Medications and Behavior Exam 1, Becknell (Chapters 1-4)
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
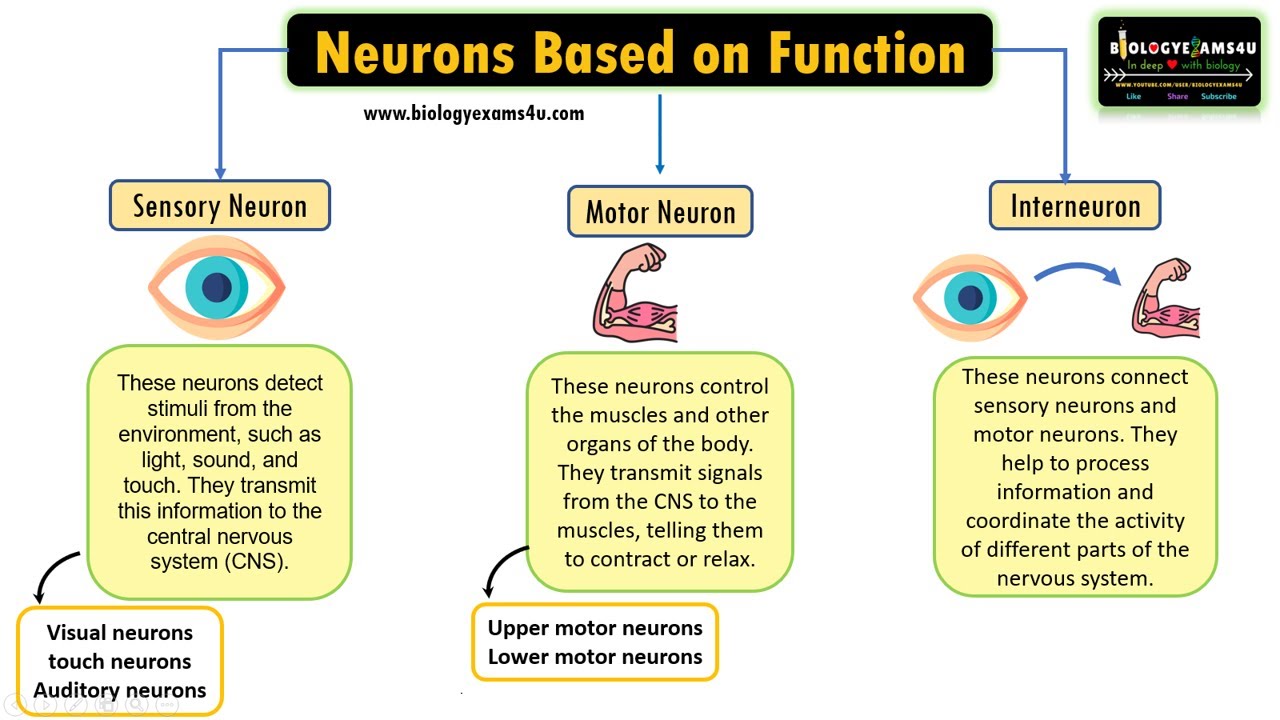
classes of neurons
sensory neuron (afferent): PNS to CNS
motor neuron (efferent): CNS to PNS
interneuron: bridge communication between the two in the CNS
Axon Hillock
point on the soma where the axon and electrical signal both originate
Neurotransmitter Reuptake
neurotransmitter is reabsorbed by the axon that released it
Ion Channels
'gates' that can be open or closed, allowing ions to pass through
Resting Potential
electrical charge across the cell membrane of a resting neuron
Graded Potential
a shift in the electrical charge in a tiny area of a neuron
Action Potential
complete depolarization of the neuronal membrane from -70 mV to approximately +40mV
depolarization: Na+ ions flow into cell creating positive charge
repolarization: brings cell back to resting potential »» Na channels close + potassium channels open causing the cell to lose more K+ than it gains (bc there is more K+ inside the cell than outside the cell)
hyperpolarization: makes cell more negative than its typical resting membrane potential (as action potential passes through, potassium channels remain open allowing more K+ ions to exit the cell)
*depolarization, repolarization, + sometimes hyperpolarization
What happens during an action potential?
