Scientific Notation, Significant Figures, and Measurement Units in Science
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Unit
A unit is a standard, agreed on quantity by which other quantities are measured.
Scientific Notation
A method to write large and small numbers more compactly.
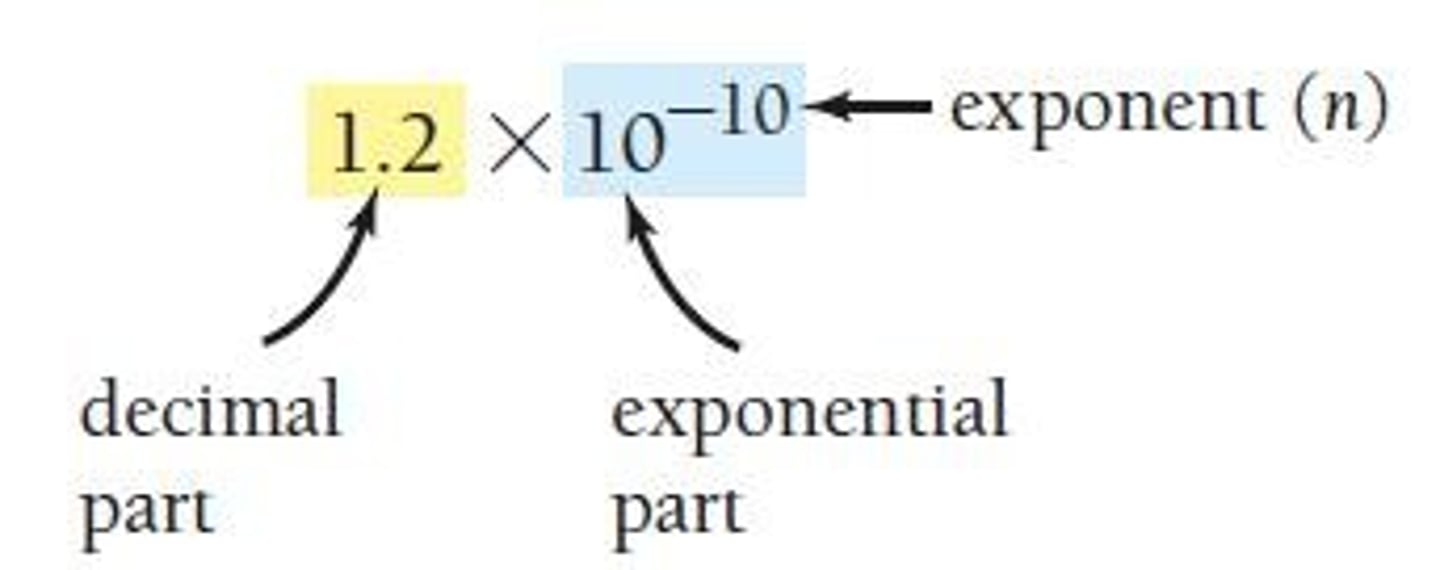
Positive Exponent
Means 1 multiplied by 10 n times.
