Cram time babey
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Homoplasy
the development of organs or other bodily structures within different species, which resemble each other and have the same functions, but did not have a common ancestral origin
Paraphyletic
a group of any size and systematic rank that originated from a single common ancestor, but does not – as opposed to a monophyletic group – contain all descendants from this ancestor.
Polyphlyetic
of, relating to, or derived from more than one ancestral stock
specifically : relating to or being a taxonomic group that includes members (such as genera or species) from different ancestral lineages
Monopyhletic (if a group is sometimes called a clade)
includes an ancestral taxon and all of its descendants
Cuckoldry
Cuckoldry, or being deceived into providing investment into genetically unrelated offspring, is an adaptive problem that males face primarily in species in which fertilization occurs within the female
Sneaking
is any strategy that allows a male to access a female partner, avoiding more dominant males, for example those guarding a harem, as in the red deer and elephant seal.
Monogomy
Monogamy is a mating system in which a single adult male and a single adult female mate. Such pair bonds may last for a single breeding attempt, a breeding season, or many breeding seasons
Polyandry
one female mates with many males
• Male may provide majority of parental care
polygynous
one male mates with many females
pre-zygotic barriers
prevents mating/fertilization if mating is even possible
Allopatric speciation by vivarance (/ geographical isolation)
speciation that occurs when biological populations of the same species become isolated due to geographical changes such as mountain building
Allopatric speciation by dispersal
literally just the organisms migrate far enough away from eachother, or are just spread over such a large area (due to movement) that the population is no longer continous and new species begin to form
Peripatric Speciation
just like allopartic speciation by vicarance, just with the spefication that the leaving group is WAAAY smaller than the og group
Parapatric Speciation
Geographically continuous populations over extremely vast distances, become functionally isolated as well as subject to different selectional pressures
Sympatric speciation
speciation occurs in populations that live in the same geographic
area
Evolution will not occur if:
mating is random, natural selection is not acting on the population, mutations are not occuring, the population is sufficently large, and migration is impossible
Genetic drift
Random change in allele frequncy from generation to generation (naturally impacts smaller populations moreso than larger, possibily bad for genetic diveristy in small pops)
Gene flow
Genetic information being added or taken away from a species by either, another subgroup of another population of that species coming to interbreed (addative), or by members of the orginal population leaving for a different one (subtractive)
Alelle fixation
the change in a gene pool from a situation where there exists at least two variants of a particular gene (allele) in a given population to a situation where only one of the alleles remains. That is, the allele becomes fixed.
Hetrozygozity
the thing that measures the probability of drawing 2 different alelles from gene pool of population, modeled by the equation H=1-(p²+q²)
Mark recapture method =
marking x amount of indivudals and releasing them back into orginal (and unknown of size) population, then later capturing another subset of the population and using the proportion of how many of this new subset are marked to calculate total population size
Mark recpature method equation
(# marked in second sample/ total caught in second sample)= (# marked in first sample/ size of whole population)
Simplest growth model
( delta N [change in N, number of indivudals in population/ delta t)= B -D
Per capita B rate
number of offspring sired by average member of population/ unit time
Per capita D rate
expected D rate per unit time
Model with B and D rates =
delta N/ delta t = bN-dN
per capita population growth rate (R)
r = b - d
Per capita population growth rate (with other rates)
delta N/ delta t= r N
Logisitc growth model =
Population caps at certain point and approaches that point slower and slower per every unit time
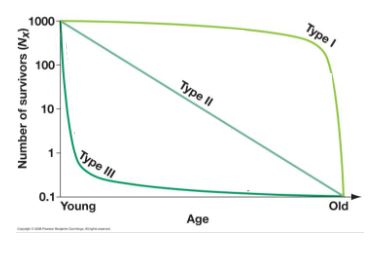
Suvivorship
= % of population that survies to a given age
Suviorship curves
interspecific interactions
= interactions between individuals of different species
Intraspecific interactions
interactions between members of the same species
Symbioses
the term denoting that indviduals of two species have lived in direct intamate contact with one another for a long long time (dont think venom, symbioses are not always good)
Symbioses: Parasitism
+/- relationship in which the parasite derives nutrition from its host which is harmed in the process
Symbioses: Commensalism
a +/0 relationship between two species in which one benefits while the other is unaffected
Symbioses: Mutulaism
the one you think of when you think of symbioses, +/+ relationship where both benefit
Ecosystem Engineer
a speices that so dramatically alters its surrounding habitat in a pyshical way such as to create a new/new forms of habitat, or to maintain the current habitat
keystone species
Similar idea to Ecosystem Engineers, but they maintain/create habitat in a non-pyshical manner (i.e., not through cutting down trees, but by interacting with other species)
Non-symbiotic interspecific interactions
species do NOT live in prolonged intimate contact, but still periodically associate with each other (e.g, predation of competition)
Ecological niche
the sum of a species’ use of its biotic and abiotic environment (two species never share this)
Resource partitioning
differentiation of niches in response to interspecific competition that results in limitation of competition for shared resources
Fundamental niche
the full suite of resources potentially used by a species in absence of competition
Realized niche
the portion of a species’ fundamental niche actually used in the presence of competition
Trophic cascades:
effects of higher trophic level trickle down to lower levels
Greenhouse Gases
gas in atmo that absorbs the big boy long radiation reflected off of the earths surface, and the naturally re-radiates that heat back down to earth (e.g., CO2, Methane, nitrous oxide, even water vapor suprisgnly)
Carbon cycle
like water cycle (or any or cycle really) but just for carbon : describes the movement of C through biotic and abiotic components of the Earth system
Carbon pools
exactly what they sound like, resviors of carbon
Carbon fluxes
movement of C from one compnent of cycle to another
Biospheric pool
amount of C stored in living tissue (mostly planty boys), characterized by fast turnover and short residence time (respiration, death/ decomposition
Carbon fixation
process of converting inorganic C into organic C compounds in livin tissues
Highest Co2 conc we’ve ever had, solar radiation does not alone explain variations in temperature
just remember this
Best case climate scenario
2.5 degrees F warming
Bussiness as usual scenario
8 degrees f warming (4.5 degrees C)
Cooperative breeding
indidvual loses out on breeding (and thus fitness), to devote energy towards rearing young of relatives (usually siblings)
Altruism
any action that innatley reduces a gvien organisms chance at breeding (thus reducing their overall fitness) that also increases the fitness of another indivual.
