B6 (mine)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
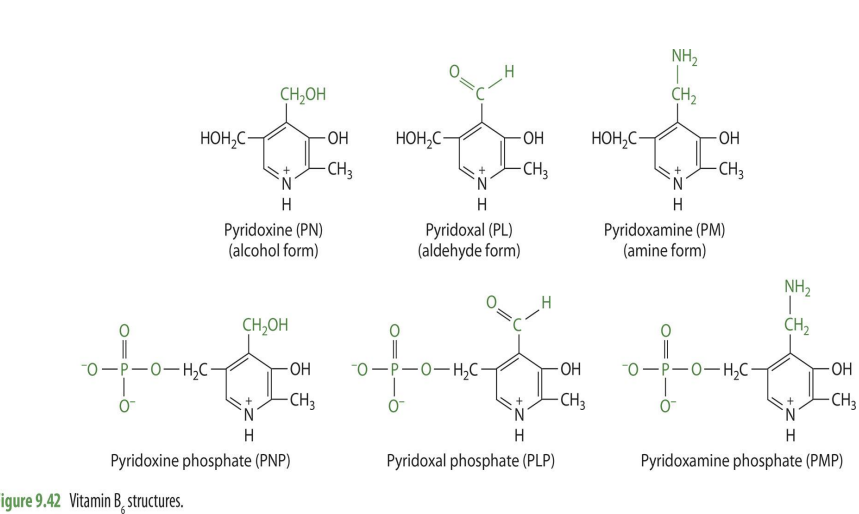
what are the forms of B6 (6)
Pyrixidone (PN)
Pyridoxal (PL)
Pyridoxamine (PM)
Pyridoxine phosphate (PNP)
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
pyridoxamine phosphate (PMP)
what is the stable form of B6?
pyridoxine
where is pyridoxine mainly found?
primarily found in plants
what other forms can be found in plants?
smaller amounts found of the other 2 forms (pyridoxal and pyridoxamine), as well as phosphorylated form
Animal sources consist of what form(s) of B6?
pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) & pyridoxamine phosphate (PMP)
what is main functional form in the body?
pyridoxal (PL) and pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
Some _____ forms found in plants are less ____
glucoside
bioavailable
what is a major issue with B6
bioavailability due to processing
alcohol form of B6
Pyridoxine
aldehyde form
pyridoxal
amine form
Pyridoxamine
prior to absorption, what must occur
phosphorylated forms must be dephosphorylates
How are phosphorylated forms dephosphorylated?
by alkaline phosphatase (zn dependent)
alkaline phosphatase is dependent on what?
Zinc
absorption occurs in ___ via ___
jejunum via passive diffusion
absorption rates
61-92%
within intestinal cells, what can occur
some pyridoxine can be phosphorylated
Most PN, PL & PM are released to ____
portal blood
what occurs in the liver to B6 that allows for function?
forms are converted into PLP (interconversion)
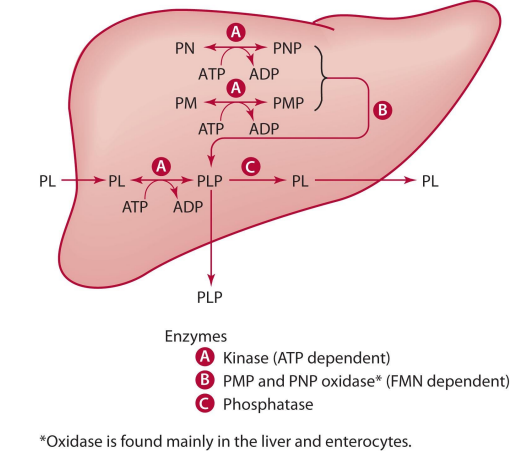
where does interconversion of B6 forms occur?
liver (SUPER IMPORTANT)
PN become what, how?
