NEUROLOGICAL SYSTEM
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Autonomic response
functional division of the efferent branch of the PNS that is responsible for control of cardiac and smooth muscle, as well as glandular tissue
Somatic response
functional division of the nervous system that is concerned with conscious perception, voluntary movement, and skeletal muscle reflexes
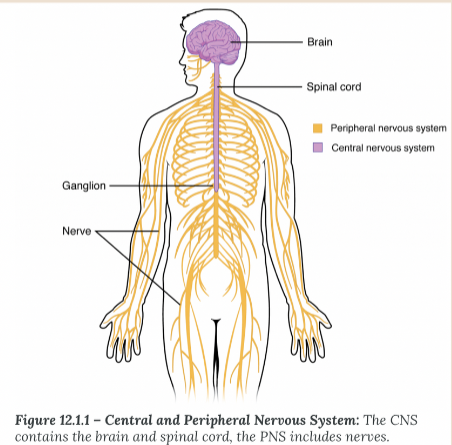
CNS
Central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and transmitting information throughout the body.
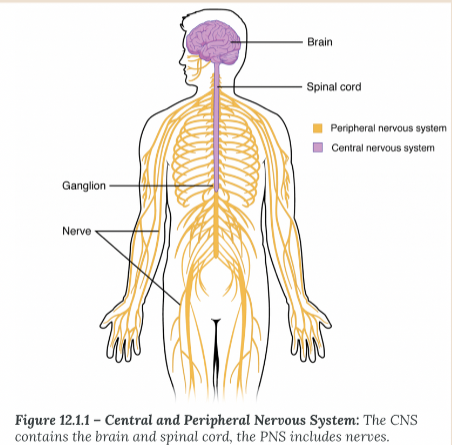
PNS
Peripheral nervous system; nerves
Stumili
Sensation- multiple things happening
From the PNS bringing the information to the brain and spinal cord to create a response
Afferent V. efferent brances of cns
Afferent - sensation
branch of the PNS. When information arises from sensory receptors in the skin, skeletal muscles, or joints, it is transmitted to the CNS using somatic sensory neurons; when information arises from sensory receptors in the blood vessels or internal organs, it is transmitted to the CNS using visceral sensory neurons.
