Chemistry SAC 4 Flashcards: Organic Chemistry
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For memory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Diversity of carbon
All 4 valence electrons available for bonding
Forms chains & rings via single, double, or triple bonds
Bonds with non-metals (eg. O, N, S, P, Cl)
Forms strong, stable bonds taking lots of energy to break
Saturated hydrocarbons
A molecule which only contains single carbon-carbon bonds between atoms
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
A molecule which contains at least one double/triple bond between atoms
Bond energy
The energy (kJ) required to break 1 mole of covalent bonds in gaseous state
The higher bond energy, the higher bond strength and stability
The relative strength of C-C bonds explains the frequency of carbon chains on Earth.
Organic molecule representation
Molecular: indicates the number & type of each atom present in a molecule (C4H8O)
Structural: shows the location of atoms relative to each other, and the number and location of covalent bonds
Semi-structural: indicates the connections in compound’s structure without showing 3D arrangement of atoms
Skeletal: a shorthand version of structural formula, showing only C-C bonds and functional groups
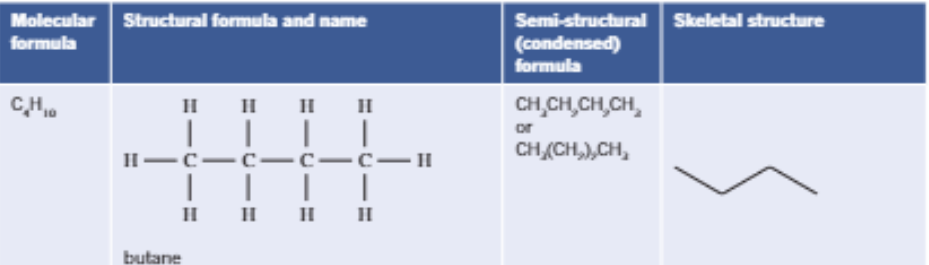
Isomers
Molecules with the same number & type of atoms but different arrangements:
Chain: different chain lengths due to branching
Positional: branch/functional group is moved
Stereoisomer: when groups around an atom are arranged differently
Homologous series
A family of organic molecules that have similar structures and properties, general formula, a pattern in physical properties.
Alkanes (and naming)
Saturated hydrocarbons (single C-C) with the general formula: CnH2n+2
Naming:
Named with a prefix of # Cs and the suffix -ane
Side branches are named using a prefix and -yl
Use prefixes di, tri for multiple branches of one type
Branch position is found by numbering each main chain C
Give branches lowest number possible and list branches in alphabet order
Eg. 5-methylpropane
Cycloalkane
Carbon atoms which form rings, and only single C-C bonds are present, with the general formula: CnH2n
Eg. Cyclohexane (C6H12)
Alkenes (and naming)
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (double C-C) with the general formula: CnH2n
Naming:
Names end in -ene
2Hs are lost for each C-C double bond
Double bond position must be given the LOWEST number —> insert position before -ene
Eg. 3,3-dimethylpent-1-ene
Degree of unsaturation
Refers to the number of double bonds/rings in a molecule
Calculated by: ([(2 * no of Cs)+2] - no of Hs) / 2
Benzene
An unsaturated 6C ring (C6H6):
Fourth electron of each C becomes delocalized and shared by all Cs (1 ½ bonds)
When bonded to an alkyl/functional group, it is known as a phenyl functional group (C6H5-)
Haloalkanes (and naming)
Alkanes with one or more H atoms replaced by a halogen atom (Cl, I, Br, F) —> this results in a polar bond
Naming:
Prefixes (fluoro, chloro, bromo-)
Location must be given (eg. 4-bromo)
Numbers must be as low as possible
For multiple halogens use dichloro, trichloro, etc.
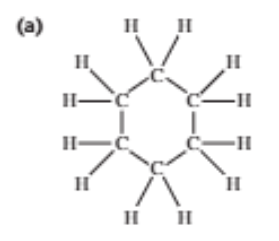
Types of alcohols
Contains the -OH group (hydroxyl), classified based on structure:
Primary: the C bonded to -OH group is bonded with one alkyl chain (R group)
Secondary: the C bonded to -OH group is bonded with two alkyl chains
Tertiary: the C bonded to -OH group is bonded with three alkyl chains
NOTE: The polar bond from OH allows for H bonding and CO bond makes it reactive
Naming alcohols
Suffix with -ol (eg. ethanol)
In some cases, the prefix hydroxy- is used
Insert a number before -ol to indicate position of -OH groups, and give the lowest number possible
For multiple alcohol groups use diol, triol, tetraol, etc.