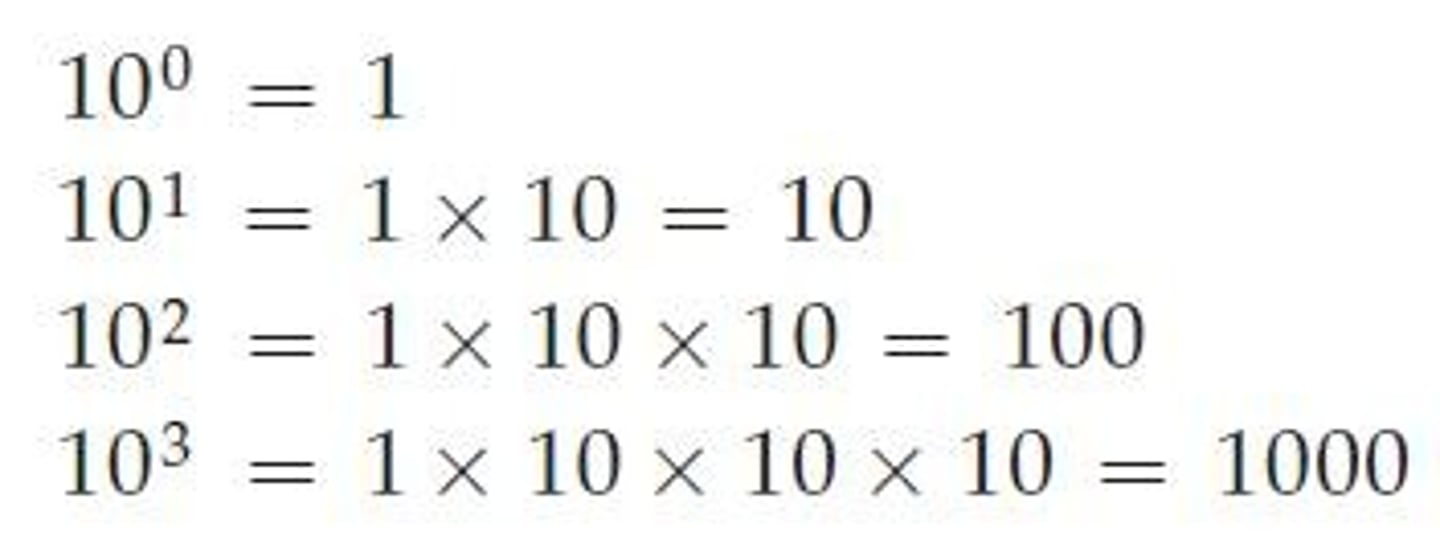
Negative Exponent
Means 1 divided by 10 n times.
