SL Chem - Unit #1: Electronegativity
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Electronegativity
The ability for an atom to attract and hold onto electrons
Electronegativity trend on the periodic table
On the periodic table it electronegativity increases by going up diagonally towards the top right (Uses the Pauling Scale)
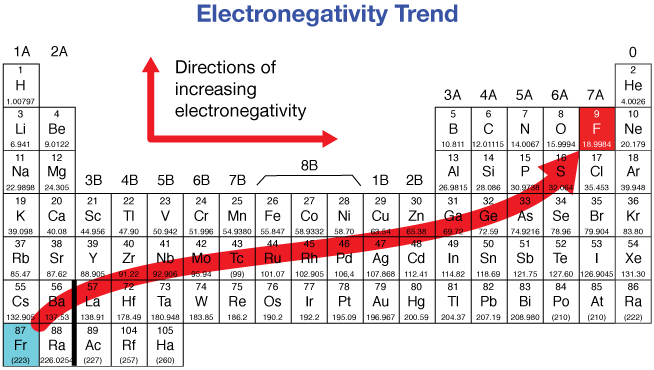
Electronegativity trends going down the group
It decreases down a group
This is because of a greater shielding affect and lower affective nuclear charge making the valence electrons more loosely held and easier to rid of (rather than attracting electrons)
Electronegativity trends going across the period (to the right)
It increases as we go across the row
Because more protons in the nucleus creates a stronger effective nuclear charge that attracts and holds onto electrons a lot better
Electronegativity for Noble Gases
Noble gasses are stable elements (already have a full valence shell) that don’t attract any electrons so they have no electronegativity value
Diatomic
Elements that can self stabilize by creating covalent bonds with themselves to create a stable shell
HOFBrINCl
Monoatomic
An element that is naturally found on it’s own because it’s already stable and doesn’t need to bond with anything else to stabilize
All Noble Gases
Pauling Scale
Is the scale that measures the strength of bonds between covalent bonds
Despite being derived from physical quantities (the bonds energy) the electronegativity number itself have no value, they are just used for comparative ways among themselves
Electrostatic Charge
The interaction that between a covalent bond that helps hold them together
Electronegativity Difference In Ionic Bonds
ΔEn ≥ 1.7
The electron is fully transferred between atoms making the dipole moment either ±
Electronegativity Difference In Polar Covalent Bonds
0.5 ≤ ΔEn < 1.7
Electronegativity Difference In Non-Polar Covalent Bonds
0 < ΔEn < 0.5
Non-Polar Covalent
The electron is equally shared between both elements and it’s located in the middles
No dipole Moment
Polar Covalent
The electron is shared unbalanced between the two, the atom with the higher electronegativity pulls the electron towards itself more than the other
It has partial dipole movement
Slight negative end: “δ− “
Slightly positive end: “δ+”
Which End is δ− / δ+
the element that has a higher electronegativity is the δ- end of the bond