Types of amines
Contains the -NH2 group (amino), classified based on structure:
Primary: N is bonded to one alkyl chain and two Hs
Secondary: N is bonded to two alkyl chains and one H
Tertiary: N is bonded to three alkyl chains and no Hs
Only primary amines have to be known
Naming amines
Suffix with -amine
Use numbers to determine amino group position, and lowest number possible
Carbonyl group
A C double bonded to an O:
Polar
Angle between bonds is 120 degrees
Includes amides, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters
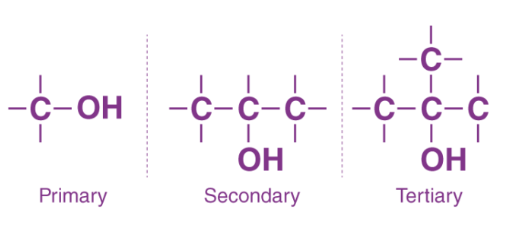
Aldehydes
Contains a carbonyl group located at one end of an alkyl chain
Written as -CHO in semi-structural formulas
The carbonyl is always given the 1st position
Suffix is -al and sometimes the prefix oxo- (eg. ethanal)
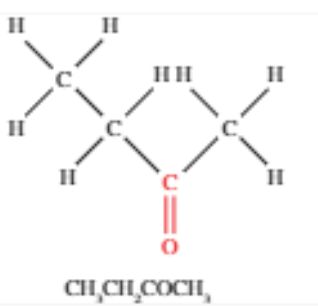
Ketones
Contains a carbonyl group bonded to two other alkyl chains (never at the end)
Written as -CO- in semi-structural formulas
Suffix is -one and sometimes the prefix oxo-
Carbonyl group position is always indicated
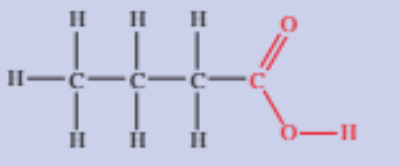
Carboxylic acids
Contains a carbonyl group (-COOH), with the C bonded to a hydroxyl group
Written as -COOH in semi-structural formulas
The C in the carboxyl group is always at the end of the chain, hence its position is always 1
Suffix is -oic acid
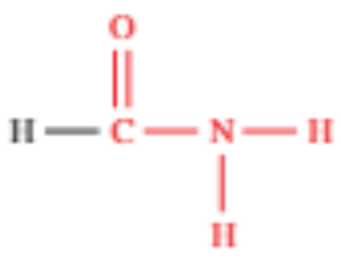
Amides
Contains a amide group (-CONH2) bonded to the C of the carbonyl group
Usually derived from carboxylic acids
Primary amides have N bonded to one alkyl chain, while in secondary and tertiary it is bonded to two and three
Suffix is -amide
Esters
Formed from condensation reactions (H2O) between an alcohol and carboxylic acid.
Eg. Ethanoic acid + Methanol —> Methyl ethanoate + water
Written as -COO or -OCO- in semi-structural formulas
Two part suffixes: -yl suffix derived from the alcohol reactant, -oate suffix derived from the carboxylic acid.
IUPAC Nomenclature (priority)
Use suffixes for higher priority and start chain there, use prefixes for lower priority
Carboxylic acid: -oic acid
Aldehyde: -al, oxo-
Ketone: -one, oxo-
Hydroxyl: -ol, hydroxy-
Amino: -amine, amino-
Alkene: -ene, -en-
Halogen: halo- (eg. fluoro-)
Physical properties of homologous series
Factors such as molecule size, molecule shape, and type of bonding can affect compounds’ melting points, boiling points, viscosities.