PNP through kinase (ATP)
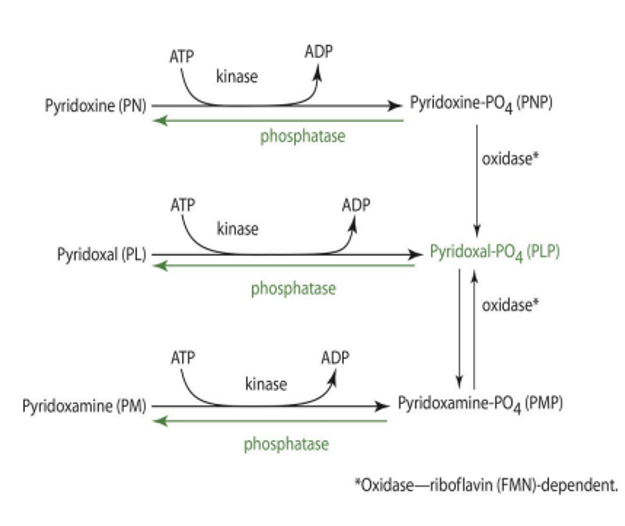
PM becomes what, how?
PMP through kinase (ATP)
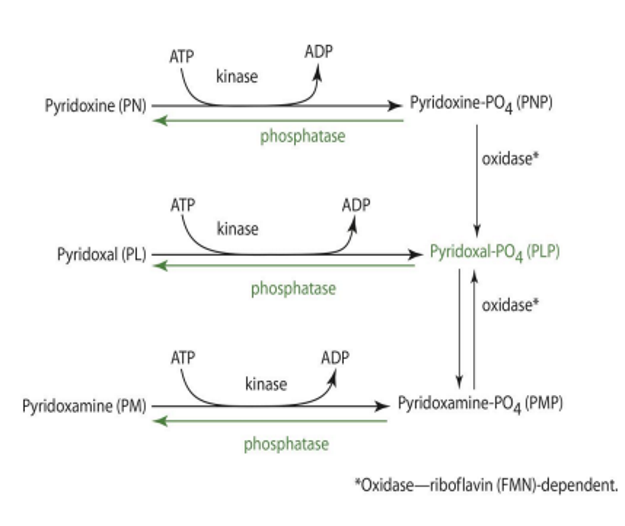
kinase is _____ dependent
ATP
PMP/PNP can become what?
PLP
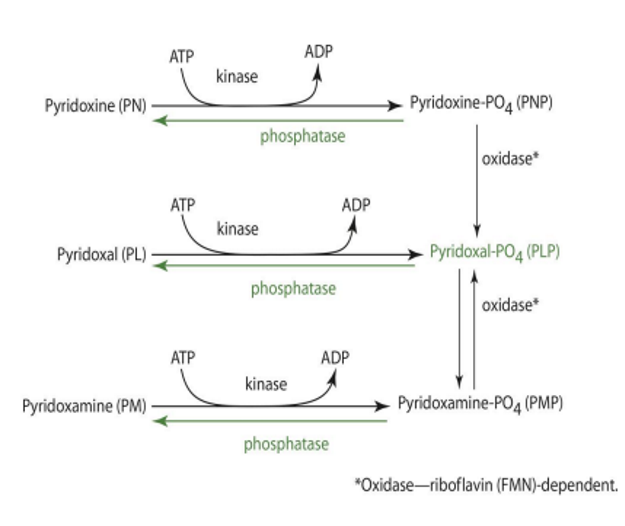
in order for PMP/PNP to become PLP, what is needed?
oxidase (PMP or PNP oxidase)—> FMN dependent
LACKING IN MANY OTHER TISSUES
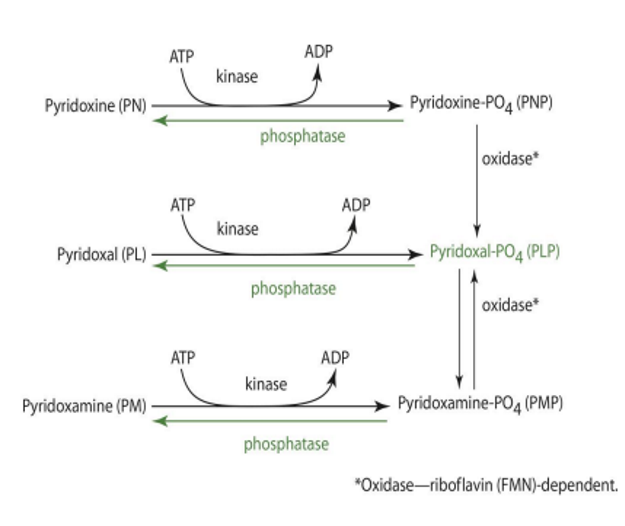
PMP & PNP oxidase is dependent on
FMN (riboflavin)
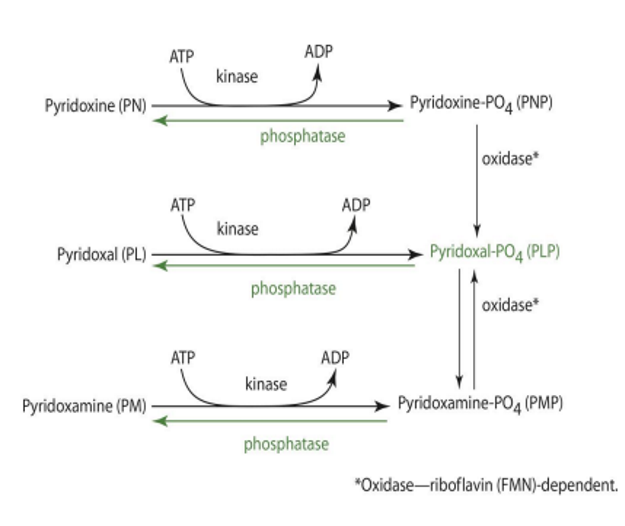
in order for PLP, PMP, and PNP to be converted back into unphosphorylated form, what is needed?