Things like altruism and cooperative breeding are
Never actually selfless, to be possible in an evolutionary enviorment they must provide some selfish benefit to the enactor
Cooperative individuals are
generally less succesful
Fitness (in the context of animal behavior is defined as)
number of an individuals’ alleles transmitted to the next generation
Direct fitness
fitness gained through allele transmission by offspring (directly having babies)
Indirect fitness
fitness gained through allele transmission by helping relatives rear their offspring (dont raise your own exact babies, but ensure many of your alleles will be passed on by helping a realtive who you naturall share many alleles with)
Inclusive fitness
fitness gained through both direct and indirect fitness (why not both babey?)
Hamilton’s Rule
Individuals should behave altruistically (help raise relative’s offspring) IF fitness gained is greater than fitness lost from not reproducing (straight up just common sense considering everything else we’ve learned)
Kin selection
evolutionary strategy in which organisms forego reproduction (lose direct fitness) to benefit a relatives’ reproductive success (gain indirect fitness) (sounds identical to cooperative breeding to me, seemed to be used just to empahsize why they are doing it)
Inclusive fitness
= direct fitness + indirect fitness (how actually fit an organism is in terms of passing alelles and stuff on)
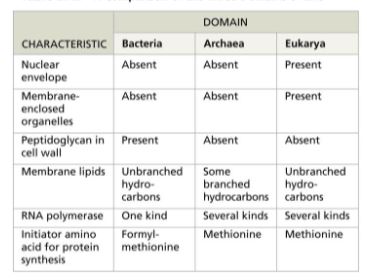
Prokaryotes
organisms with cells that lack membrane-bound organelles and a membrane-bound nucleus (Include Domains Bacteria and Archaea)
Eukaryotes
organisms with cells that have membrane-bound organelles and a membrane-bound nucleus (domain Eukarya) (include protists, plants, fungi, and animal)
plasmids
prokaryotes have them, and they are cicrular segements of self replicating dna and often have alleles for antibotic resistance
prokaryotes fuck via
binary fission:
Archaea/ single cell prokaryotes
Often (but not always) extremophiles, either Extreme thermophiles, or Extreme halophiles (super salty enviroment.
Comparosion of domains of cellular stuff
Endosymbiont theory
the at some point, cellular life joined up with independetly living mitochondria feeling
Eukayrotes: Protists
a group of mostly unicellular eukaryotic organisms that are not fungi, plants, or animals (not valid evo group, must be monopyhletic to be valid)
Fungi are
Heterotrophs that feed by breaking down compounds outside their bodies
Green algae is the closest relative to
closest relative of land plants
Land Challenges
avoid dessication (dry out), develop supportive tissue to remain upright (and compete for some o dat sunny d), need to have gametes that don’t require the need to swim in water
Chytrid (type of fungi) are a
unicellular parasitic fungus
Major fungal groups are:
Chytrids (both 1000), Zygomycetes, Glomeromycetes (least amount of these), and Ascomycetes (most amt of these)
Adaptations to living on land (spefic in refrence to horny plants)
vasc tissue, pollen, seeds, and flowers
Land benefits
Unfiltered sunlight, Higher CO2 concentrations, Fewer herbivores and pathogens (during initial land colonization), Nutrient rich soils
Bryophytes are
non-vascular plants tend to be small and live in moist places (no vasc tissue to support or move water/ nutrients), they also have flagellated (water needing) sperm, and they disperse by spores
Types of vascular tissue are
Xylem: dead tracheid or vessel element cells form tubes that transports water from root to shoot (basically xylem = pipes), and Phloem: Living sieve tube cells form tubes that transport sugar formed via photosynthesis from leaves to the rest of the plant (pipes but alive)
Seedless vascular plants are
Pteridophytes, including ferns, horsetails, and club mosses
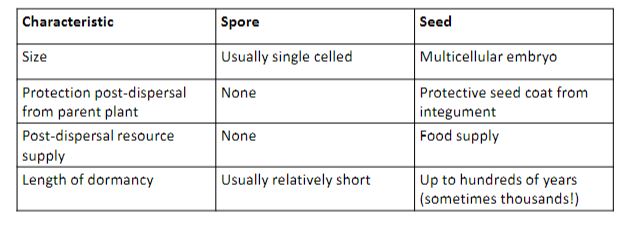
Seeds =
diploid plant embryo + food supply + seed coat
Advantages of seeds vs spores
Gynosperms differ from angiosperms in that…
they bear “naked” (just meaning not within a fruit) seeds, they also breed a little bit differently, they don’t have any adaptaions for any animals to take and distribute their seeds so they just disperse fucking massive clouds of pollen, also their are ovulating cones (the brown ones), and sperm/pollen producing cones (yellow smaller ones)