Amino Acids
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
structures and features
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
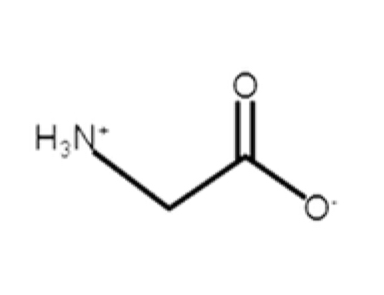
Glycine
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: -H
the only amino acid with 2 protons
the only amino acid that is not chiral
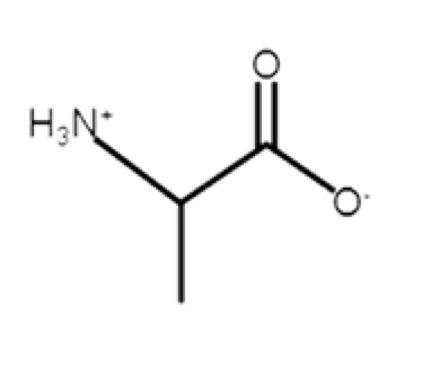
Alanine
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: -CH3
pretty hydrophobic
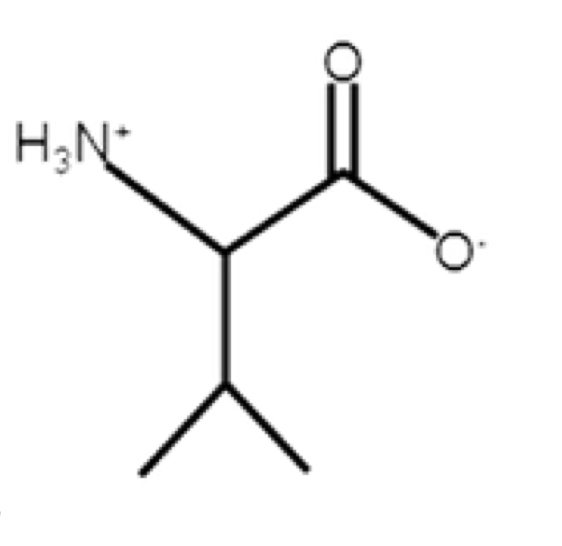
Valine
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: -CH(CH3)2
looks like a “V”
multiple saturated hydrocarbons
can become bulky
would put as far away from water when it comes to structure
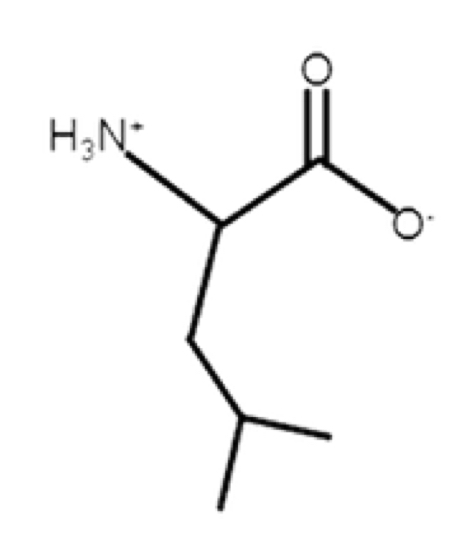
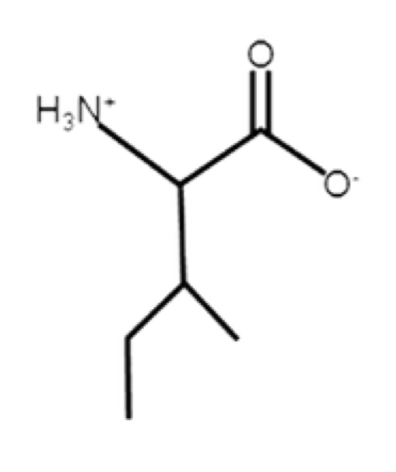
Leucine
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: -CH2CH(CH3)2
compared to valine, similar but has extra CH2
high hydrophobicity
larger
Isoleucine
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: CH(CH3)2CH2
isomer of leucine so same number of C and H
methyl sticking out to side affects packing
has a second chiral carbon (C that is attached to 4 different groups)
