Practical (from checklist)
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
List the 6 nuclei of the Papez circuit
hippocampus, mammillary body, anterior nucleus of thalamus, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus
List the 5 connections of the Papez circuit
perforant pathway (EC → hippocampus)
fornix (hippocampus → mammillary bodies)
mammillothalamic tract (mammillary bodies → ant nuc of thalamus)
internal capsule (ant nuc of thalamus → cingulate gyrus)
cingulum (cingulate gyrus → parahippocampal gyrus)
papez circuit (start at hippocampus)
hippocampus → fornix → mammillary body → mammillothalamic tract → ant nucleus of thal → internal capsule → cingulate gyrus → cingulum → parahippocampal gyrus → entorhinal cortex → perforant path → back to hippocampus
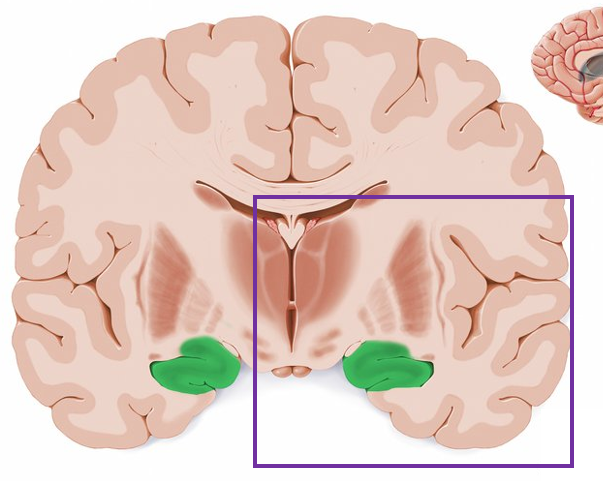
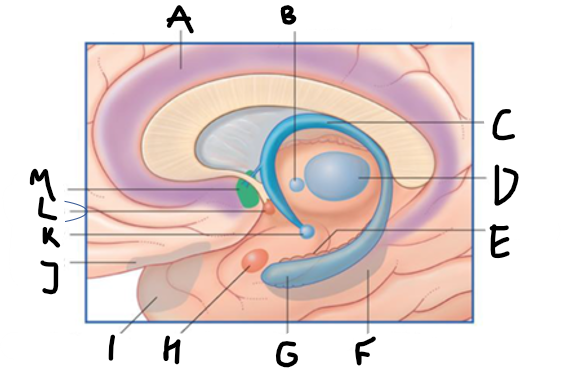
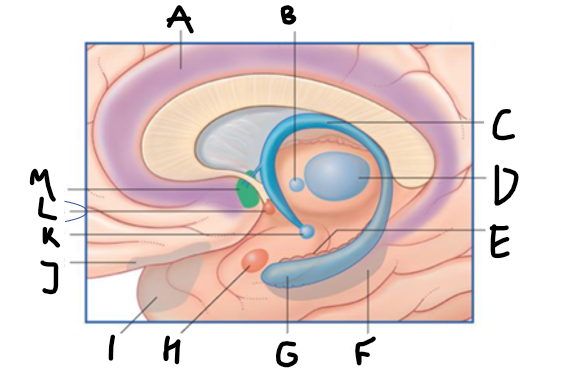
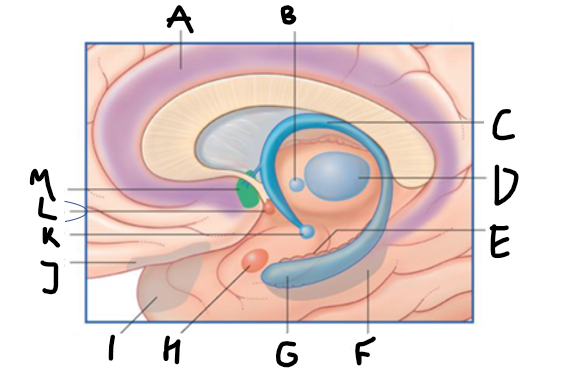
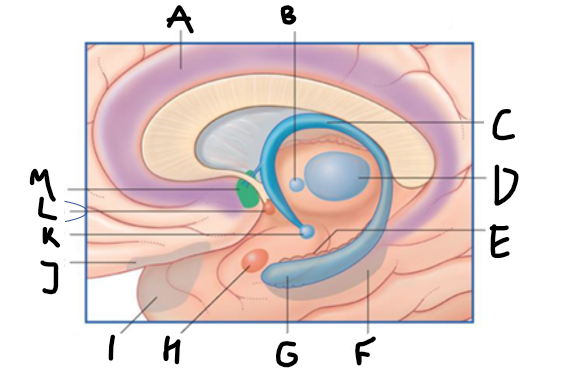
what is highlighted in green?
hippocampus
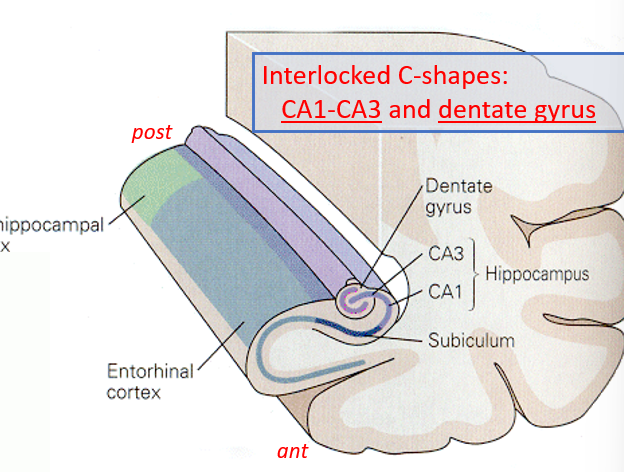
what structures make up the interlocking C shapes of the hippocampal formation?
CA1-3 (hippocampus) and the dentate gyrus
afferents and efferents of the hippocampus are
bundled together in the same paths
list the sections of the hippocampal formation from outermost to innermost (ending with dentate)
parahippocampal (on posterior edge) and entorhinal cortex (anterior), subiculum, CA1-CA3, dentate gyrus
what are the inputs to the hippocampus?
subiculum → hippocampus
EC → subiculum → hippocampus
Amygdala → EC → hippocampus
what are the outputs of the hippocampus?
hippocampus → subiculum → cortex
hippocampus → cortex → subcortical areas
what are the inputs to the mammillary bodies?
hippocampus
what are the outputs of the mammillary bodies?
anterior nucleus of the thalamus
what are the inputs of the cingulate gyrus?
anterior nuc of thalamus, visual cortex
what are the outputs of the cingulate gyrus?
parahippocampal gyrus
what are the inputs of the parahippocampal gyrus?
cingulate gyrus
what are the outputs of the parahippocampal gyrus?
entorhinal cortex
what are the inputs to the amygdala?
thalamus
what are the outputs of the amygdala?
cerebral cortex, hypothalamus
what are the inputs of the septal nuclei?
hippocampus
what are the outputs of the septal nuclei?