phosphatase enzyme
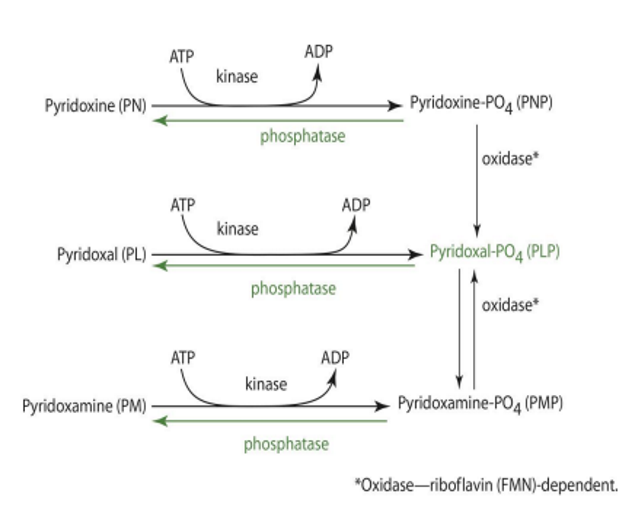
what is the main form of B6 in blood?
pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) —> 60-90%
what can happen to PL in RBC
phosphorylated into PLP and bound to hemoglobin
must PL be phosphorylated?
no, it may stay as PL
In RBC, PL binds to ___ of ____ & PLP bind to ____
PL binds to alpha chain of hemoglobin
PLP binds to beta chain of hemoglobin
In plasma, PLP & PL are bound to ____
albumin (small amounts of PM also binds)
before it PLP can be uptake into other tissues, what must occur to it?
hydrolyzed by alkaline phosphatase
conversion of Pyridoxamine or pyridoxamine phosphate -> Pyridoxal phosphate uses what
FMN-dependent oxidase

liver stores how much of B6?
5-10% (NOT MAJOR STORAGE, but major for metabolism)
what occurs to all 3 forms of B6 in the liver?
they are phosphorylated
where is PLP mostly stored?
muscle (75-80%)
PLP in the muscle is bound to
glycogen phosphorylase
glycogen phosphorylase is an enzyme associated w/ ...
glycogen utilization (breakdown of glycogen into glucose uses PLP; PLP adds the phosphate to glucose to form G6P and make it useful)
can most tissues form PLP?
NO..
what cant most tissues make PLP?
they lack PMP/PNP oxidase enzymes (FMN dependent) needed to convert PN/PM into PLP
what tissues can the coenzyme form also be found in
brain
kidneys
spleen
Functions of B6 (9 general)
100+ reactions
• decarboxylation of AA (decarboxylase)
• transamination (transaminase)
• Transelenation (selenium)
• rearrangement of Amino Acids (D- & L- AA)
• Heme synthesis
• CHO metabolism
•Lipid metabolism
• Neurotransmitter synthesis
• Conversion of tryptophan -> niacin
Transamination Rx uses what forms of B6 as coenzyme?