second choral carbon is the CH attached to the alpha carbon
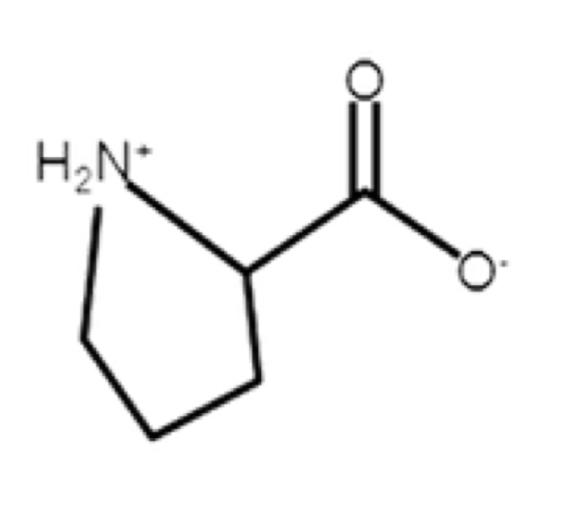
Proline
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: a cyclic 𝛂-imino acid (-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH)
only amino acid that makes contact with either functional group
severely constraining rotation and bonding
the H2C and H2N+ makes a covalent bond
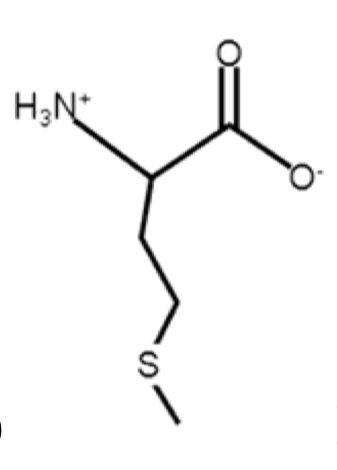
Methionine
non polar, aliphatic, hydrophobic
R-group: -CH2-CH2-S-CH3
one of two amino acids with sulfur
cannot form disulfide bonds
doesn't do much because S isn’t at the end
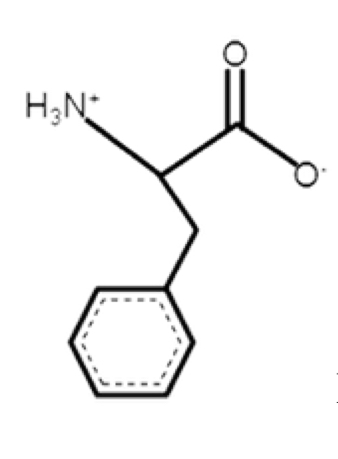
Phenylalanine
non polar, aromatic (lots of delocalization of electrons)
R-group: -CH2-C6H5 (benzene ring)
benzene ring
very rigid
can’t bend cause of partial double bonds
absorbs less light compared to other aromatics
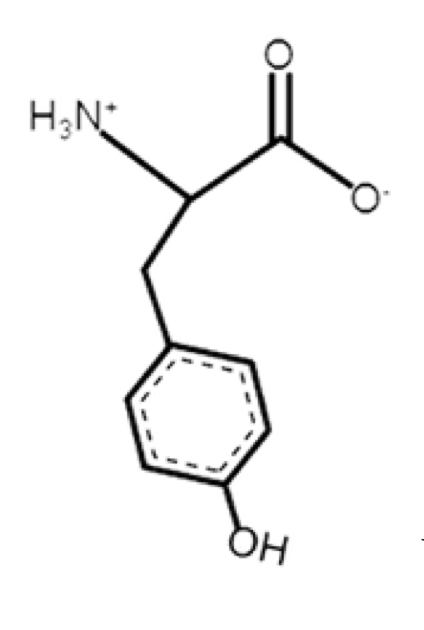
Tyrosine
polar, aromatic
R-group -CH2-C6H4OH
so CH2 with benzene ring and hydroxyl
not as hydrophobic compared to phenylalanine
rigid side chain (due to benzene)
very weak weak acid