hypothalamus
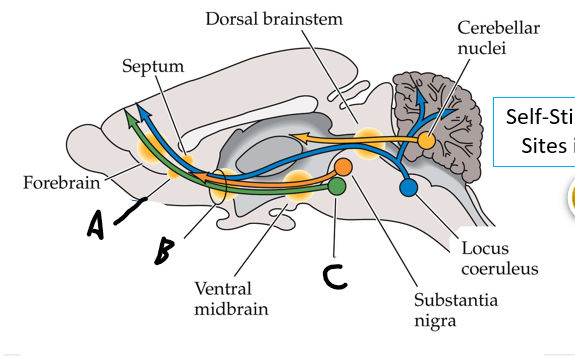
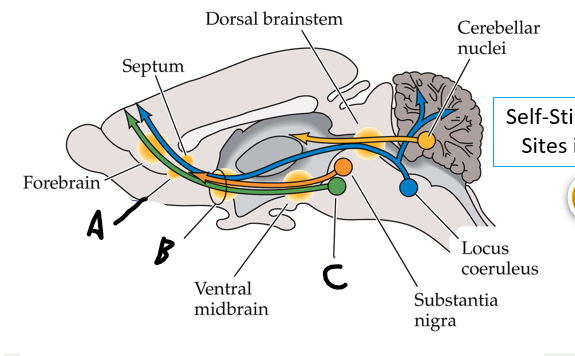
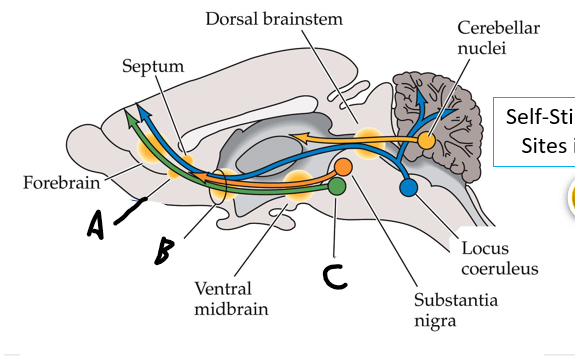
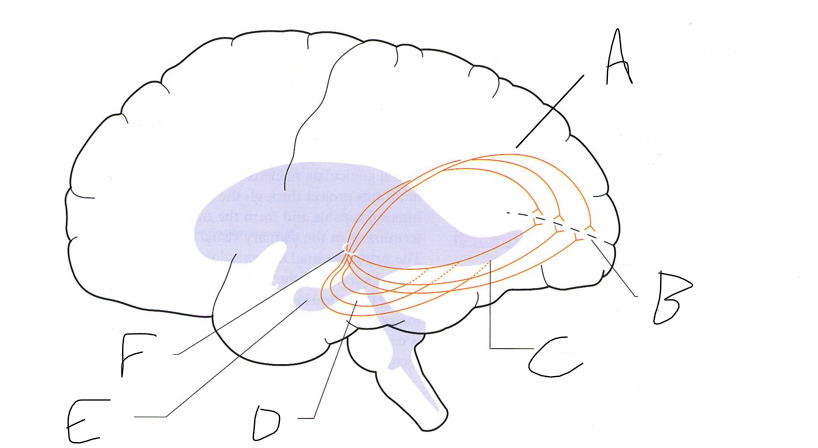
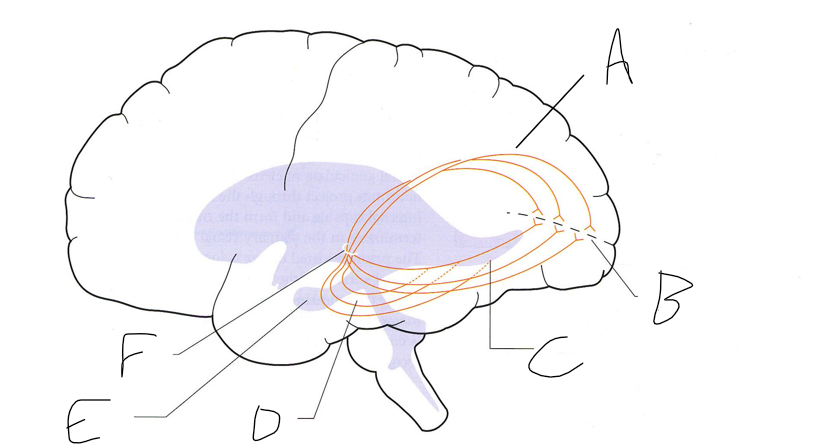
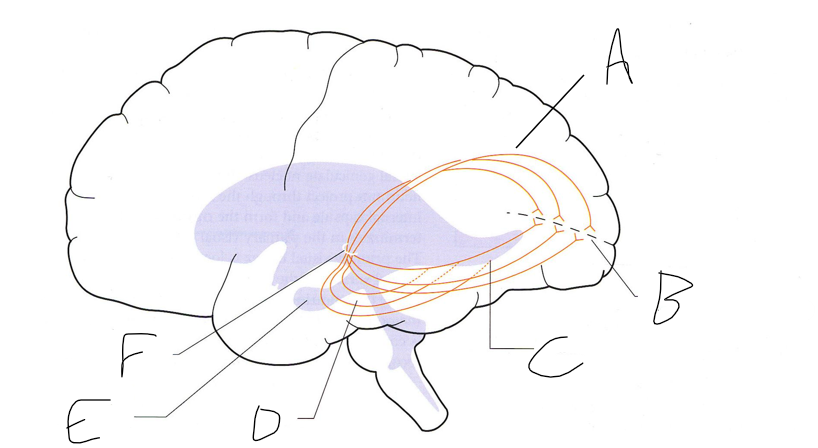
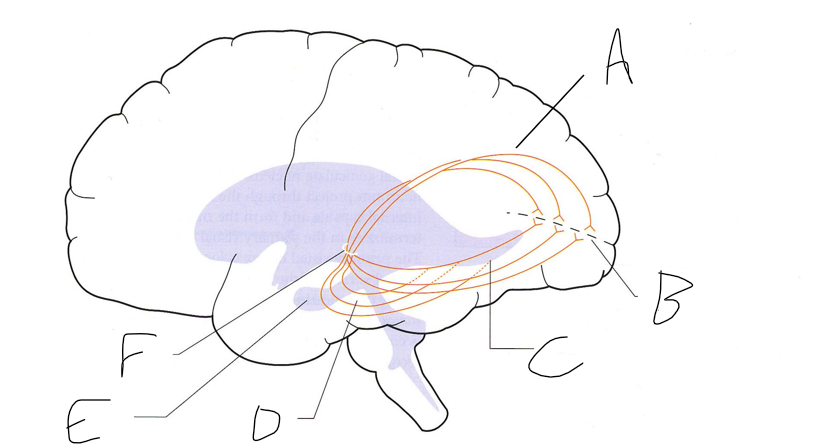
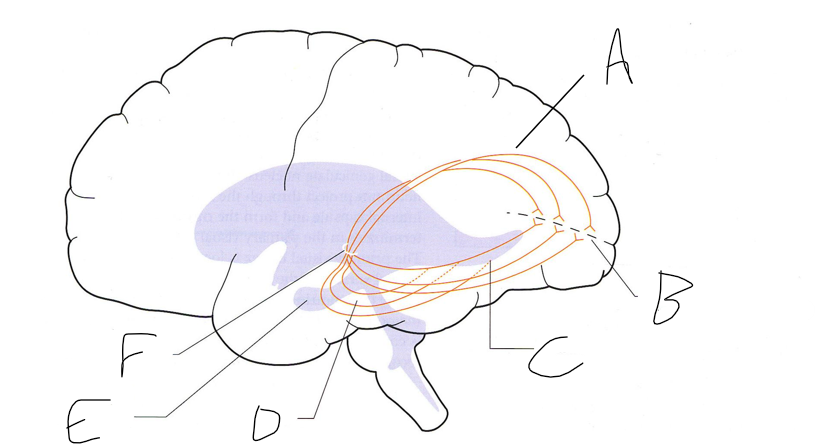
what is shown?
septal nuclei
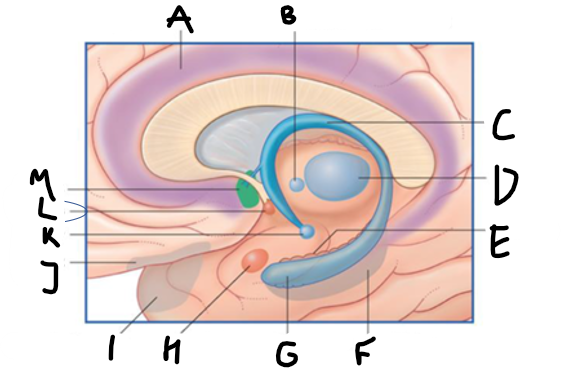
cingulate gyrus
A
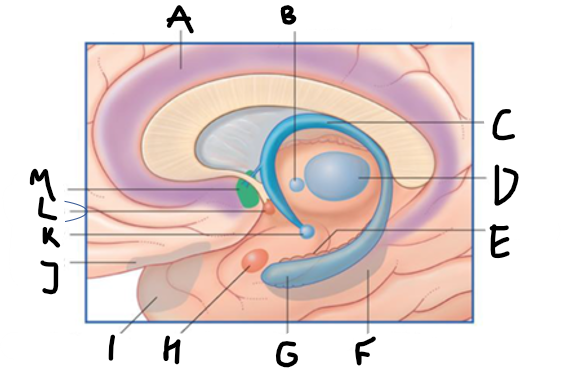
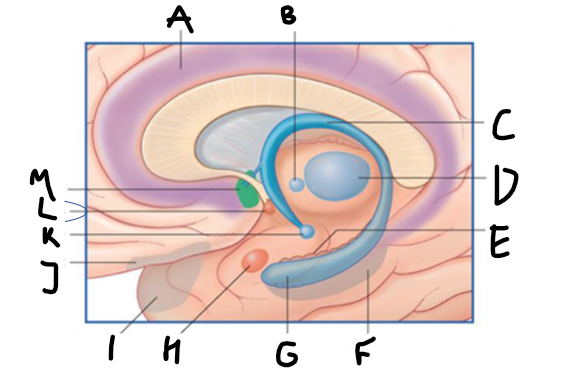
anterior nucleus of thalamus
B
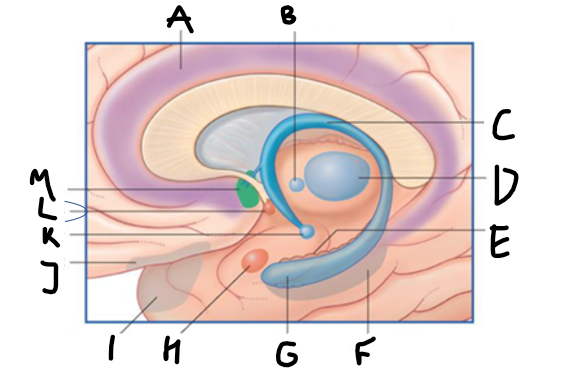
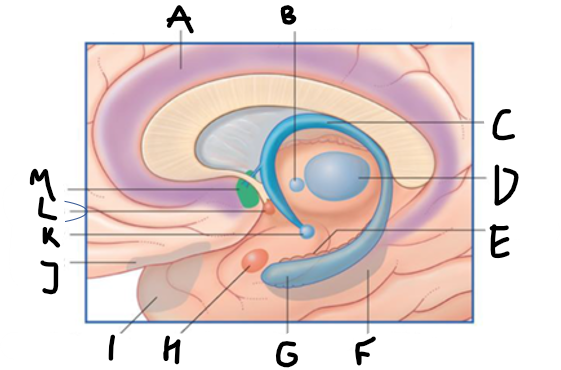
fornix
C
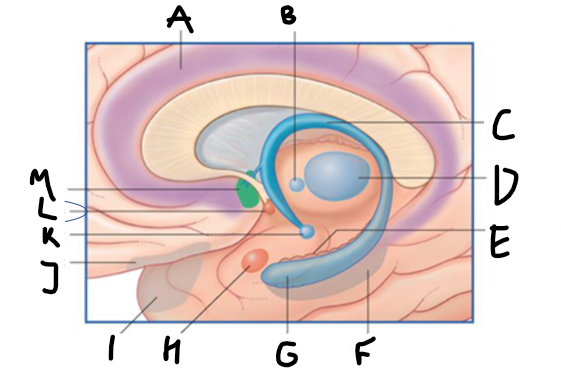
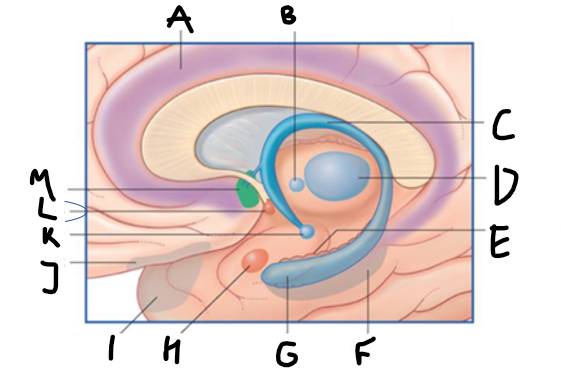
dentate gyrus
E