PMP & PLP
Transamination Rx is related to what enzyme
transaminase
what are the main 2 aminotransferase enzymes?
aspartate aminotransferase (AST) also known as glutamate oxaloacetate (GOT)
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) also known as glutamate pyruvate tranaminase (GPT)
Transamination Rx: important for formation of what
Schiff base compounds (Carbon Nitrogen double bonds)
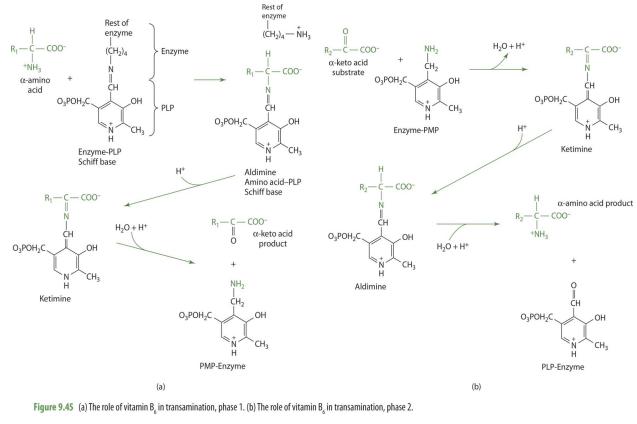
how does PLP/PMP work in transamination of AA
PLP will bind to enzyme --> Amino acid will bind to PLP (forming schiff base compounds) --> then whole structure becomes ketimine when it rearrange samino acid to become keto acid--> then release keto acid
PMP will bind to enzyme --> keto acid will bind to PMP becoming ketimine--> then will become aldimine when rearranges keto acid to become amino acid--> then PMP will release amino acid
cysteine is made from what starting compound?
methionine
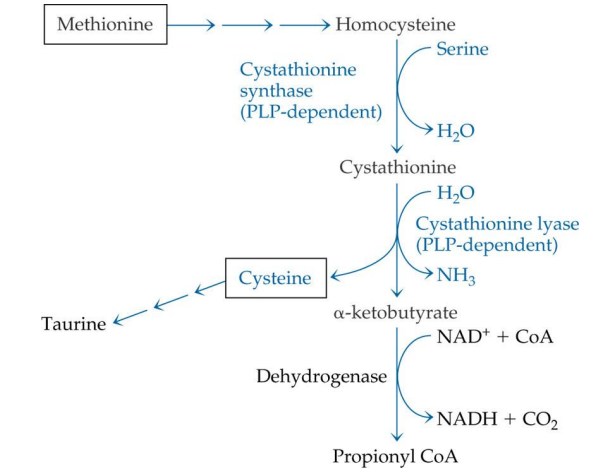
what is needed for cystein synthesis?
PLP for transsulfyhydration
___ is synthesized from methionine via ___ (what reaction)
cysteine; transsulfyhydration
cysteine can eventually lead to the synthesis of what compound
pyruvate
Cysteine undergoes ____ followed by ___ to generate pyruvate
dehydration , transamination
Transelenation involves conversion of ___ to ____
selenomethionine to selenocysteine
how does cysteine metabolism begin? (what compound)
with methionine
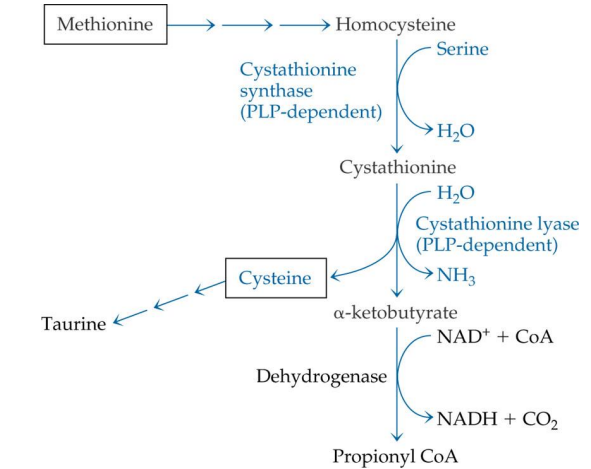
methionine is converted into what?
homocysteine
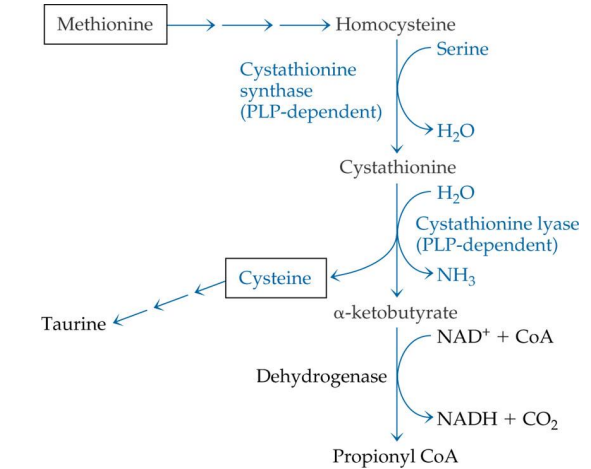
homocysteine -> is converted into what (enzyme?)