efferent- response side
branch of the PNS carries signals away from the CNS to the effector organs. When the effector organ is a skeletal muscle, the neuron carrying the information is called a somatic motor neuron;
Effector organ
An effector organ is a muscle or gland that responds to signals from the nervous system, executing the appropriate action or response in reaction to stimuli.
deliver a response
Integration
nervous system function that processes sensory perceptions and produce a response
Somatic sensory
When a muscle is delivering information
For example- using your feet to touch the treadmil
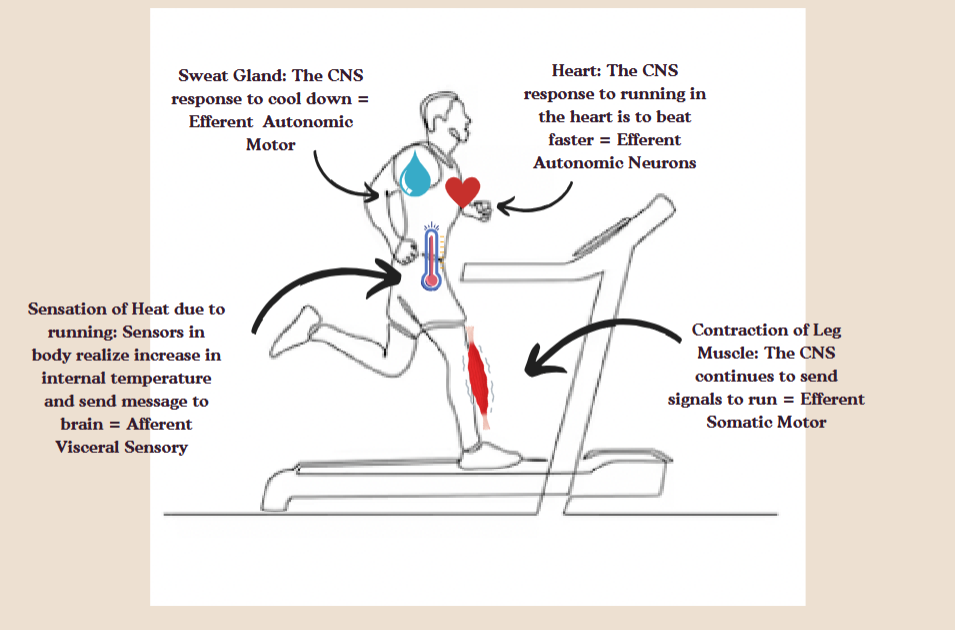
Visceral sensory
When blood or an organ is delivering information
For example- sensation of heat due to running
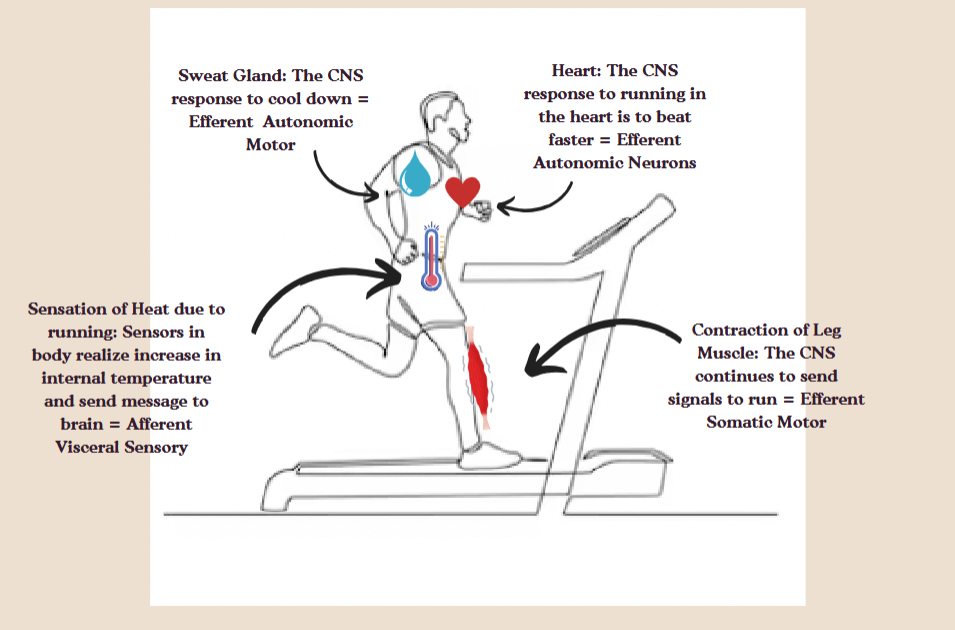
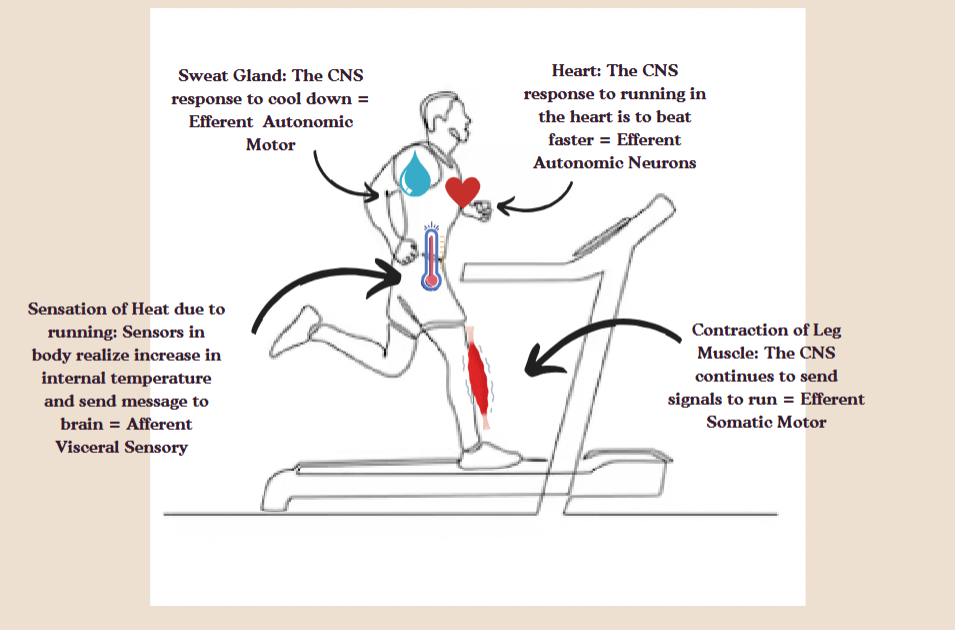
Somoatic monitor
a system that detects and processes sensory information from the skeleton and muscles.