the H in OH can ionize off at high pH
absorbs light better than F
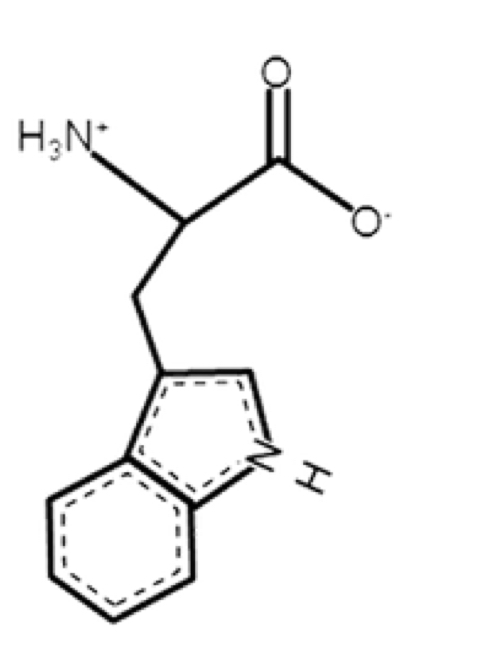
Tryptophan
non polar, aromatic
R-group: -CH2-C8H6N (indole ring)
2 rings
absorbs light really well
can fluorescence
big, heavy
can affect what proteins can do
the N in the ring DOESN”T gain or lose proton
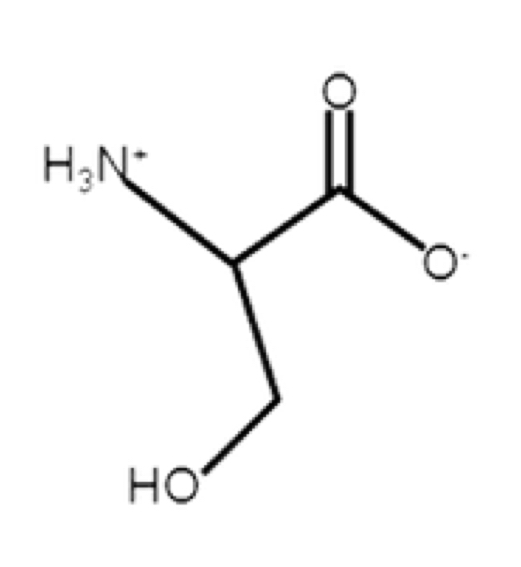
Serine
polar, uncharged, hydrophilic
can hydrogen bond, more on outer surface of protein
R-group: CH2OH
the H at the end, it can lose but because of high pKa (alcohol pKa = 13.6), not likely
not too important but that H at the end can be replaced with a phosphate (helps to signal)
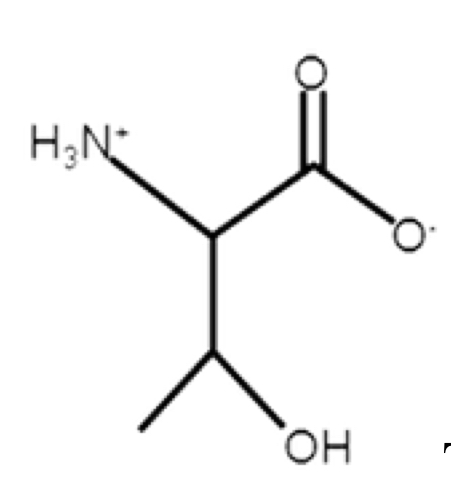
Threonine
polar, uncharged, hydrophilic
R-group: -CH(OH)-CH3
not as polar as serine because of methyl
proton in OH wouldn’t come off because of high alcohol pKa (13.6)
has a second chiral carbon
Cysteine
polar, uncharged, hydrophilic
R-group: -CH2-SH
has a thiol/sulfhydryl group
other amino acid with sulfur in it
the H in the thiol group can come off
2 nearby Cys can form a disulfide bond in an oxidizing environment
sulfur must lose BOTH proton and electron