Node of Ranvier
small gap between myelinated segments where axonal membrane is exposed; increase speed of impulses
Ionotropic Receptor
when a receptor directly controls an ion channel
Metabotropic Receptor
when a receptor is not part of the ion channel and other proteins are involves in controlling the ion channel; utilizes second messengers
Phosphoralation
process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
a slight depolarization of a postsynaptic cell, bringing the membrane potential of that cell closer to the threshold for an action potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
an inhibitory hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane of a synapse caused by the liberation of a neurotransmitter by the terminal button
Neural Integration
neuron combines multiple inputs (inhibitory + excitatory synaptic potentials) to generate a single output (action potential)
*impacts rate of firing of a neuron
Presynaptic Facilitation
presynaptic axon releases neurotransmitter that slightly depolarizes the axon terminal of the second neuron; due to chemical action at axoaxonic synapse (one axon synapses w/ another axon)
*more neurotransmitter is released
red = facilitation, gray = inhibition
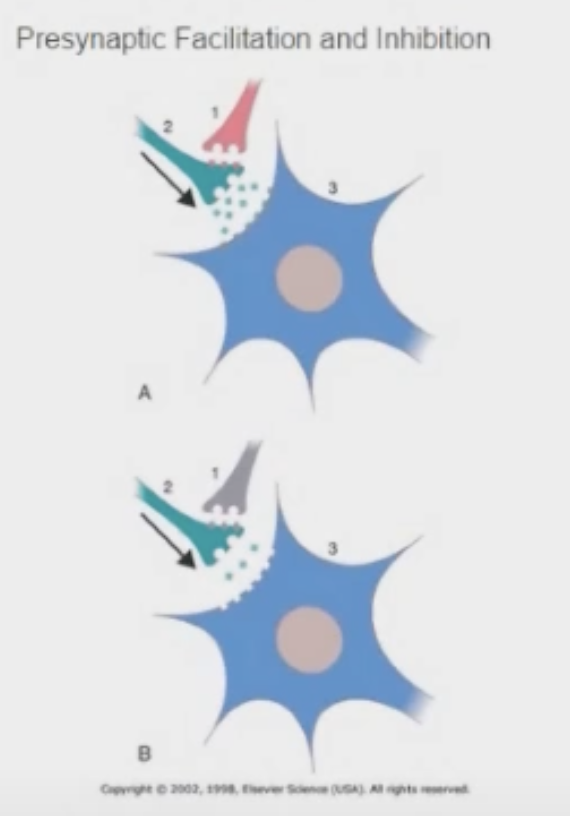
Presynaptic Inhibition
action of an axoaxonic synapse at a synaptic terminal that decreases the neurotransmitter released by presynaptic membrane
Autoreceptors
receptors that respond to the released transmitter by inhibiting further synthesis and release
Heteroreceptors
receptors located on the presynaptic button that are sensitive to a neurotransmitter from another neuron
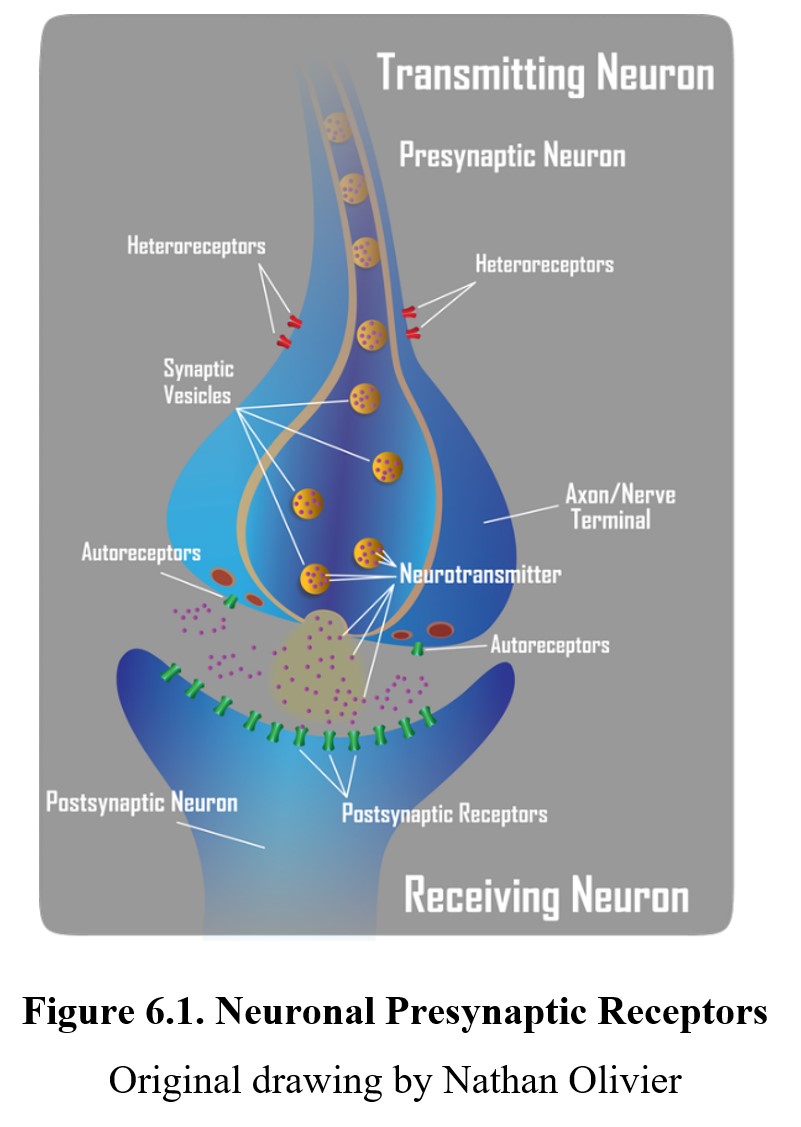
Neuromodulators
a substance produced and released by neurons or glia that alters cell functioning; they may alter the effects of neurotransmitters at synapses and may act at greater distances from the releasing cell, unlike neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine
What was the first neurotransmitter to be discovered?
- Acetylcholine (excitatory)
- Norepinephrine (both)
- Dopamine (inhibitory)
- Serotonin (inhibitory)
- GABA (inhibitory)
- Endorphins (inhibitory)
- Glutamate (excitatory)
- Glycine (inhibitory)
- Substance P (excitatory)
- Anandamide (inhibitory)