For example- contraction of leg muscle
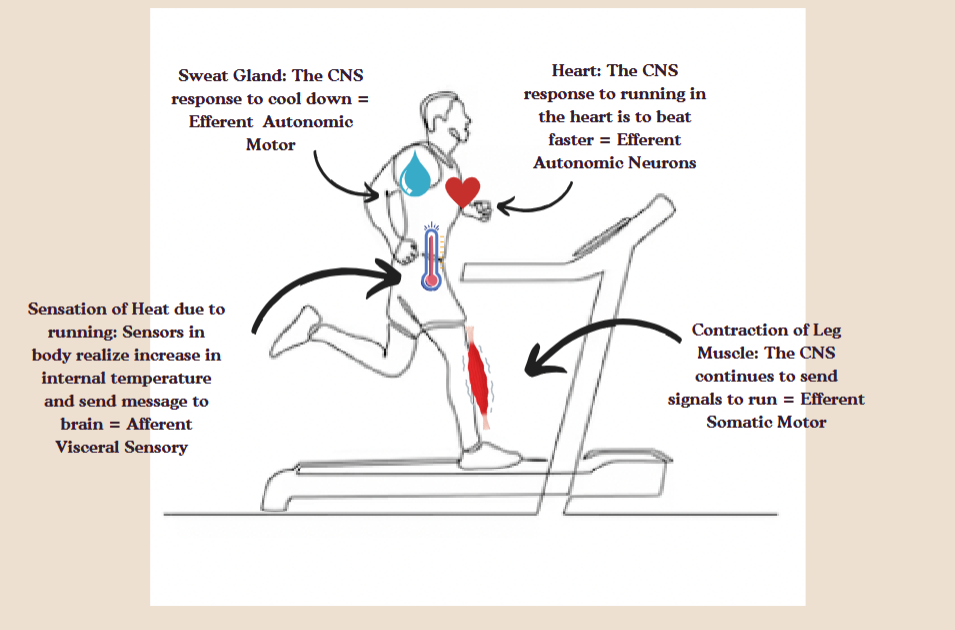
Automatic motor
Neurons that control involuntary actions of internal organs.
For example- sweat glands activation, heart beating
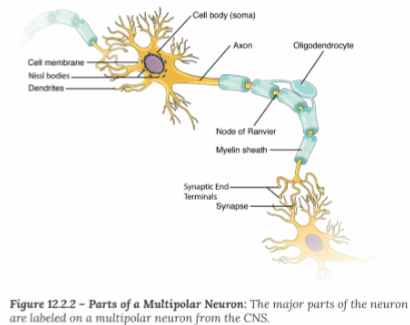
Axon Hillock:
Where the soma and axon meet
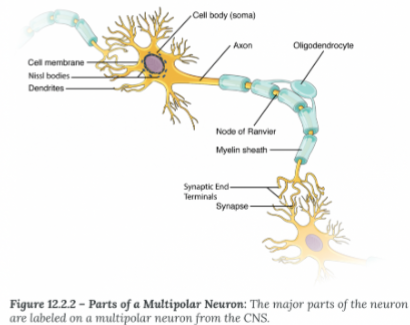
Initial Segment
Where an action potential is generated (usually the axon hillock)
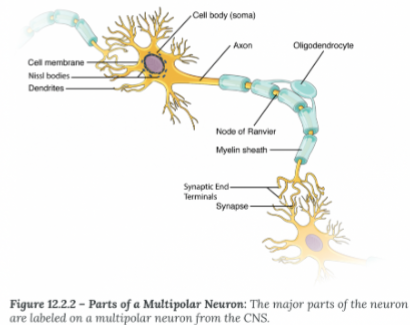
Myelin Sheath:
Electrical insulation, speed up the rate of conduction
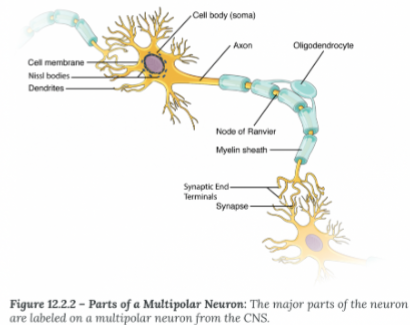
Node of Ranvier:
Exposed segments of the axon
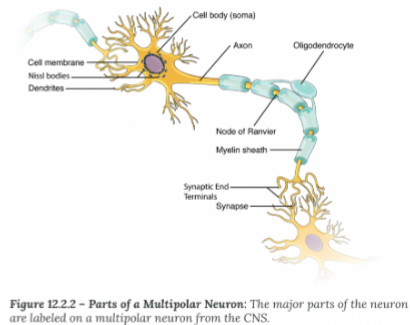
Terminal End
Site of information transfer between neurons
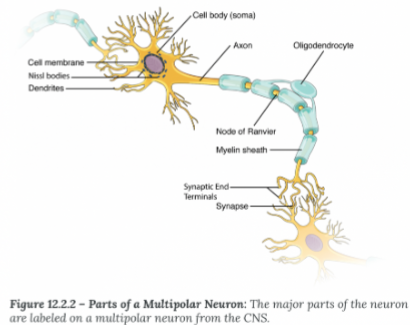
Synapse