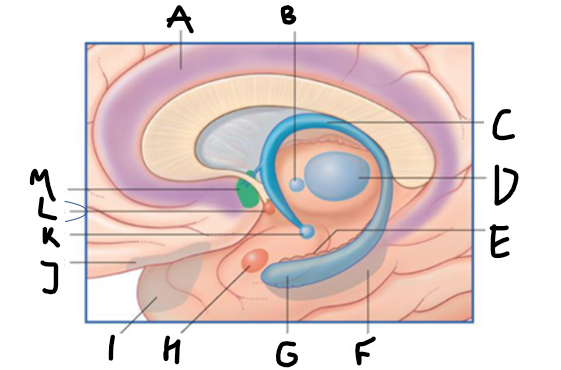
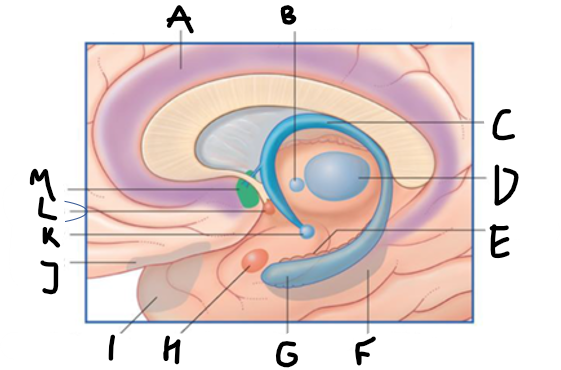
entorhinal cortex
F
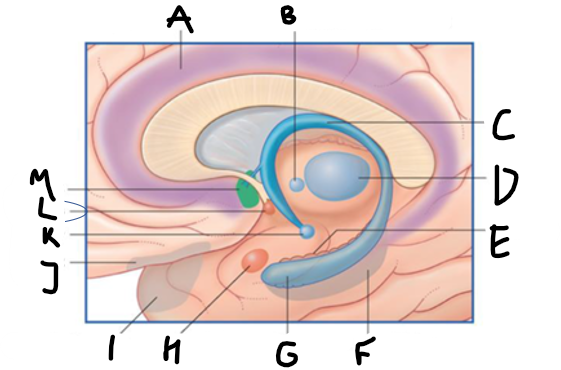
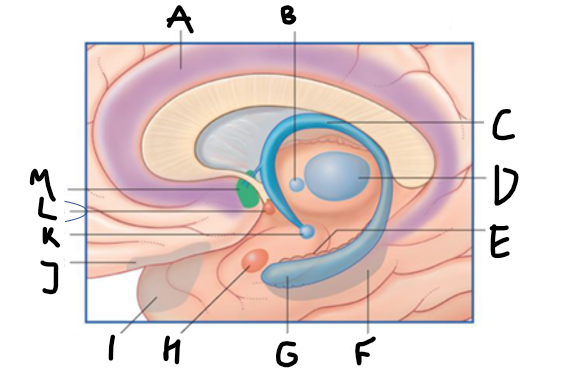
hippocampus
G
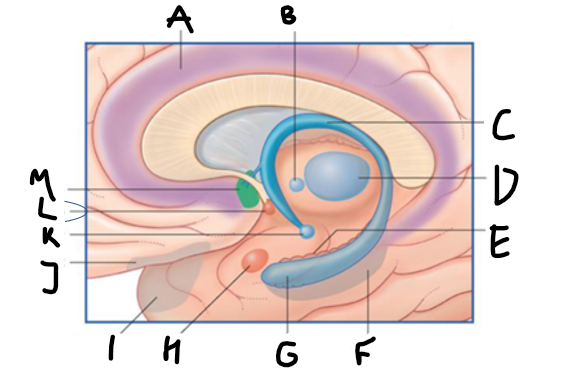
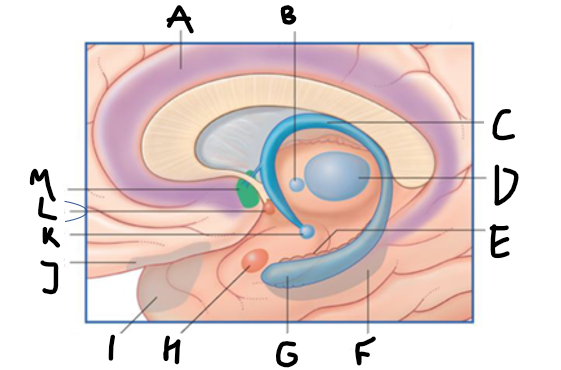
amygdala
H
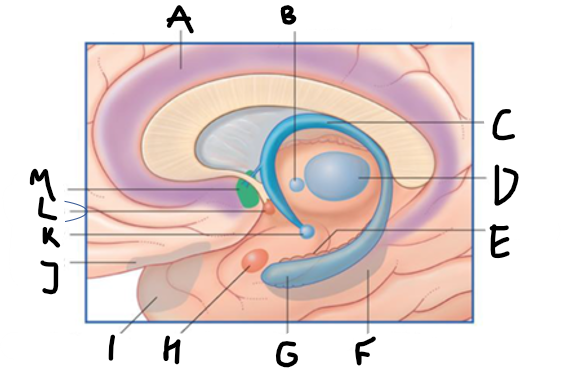
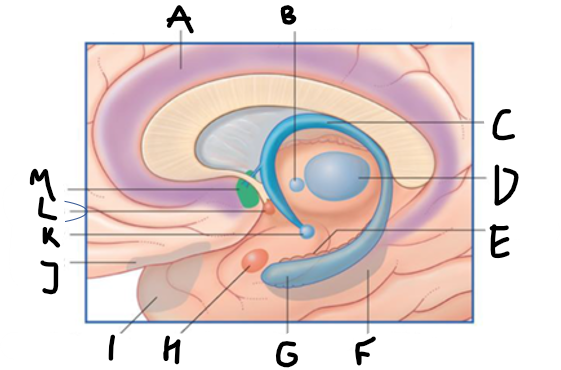
mammillary body
K
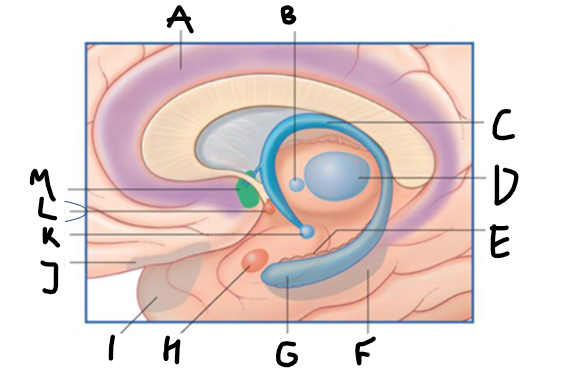
nucleus accumbens
L
septal area
M
accumbens
A

medial forebrain bundle
B
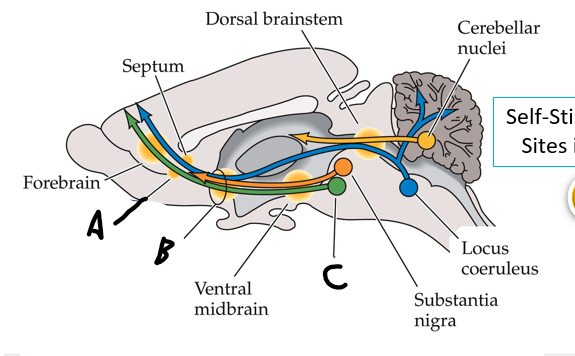
ventral tegmental ares
C
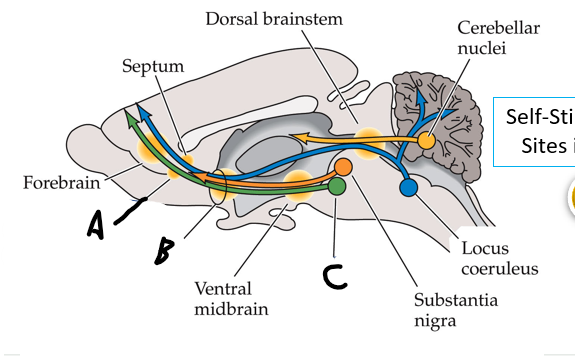
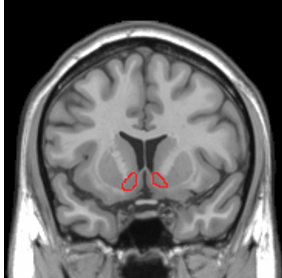
nucleus accumbens (recall: where caudate and putamen meet)
what is the function of the limbic system?