cystathione via Cystathione synthase (PLP)
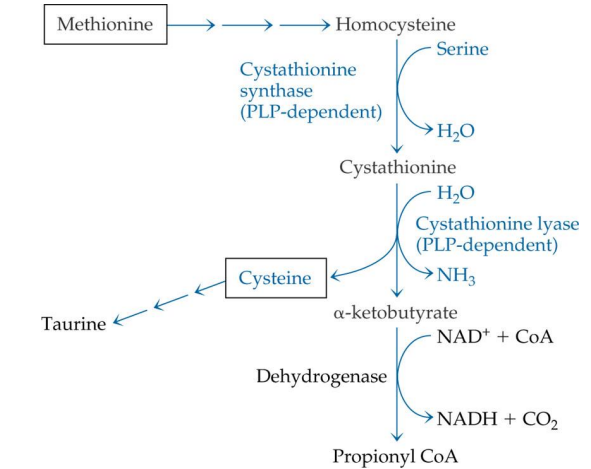
what enzyme is used to convert homocysteine into cystathione?
cystathionine synthase
cystathionine synthase depends on
PLP
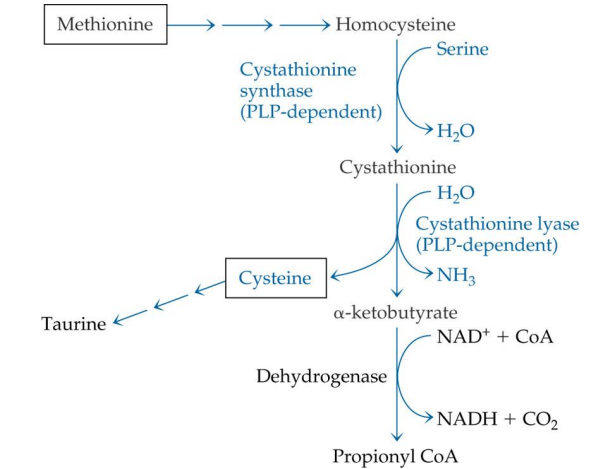
Cystathione is converted into what? enzyme?
Cysteine via cystathione lyase (PLP)
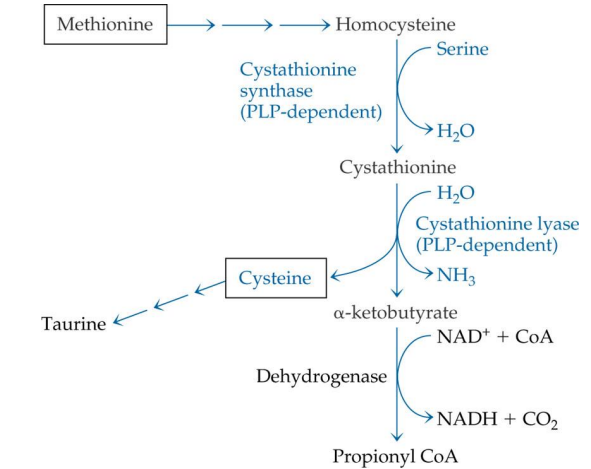
conversion of cystathionine to cysteine uses what enzyme?