covalent bond will be formed between S and S, meaning strong
help stabilize protein structure
Asparagine
polar, uncharged, hydrophilic
R-group: -CH2-C(O)-NH2 (amide side-chain)
polar, hydrogen bonding potential
Glutamine
polar, uncharged, hydrophilic
R-group: -CH2-CH2-C(O)-NH2 (amide side-chain)
extra CH2 between alpha carbon and amide
Aspartate
acidic, negative at pH 7
aspartic acid (protonated); aspartate (deprotonated)
R-group: -CH2-C(O)-O-
can be deprotonated in biological pH
at pH 7, lose side chain
carboxyl pKa = 3.9 (acid)
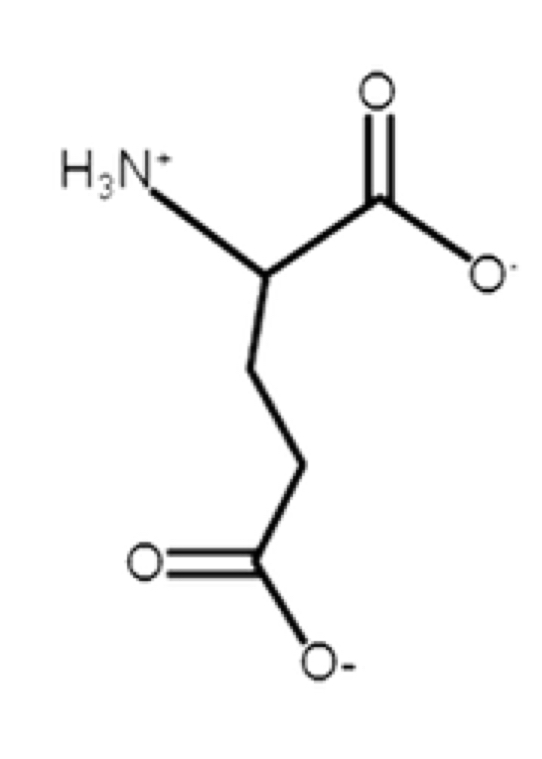
Glutamate
acidic, negative at pH 7
glutamic acid (protonated); glutamate (deprotonated)
R-group: -CH2-CH2-C(O)-O-
side chain will be deprotonated
similar to glutamine except for O- at end
carboxyl pKa = 4.2
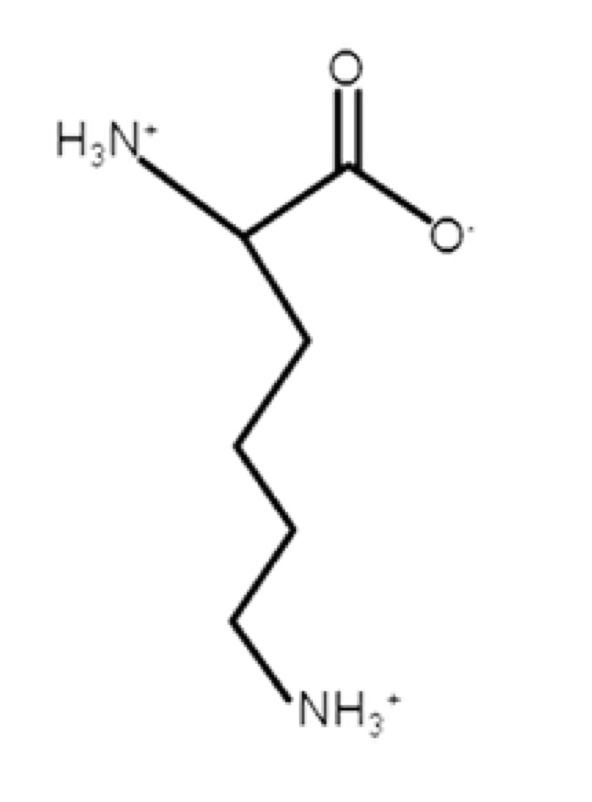
Lysine
basic, positive at pH 7
R-group: -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH3+
will be protonated under biological conditions
epsilon-amino pKa = 10.5
very weak acid (also tyrosine)
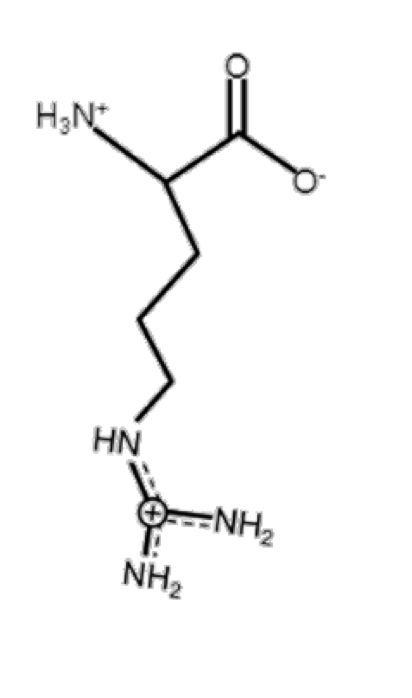
Arginine
basic, positive at pH 7