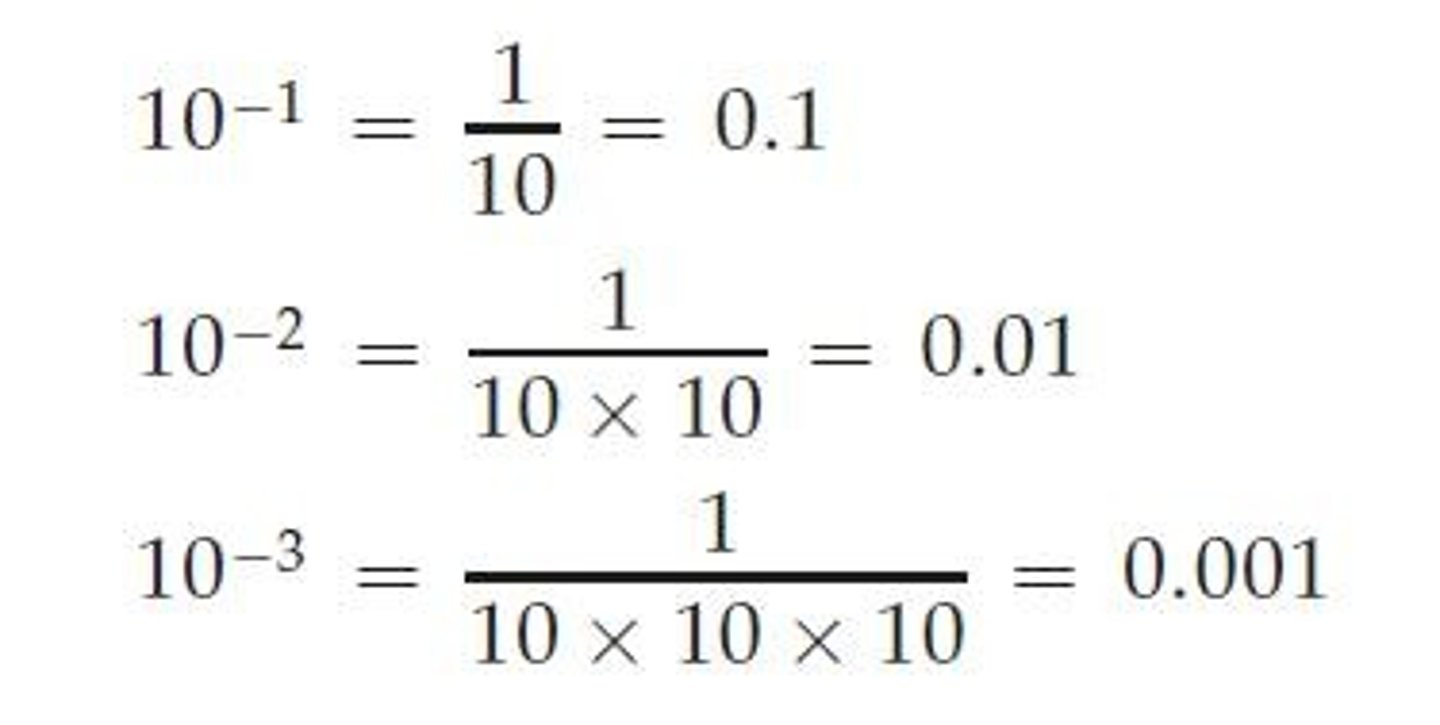
Decimal Part
The part of a number in scientific notation that is between 1 and 10.