fight/flight
feeling (especially fear)
forgetting/memory
sexual function
what is the function of the hippocampus?
spatial memory, learning
amygdala function
anger and fear
involved in reward, pleasure, and addiction, located where the caudate and putamen meet
nucleus accumbens
cingulate gyrus function
emotion processing, learning and emotional memory
attention flexibility (shifting attention, switching from ideas)
empathy
septal nuclei function
serve as relay of hippocampus to hypothalamus, septal rage, emotional memory
loss of episodic memory, but not semantic memory. patient cannot recall personal details. patient likely has an injury to
the hippocampus
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome: lesion, characteristics
caused by thiamine/B2 deficiency, resulting in damage to mammillary bodies. common in alcoholics (due to poor nutrition, not the alcohol itself).
characteristics: confabulation, delusions, hallucinations, disorientation. due to relation to alcoholism, patients may also present with cerebellar degeneration (ataxic gait and dysmetria).
Kleine-Levin syndrome: lesion, characteristics
hypothalamic injury, most often found in adolescent males
cycling periods of hyperphagia, hypersomnolence, sexual aggression, general aggression. think of hypothalamus/pituitary
Kluver-Bucy syndrome: lesion, characteristics
Amygdala injury
memory deficits, flat affect, oral fixation, hypersexuality. hard time recognizing fear
Limbic encephalitis: lesion, characteristics
not one specific lesion, limbic-area issues that may arise from lung carcinoma.
short term memory impairment, quick changes in mood (emotional lability), agitation, sexual disinhibition).
Abulia: lesion, characteristics
frontal lobe lesion. personality changes, apathy, lack of initiation of action. patient may not eat when hungry, move when in pain, speak much/at all, use the restroom on own.
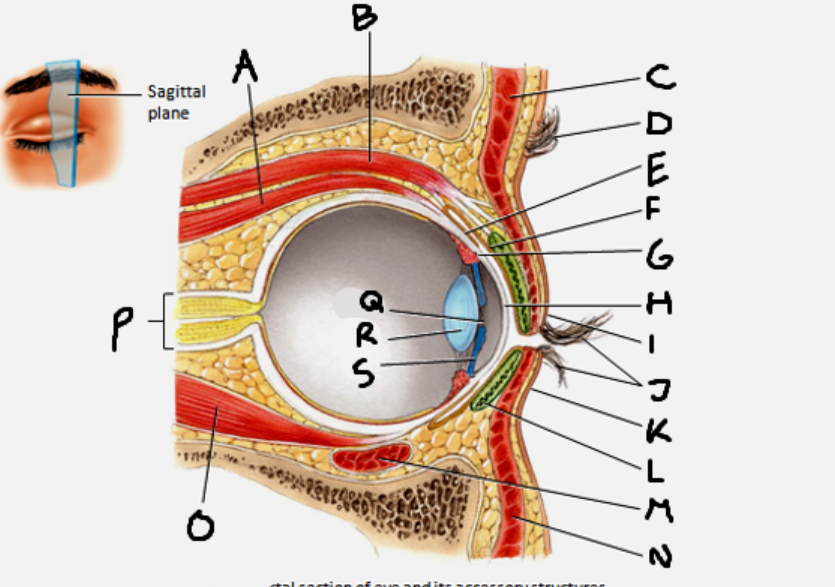
which structures arise from the fibrous tunic?
cornea and sclera
which structures arise from the vascular tunic?