- Adenosine (inhibitory)
List of Major Neurotransmitters/Neuromodulators
synthesized + stored in presynaptic neuron
released into the synapse when neuron fires
cause a postsynaptic effect after it interacts with a receptor
there must be some mechanism for degradation or reuptake
****What are the qualifications of a neurotransmitter?
Long-Term Potentiation
strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity
*postsynaptic membrane can now more readily depolarize when stimulated
Excitotoxicity
excessive exposure of postsynaptic neurons to glutamate
Nocioceptors
pain receptors to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
Neocortex
"new cortex"; outermost surface of the brain/cortex and most recently evolved
Limbic System
portion of the brain most closely associated with emotional expression and motivation
Reticular Activating System
the part of the brain that is involved in attention, sleep, and arousal
mesolimbic-cortical system
involved in motivation, reward, reinforcement; mediates the reinforcing effects of eating, sex, and addictive drugs
system of dopamine-containing neurons that originate in the ventral pons (VTA), project through the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and septum, and terminate in the frontal cortex (PFC),
Orexin
neurotransmitter secreted by the hypothalamus; triggers hunger
Pituitary Gland
produces and secretes a variety of essential hormones
Tardive Dyskinesia
severe motor disorder characterized by facial tics, lip smacking, tongue extensions, and rapid eye blinking; can be cause by long-term use of antipsychotic medication
Pharmacokinetics
science of how drugs are:
absorbed
distributed to body tissues
and eliminated from the body after metabolism
Chemical Name
describes chemical composition + molecular structure of a drug
Brand Name
the patented trade name for a drug (Prozac)
Generic/Trade Name
a medication that can be made by many different companies; costs less than brand-name medicines but have to be pharmacologically equivalent (fluoxetine)
Drug Absorption
mechanisms by which drugs get into the blood stream and distributed throughout the body
- Orally
- Inhalation
- Intravenous
- Intramuscular
- Transdermal
- Subcutaneous
- Intraperitoneal
What are the different ways to administer a drug?
