bio 161 exam 3
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Eukaryotic chromosomes
Molecular composition includes DNA and histone proteins; chromatin is 40% DNA and 60% protein.
Nucleosomes
Structures that organize eukaryotic chromosomes, consisting of DNA wrapped around histones.
Centromeres
The part of a condensed chromosome that helps in spindle attachment.
Telomeres
The ends of chromosomes, important for stability.
Chromatin
The uncondensed form of chromosomes found in non-dividing cells.
Chromosome
The condensed form of chromatin seen in dividing cells.
Heterochromatin
Inactive, tightly packed form of chromatin.
Euchromatin
Active, loosely packed form of chromatin.
Drosophila polytene chromosomes
Giant chromosomes found in fruit fly salivary glands, used for gene mapping.
Karyotype
A chromosome chart used to detect number abnormalities, sex chromosomes, and genetic diseases.
Homologous chromosomes
Pairs of chromosomes with the same genes, one from each parent.
Phases of the cell cycle
Include Interphase (G1, S, G2), M phase (mitosis), and cytokinesis.
G1 phase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows.
S phase
The phase of the cell cycle where DNA replication occurs.
G2 phase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell prepares for division.
Importance of mitosis
Ensures growth, repair, and identical genetic information in diploid organisms.
Stages of mitosis
Include Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
Spindle apparatus
Structure that moves chromosomes during mitosis.
Purpose of mitosis
Produces genetically identical daughter cells to maintain tissue and function.
Mitosis in animal cells
Characterized by the formation of a cleavage furrow.
Mitosis in plant cells
Characterized by the formation of a cell plate.
Cytokinesis
The division of cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells.
Cell cycle control
Managed by checkpoints (G1/S, G2/M, spindle) that ensure proper division.
p53
A tumor suppressor protein that halts the cell cycle if DNA is damaged.
Proto-oncogenes
Genes that stimulate cell division; can lead to cancer when mutated.
Meiosis
Type of cell division essential for sexual reproduction, creating genetic diversity.
Haploid gametes
The cells formed by meiosis, which include egg and sperm.
Haploid vs Diploid
Haploid (n) has 1 set of chromosomes; Diploid (2n) has 2 sets.
Meiosis vs Mitosis
Meiosis involves 2 divisions and creates 4 genetically unique haploid cells.
Stages of Meiosis I
Include Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, and Telophase I.
Stages of Meiosis II
Include Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II.
Result of meiosis
Produces four haploid cells, each genetically different.
Synaptonemal complex
Holds homologs together during Prophase I.
Crossing over
Process where non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material, increasing variation.
Independent Assortment
Random alignment of chromosomes during Metaphase I, leading to genetic variation.
Spindle attachments in mitosis
Each chromatid attaches to opposite poles.
Spindle attachments in meiosis
Sister chromatids attach to the same pole in Meiosis I.
Sexual reproduction vs Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction leads to variation; Asexual reproduction yields identical offspring.
Advantages of sexual reproduction
Diversity is a major benefit.
Disadvantages of sexual reproduction
Requires more energy and a mate.
Impact of meiosis
Essential for producing diversity and aiding in evolution.
Mendel’s experiments
Studied pea plants and observed inheritance patterns leading to genetic laws.
Mendel’s success factors
Large sample sizes, controlled breeding, and quantitative data.
Mendel’s model vs Sutton’s theory
Mendel described inheritance; Sutton tied it to chromosome behavior in meiosis.
Phenotype
The observable traits of an organism.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait.
Dominant
An allele that is expressed in the phenotype.
Recessive
An allele that is hidden in the phenotype.
Monohybrid cross
A genetic cross that examines the inheritance of a single trait.
Dihybrid cross
A genetic cross that examines the inheritance of two traits.
F2 phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross
3:1 ratio.
F2 genotypic ratio of monohybrid cross
1:2:1 ratio.
Phenotypic ratio of dihybrid F2
9:3:3:1 ratio.
Test cross
Crossing an unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive to determine the unknown.
Segregation
The process during gamete formation where alleles separate.
Independent Assortment
The random distribution of alleles during gamete formation.
Incomplete dominance
An intermediate phenotype is expressed in offspring (e.g., red + white = pink).
Codominance
Both alleles are expressed simultaneously (e.g., AB blood type).
Pleiotropy
A single gene influences multiple traits.
Continuous variation
Traits that exhibit a range of phenotypes.
Environmental influence on phenotype
External factors can affect gene expression.
Epistasis
One gene can mask the expression of another gene.
