Electrical circuits
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
State Kirchoff’s 2nd law?
The sum of the E.M.Fs in a circuit is the same sum of the P.Ds in a circuit
What is the definition of e.m.f?
the amount of energy transfered to electrical energy per unit charge from chemical energy
Explain why Kirchoff’s second law is the conservation of energy applied to circuits?
It is an electrical circuit so it is a closed loop
Therefore the energy transferred in the circuit is equal to the energy changes of the circuit
Σε=ΣV
How is the E.M.F of a circuit, split between components in series and how is the total e.m.fs of the circuit related to the P.D of the individual components?
E.M.F is shared between components but still is equal to the P.D. Depending on the resistance of the components they may be shared equally or not
The total e.m.fs of the circuit must add up to the total P.D
Use Kirchoff’s second law to describe how E.M.F and P.D are related in a parallel circuit
Parallel circuits have many different loops, each loop can be seen as a separate circuit
In each loop the sum of the E.M.Fs must equal the sum of the P.Ds
If one branch is changed it will not affect other branches
In a parallel circuit, the current in each loop adds up to the total current. The p.d. across each loop is the same
How is the total resistance of a number of resistors connected in series determined and calculated?
It increases the overall resistance as a series circuit is one loop so it is effectively adding more resistance
R (Total) = R(1) + R(2) + R(3)
How is the total resistance of a number of resistors connected in parallel determined and calculated?
It decreases the overall resistance as it provides another loop due to it being a parallel circuit. Effectively increasing cross-sectional area and lowering resistance
R(Total) = ( 1/R(1) + 1/R(2) + 1/R(3) )^-1
What are the 4 key electrical relationships/equations that can be used to analyse circuits?
I= Q/t
V= W/Q
P=VI
V=IR
How is internal resistance defined in words?
The resistance of a source of e.m.f due to its construction (chemicals and wires), which causes a loss in energy/voltage as charge passes through the source
What equation can be used to find out internal resistance?
ε= I(R+r)
r= internal reistance
What is the reason for internal resistance in a battery?
So it can determine the amount of current needed in the circuits they power. (If a large current is needed, a power source would have a small internal resistance)
What is meant by lost volts and why does it occur?
The voltage difference between the e.m.f of a power source and the terminal potential difference (p.d.).
Energy is lost due to internal resistance when there is a current in a source of e.m.f → not all energy transferred to the charge is available to the circuit
What is meant by terminal P.D?
The potential difference measured at the terminals of the source of the e.m.f
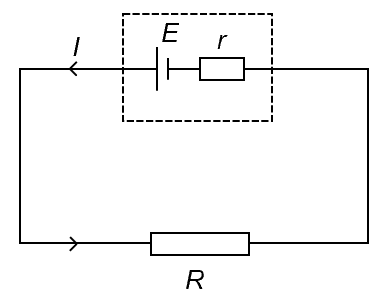
Draw a circuit diagram and label the internal resistance, the lost volts and the terminal P.D?
E-r = Terminal P.D
r= Internal resistance
Loss volts= E-V
What is the relationship of E.M.F and terminal P.D and lost volts?
E.M.F (V)= Terminal P.D(V) + Lost volts(V)
Explain why the amount of lost volts increases when the current in a circuit is high?
Increasing the current means that more charges travel through the cell each second
Therefore more work is done on the charges, increasing the lost volts→ decreasing terminal P.D
Which is greater: E.M.F or terminal P.D?
E.M.F
Under what condition is E.M.F= terminal P.D?
When there is no current in the circuit
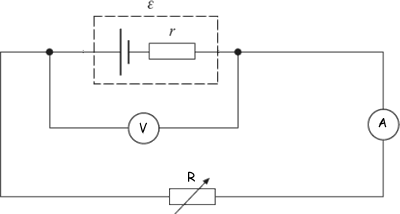
Describe an experiment that can be used to determine the internal resistance and E.M.F of a cell?
Record values of terminal P.Ds for different values of current.
Use a variable resistor to change the resistance of the circuit.
By considering y=mx+c and rearranging the equation ε= V+Ir to give
V=-rI+ε, we can plot a graph of terminal P.D against current
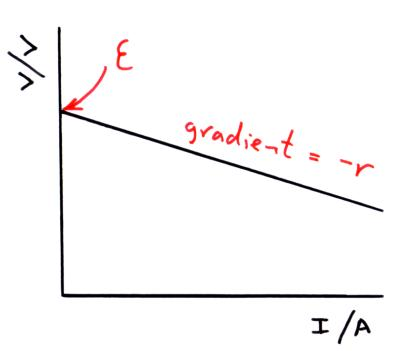
Describe the graph for the experiment that can be used to determine the internal resistance and E.M.F of a cell?
What is the function of potential dividers?
Potential dividers can be used to divide the P.D to give any value you require up to the maximum supplied from the power source
Sketch a basic potential dividers circuit with 2 resistors, R(1) and R(2)?

In a potential divider circuit how is the ratio of the resistance (R1 and R2) related to the ratio of the P.Ds (V1 and V2)?
V1/V2 = R1/R2
State the equation for potential dividers? Define all terms
V out= (R2 / R1 + R2) X V in
Finds out resistance of R2

Explain why the output P.D of a potential divider circuit drops when it is loaded (has a component connected across it)?
Loading (Connecting a component or circuit to V out that is placing a component in parallel with R2)
This lowers the resistance of this part of the potential divider circuit, which lowers a fraction of the total P.D across this part of the circuit → Lowers V out
Sketch a circuit that can be used for sensing temperature?
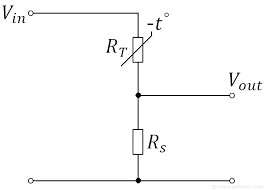
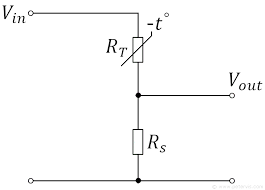
For the circuit drawn above, explain what happens to the output P.D when the temperature increases?
As the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases and so V out decreases
(R(s) will receive a greater amount of voltage due to this as it has a higher resistance now)
Sketch a circuit that can be used for sensing light intensity?
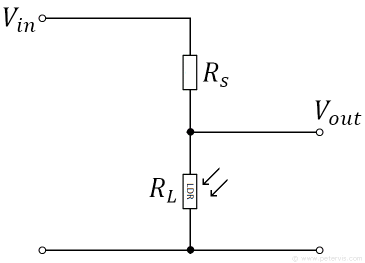
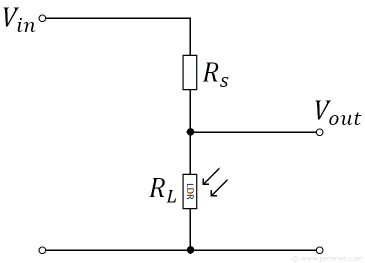
For the circuit drawn above, explain what happens to the output P.D when the light intensity increases?
As the light intensity increases, the resistance of the LDR falls and so the V out decreases.
(R(s) will receive a greater amount of voltage due to this as it has a higher resistance now)
Draw the circuit symbol for a potentiometer and explain the function of this component and name its uses?
A potentiometer is a variable resistor with three terminals and a sliding contact
Adjusting this contact varies the P.D between 2 of the terminals, giving a variable V out
Potentiometer can be made very compact, making them useful for portable electronic devices