the iris, pupil, ciliary body, choroid, and lens
which structures arise from the neural tunic?
the retina
the sclera is an extension of ___
dura
in the iris, the circular fibers ___ and the radial fibers ___
circular constrict, radial dilate
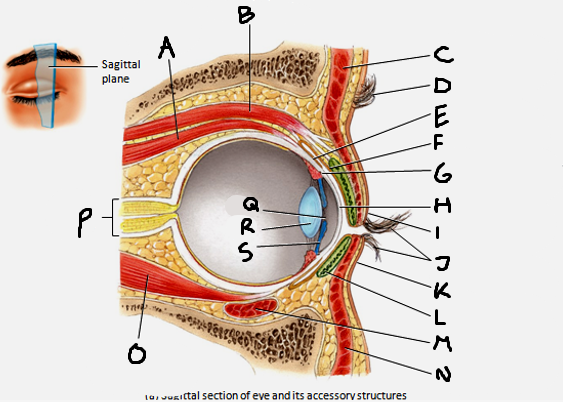
superior rectus muscle
A
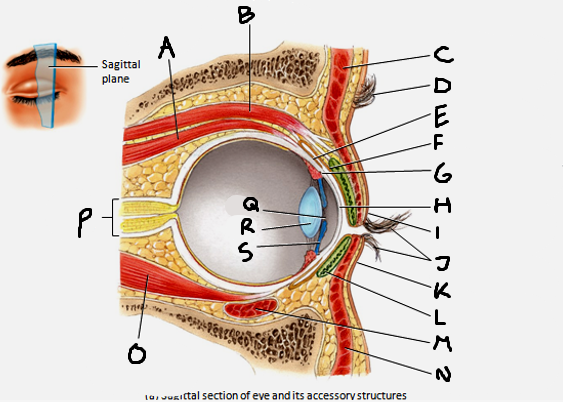
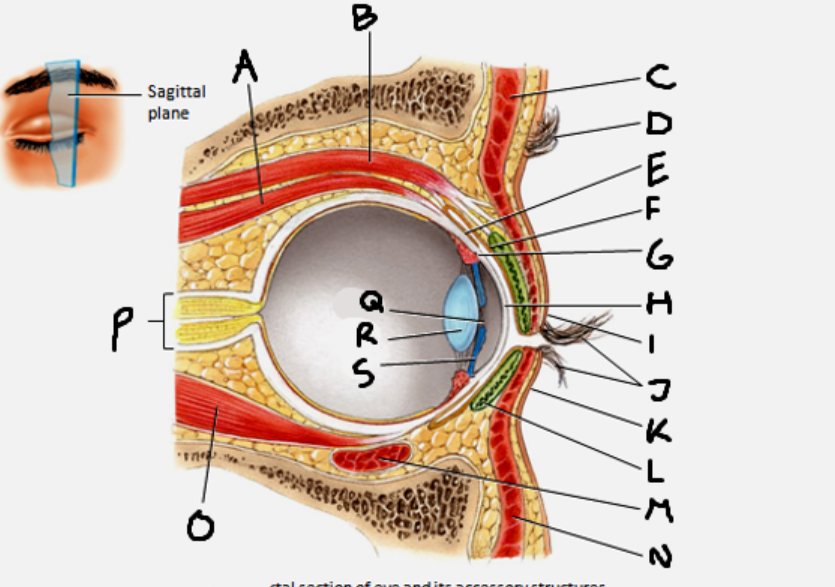
conjunctiva
E
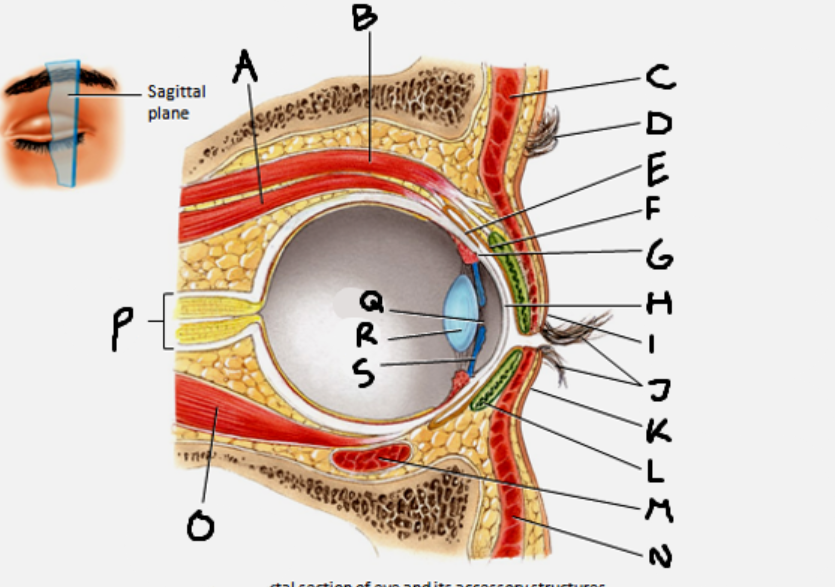
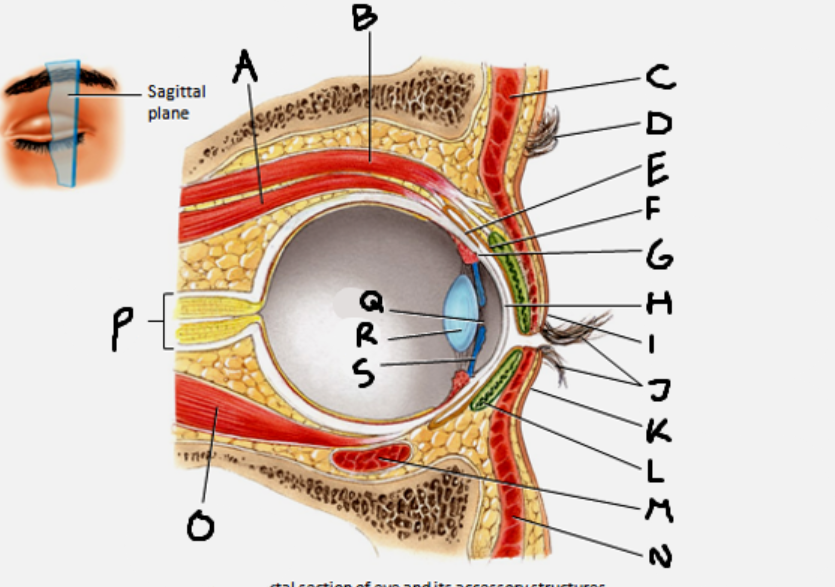
cornea
H
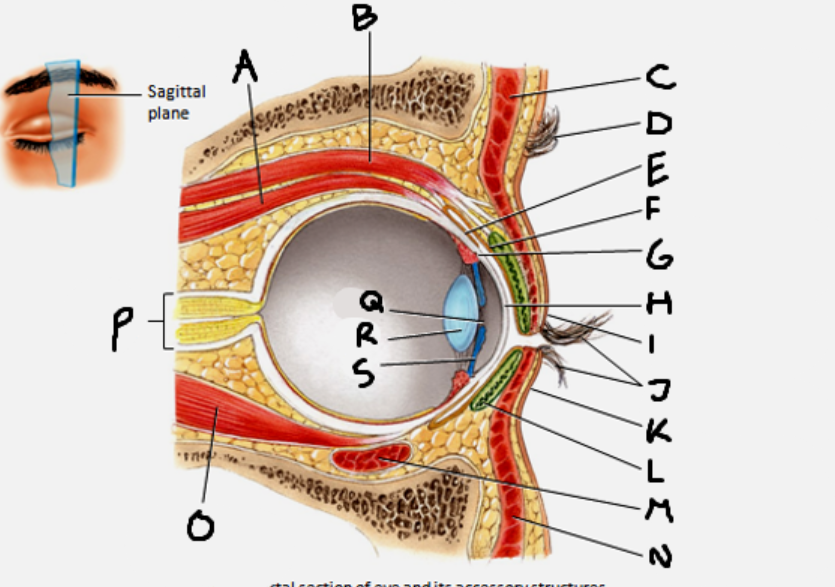
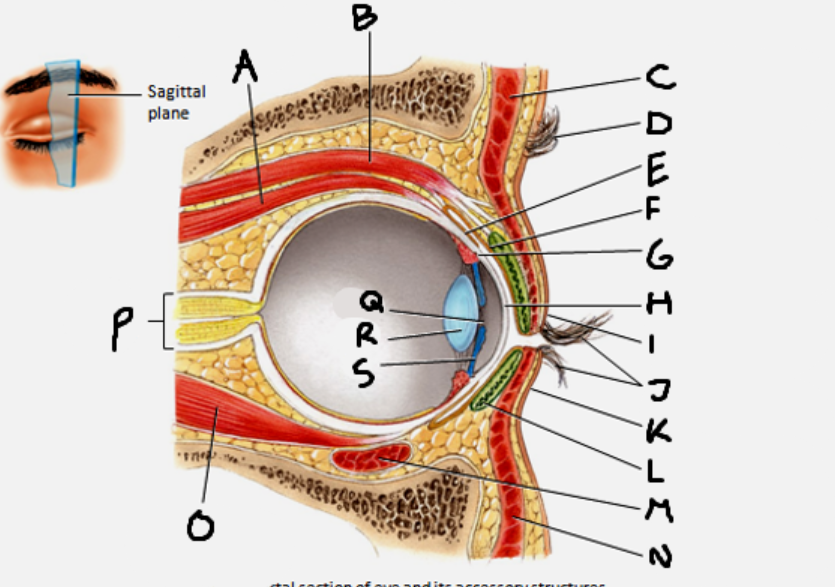
inferior rectus muscle
O
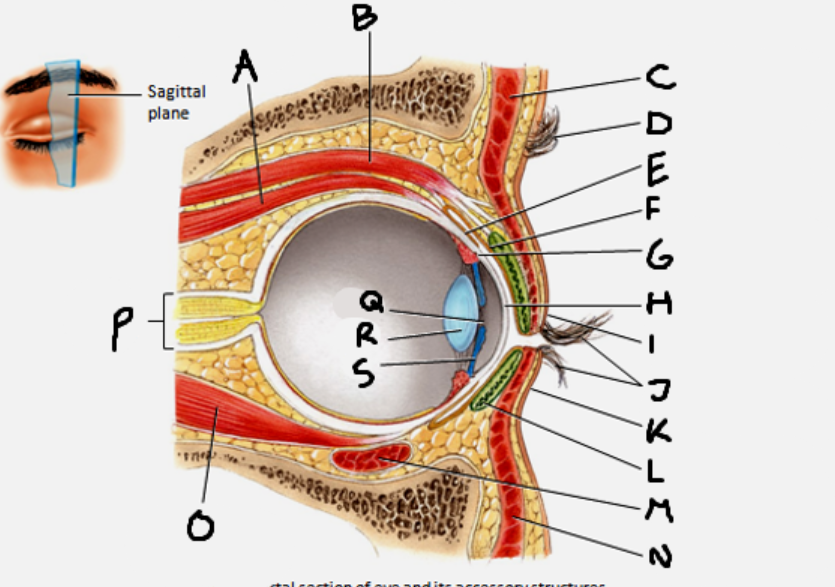
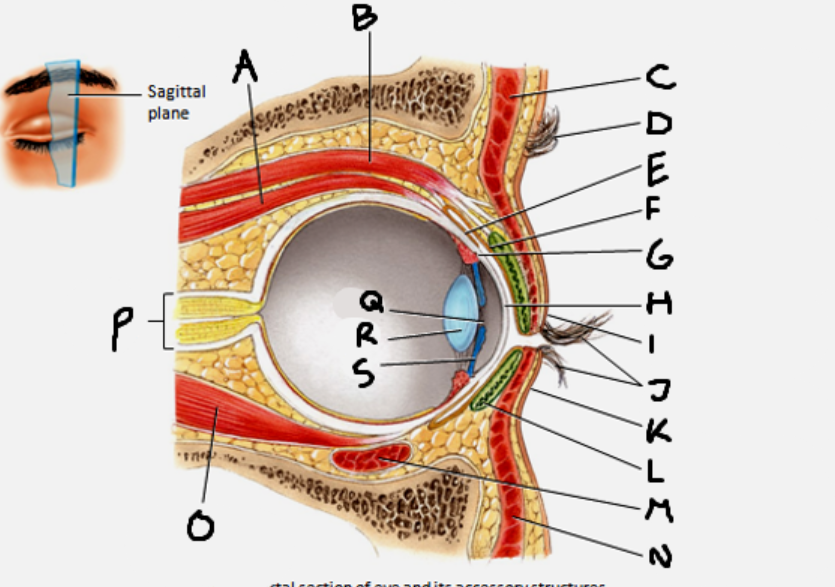
optic nerve
P
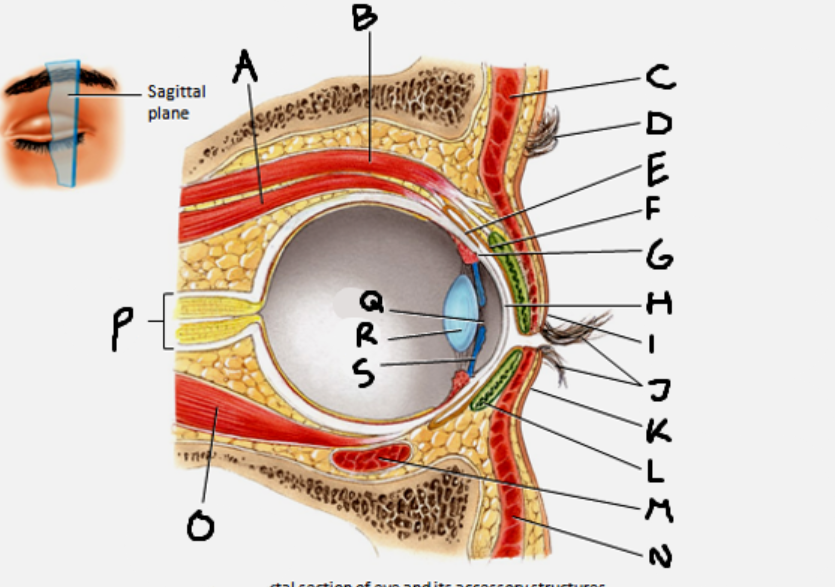
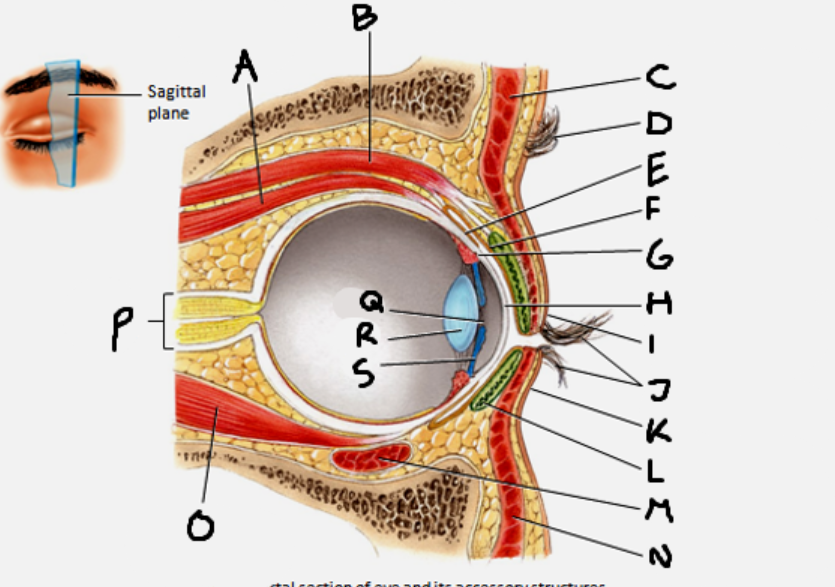
pupil
Q
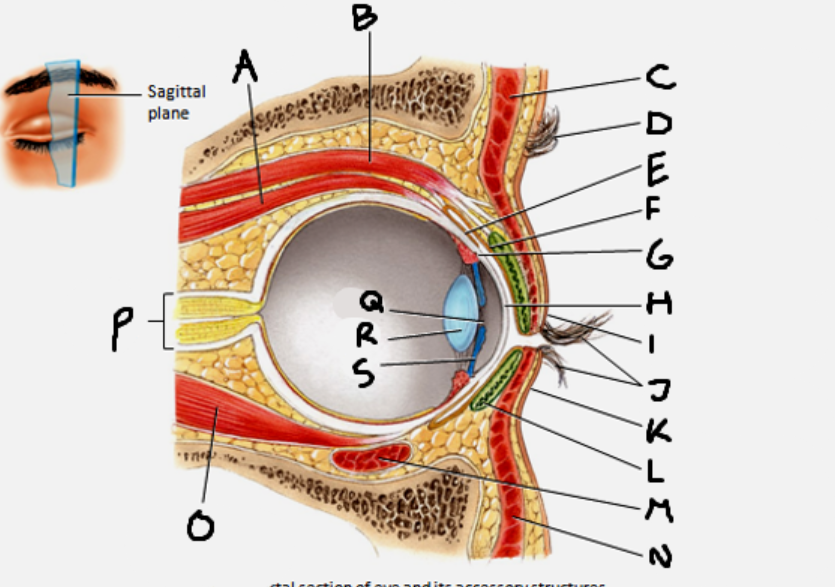
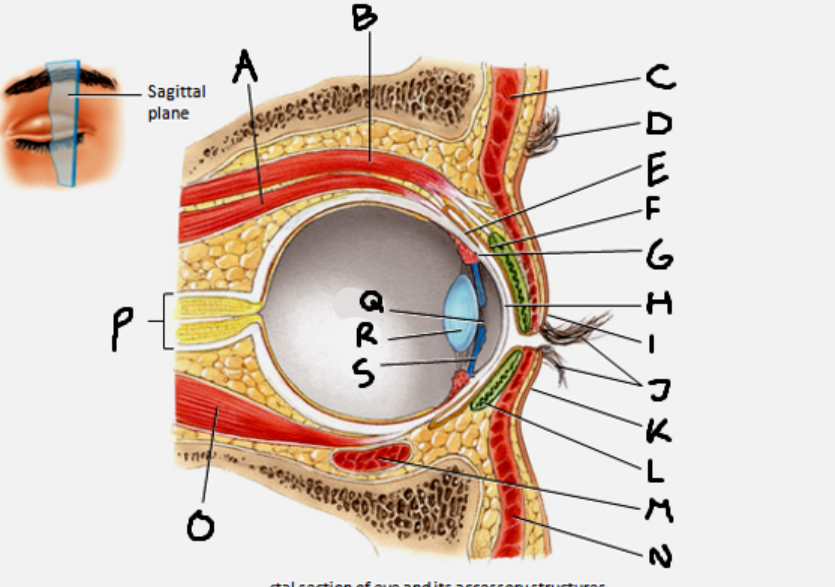
Lens
R
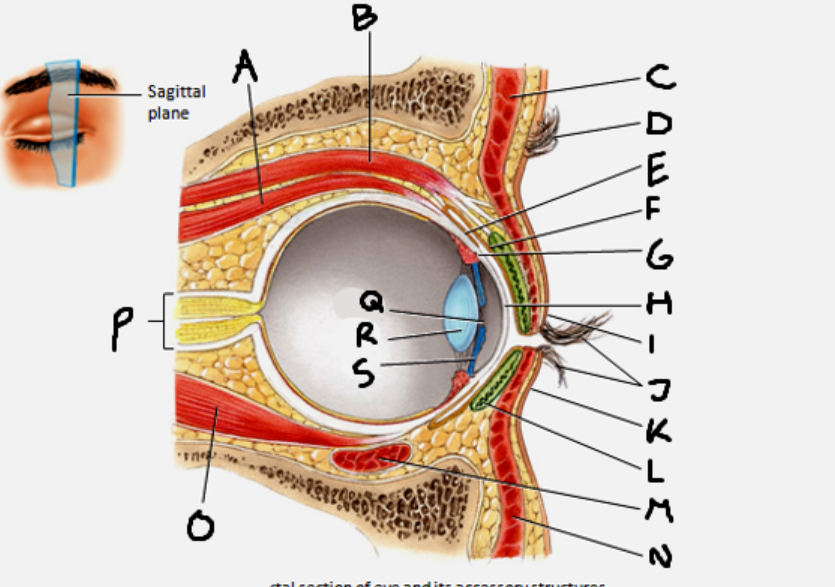
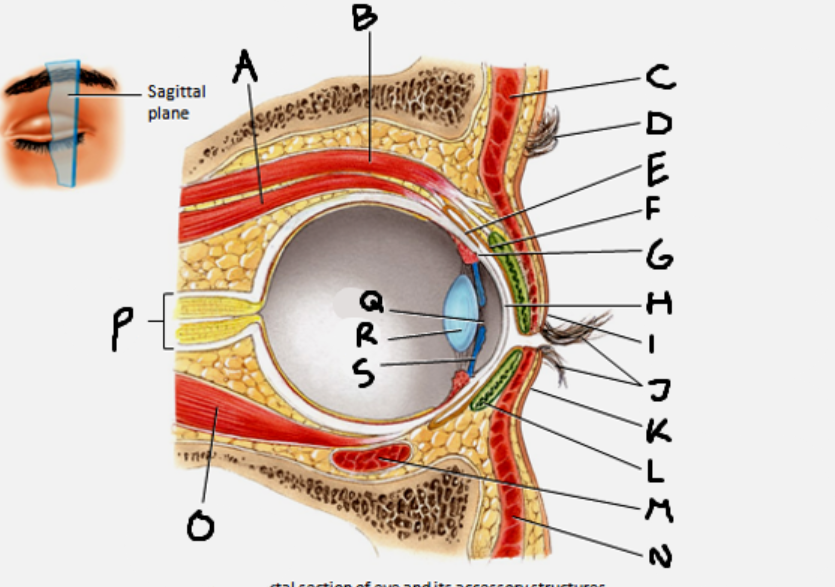
Iris
S
CN III innervates which eye muscles?
medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique
CN IV innervates which eye muscle?
superior oblique (for intorsion)
CN VI innervates which eye muscle?
lateral rectus (for abduction)
circular fibers are innervated by ___ neurons, while radial fibers are innervated by ___ neurons
circular - parasympathetic
radial - sympathetic
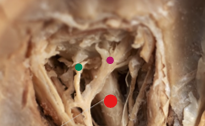
red
optic nerve
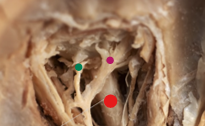
green
short ciliary nerve
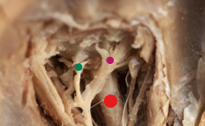
purple
long ciliary nerve
vitreous body is the gel within the ___ chamber
anterior
rods contain ___ and cones contain ___. which is more numerous?
rhodopsins, iodopsins, rods.
what do horizontal cells do?
modify responses of bipolar cells
what do amacrine cells do?
modify resp
which cell in the retina can generate action potentials?
ganglion cells
what are the three layers of the LGN? describe each.
parvocellular - 4 dorsal layers, small cells, small receptive fields
magnocellular - 2 ventral layers, large cells, large receptive fields
koniocellular - between each layer
on a fundus exam, the dark area is the ___. the light spot is the ___.
macula, optic disk (blind spot)
at the center of the macula is the
fovea
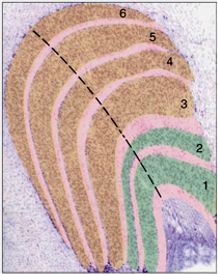
what is in orange?
parvocellular layers
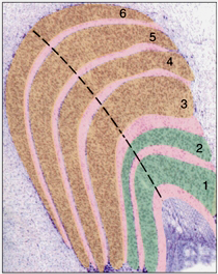
what is in green?
magnocellular layers
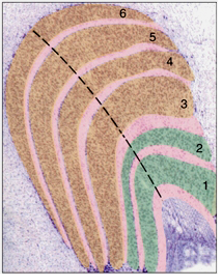
what is in pink?
koniocellular layers
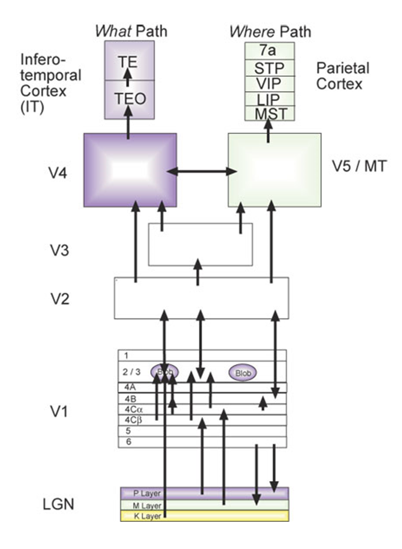
give the main functions for each section of the visual cortex.
V1 - primary visual cortex, perceives object
V2/V3 - fills in gaps, perceives complex form
V4 - perceives complex form
V5 - motion perception
describe the visual streams
dorsal stream (where) - dorsolateral parietotemporal
ventral stream (what) - inferior occipitotemporal cortex
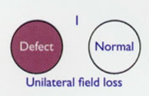
lesion to the optic nerve results in
unilateral field loss
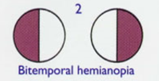
lesion to the optic chiasm results in
bitemporal hemianopia
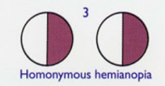
lesion to the optic tract results in
homonymous hemianopia
lesion to optic radiation results in
quadrantanopia (myers loop - superior quadrantanopia, parietal loop - inferior)

meyer’s loop
D
what is B
calcarine sulcus
what is F?
lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus
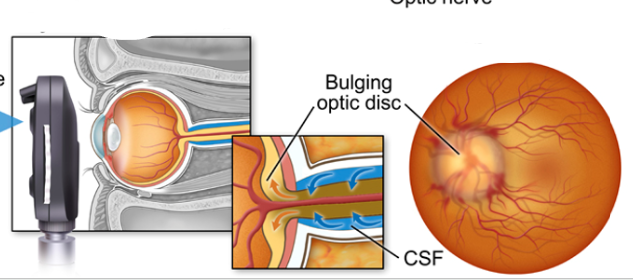
what diagnosis
papilledema
papilledema is characterized by
a bulging optic disk. can see a large dark ring around the optic nerve on fundus. no visual field deficit except enlarged blind spot.
inflammation of the optic nerve, presents with a blind spot. eye pain common.
optic neuritis
visual spells (can be transient) are a sign of
ophthalmic artery occlusion
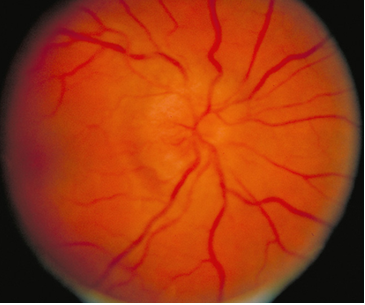
A 28-year-old former gymnast noticed difficulty seeing fine lines with her left eye. The symptoms progressed over the next day, and she had difficulty reading newspaper headlines. Pain in the left orbit was minor at first but worsened and increased with eye movement.
Vision was 20/200 in the left eye and 20/30 in the right eye. There was a central scotoma (blind spot), and red was less intense in the left eye.
optic neuritis
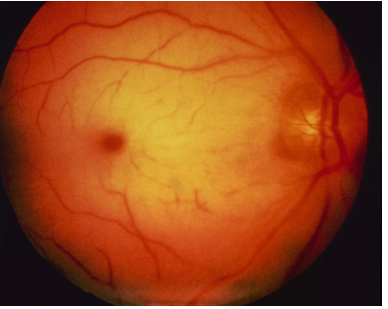
A 66-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with a 3-week history of visual spells
During each spell she had sudden onset of cloudy darkening of vision in her left eye. Each spell lasted a few minutes and abated suddenly
During one spell she covered the left eye and noted normal vision in the right eye
ophthalmic artery occlusion
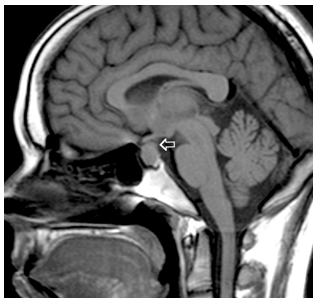
A 25 yo woman became ‘sluggish’ and easily fell asleep. She had gained 17 pounds in the last three months, and on exam her face looked ‘like a mask’ – her jaw was large and her eyebrow ridges prominent.