cystathionine lyase
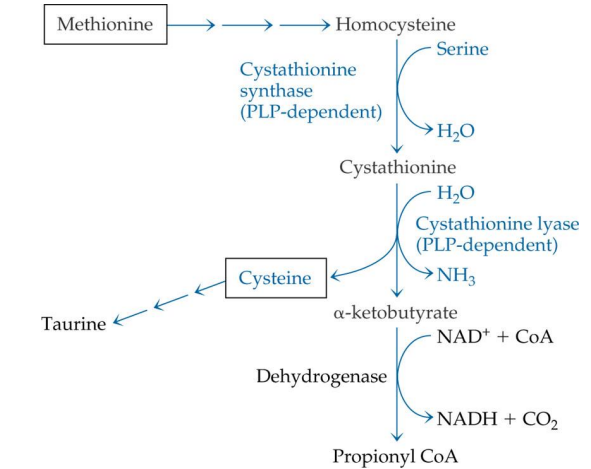
cystathionine lyase depends on
PLP
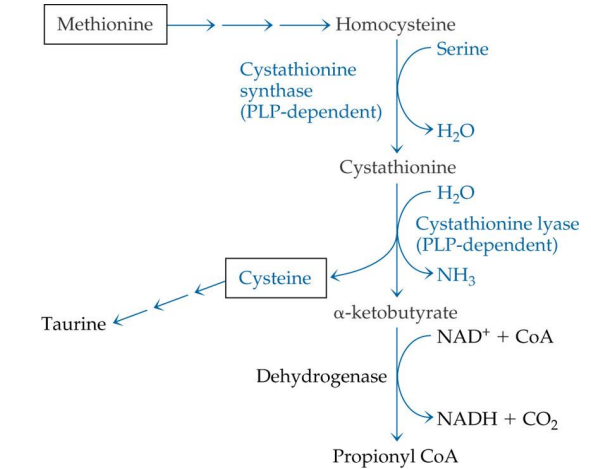
Cysteine can convert to?
Taurine (no PLP needed)
B6 role with neurotransmitter?
involved in decarboxylation
in which reactions is B6 involved regarding neurotransmitter decarboxylation?
Glutamate —> GABA (via glutamate decarboxylase)
Tryptophan —> serotonin (decarboxylation reaction)
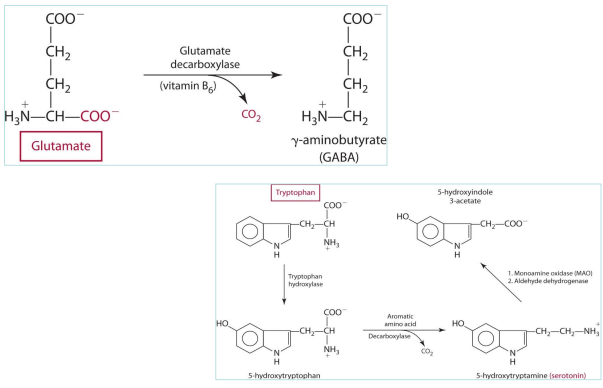
Glutamate -> GABA uses what
Glutamate decarboxylase (B6)
homocysteine (from methionine metabolism) produces what? (effect)
toxic effect on arterial wall (atherosclerosis)
S-hydroxytryptophan -> S-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) uses what
Aromatic AA & Decarboxylase (PLP)
homocysteine is metabolized by what vitamins?
B6, B12, Folate
regarding heme synthesis, what form of B6 is needed?
PLP
how is PLP involved in heme synthesis
required for amino-levulinic acid synthase (uses glycine and succinyl CoA to synthesize delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA))
What does amino-levulinic acid synthase do?
uses glycine and succinyl CoA to synthesize delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)
ALA is used to synthesize ___
porphobilinogen
porphobilinogen is a precursor for?
porphyrin synthesis which will results in formation of heme
other functions of B6? (5)
Formation of niacin from tryptophan also requires PLP as a cofactor for a rate limiting enzyme
Involved in formation of histamine from histadine
Synthesis of dopamine from taurine
Steroid receptor binding activity is modulated by presence of B6
serine synthesis and metabolism (shown in folic acid lecture)
B6 and niacin?