Exponential Part
The part of a number in scientific notation that indicates the base (10).
Exponent Part
The part of a number in scientific notation that indicates how many times to multiply or divide by 10.
Population of China in 2017
Approximately 1,387,000,000 people, expressed in scientific notation as 1.387 x 10^9 people.
0.00000867 in Scientific Notation
Expressed as 8.67 x 10^-6.
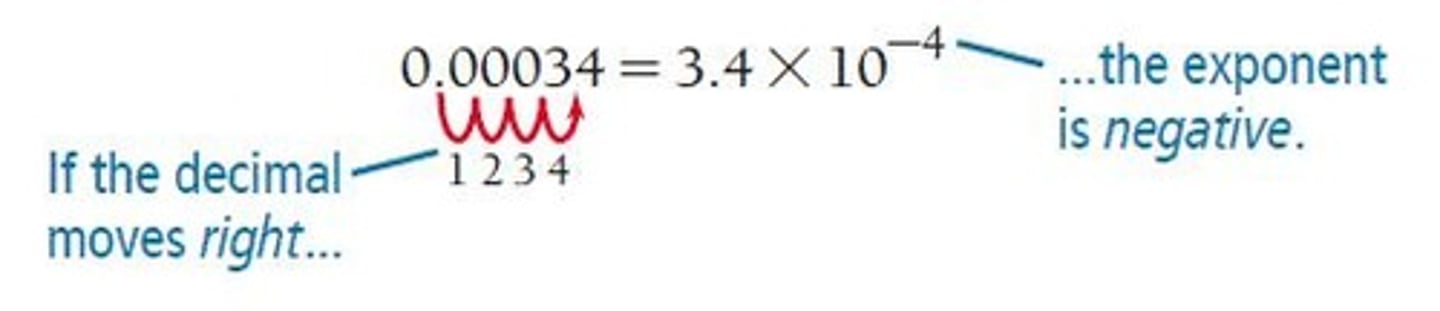
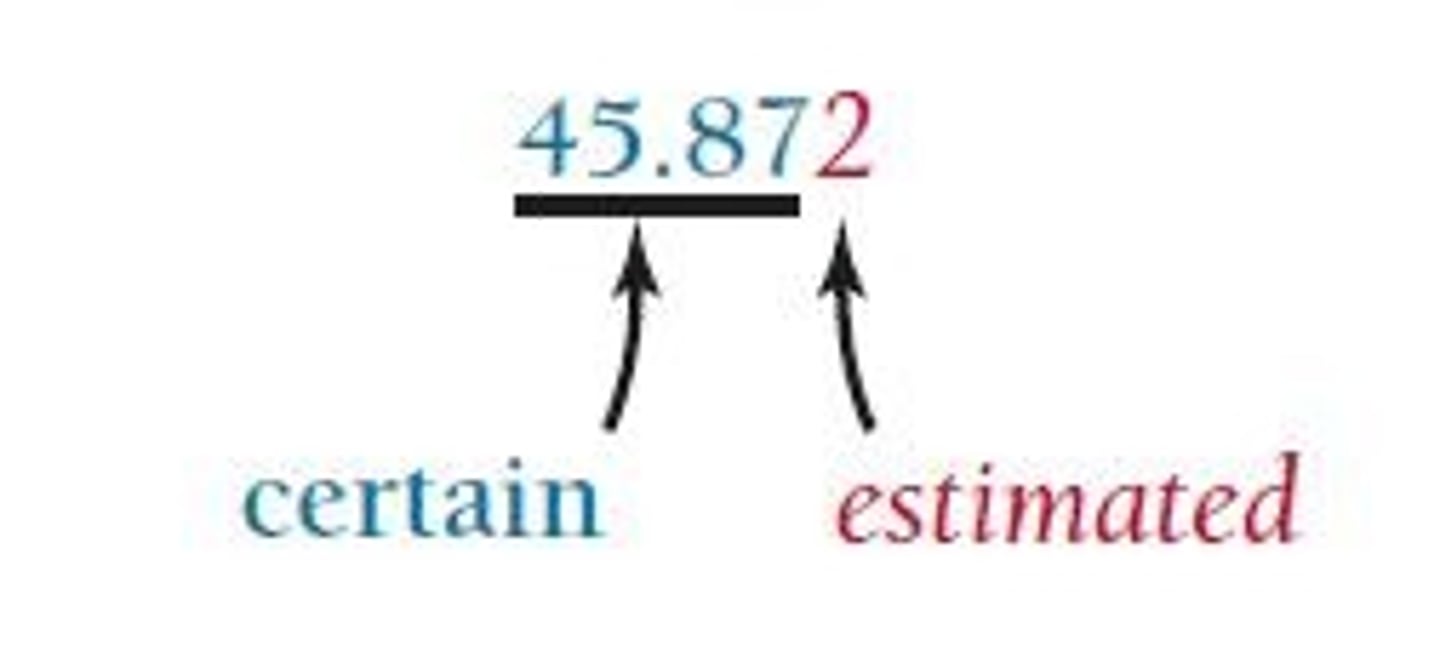
Precision in Measurement
The number of reported digits reflects the precision in the measurement.
Average Global Temperature Increase
Reported as 0.7 °C, meaning 0.7 ± 0.1°C.
Significant Figures
The non-place-holding digits in a measurement that represent the precision of a measured quantity.
Leading Zeros
Do not add to the precision of the measurement.
Trailing Zeros
Add to the precision of the measurement when they follow a decimal point.

Measurement of Copper Sulfate Salt
The correct reading is 1.3 g, estimated from a balance with markings every 1 g.
Measurement of Pistachio Nut
The correct reading is 1.26 g, estimated from a balance with markings every 0.1 g.
Significant Figures in 350
350 = 3.5x10^2 (two significant figures), 350 = 3.50x10^2 (three significant figures).
Uncertainty in Measurement
Indicated by the last reported digit.
Decimal Point Movement
If moved to the left, the exponent is positive; if moved to the right, the exponent is negative.
