Patient safety and root cause analysis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is patient safety
Patient safety is the avoidance of unintended or unexpected harm during the provision of healthcare
In context of pharmacy, provision of healthcare includes
prescribing
procurement of medicines
storage of medicines - temperature, atmospheric humidity, cleanliness
preparing and dispensing
supply/sale of GSL, P and POM medicines
administering medicines
monitoring
providing advice on health and/or use of medicines
signposting and referral
patient care, understanding each patient’s circumstances
Case study
Child prescription for propranolol
Propranolol is a beta blocker which slows your heart rate. It is used to help treat a number of conditions but in the following scenario it is to help control the symptoms of heart arrhythmias.
Prescription - Propranolol 5mg/5ml SF oral solution 12.5 (12.5mg) tds Quant - 1200ml
Theo’s weight is 25 kg
Medicine will be available in the morning
Used syringe from hospital to meausre out
Two days later he is admitted to hospital
Pharmacist didn’t check that with the patient properly if she could use the syringe.
Hospital had given 50mg/5ml, and the mum was supposed to give 1.25ml for this. But for what was given by the community it was meant to be 12.5ml.
Seven steps to patient safety
develop and maintain a safety culture - pharmacist will need to make quick and efficient decisions. Create a culture that is open, fair and supportive which prioritises patient safety through everything you do. However, remember humans will always mistakes
lead and support staff - effective training programmes, learning from mistakes
integrate risk management procedures - develop systems and processes to manage your risk and identify and assess things that could go wrong.
promote reporting - Reporting systems are essential to identify areas for improvement or additional strengthening. Create a culture that is open, fair and supportive which prioritises patient safety through everything you do
involve and communicate with patients - duty of candour. Pharmacy professionals must speak up when they have concerns or when things could go wrong.
learn and share safety lessons - share and learn from patient safety incidents.
implement solutions to prevent harm - embed changes to practice, processes or systems to help prevent recurrence of an incident.
NHS patient strategy describes how NHS will continuously improve patient safety, building on the foundations of a safer culture and safer systems.
Errors in pharmacy practice
patient safety incidents
Any unintended or unexpected incident, which could have or did lead to harm for one or more patients receiving healthcare is defined as a patient safety incident.
In pharmacy the most probable patient safety incident originate in
the prescribing, preparing, storage, dispensing, administering, monitoring or sale/supply of medicines
the provision of advice on health and/or use of medicines
delays or omission in the supply of medicines to the patient
Near misses
- near miss is an error which is detected before the patient is handed the dispensed medication/item and in doing so, a patient safety incident is prevented.
The most frequent types of errors in pharmacy
wrong dose/strength (30.5%)
wrong meds (28%)
wrong formulation (12%)
wrong quantity (9%)
Majority of errors in this report don’t result in harm, less than 1 % resulted in severe harm or death
Case study 1
Patient wanted to pick up regular medicines. Had Crohn’s and takes prednisolone
However dispensing error was spotted - gliclazide was given instead.
As a result suffered a severe hyperglycaemic episode and collapsed into coma - she died one month later.
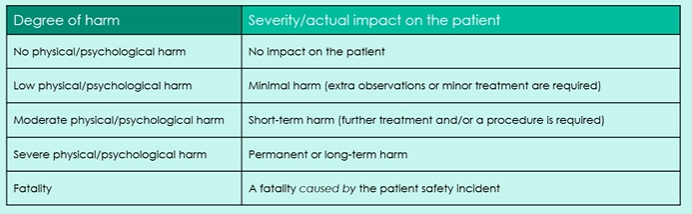
Degree of harm from patient safety incidents
Why do errors occur
System errors
SOP
Patient group directions
technology.
