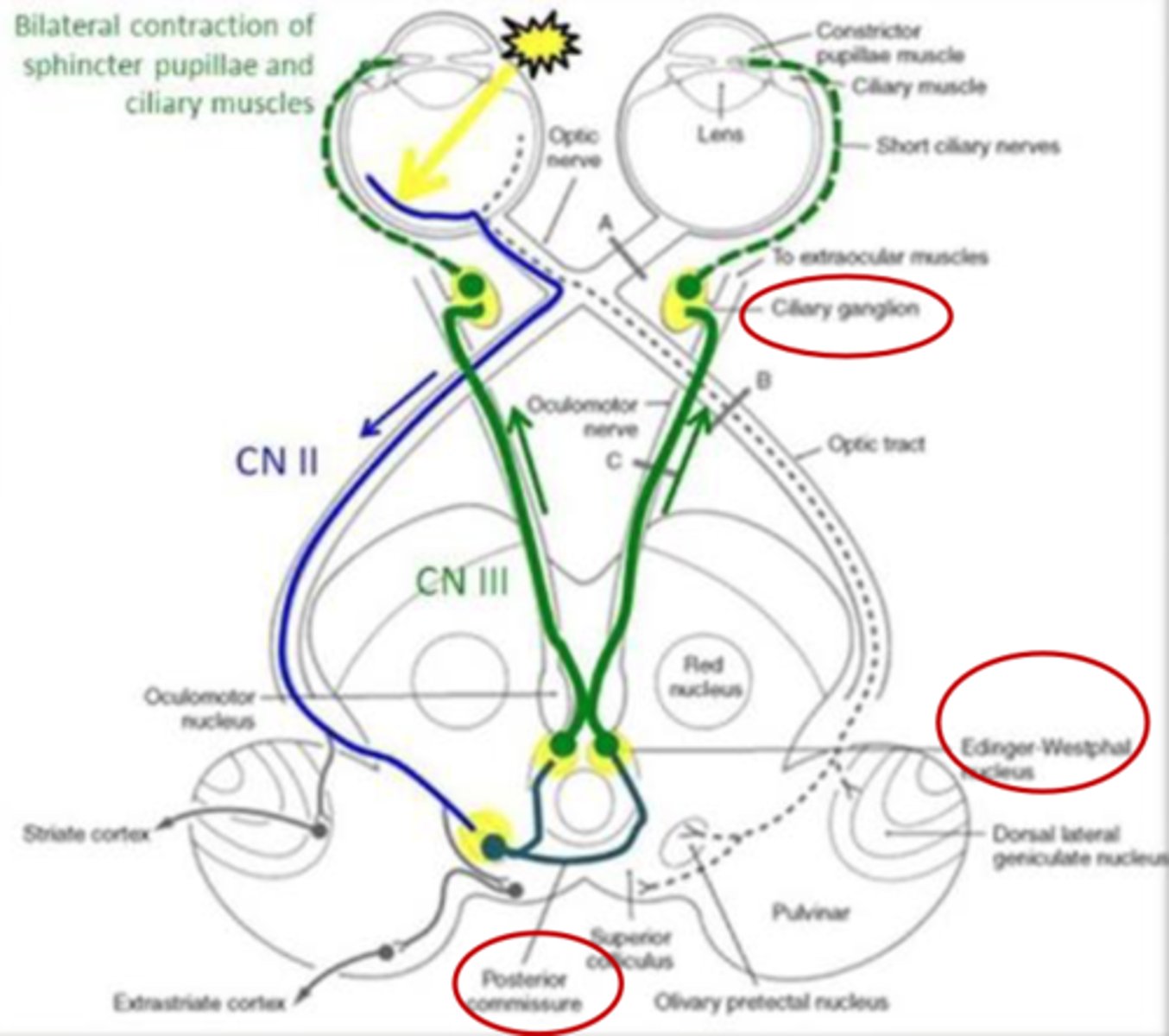
What happens if light is shown in left eye and right CN III is impaired?
