RCC Midterm
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Host Countries - FDI Promotion
tax incentives, low-interest loans, infrastructure improvements
Host Countries - FDI Restriction
ownership restrictions, performance demands
Home Countries - FDI Promotion
insurance, loans, tax breaks, political pressure
Home Countries - FDI Restriction
differential tax rates, sanctions
current account
Records transactions involving the export and import of goods and services, income receipts on assets abroad, and income payments on foreign assets inside the country
capital account
A national account that records transactions involving the purchase and sale of assets
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
Purchase of physical assets or a significant amount of the ownership (stock) of a company in another country to gain a measure of management control
portfolio investment
An investment that does not involve obtaining a degree of control in a company
Greenfield Investment
purchase of land in another country and construction of new facilities or an entire subsidiary from the ground up
Eclectic Theory
A theory stating that firms undertake foreign direct investment when the features of a particular location combine with ownership and internalization advantages to make a location appealing for investment
Market Power
theory stating that a firm tries to establish a dominant market presence in an industry by undertaking foreign direct investment
Vertical Integration
extension of company activities into stages of production that provide a firm's inputs (backward integration) or that absorb its output (forward integration)
Following Rivals
FDI decisions frequently resemble a "follow the leader" scenario in industries that have a limited number of large firms. In other words, many of these firms believe that choosing not to make a move parallel to that of the "first mover" might result in being shut out of a potentially lucrative market.
Free trade
pattern of imports and exports that occurs in the absence of trade barriers
Why do governments intervene in trade?
Political Motives, Economic Motives, Cultural Motives
Political Motives
protect jobs, preserve national security, respond to unfair trade, and gain influence
Economic Motives
Protect infant industries, pursue strategic trade policy
Cultural Motives
Achieve Cultural Objectives, Protection of National Identity
Instruments of trade promotions
subsidies, export financing, foreign trade zones, and special government agencies
subsidy
Financial assistance to domestic producers in the form of cash payments, low-interest loans, tax breaks, product price supports, or other forms
managed trade
Government efforts to achieve trade objectives pertaining to market shares or quantities of specific products
Export Assistance
low-interest-rate loans, loan guarantee
Export assistance in the US
Export-Import Bank of the United States, International Development Finance Corporation
Foreign Trade Zones (FTZ)
designated geographic region through which merchandise is allowed to pass with lower customs duties (taxes) and/or fewer customs procedures
Instruments of Trade Restriction
tariffs, quotas, embargoes, local content requirements, administrative delays, currency controls
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
A treaty designed to promote free trade by reducing both tariffs and non-tariff barriers to international trade
uruguay round of negotiations (1986-1994)
agreement on services, agreement on intellectual property, agreement on agricultural subsidies, and creation of the WTO
World Trade Organization (WTO)
The International organization that regulates trade among nations
individulaism
A belief that individual rights and responsibilities should be placed above the group's welfare
Collectivism
Stresses the relative importance of a group's welfare over that of the individual
political system
Structures, processes, and activities by which a nation governs itself
Theocracy
A government controlled by religious leaders
Theocratic Totalitarianism
A political system under the control of totalitarian religious leaders (iran)
secular totalitarianism
A political system in which leaders maintain control through military and bureaucratic power
Examples of secular totalitarianism
Communism, Socialism, Tribal Totalitarianism, Right-wing totalitarianism
Democracy
A political system in which government leaders are elected directly by the wide participation of the people or by their representatives
representative democracy
democracy in which citizens elect individuals from their groups to represent their political views
Representative democracy strives for:
freedom of expression, periodic elections, full civil and property rights, minority rights, nonpolitical bureaucracies
economic system
structure and processes that a country uses to allocate its resources and conduct its commercial activities
Range of Economic Systems
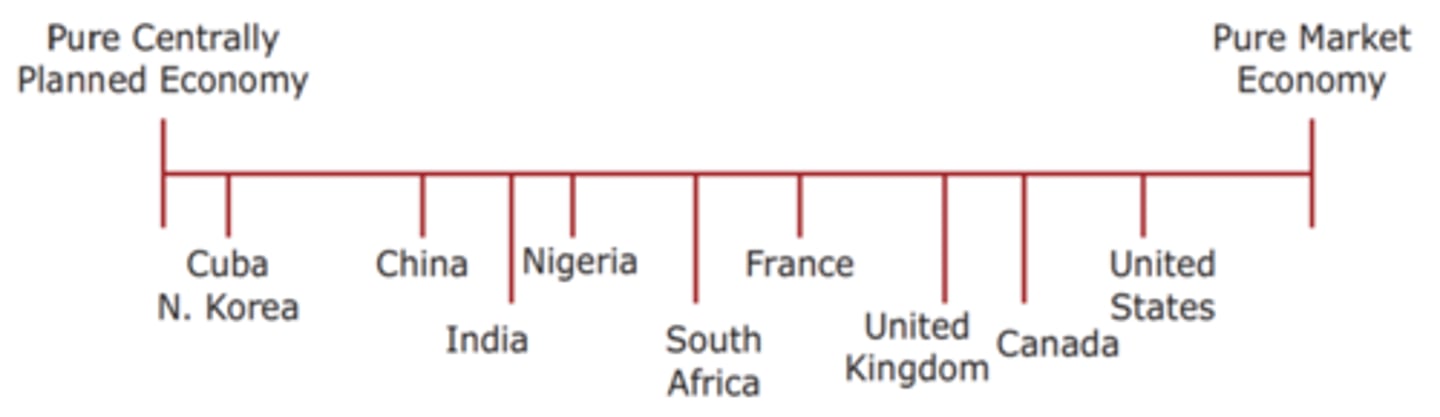
state capitalism
An economic system in which the state plays the role of leading economic actor and uses markets primarily for political gain (China)
mixed economy
An economic system in which land, factories, and other economic resources are split relatively equally between private and government ownership
Privatization
To change from government or public ownership or control to private ownership or control.