R-group: -CH2-CH2-CH2-NH-C(NH2)2+ (guanidine, pKa = 12.5)
look for the two N at the end for help identifying
long
some hydrophobicity character
ex. Glu + Arg can have electrostatic interaction
Histidine
basic, positive at pH 7/polar
R-group: -CH2-C3H3N2 (imidazole, pKa = 6.0)
pKa is close to physiological pH (90% will be in form at pH 7, while 10% will be in protonated form
can buffer/has buffering capacity
fairly rigid ring
2 nitrogens
Leucine
Isoleucine
Proline
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
Tryptophan
Serine
Threonine
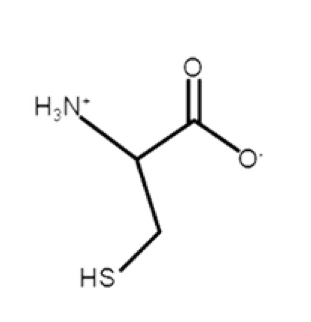
Cysteine
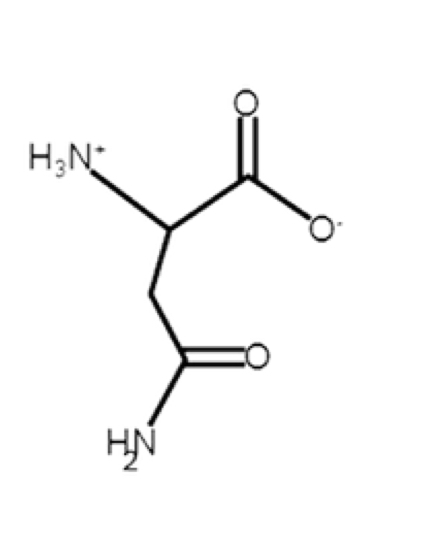
Asparagine
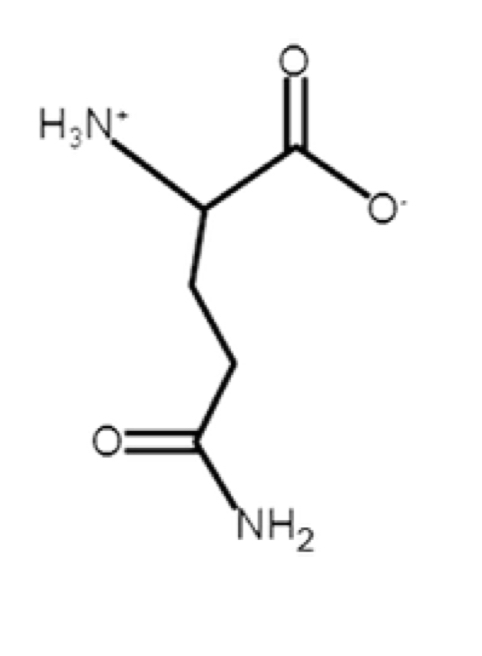
Glutamine
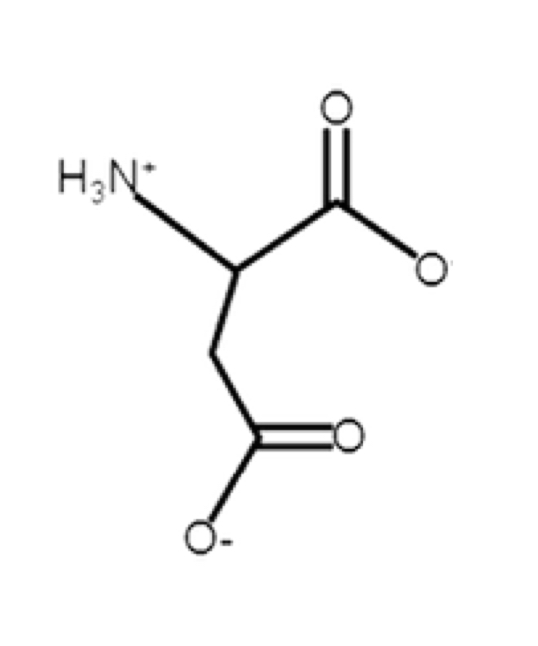
Aspartate
Glutamate
Lysine
Arginine

Histidine
Glycine
Gly, G
Alanine
Ala, A
Valine
Val, V
Leucine
Leu, L
Isoleucine
Ile, I
Proline
Pro, P
Methionine
Met, M
Phenylalanine
Phe, F
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y
Tryptophan
Trp, W
Serine
Ser, S
Threonine
Thr, T
Cysteine
Cys, C
Asparagine
Asn, N
Glutamine
Gln, Q
Aspartate
Asp, D
Glutamate
Glu, E
Lysine
Lys, K
Arginine
Arg, R
Histidine
His, H