She had trouble seeing to the left in the left eye, and to the right in her right eye
pituitary tumor pressing on chiasm, leading to bitemporal hemianopia
prosopagnosia
face blindness, lesion to fusiform gyrus
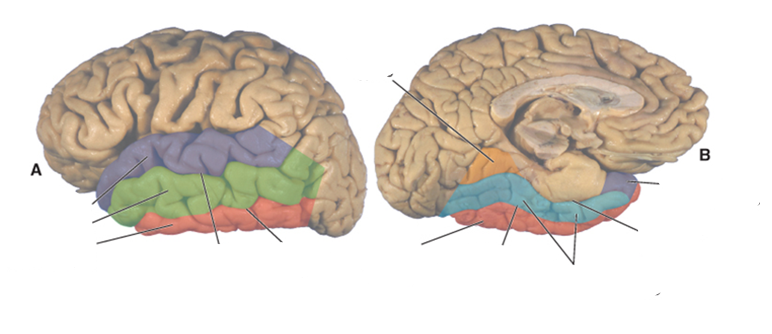
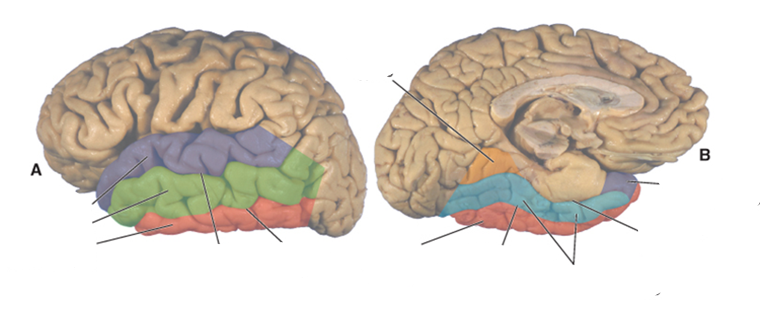
what color is the superior temporal gyrus?
purple
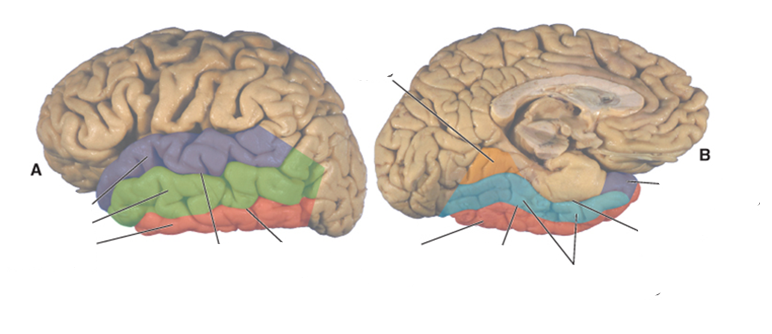
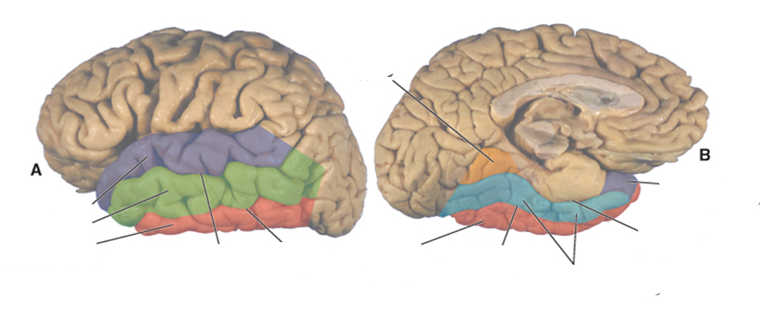
what color is the middle temporal gyrus?
green
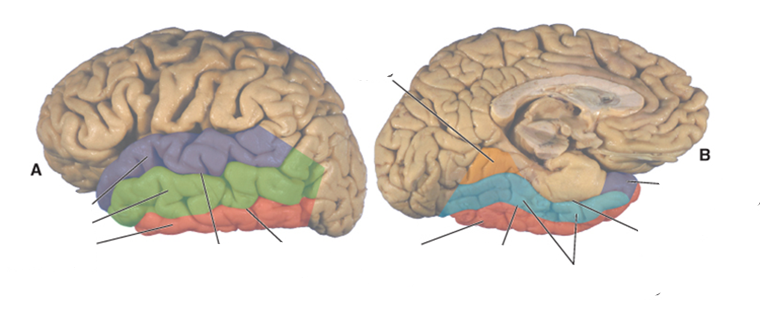
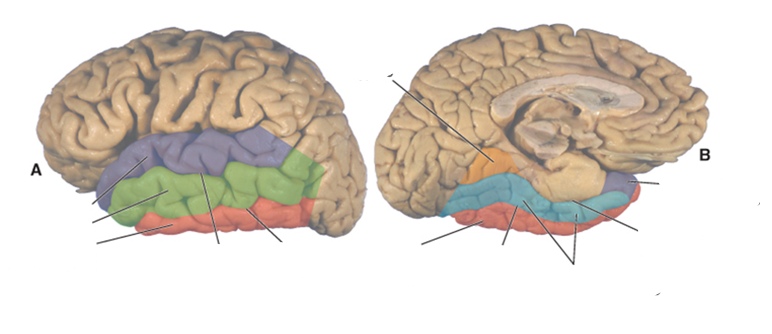
what color is the inferior temporal gyrus?
red
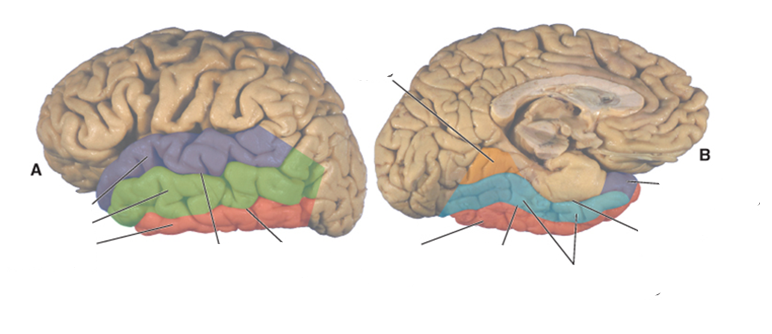
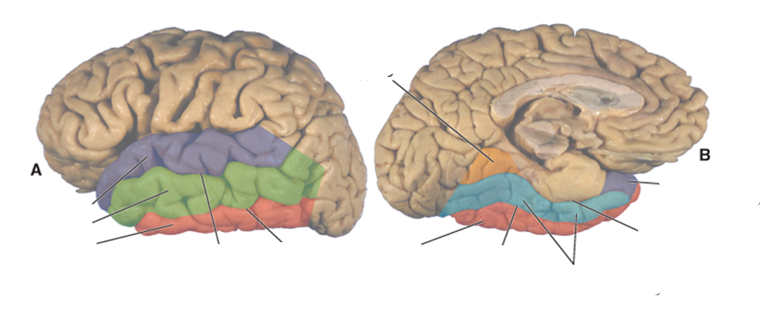
what color is the occipitotemporal (fusiform) gyrus?
blue
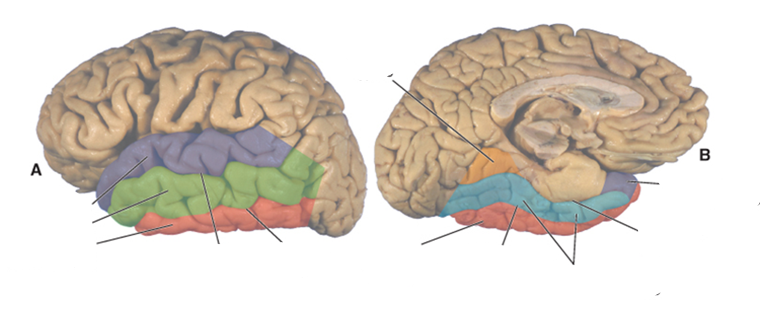
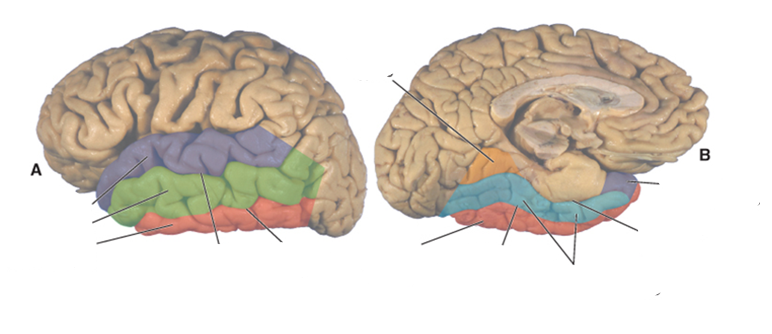
what color is the lingual gyrus?
orange
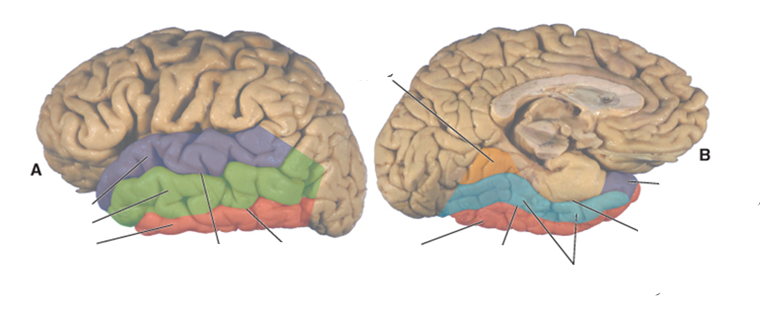
where is the superior temporal sulcus?
between the superior and middle temporal gyri