Market Economy (Capitalism)
An economic system in which most of a nation's land, factories, and other economic resources are privately owned by either individuals or businesses
Supply
the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing to provide at a specific selling price
demand
the quantity of a good or service that buyers are willing to purchase at a specific selling price
Laissez-faire
a type of economic system in which transactions between private individuals are free from any form of economic interventionism.
antitrust (antimonopoly) laws
laws designed to prevent companies from fixing prices, sharing markets, and gaining unfair monopoly advantages
property rights
legal rights to resources and the income they generate
legal system
The country's set of laws and regulations, how its laws are enacted and enforced, and how its courts hold parties accountable. influenced by political moods and upsurges of nationalism. (india)
Types of Legal Systems
common law, civil law, theocratic law
Elements of Common law
tradition, precedent, usage
Civil Law
A legal system based on a written code of laws
Theocratic law
legal system based on religious teachings
Cloud Computing
delivery of computing services over the internet, or the cloud
industrial property
Intellectual property consisting of patents and trademarks
patent
A property right granted to the inventor of a product or process that excludes others from making, using, or selling the invention
Trademark
property right in the form of words or symbols that distinguish a product and its manufacturer
Copyright
•Property right giving creators of an original work the freedom to publish or dispose of it as they choose
product liability
Responsibility of manufacturers, sellers, individuals, and others for damage, injury, or death caused by defective products
Value-added tax (VAT)
A tax levied on each party that adds value to a product throughout its production and distribution
International Business
commercial transaction that crosses the borders of two or more nations
Imports
goods and services purchased from other countries
Exports
Goods and Services sold to other countries
multinational corporation (MNC)
business that has direct investments abroad in multiple countries
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Purchase of physical assets or a significant amount of the ownership (stock) of a company in another country to gain a measure of management control
Born Global Firm
A company that adopts a global perspective and engages in international business from or near its inception and quickly gains a competitive advantage
Features of born global firms
innovation and knowledge-based organizational capabilities (tiktok, spotify, uber, airbnb)
Globalization
The trend toward greater economic, cultural, political, and technological interdependence among national institutions and economies.
–Characterized by denationalization
–Different from internationalization
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
the value of all goods and services produced within a country in a single year
Gross National Product (GNP)
The total value of goods and services, including income received from abroad, produced by the residents of a country within a year.
GDP or GNP per capita
Nation's GDP or GNP divided by its population
Globalization of Markets
Convergence in buyer preferences in markets around the world
benefits of globalization of markets
reduces marketing costs, creates new market opportunities, levels uneven income streams, local buyers' needs, global sustainability
Globalization of Production
Dispersal of production activities worldwide to minimize costs or maximize quality
Benefits of globalization of production
Access to lower-cost workers, technical expertise, and production inputs.
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
a treaty designed to promote free trade by reducing tariffs and nontariff barriers to international trade
Tariffs
taxes on traded goods
nontariff barriers
limits on the quantity of an imported product
World Trade Organization (WTO)
international organization that enforces the rules of international trade
Regional Trade Agreements
- United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA)
- European Union (EU)
- Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
World Bank
An agency created to provide financing for national economic development efforts
International Monetary Fund
An agency created to regulate fixed exchange rates and to enforce the rules of the international monetary system.
e-commerce
the use of computer networks to purchase, sell, or exchange products; to service customers; and to collaborate with partners
Internet of Things (IoT)
All devices and equipment that are readable, recognizable, locatable, addressable, and/or controllable via the internet.
Digitization
The process of changing information from analog to digital form for use by computers and other information technologies.
Digitalization
The use of digital data and technology to develop new business operations, strategies, or business models.
Digital Transformation
Fundamental change in which digital technologies penetrate all areas of operations, strategy, and culture to produce customer-focused competitive advantage
Employability Skills
application of knowledge, reflective (critical) thinking, communication skills, ethical understanding, and social responsibility
International Trade
purchase, sale, or exchange of goods and services across national borders
Primary benefits of international trade
A greater choice of goods and services, job creation, greater consumption possibilities, and higher standards of living
blockchain
A distributed digital database that stores information and creates a secure record of transactions
trade surplus
condition that results when the value of a nation's exports is greater than the value of its imports
trade deficit
condition that results when the value of a country's imports is greater than the value of its exports
zero-sum game
belief that a nation could increase its share of wealth only at the expense of others (restricts international trade)
absolute advantage
The ability of a nation to produce a good more efficiently than any other nation
Positve- Sum Game
The belief that both countries can benefit from an exchange, such as international trade
comparative advantage
Inability of a nation to produce a good more efficiently than other nations but an ability to produce that good more efficiently than it does any other good
Factor Proportions Theory
trade theory stating that countries produce and export goods that require resources (factors) that are abundant and import goods that require resources in short supply
Leontief Paradox
US exports were less capital intensive than US imports