Blood Brain Barrier
mechanism that prevents certain molecule from entering the brain but allows others to cross
Depot Binding
drug binds to inactive sites + re-enters the bloodstream due to concentration gradient when some of the other supply is secreted
*delays drug’s elimination from the body; prolongs effects
Tissue Equilibrium
when the concentrations of a drug in the blood and tissues are essentially the same
Cytochrome P450
integral enzymes involved in the metabolism of drugs; produced by cells in the liver
Dose Response Curve
a graph of the magnitude of an effect of a drug as a function of the amount of drug administered
Respiratory Depression
decrease in respiratory rate
Tolerance
a progressive decrease in a person's responsiveness to a drug
Cross-Tolerance
tolerance for a substance one has not taken before as a result of using another substance similar to it
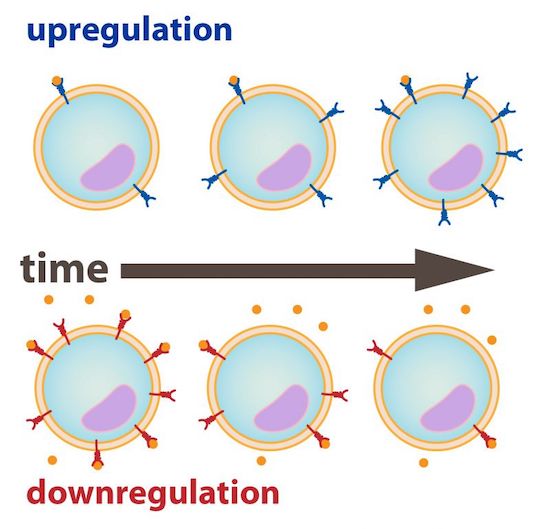
Downregulation
# neurotransmitter receptors (and synthesis) on cell surface decreases due to prolonged stimulation from other neurotransmitters/molecules
*can be caused by drug action on target receptors
State Dependent Learning
learning that becomes associated with the conditions under which it occurred, so that it is best remembered under the same conditions
Therapeutic Index
the ratio between the toxic and therapeutic concentrations of a drug
Placebo
a fake drug used in the testing of medication
Double-Blind Procedure
an experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant (blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo
Pharmacodynamics
what the drug does to the body
Agonist
drug that facilitates neurotransmission
Antagonist
a drug that inhibits neurotransmission
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
block the serotonin reuptake transporters so that there is more serotonin available in synapses
*** Catecholamines (DEN)
Dopamine
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
*group hormones + neurotransmitters that play a role in body’s stress response
- 5-Hydroxytriptamine (5-HT)
- Monoamine, but not a catecholamine
- Receptors: mostly metabotropic
- Synthesized from: tryptophan
*** Serotonin
Nigra Striatal: substantia nigra -> caudate nucleus / putamen; implicated in Parkinson's
Mesolimbic: reward, nucleus accumbens
Mesocortical
Tuberoinfundibular: prolactin (breast hormone)
**** Dopamine Pathways
1st neurotransmitter discovered (advanced by Otto Loewi)
receptors: muscarinic (metabotropic), nicotinic (ionotropic)
synthesized from: choline
Acetylcholine (***receptors)
- Synthesized from: tyrosine
- Receptors: metabotropic
- Monoamine Oxidase breaks it down
Norepinephrine
#1 excitatory neurotransmitter
Involved in long-term potentiation
Receptors = ionotropic + metabotropic
Glutamate
#1 inhibitory neurotransmitter
Receptors = ionotropic + metabotropic
Synthesized from glutamate
GABA
peptide; associated with pain ("P"ain)
Substance P
- Rostral (toward beak), Caudal (toward tail)
- Anterior (front), Posterior (back)
- Superior (higher), Inferior (lower)
- Dorsal (toward back), Ventral (toward stomach)
- Lateral (away from middle), Medial (toward middle)
- Proximal (toward body), Distal (toward end of limb)
Anatomical Directions
What neurotransmitters are monoamines?
Serotonin
Dopamine
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
*single amine group connected to aromatic ring
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
measure of fat solubility
- Philic = love, phobic = repulsion
- Liver makes items lipophilic (fat soluble), and detoxifies xenobiotics
- Kidneys make items hydrophobic for excretion
- Drug metabolized in liver and excreted through kidneys
*** Metabolism/excretion and suffixes
Blood-Brain Barrier
makes it more difficult for substances to pass through, but fat soluble ones get to brain by diffusion
Drug/Elimination Half-Life
the time it takes for the amount of drug in the body to be reduced by half
- How much of a drug do we give?
