L15: Rapid Evolution of Pathogens
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
large scale patterns example:
immune escape and variable outbreak size of seasonal flu A
antigenic drift:
a slow and gradual change in the genotype of a virus
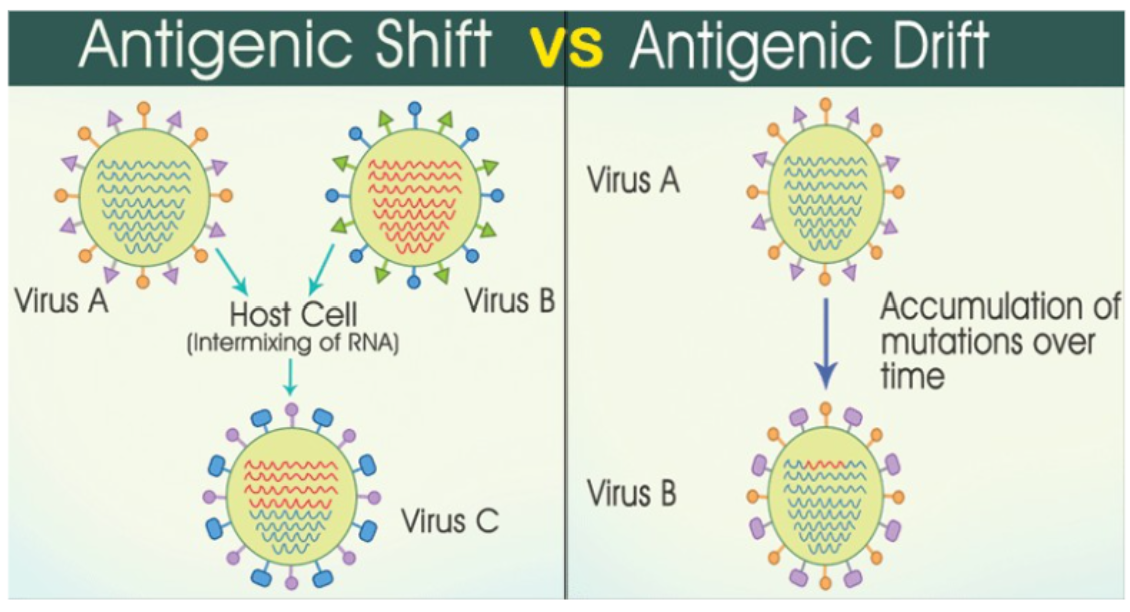
antigenic shift vs antigenic drift
shift: virus A and virus B intermix of RNA to create an all new virus C
drift: virus A with the accumulation of mutations over time makes virus B
the co-occurence of animal species can …
promote coinfection
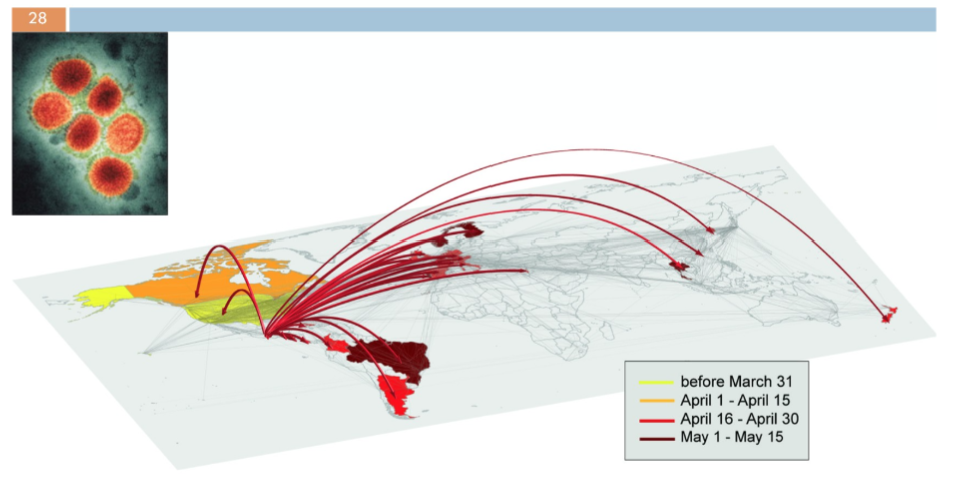
example of rapid geographic spread:
H1N1 swine flu that emerged in Mexico in 2009 and spread rapidly
for antibiotics there is a need to …
constantly innovate new drugs and mechanisms to attack bacteria
why are vaccines more manageable?
they have a long shelf life, sometimes we have to update them
six reasons why antimicrobial resistance is a global concern:
AMR kills, AMR hampers the control of infectious diseases, AMR threatens a return to the pre-antibiotic era, AMR increases the costs of health care, AMR jeopardizes health-care gains to society, AMR threatens health security (and damages trade economies)
resistance strains (mutants) will increase quickly if …
the benefits (ability to infect treated hosts) outweigh the costs (reduced fitness in untreated hosts)
if there are many treated hosts (wide use of antimicrobials)