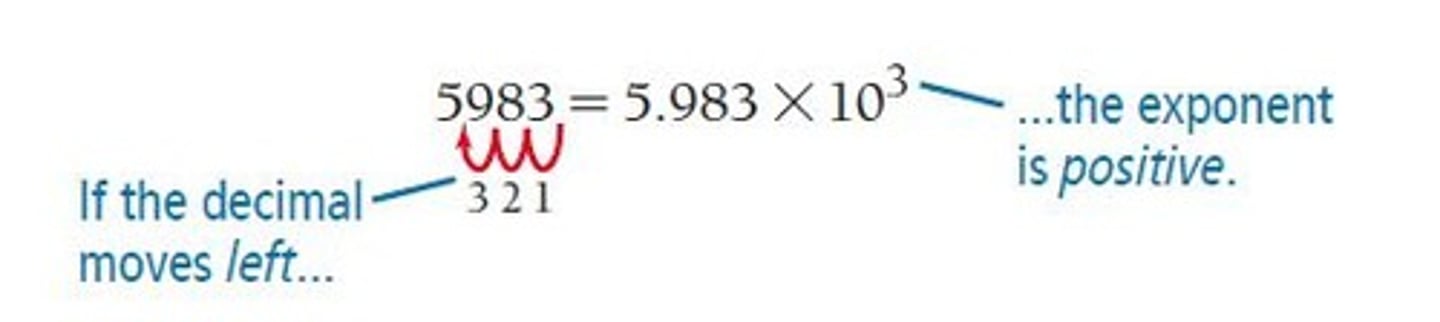
Cumbersome Numbers
Many zeros in large or small numbers make them cumbersome to write.
Example of Temperature Reporting
The temperature rise could be as much as 0.8 °C or as little as 0.6 °C.
Exact Numbers
Numbers that have an unlimited number of significant figures.
Defined Quantities
Quantities that are exact, such as the number of centimeters in a meter.
Ambiguous Significant Figures
Numbers like 2100 that can have different significant figures based on context.
Rounding Rules
Round down if the last digit dropped is 4 or less; round up if it is 5 or more.
Addition and Subtraction Rule
The quantity with the fewest decimal places determines the number of decimal places in the answer.
Multiplication and Division Rule
The quantity with the fewest significant figures determines the number of significant figures in the answer.
SI Units
The International System of Units used for scientific measurements.
Mass
A measure of the quantity of matter within an object.
Weight
A measure of the gravitational pull on an object, calculated as W = mg.
Kilogram
The base unit of mass in the SI system, defined as 1000 grams.
Gram
A common unit of mass defined as 1/1000 of a kilogram.
Decimal Point Significance
A decimal point indicates that trailing zeros are significant.
Significant Figures in Scientific Notation
The number of significant figures can change based on how the number is expressed in scientific notation.
Calculations with Significant Figures
In calculations involving both multiplication/division and addition/subtraction, complete steps in parentheses first.
Example of Rounding
To round 2.349 to two significant figures, it becomes 2.3.
Example of Addition
3 + (1.25) = 4.25 rounds to 4 (one significant figure).
Example of Division
18/12 = 1.5 (two significant figures).
Significant Figures in 2100
2100 can be ambiguous without a decimal point; with a decimal, it has 4 significant figures.
Measurement Systems
The two most common systems are the English system and the Metric system.
Integral Numbers in Equations
Integral numbers that are part of an equation are considered to have an unlimited number of significant figures.
Example of Significant Figures
58.31 has 4 significant figures.
SI Prefix Multipliers
They change the value of the unit by powers of 10.
1 km
1000 m = 10^3 m
1 ms
0.001 s = 10^-3 s
Derived units
A derived unit is formed from other units.
Volume
Any unit of length raised to the third power.
Density
Mass per unit volume.
Speed
Distance covered per unit time.
Dimensional analysis
Using units as a guide to solving problems.
Conversion factor
A quotient with the desired unit on top and the given unit on the bottom.
1 in.
2.54 cm
1 ft
12 in.
Velocity of a car
65 km/hr = 18 m/s
Cubic centimeters (cm3)
When converting, raise the conversion factor to that power.
Density of a substance
The ratio of its mass to its volume.
Units for density
g/cm3 or g/mL
Density of water
1 g/mL
Density of mercury
13.6 g/mL
Density of the Dead Sea
1.24 g/mL
Density of sea water
1.03 g/mL
Density calculation example
Density = 9.67 g / 0.452 cm3 = 21.393 g/cm3
Volume measurement example
To measure 68.4 g of a liquid with a density of 1.32 g/cm3, measure 0.052 cm3.
Mass (m)
35 mg
Density (d)
0.788 g/cm3
Solution Map for density
mg -> g -> cm3
1000 cm3
1 L
Density of Platinum
21.4 g/cm3