Properties of alkanes
Non-polar molecules, hence only weak dispersion forces can form
As chain length increases, melting & boiling points increase due to more dispersion forces as there are more contact points
The strength of temporary dipoles increase as chain length increases
As linear molecules pack more closely with more SA in contact compared to branched molecules, dispersion forces are stronger in linear molecules.
Viscosity
Defined as the resistance to pouring, and depends on forces of attraction between molecules
Properties of alkenes
Non-polar molecules, hence can only form dispersion forces
Boiling and melting points of alkenes are similar to alkanes of a similar length
Properties of haloalkanes
Polar molecules, hence dipole-dipole and dispersion forces can form
As dipole-dipole forces are stronger than dispersion forces, BP and MP is usually higher
A chain length increase also leads to increased strength of bonds
Properties of alcohols
Polar molecules, and can form H bonds due to the O atom present
Hence MP, BP, and viscosity is higher than alkanes of the same length due to the higher strength of H bonds.
Primary alcohols have higher BPs and MPs than secondary/tertiary alcohols:
This is due to the hydroxyl position which does not restrict the formation of H bonds as much
Properties of amines and amides
H bonds form between amines and amides, hence this leads to higher MPs, BPs, and viscosity than hydrocarbons of a similar size
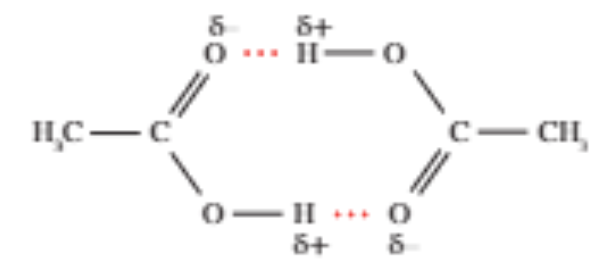
Properties of carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acid can form hydrogen bonded dimers, hence leading to higher MP and BP than alcohols
Dimers have double the molar mass of the carboxylic acid, hence resulting in stronger dispersion forces between dimers.
This process is called dimerisation
Properties of aldehydes, ketones, and esters
These compounds contain a C-O double bond, resulting in polar molecules
Hence they can form dipole-dipole bonds but not H bonds due to no O-H bond present.
Their BPs and MPs are higher than alkanes but lower than alcohols.
Combustion reactions
Alkanes, alkenes and alcohols readily undergo combustion to produce CO2 and H2O
Eq: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) —> CO2 (g) + 2H2O(l)
Substitution of alkanes
Substitution: when another replaces an atom/functional group
Alkanes undergo substitution with halogens under UV light to produce haloalkanes and hydrogen halides
Eq: CH4(g) + Cl2(g) —UV light—> CH3Cl(aq) + HCl(aq)
Any H atom can be substituted and replaced one at a time, allowing it to react multiple times.
Substitution of haloalkanes
Due to polarity, the C atom carries a d+ charge and react with negatively-charged particles such as OH- or d- N in NH3.
Nucleophile
A negative particle that can share a pair of electrons with a d+ carbon (eg. OH-, NH3, H2O)
Water as a nucleophile
As water is a weak nucleophile, it requires a catalyst/heat to react with haloalkanes
Different haloalkane substitution reactions
OH: Haloalkanes + OH —> alcohol + salt
Eq: NaOH(aq) + CH3Cl (aq) —> CH3OH + NaCl(aq)
NH3: Haloalkanes + NH3 —> amine + hydrogen halide
Eq: C2H5Cl + NH3 —> CH3CH2NH2 + HCl
Water: Haloalkanes + H2O —> alcohol + hydrogen halide
Eq: H2O(l) + CH3Cl(aq) —> CH3OH(aq) + HCl(aq)
Addition reactions of alkenes
Addition reactions:
Two molecules combine to form one product
The C=C double bond becomes C-C single bond
An unsaturated compound becomes saturated
The atoms are added across the double bond
Alkenes + hydrogen gas
This reaction is called hydrogenation (high activation energy)
Under the presence of a solid catalyst (Ni, Pt), alkenes react with H2 to form alkanes
Eq: CH2CH2 + H2 —Ni—> CH3CH3
Alkenes + halogens
This reaction does not require a catalyst
Halogens such as Br2, Cl2 can be added across a double bond
Eq: CH2CH2 + Br2 —> CH2BrCH2Br
Bromine test (Br2)
This test is used to test for double bonds
When Br2 is added across a double bond, the solution goes from reddish-brown to colourless (final haloalkane)
Alkenes + hydrogen halides
Hydrogen halides are added across a double bond to form a haloalkane
If symmetrical alkene (eg. but-2-ene): only one product is formed
If asymmetrical alkene (eg. but-1-ene): two different isomers are possible
Alkenes + water
Water added across a double bond produces an alcohol
Under solid phosphoric acid and high temps (300C), this reaction can proceed
Eq: CH2CH2 + H2O —300C & H3PO4—> CH3CH2OH
Multiple isomers can form if the alkene is asymmetrical
Oxidation of alcohols
Alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids using strong oxidising agents.
Oxidation is the process of breaking C-H bonds and replacing them with C-O bonds, hence more C-O bonds = more oxidised
Oxidation of primary alcohols
Primary alcohols: the carbon attached to OH group is connected to one carbon
When oxidised, alcohols convert into aldehydes and then carboxylic acids, but sometimes the intermediary stage is skipped
Ethanol —KMNO4/H+—> Ethanal —KMNO4/H+ & heat—> Ethanoic acid
Oxidation of secondary alcohols
Secondary alcohols: the carbon attached to OH group is connected to two carbons
When oxidised, alcohols convert into ketones
Propan-2-ol —K2Cr2O7/H+ & heat—> Propanone
Oxidation of tertiary alcohols
Tertiary alcohols: the carbon attached to OH group is connected to three carbons
These cannot undergo oxidation as there are no C-H bonds to give electron pairs for the conversion of -OH to =O group.
Oxidants of alcohols
Dichromate: Cr2O72- is orange, while Cr3+ is green
Permanganate: MnO4- is purple, while Mn2+ is colourless
Colour changes can indicate if an oxidation reaction has occurred
Ionisation of carboxylic acids in water
Carboxylic acid + water —> -oate ions + hydronium ions
Eq: CH3COOH + H2O —> CH3COO- + H3O+
Formation of esters (esterification)
Esters are formed from condensation reactions between an alcohol + carboxylic acid, known as an esterification reaction
The H in the hydroxyl group reacts with OH from the cabroxyl group, forming H2O
This reaction can only occur under concentrated H2SO4 and heat.
Eg: ethanoic acid + ethanol —> ethyl ethanoate + water
Hydrolysis of esters
Hydrolysis is the reverse reaction of condensation, hence H2O can break ester bonds and produce a carboxylic acid + alcohol.
Hydrolysis is catalysed using a dilute acid or an alkali
Hydrolysis of esters (dilute acid)
Products are an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
Eq: ethyl propanoate + H2O —> propanoic acid + ethanol
Hydrolysis of esters (dilute alkali)
Products are a salt of the carboxylic acid and an alcohol
The salt can be converted to a carboxylic acid using a dilute acid
Eq: ethyl propanoate + H2O —NaOH—> sodium propanoate + ethanol —> propanoic acid after acidification
Triglyceride
A fat molecule consisting of three long hydrocarbon chains attached to a three-carbon backbone through ester bonds.
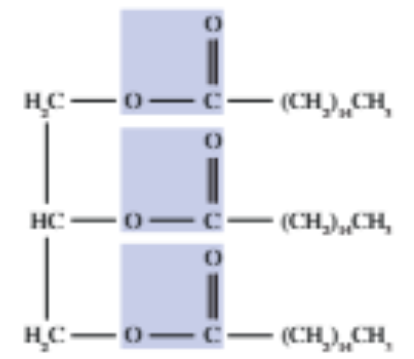
Transesterification
This reaction occurs when triglycerides react with alcohols —> the alcohol R group swaps positions with the R group attached to the -O- of the ester.
Eq: triglyceride + methanol —KOH—> three fatty acid esters + glycerol
Biodiesel formation
Biodiesel is formed by triglycerides reacting with an alcohol in the presence of KOH catalyst, as the fatty acid esters are biodiesel.
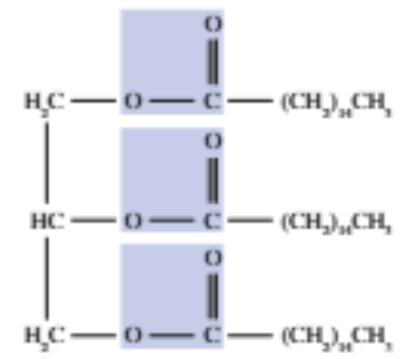
Reaction pathways
A series of steps to convert starting materials (alkanes, alkenes) into desired products
Alkenes to alcohols
Eg: ethanol from ethene
ethene + HCl —> chloroethene + OH —> ethanol
OR ethene + H2O —H3PO4—> ethanol
Alkanes to carboxylic acids
Eg: propane to propanoic acid
propane + Cl2 —UV—> 1-chloropropane + OH —> propan-1-ol —Cr2O72—> propanoic acid
Alkanes + alkenes to form esters
Ethene + H2O —> ethanol
Propane + Cl2 —UV—> 1-chloropropane + OH —> propan-1-ol —Cr2O72—> propanoic acid
Ethanol + propanoic acid —H2SO4—> ethyl propanoate
Summary of reaction pathways
Alkanes: addition of halogen to form haloalkanes
Alkenes:
Addition of H2 & catalyst to form alkanes
Addition of catalyst to form polyethane
Addition of hydrogen halides & catalyst to form haloalkanes
Addition of water to form alcohols
Haloalkanes:
Addition of OH- ions to form alcohols
Addition of NH3 to form aminoalkanes
Alcohols:
Oxidation using Cr2O72- to form carboxylic acids
Addition with carboxylic acids to form esters
Carboxylic acids:
Addition with alcohol to form esters
Yield
The efficiency of processes that involve chemical reactions found by calculations.
Actual yield
The amount of desired product formed in the reaction
Theoretical yield
The mass of the product that can be formed if the limiting reactant reacts according to stoichiometric ratios —> assumes 100% efficiency
Percentage yield
Measures a chemical reaction’s efficiency by comparing actual yield to theoretical yield as a proportion.
% yield = actual / theoretical * 100
Use limiting reagent to find theoretical yield
Overall percentage yield
This is the percentage yield of EACH step multiplied together
Overall % yield = actual1 / theoretical1 x actual2 / theoretical2 × 100%
Why actual yield < theoretical yield?
Slow reaction rate, hence reaction may not proceed in the time available
Reaction reaches equilibrium rather than completion
Loss of reactants/products during transfer between containers
Unwanted side reactions occurring, hence forming unwanted products.
Atom economy
The proportion of atoms in reactants that become useful products —> measures waste produced
Formulas:
Molar mass of useful product / molar mass of all reactants * 100
Molar mass of useful product / molar mass of all products * 100
These two formulas are interchangable as total mass of products = total mass of reactants
Green Chemistry principles
Use renewable feedstocks (raw materials)
Catalysts
Designing safer chemicals
Renewable feedstocks
These are beneficial as they are not as finite as fossil fuels, and some are also biodegradable, meaning they do not persist in the environment as wastes
Catalysts
Allows reactions to proceed at low temperatures, reducing costs and saving energy
Increase reaction rates hence more yield in a shorter time
Not consumed directly so they can be continuously reused
Safe chemicals
These are chemicals which have low impact on humans and the environment
Eg. toxic chemicals such as perfluoroalkyls used in firefighting foam have been found to harm both environment and humans, hence replacements must be found.
Condensation reaction
These endothermic reactions occur when two functional groups react and water is formed as a by product.
Types of polymers
Homopolymer: contains one type of monomer
Copolymer/Heteropolymer: contains two or more different momoners
Proteins
These are polymers of amino acids
The general formula of amino acids is H2NCHRCOOH (variable R group —> defines properties of protein)
Amino acids in proteins are called 2-amino acids as the main functional groups are attached to the number 2 carbon
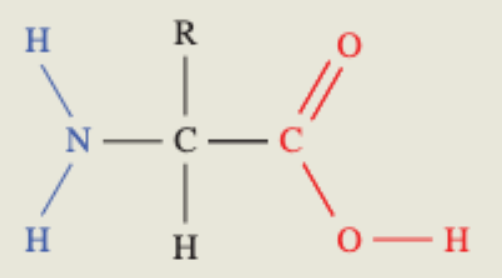
pH vs protein charge
Low pH: the amine group becomes NH3+, meaning it has a positive charge
Neutral pH: known as a zwitterion, both amine and carboxyl group are charged positively and negatively respectively (hence neutral)
High pH: the carboxyl group becomes COO-, meaning it has a negative charge.
R groups’ properties
Non-polar
Polar
H+ acceptors (basic)
H+ donors (acidic)
Peptide bond
These bonds form when two amino acids combine through a condensation reaction.
Types of peptides
Dipeptide: two amino acids bonded together
Tripeptide: three amino acids bonded together
Polypeptide: many amino acids bonded together
Protein: >50 amino acids bonded together + polypeptide folding
Polypeptide ends
The free amino group is called the N-terminus (on the left)
The free carboxyl group is called the C-terminus (on the right)
Carbohydrates
These biomolecules are made from the elements C, H and O, with the general formula CxHyOz.
Types of saccharides
Monosaccharide: a subunit of a carbohydrate, generally white, sweet-tasting, and water-soluble
Disaccharide: two monosaccharides bonded together through a condensation reaction
Polysaccharide: long polymers of monosaccharides, often water insoluble and tasteless
The link between monosaccharides is called an ether group, also known as a glycosidic link
Monosaccharides
C6H12O6 isomers:
Glucose (has 2 stereoisomers)
Alpha-glucose: found in starch and glycogen
Beta-glucose: found in cellulose
Galactose (not found free in nature)
Fructose
Disaccharides
Occurs when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction, forming an ether group/glycosidic link and water
Maltose (used as a sweetener)
Sucrose (table sugar)
Polysaccharides
Starch: produced in plants through the actions of enzymes —> used for energy storage
Amylose is linear while amylopectin is branched
Amylopectin may be more soluble than amylose as -OH groups are more exposed due to branching
Glycogen: used in animals for energy storage —> a branched polymer of glucose, more so than amylopectin.
Lipids (fats & oils)
Non-polar food molecules used for energy storage —> triglycerides are major parts of lipids.
Triglycerides
Produced through condensation reactions between three fatty acids and glycerol, producing water and a triglyceride containing three ester links (-COO-)
Eq: 3 Fatty acids + glycerol —> Triglyceride + 3H2O
Types of fatty acids
Saturated: fatty acids only contain single C-C bonds
Monounsaturated: fatty acids contain one C=C bond
Polyunsaturated: fatty acids contain multiple C=C bonds.
Cellulose
A structural material in plants (cell wall) which provides structure and rigidity
Fats vs oils
Fats: contains more saturated fatty acids (meaning more contact between side chains, increased dispersion forces, hence solid at room temp)
Oils: contains more unsaturated fatty acids (meaning more double bonds & kinks, hence leading to liquid at room temp)
Hydrolysis
These exothermic reactions occur when large biomolecules are SPLIT through reactions with water molecules (essentially the opposite of condensation)
Hydrolysis of proteins
A water molecule is added to each peptide bond (amide link)
C-N bond breaks
The -OH of water adds to the free C=O forming COOH group
The -H of water adds to the free NH forming NH2 group
The breaking of C-N bonds is sped up by enzymes, as without enzymes it would require harsh conditions such as 100C and 6M HCl
Hydrolysis of carbohydrates
A water molecule is added to each glycosidic link
C-O bond breaks
The -H of water is added to the free O
The -OH of water adds to the free neighboring glucose
Amylase is used to catalyse starch hydrolysis, maltase is used to catalyse maltose hydrolysis, and cellulase is used to catalyse cellulose hydrolysis
Hydrolysis of lipids
Lipids are insoluble in water, so molecules remain intact until they reach bile in the small intestine.
Bile breaks lipids into globules and then small droplets which increases surface area, hence enabling hydrolysis.
Lipase catalyses lipid hydrolysis by adding three H2O molecules to the ester links in the triglyceride
-OH of water is added to the CO of each fatty acid
-H of water is added to each O of glycerol
Digestion
Involves large numbers of enzymes through the digestive system, which breaks down different components of food.