#1 Basic Principles & HydroCarbons
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Organic Compounds
Soluble in organic solvents – CCl4
Nonpolar
Molecules
Covalent bonds
Highly flammable
Insoluble in water (unless a polar group is present)
Low boiling point and low melting point
C, H, N, O, S, P, X = F, Cl, Br, I (halogens)
X represents halogens
Inorganic compounds
Soluble in inorganic (polar) solvents – H2O
Polar
Ions
Ionic bonds, polar & nonpolar covalent bonds
Low flammability
soluble in water (unless a non polar group is present)
High boiling point and high melting point
Metals & nonmetals
Types of Ions
Cation (+)
Anion (-)
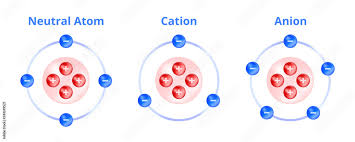
Cation
are positively charged ions, formed when an atom loses electrons
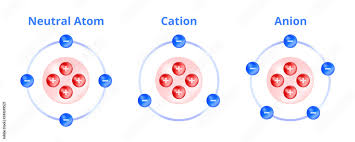
Anion
are negatively charged ions, formed when an atom gains electrons.
Types of chemical bonds
Covalent - sharing electrons
Ionic - give and take
Carbon
4 bonds
Oxygen
2 bonds
Hydrogen
1 bond
Nitrogen
3 bonds
Halogens
F, Cl, Br, I
1 bond
Valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost shell
Homologous series
Alkanes
Alkenes
Alkynes
Alkanes
General formula: CnH2n+2
# Bonds: single
Saturated
Ex: Methane, Ethane
Alkenes
General formula: CnH2n
# Bonds: double
Unsaturated
Ex: Ethene, Propene
Alkynes
General formula: CnH2n-2
Bonds: Triple
Unsaturated
Ex: Ethyne, Propyne
# of Cs: 1
Meth
# of Cs: 2
Eth
# of Cs: 3
Prop
# of Cs: 4
But
# of Cs: 5
Pent
# of Cs: 6
Hex
# of Cs: 7
Heat
# of Cs: 8
Oct
# of Cs: 9
Non
# of Cs: 10
Dec
Molecular Formula
General form with total number of each atoms:
C5H10, C4H10
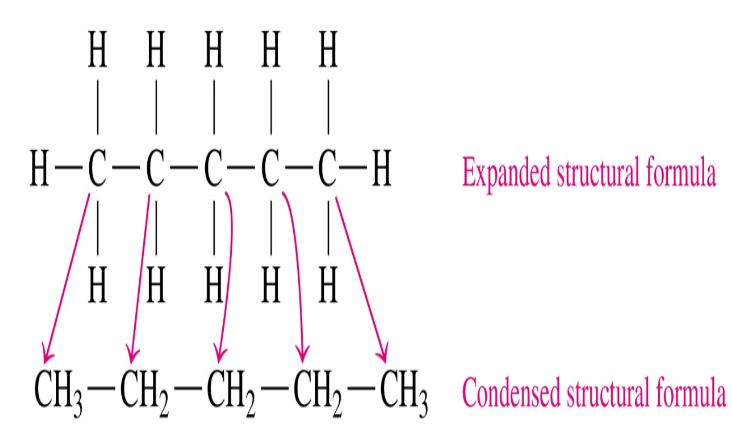
Structural Formula
Detailed form with chemical bonds between atoms
Condensed structural
Expanded structural
Line angle
Expanded
all chemical bonds are shown
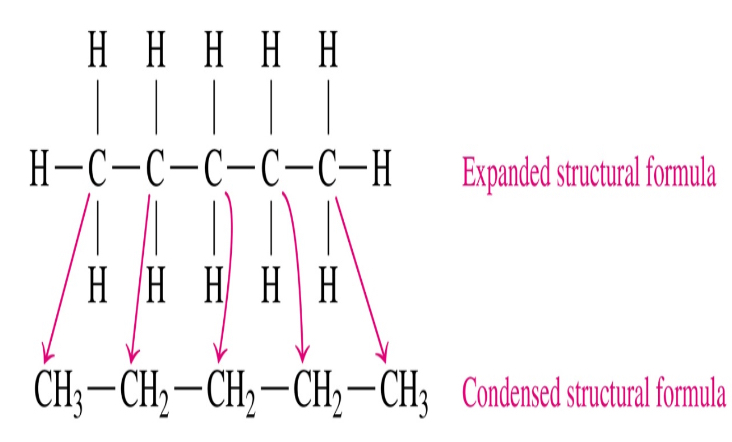
Condensed
H atoms attached to each C atom are grouped together
Line angle
C and H atoms are not written, instead represented using lines; each joint represents a carbon atom