Genetic factors and disease
Conditions like pleiotropy, incomplete dominance, and environmental influences affect diseases.
Inheritance patterns of genetic diseases
Includes autosomal dominant/recessive, X-linked dominant/recessive, and mitochondrial inheritance.
Pedigree chart
A diagram showing inheritance patterns across generations.
Mitochondrial and chloroplast contributions
Provide maternal inheritance and play roles in cellular energy.
Examples of genetic disorders
Sickle cell anemia, albinism, Down syndrome, etc.
Nondisjunction
The failure of chromosomes to separate properly in meiosis.
Disorders caused by nondisjunction
Examples include Turner’s syndrome (XO), Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY), and Down syndrome (trisomy 21).
Genetic counseling
The process of assessing genetic risks in families, often using pedigree charts.
Prenatal screening techniques
Include Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS).
How many chromosomes do people with Down syndrome have
People with Down syndrome typically have three copies of chromosome 21, resulting in a total of 47 chromosomes
How many chromosomes do women with turner syndrome have
Women with Turner syndrome typically have 45 chromosomes, with a missing X chromosome, resulting in a genotype of 45,X.
What is the sex chromosome for Turner syndrome
XO
How many chromosomes do men with Klinefelter syndrome have
47
What is the sex chromosome Klinefelter syndrome
XXY
How many chromosomes do men with jacob’s syndrome
47
What is the sex chromosome for jacob’s syndrome
XYY
How many chromosomes do women with Poly X syndrome have
47
What is the sex chromosome for Poly X
XXX
What goes on during prophase in meiosis
During prophase in meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over, while the nuclear envelope begins to break down.
What goes on during anaphase in meiosis
During anaphase in meiosis, sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell, and the spindle fibers shorten, ensuring each new cell will receive an equal set of chromosomes.
What goes on during metaphase in meiosis
During metaphase in meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, and spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores of each chromosome, preparing for separation.
What goes on during telophase in meiosis
During telophase in meiosis, the separated chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the cell prepares for cytokinesis, which will divide the cytoplasm and complete the formation of two distinct daughter cells.
What goes on during interphase in meiosis
During interphase in meiosis, the cell undergoes growth and DNA replication, resulting in duplicated chromosomes, followed by preparation for the two meiotic divisions.
What goes on during cytokinesis in meiosis
Cytokinesis in meiosis occurs after telophase, where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two daughter cells, each with half the original chromosome number.
What goes on during interphase in mitosis
During interphase in mitosis, the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division by ensuring all necessary organelles are duplicated.
What goes on during prophase in mitosis
During prophase in mitosis, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form, anchoring at the centrosomes.
What goes on during anaphase in mitosis
During anaphase in mitosis, the sister chromatids are pulled apart towards opposite poles of the cell as the spindle fibers shorten, ensuring that each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
What goes on during metaphase in mitosis
During metaphase in mitosis, the chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, known as the metaphase plate, and the spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each chromosome, ensuring proper distribution to the daughter cells.
What goes on during telophase in mitosis
During telophase in mitosis, the chromosomes begin to decondense back into chromatin, the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes, and the mitotic spindle disassembles, concluding the process of mitosis.
What goes on during cytokinesis in mitosis
During cytokinesis in mitosis, the cytoplasm divides between the two daughter cells, forming a cleavage furrow in animal cells or a cell plate in plant cells, leading to the complete separation and formation of two distinct cells.
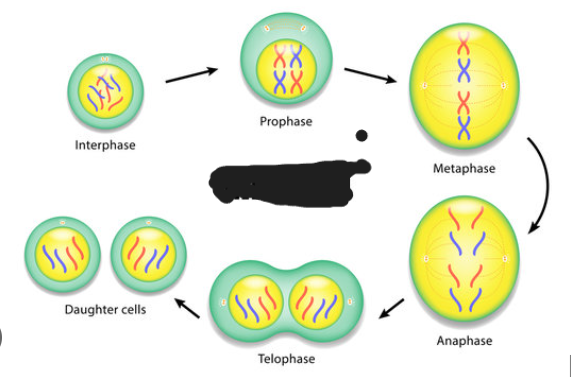
what type of cell division is this
mitosis

what type of meiosis is this
meiosis 1
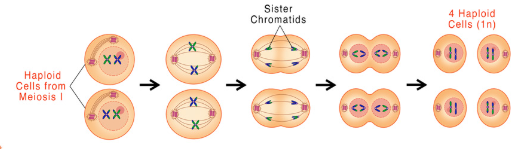
what type of meiosis is this
meiosis 2