workload management
environment
Human factors
poor communication, low competency
distraction or inattention
forgetfulness
non-compliance, carelessness, negligence
limits/nature of human brain and behaviour
e.g. selective attention, skim reading and attempts to multi task
What are the outcomes of these errors in the dispensing process
selection errors, including LASA (look like, sound alike) drug errors; incorrect medication
bagging errors: someone else’s medication
labelling errors (including transposing labels between medicines); wrong instructions on the medication
dispensing of date expired medicines; potential safety issues', including underdosing and loss of control of the therapeutic effect
incomplete or incorrect counselling for the patient
What are the outcomes in the clinical checking process, as part of prescribing or dispensing and supply
incorrect drug for the condition
incorrect dose/strength/dose frequency for the condition/patient; incorrect calculation
incorrect formulation for the patient
oversight of patient’s comorbidities, allergies, dietary intolerance, beliefs
oversight of the patient’s social and environmental circumstances
interactions
LASA ERRORS
Amlodipine 10mg, amitriptyline 10mg
Atenolol 100mg, allopurinol 100mg
Quinine 300mg, quetiapine 300mg
Azathioprine 25mg, azithromycin
Hydralazine, hydroxyzine
Reducing risk of LASA
staff awareness, training and behaviour change problems
tall-man lettering
physical separation
visual warnings (shelf stickers, dispensing tray warning cards)
automation/scanning dispensing processes
warning details on the PMR
Errors with high-risk medication
Lithium
Clozapine
methotrexate
anticoagulants
opioids
insulin
sulfonylureas
sodium valproate - pregnancy prevention programme.
Error in dose can lead to toxicity, or ineffective therapeutic action
Safeguarding against errors
Swiss cheese model
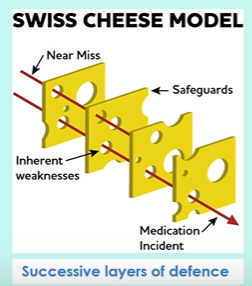
Community pharmacy patient safety group incident investigation model
The reports from all investigators and their outcomes are then shared, not only with the pharmacy team and organisation but also nationally within the NHS, via a regular upload of information to the NHS ‘Learn from patient safty events’

Possible barriers to error reporting
knowledge
time
fear
A just culture
A just culture within the organisation is one which focuses on learning from incidents and improving practice to prevent their recurrence. It applies to all incidents and near misses.
A just culture
the factors which contributed to an error are identified, and then where applicable
pharmacy team members are supported to carry out specific activities
which leads to a change in which they work
So that they avoid repeating the error in the future
Benefits and drawbacks from root cause analysis
Benefits
minimises the risk of errors and patient harm in the future
improves the patient care/safety
enables review and reflection of processes and performance in the dispensary
enables the implementation of change in order to improve processes
Drawbacks
time consuming - needs to be used when appropriate e.g. as part of investigation into complicated errors, serious errors or a type of error which has not occurred before
staff may be fearful - root cause identification risks creating a blame culture
teams may fall into the trap of only addressing root cause and not other contributing factors.
Clinical governance
is the system through which NHS organisations are accountable for continuously improving the quality of their services and safeguarding high standards of care by creating an environment in which clinical excellence will flourish
Seven pillars
clinical effectiveness
information
risk management
education and training
audit
patient and public involvement
staff management
Clinical effectiveness
Every action you take provides the best outcomes for each patient
adopting an evidence based approach to your practice
implementing national standards e.g. NICE guidelines to ensure optimal care
update your practise based on your experience and evidence
carry out research to enhance your level of care for patients in the future
Information
information and IT is sued to ensure than
patient data is accurate and up to date
confidentiality of patient data is respected
data is appropriately used to measure quality of outcomes (e.g. via audits) and to develop services for local needs
Risk management
Having systems in place to understand, monitor and minimise risks to patients and staff, and learning from mistakes
an effective and honest reporting culture
learning from errors and near misses; anticipating risks in new procedures
assessing risks for their probabilty of occurence and impact, and implementing procedures to reduce risks
Education and training
Providing support to enable staff to be competent, confident and up to date with their skills and knowledge.
supporting continuous learning so that staff can offer up to date information and skills
regular assessment
appraisal to identify and discuss weaknesses and provide opportunities for personal development
Audit
Audits are used to monitor practice and ensure that any deficiencies or weaknesses in the standards of care are rectified.
Patient and public involvement
Ensuring that the services provided suit patients and that patient feedback is used to improve practice in terms of quality, suitability and outcomes
patient feedback forums
patient forums
patient advice and liaison services
Staff management
Ensuring that staff offer a quality service by
recruiting appropriate staff who are suitable to carry out the work
managing the staff electively and providing adequate staffing levels
identifying and addressing underperformance
motivating, involving and developing staff to encourage retention providing good working conditions