Formation of niacin from tryptophan requires PLP as a cofactor in rate limiting enzyme (kynureninase)
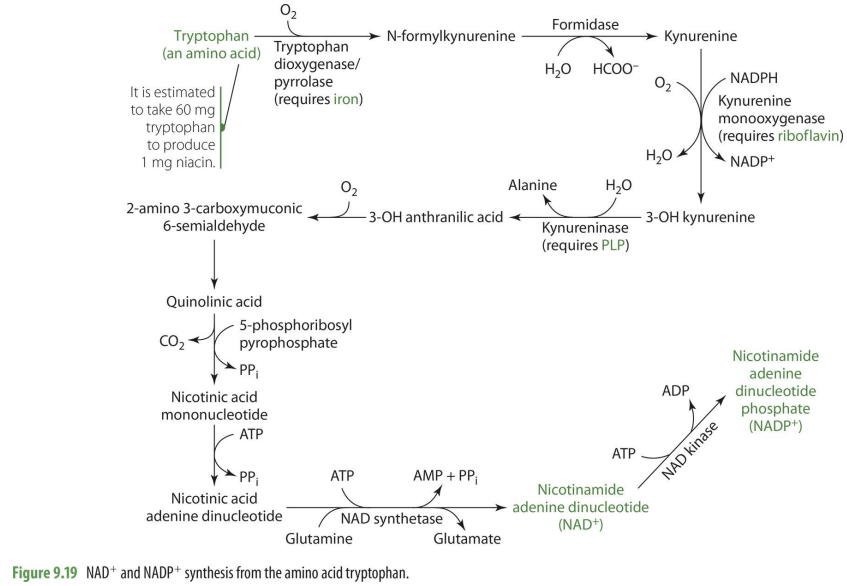
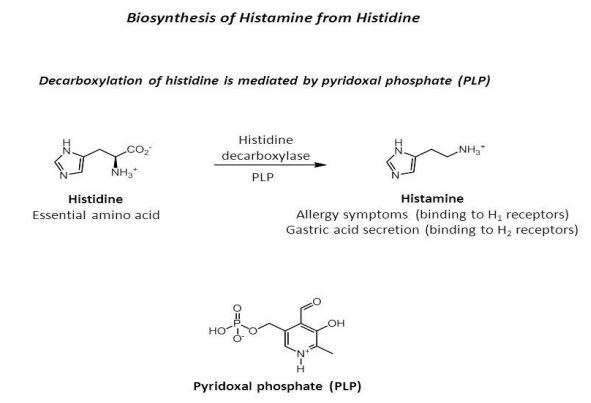
B6 is involved in formation of ___ from histidine
histamine
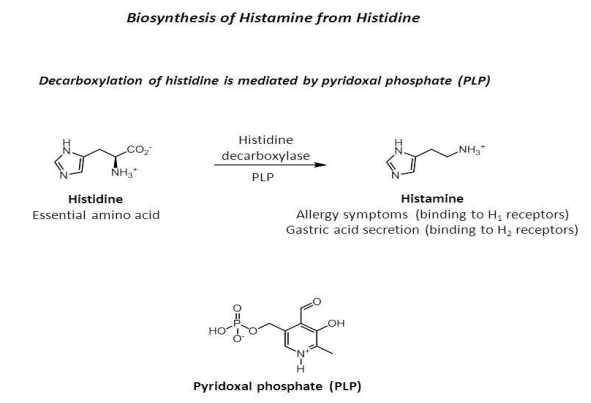
what enzyme is needed to form histamine from histidine (dependent on?)
histidine decarboxylase (PLP)
B6 is involved in the synthesis of ___ from taurine
dopamine
What is modulated by B6
steroid receptor binding
what covered in folate lecture uses B6 (for its synthesis and metabolism)
serine
glycogen degradation and B6?
PLP is needed for glycogen phosphorylase activity
Glycogen degradation: ___ from PLP bind to form ____
phosphate
glucose-1-phosphate
major metabolite of B6?
4-pyridoxic from PL oxidation
4-pyridoxic is excreted how?
excreted via urine
4-pyridoxic excretion is indicative of
intake levels
Large doses of PN can result in....
intact urinary losses & 5-& 4- pyridoxic acid
excretion via feces
little or no excretion
RDA for men & women
Men 19-50: 1.3mg
men 51<: 1.7mg
women: 19-50: 1.3mg
women 51<: 1.5mg
RDA for prg & lact & daily value
pregnancy: 1.9mg
lactation: 2.0mg
DV: 2mg
Deficiency of B6 can result in (5)
• Microcytic hypochromic anemia
• Seborrheic dermatitis
• Convulsion, depression, confusion
• Reduced immune response
• Peripheral nerve damage
Toxicity of B6 (causes what?)
• Sensory & peripheral neuropathy
• UL = 100 mg
Alcohol effects formation of what
PLP formation
L-DOPA-medication used to treat Parkinson's disease and anti-tuberculosis medication isoniazids affects of PLP
-Reduce blood concentration of PLP
-require supplementation of B-6
assessment of adequacy for B6? (6)
Tryptophan loading test
xanthurenic excretion
Plasma PLP concentrations
urinary B6 & 4-pyridoxic
enterocyte transaminase activity (before & after)
transaminase enzymes (w/ B6 bolus)