- Pupillary light reflex dysfunction
- Reflex in left eye
- No reflex in right eye
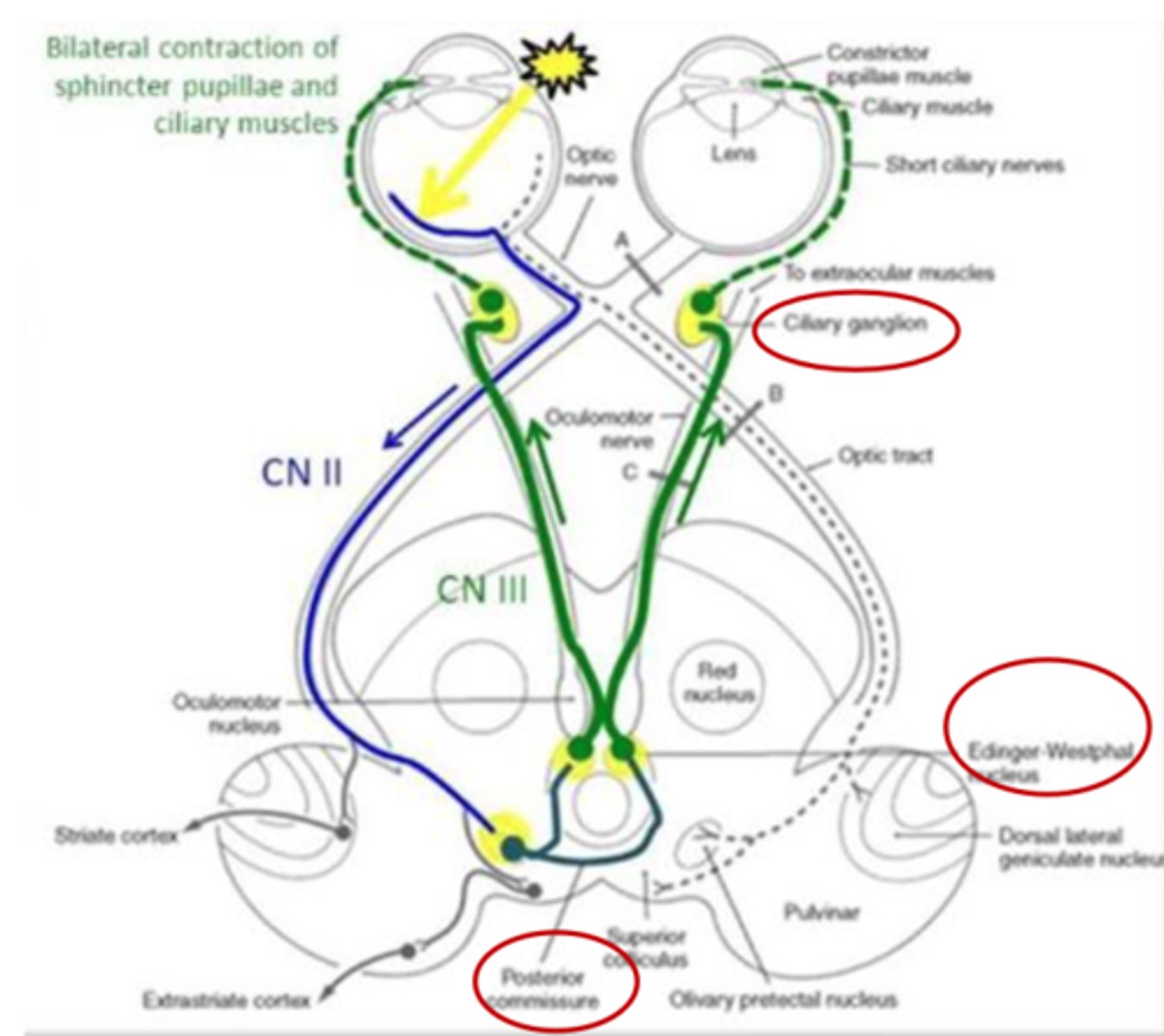
What is the function of the accommodation reflex?
Aids in focusing on objects at varying distances
What structures are involved with the accommodation reflex?
- Lens
- Pupillary sphincter apparatus
- CN II (afferent)
- CN III (efferent)
What 3 underlying mechanisms occur with the accommodation reflex?
1. Convergence of both eyes
2. Miosis (pupillary constriction)
3. Accommodation
What muscle is related to the underlying mechanism of convergence?
Medial rectus muscle
What muscles are related to the underlying mechanism of miosis?
- Pupillary muscles
- CN III (parasympathetic)
What occurs with the underlying mechanism of accommodation?
1. Ciliar muscles contract
2. Zonular fibers relax
3. Shape of lens changes to more convex
4. Refractive power of lens increased
What test is done for accommodation?
Test for convergence
What is step 1 of CN IV pathway?
Originates posteriorly (dorsal) in midbrain
What is step 2 of CN IV pathway?
Wraps around cerebral peduncle
What is step 3 of CN IV pathway?
- Into cavernous sinus
- Then into superior orbital fissure
What results from CN IV injury?
- CN IV (trochlear) palsy
- Hypertropia (strabismus)
- Extorsion
- Vertical diplopia
What results from injury to CN VI?
- CN VI palsy
- Horizontal diplopia
- Strabismus (medial)
What occurs with CN VI palsy?
- Eye remains adducted (rests in direction of nose)
- Difficulty abducting eye
What occurs with horizontal diplopia with CN VI injury?
Worse when patient tries to gaze toward affected eye (abduction)
What does vergence refer to?
Fixation of a single point by both eyes as target moves toward/away from viewer
What would you test for vergence?
Test for accommodation (convergence)
What does saccades refer to?
Rapid eye movements to bring the fovea to view target into field of view
What is the purpose of testing for smooth pursuits?
- Tracking a moving object
- Stable viewing of moving target keeping it in sharp focus
What is the visual field?
Area the eye can see when you focus on a single point
What would you test for visual field?
- Confrontation visual field test
- Static perimetry test
- Test each quadrant of eye
What test is done for contrast sensitivity?
Red dot test
What is the function of the tectospinal reflex?
Orienting reflex
What reflexes relate to blinking?
- Blink reflex
- Corneal reflex
- Glabellar reflex
What is the function of the blink reflex?
Protective reflex mediated by brainstem
What nerves mediate the corneal reflex?
- CN V
- CN VII
- Fewer connection
What is the glabellar reflex seen with?
- Habituation with successive tapping
- Dementia and Parkinson's
What is the function of the vestibular ocular reflex?
- Gaze stability
- Head moves in one direction and eyes in another
What is the vestibular ocular reflex mediated by?
Vestibular nuclei in brain stem and cerebellum
How is strabismus seem with children and infants?
- May not experience diplopia as they learn to suppress image from deviating eye
- Not good for development (first 3 months of life)
What conditions affect the visual field? (8)
- Glaucoma
- Macular degeneration
- MS
- Thyroid eye disease
- Pituitary gland disorders
- CNS problems
- Stroke
- Long-term use of certain medications