SS pulm infections
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what are the three pulmonary infections we are going to go over
pneumonia
covid-19
tuberculosis
what are the two modes of transmission you can get pneumonia
community acquired
hospital acquired (nosocomial pneumonia)
is community acquired or hospital acquired pneumonia more common
community acquired- especially in chronic disease and smoking
what are the most common causative organisms of community acquired pneumonia
strep pneumoniae
influenza virus
SARS-CoV-2
hospital acquired pneumonia is often _____-______ resistant
multi-drug resistant
there is a sub-category of healthcare acquired pneumonia, in what locations can pts acquire these
nursing homes, dialysis centers, etc
are pts at higher risk of acquiring pneumonia through hospitals or in healthcare
hospital is higher risk
what symptoms would a pt present w community acquired pneumonia
cough, dyspnea, fever, chest pain, and often anorexia
strep pneumonia often has what appearance on a chest x-ray
consolidated lobar- lung has some grey/white in it
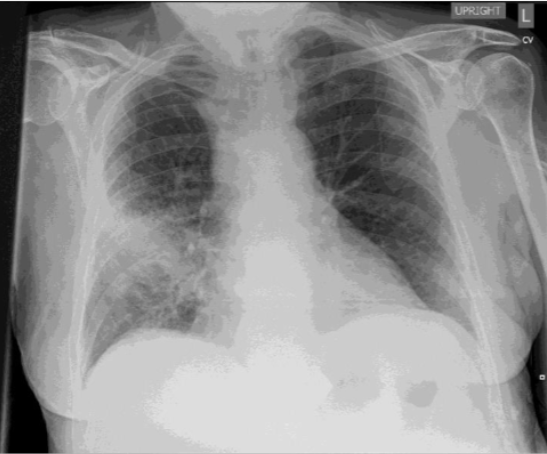
what is tx for community acquired pneumonia
30% require hospitalization
sputum culture sent but doesn’t always identify organism
antiviral and/or antibiotics based on presentation (S. pneumonia is usually targeted)
prognosis for community acquired pneumonia if hospitalization is required
mortality rate is up to 35%
prognosis for community acquired pneumonia if mild
antibiotics/antiviral are usually successful; recovery can be long (even in young/healthy people)
prevention for community acquired pneumonia
pneumococcal vaccine (<2 yrs and >65 yrs or immunocompromised)
influenza vaccine
don’t smoke
what is aspiration
refers to the entry of gastric or oropharyngeal substances into the lower airways
what is aspiration pneumonitis
if the substance aspirated is a chemical or gastric acid; inflammation of the lung
what is aspiration pneumonia
if the substance aspirated results in an infection
what are risk factors for aspiration
older age, reduced consciousness, neurological impairment, pharyngeal anesthesia, people w poor dental hygiene
COVID-19 was caused by
coronavirus, SARS-CoV- 2
what is SARS-CoV-2
an enveloped RNA virus; has receptor-binding region on its spike protein and the receptor is the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
how prevalent is tuberculosis
in 33% of the world population
how is TB caused
mycobacterium tuberculosis that are acid fast bacilli
how is TB transmitted
by infectious aerosolized droplets
what are the 4 possible outcomes after inhalation of M. tuberculosis
immediate clearance
primary disease w immediate onset of active disease
latent infection w minimal or no primary symptoms
reactivation of disease after latent infection
of the 4 possible outcomes after inhalation of M. tuberculosis, what is the most common
latent infection
is primary infection of TB be asymptomatic or symptomatic
both!
what is happening to the TB bacteria in a latent infection
bacilli proliferate in the alveoli→ granulomas called tubercles form to isolate the bacilli → hangs out until it wants to reactivate
symptomatic primary infection presentations of TB
recurring fever, night sweats, chest pain, dyspnea, cough, weight loss, fatigue, can have painful mouth ulcerations, and often presents like cancer
untreated symptomatic TB disease- primary or reactive- has a mortality rate around…
50%
if a person has latent TB, are they infectious
no
what are the screening tests for TB
skin test and blood tests
the screening tests screen for the bacilli infection but DO NOT identify…
noninfectious vs active TB disease
how do we determine if a person has noninfectious vs infectious TB
examination, sputum samples, and chest x-ray
the time of highest risk reactivation to active TB disease is during what period of latency
the first 2 years
why is it important to treat latent TB
tx while latent greatly reduces the likelihood of reactivation in the future and thus dec the spreading and dec morbidity for that person
what is the tx for latent TB
multiple daily doses for 3 mo or 24 mo
people w what medical conditions are at v high risk of TB reactivation
people w HIV, are immunocompromised or chronic diseases
if you encounter someone and you are suspicious of TB, what is the first thing you do
call the public health office to arrange for text steps- including contact tracing
if you encounter someone and you are suspicious of TB, what do you do after you contact the public health office
mask the suspected person immediately and isolate them
what are the most common meds for tx of TB
RIPE: Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol