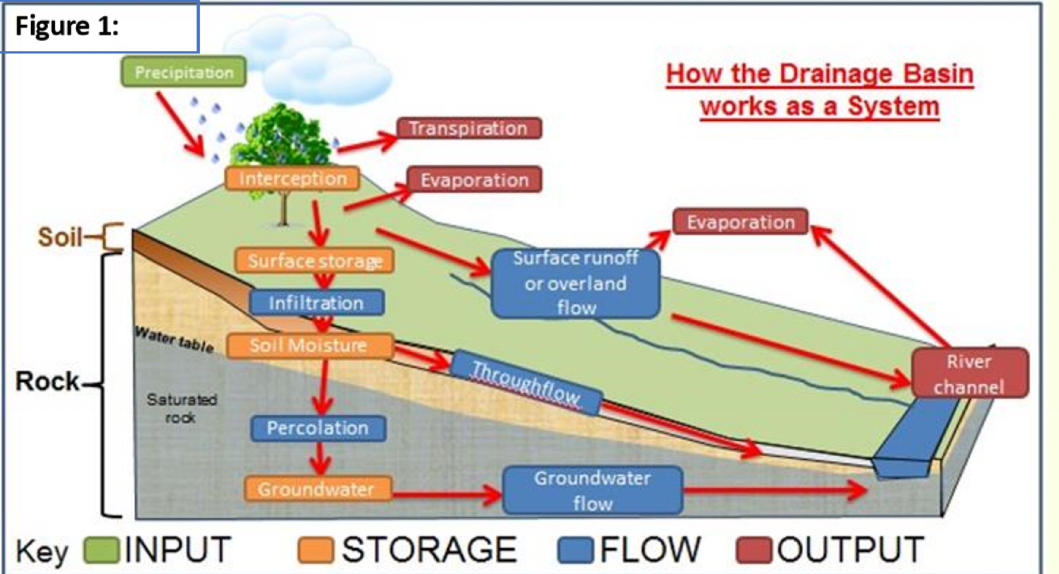
the drainage basin system
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is a drainage basin
a drainage basin is an area within which water supplied by percipitation is transferred to the ocean a lake or larger stream it includes all of the area that is drained by a river and its tributaries
throughflow
the downslope movement of water within the soil towards the river channel parallel to the surface
stem flow
water which has been intercepted by vegetation and reaches the surface by flowing down the tree trunks or stems
percolation
the downward movement of water after infiltration through the pores in the subsoil into the bedrock and joints and cracks in rock
throughflow
where precipitation is not intercepted by the vegetation and is able to fall directly onto the ground.
surface runoff
the movement of water across the surface of the earth due to over saturation of soils or impermeable surfaces, or when rates of rainfall exceed speed of infiltration
infiltration
the vertical movement of water entering the soil from the surface
interception
the trapping of water during a percipitation/rainfall even on leaves of vegetation
evaporation
the loss of water from the earths surface via the change of water to gas through the application of heat
groundwater flow
the slowest down spline movement of water through the deep bed rock
base flow
the groundwater flow that slowly enters the river from seeping in the ground(not a result of the throughflow or surface runoff
evapotranspiration
the loss of water from land water and vegetation via the combined process of evaporation and transpiration from the stomata/leaves of vegetation
river discharge
the volume of water passing a fixed point at a given time
cross sectional area x velocity=discharge
measured in cumecs
percipitation
process by which water is transferred from the atmosphere to the earths surface in the form of rain hail sleet or snow
input to the drainage basin system
drainage basin system
factors effecting evaporation
temp
humidity
winds speed(displaces the moustire layer on a puddle allowing evaporation rates to increase)
vegetation cover
vegetation colour-light=low as light reflected
dark=quick as light absorbed
field capacity
refers to the amount of water held in the soul after excess water drains away that is saturation or near saturation
infiltration capacity
is the maximum rate at which rain can be absorbed by soil in a given condition
antecedent soil moustire
is the pre existing levels of soil moisture
soil moisture deficit
the degree to which soil moisture falls below field capacity.
soil moisture recharge
occurs when precipitation exceeds potential evapotranspiration there is some refilling of water in the dried up pores of the should
soil moustire surplus
is the period when soil is saturated and water cannot enter and so flows over the surface
soil moustire utilisation
is the process by which water is drawn to the surface through capillary action
porosity
is the capacity of a rock to hold water
permeability
the ability to transmit water through a rock via joints and fissures
springs(underground water)
the point at which water emerges from the ground either where throughflow is impeded and has to rise to the surface or where underground water is held in an aquifer and water level is raised to the surface through recharge.also result of impermeable zones
water table(underground water)
upper surface of the saturated zone where soil/rock pres are filled with water
rises in wet reasons(rain or snowmelt) falls in dry periods
recharge(underground water)
water movement from the surface(infiltration) deep percolation of water into saturated zone
ground water
the subsurface water that is stored under the surface in the rocks it accounts for 96% of all freshwater on earth