- Can't give maximum amount for maximum effect, all drugs have a therapeutic window
Dose-response relationship
Threshold Dose
minimally effective dose, just large enough to produce detectable change
Maximum Dose
greatest degree of response achievable with drug
- High: take more for effects (benzodiazepines)
- Low: take less for effects (lithium carbonate, barbiturates); high risk of toxicity
*** High vs Low Therapeutic Index
Opiates
What class of drugs has the fastest tolerance?
ETOH --alcohol dehydrogenase-> acetaldehyde --alcohol dehydrogenase-> acetic acid -> CO2 and H2O
*** Process of alcohol breakdown
*** Process of alcohol tolerance
Increased ETOH consumed -> increased liver enzymes -> increased ETOH tolerance
*Metabolic tolerance
***ETOH
ethyl alcohol, drinkable alcohol
"poop out"
Fun term: Prozac =
Cellular Tolerance
cells adapt to repeated exposure to drugs
Metabolic Tolerance
metabolic system becomes more efficient at processing + eliminating a substance over time (after repeated exposure to a drug)
*reduced effect over time
Associative Tolerance
tolerance developed through CC »» environmental cues are significant to drug administration
*new environment »» higher chance of overdose
Behavioral Tolerance
animals intoxicated with ETOH before learning a motor task will perform better on that task when "under the influence"; called state-dependent learning
- Associative: classical
- Behavioral: operant
What types of conditioning are associative and behavioral tolerance?
Noecebo
negative beliefs cause harmless substance to produce (supposed) negative effects
*opposite of placebo
- Sleep
- Interests
- Guilt
- Energy
- Concentration
- Appetite
- Psychomotor
- Sex/suicide
***SIGECAPS
SSRI's (PaPaLZaC-FaPESaC)
> Prozac - fluoxetine
> Paxil - paroxetine
> Lexapro - escitalopram
> Zoloft - sertraline
> Celexa - citalopram
SNRI's (EPCaR-VaDaDaM)
> Effexor - venlafaxine
> Pristiq - desvenlafaxine
> Cymbalta - duloxetine
> Remeron - mirtazapine
Atypicals (WaDE-BaTaK)
> Wellbutrin/Zyban - bupropion
> Desyrel - trazodone
> Esketamine - ketamine
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TEPA-IANaC)
> Tofranil - imipramine
> Elavil - amitriptyline
> Pamelor - nortriptyline
> Anafranil - clomipramine
Mood Stabilizers and Anticonvulsants
> Lithium
> Neurontin
> Depalcote
> Lyrien
< Topomax
< Abilify
< Tegretol
MAOI's
> Nardil
> Marplan
***Antidepressants/Mood Stabilizers (be able to match/recognize these)
prevalence = 2:1 women:men, annual 10%; lifetime 17%
onset = late adolescence or early adulthood
depression prevalence + onset
Rx
exercise
therapy/counseling
TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)
ECT (Electroconvulsive therapy)
deep-brain stimulation
Depression tx:
- Low thyroid
- Low vitamin D
Rule-outs for depression:
- Low monoamine = low neurotransmitters
- Initial evidence: effective drugs increased these levels
- Low monoamines due to downregulation as a result of increased autoreceptor activity
*** Monoamine Hypothesis:
- Lag time between drugs and effects was an issue
- Neuronal changes: result of BDNF, key protein which is growth factor for neuron survival, receptor growth, and neurogenesis
- Mechanism: BDNF and downregulation of monoamine autoreceptors
- Stress increases cortisol which leads to BDNF downregulation
*** Revised Monoamine Hypothesis:
BDNF
brain derived neurotrophic factor; essential for neuron synthesis, growth, and survival
Ronald Dumon's contribution:
contributed to understanding of BDNF
*BDNF »» "Miracle Gro for the brain"
Tricyclic Antidepressants
accidental discovery, originally for schizophrenia
a dirty drug
increase BDNF synthesis
Dirty Drug
drugs with bad side effects
- ***Block acetylcholine receptors, causing anticholinergic effects
- Block histamine receptors
- High overdose potential
Tricyclic side effects:
Anticholinergic Effects
dry mouth, dizziness, hypotension, constipation, etc. (less lubricant all over body typically)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors:
block the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down monoamine neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine
*accidental discovery, originally for tuberculosis