The space the electiacl signal must "jump" tp reac the dendrite of the next neuron
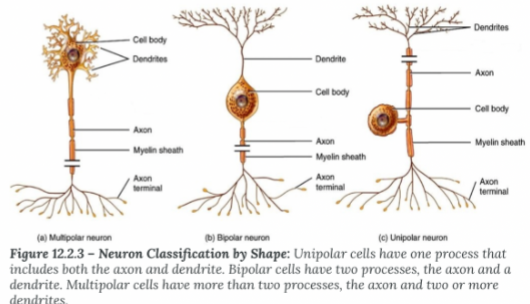
Multipolar Neurons
Muscle tissue and most of the CNS
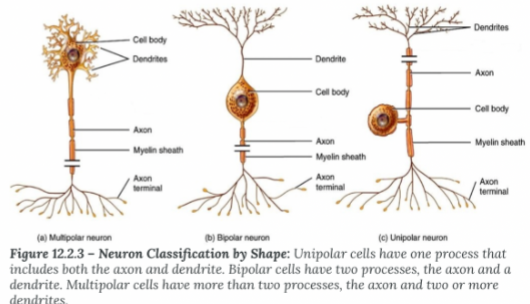
Bipolar Neurons
Specialized Sensory (not very common)
• Eyes, nasal cavity, inner ear
• Visual, smell, balance
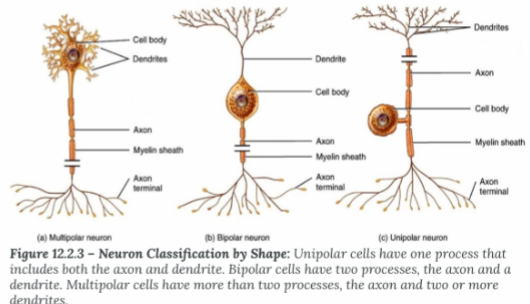
Unipolar Neurons
• Sensory only
• Touch, pain, temperature
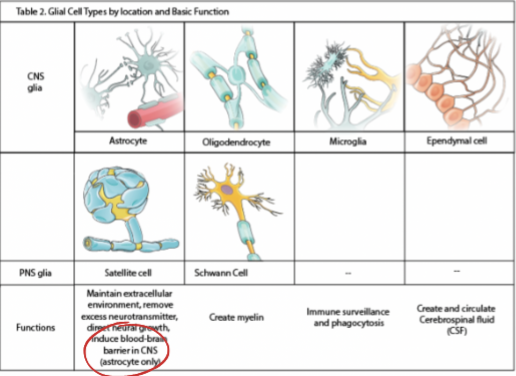
Glial cells:
supporting cells that maintain he extracellular environment, improve signal conduction & protects from pathogens
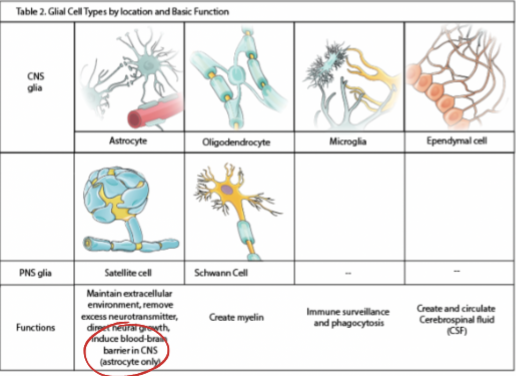
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB):
protective barrier preventing regular circulating blood from permeating the CNS (the CNS which circulates within cerebrospinal fluid)