Understanding individuals and groups
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
1
New cards
What is fundamental attribution error?
Overemphasise dispositional (internal) explanations for other’s behaviour rather than situational (external)
2
New cards
What is the person-situation controversy?
Personality traits are not good at predicting how people will behave in a given s
3
New cards
Situational factors do no explain behaviour more than personality traits
Funder & Ozer 1983
4
New cards
Studies for examining personality need to take a… approach
Aggregate (Epstein, 1973)
5
New cards
Fleeson says behaviour is… and… (2001)
Stable/unstable
6
New cards
What is rank order stability?
Set order we expect things to be (introvert vs extrovert at bar, friends…)
7
New cards
Funder and Colvin 1991-Discuss with stranger x2
Coded 62 features/45 correlated across both sessions/20 significantly differed
8
New cards
Furnham 1981 and Zuckermann 1974 - situations that match
Personality
9
New cards
What is situation evocation?
Unintentional alteration of situation by one’s own presence (Buss, 1987)
10
New cards
What is the replication crisis?
Not studies replicated (2015-67% not replicated)
11
New cards
What is the file drawer effect?
Not significant findings so work not published
12
New cards
Gergen makes a point about how studies are just infact a matter of…
Historical enquiry
13
New cards
3 components of attitudes
Thought/feeling/action (ABC model)
14
New cards
What are the four functions of attitudes?
Knowledge/instrumental/ego defence/value expressive
15
New cards
Direct measures of attitudes
Thurstone’s scale/Guttman’s scalogram/Osgood’s semantic differential/Likert
16
New cards
Indirect methods of measuring attitudes
Physiological measures/implicit association test
17
New cards
Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975 - attitudes are…
Learnt not innate
18
New cards
What is the mere exposure effect?
More exposure to stimuli leads to more attraction (Zajonc 1968)
19
New cards
Repeated exposure effect diminishes after…
10 exposures (Bornstein 1989)
20
New cards
Instrumental conditioning (Kimble 1961)
Responses which yield positive outcomes or eliminate negative outcomes are strengthened
21
New cards
Self perception is… (Bem 1972)
Attitudes are informed by our behaviour and making internal attributions for that behaviour
22
New cards
What is attitude behaviour problem? (La Piere, 1934)
Behaviour not aligning with attitudes (Discrimination for diners on phone VS in person)
23
New cards
What four things did Ajzen and Fishbein 1977 think were involved in attitude and behavioural measures?
Action/target/context/time
24
New cards
What did Fazio 1995 say about attitude strength?
Stronger the attitude, the more likely we are to enact on it
25
New cards
Those with low self monitors have a…
Higher attitude behaviour correlation
26
New cards
What can break the attitude behaviour link? (Oskamp, 1984)
Habits
27
New cards
What is the theory of reasoned action?
Behaviours controlled by attitudes and subjective norms
28
New cards
What is theory of planned behaviour?
Behaviour controlled due to attitudes, subjective norms and perceived behavioural control
29
New cards
What are cognitive consistency theories?
Attitudes change to be consistent with each other
30
New cards
What is cognitive dissonance?
Tension between attitudes
31
New cards
What is forced compliance? (Festinger and Carlsmith 1959)
Forced into making a choice
32
New cards
What is effort justification?
Lots of effort = rate goal as more positive
33
New cards
What is selective exposure hypothesis?
Avoid information that goes against beliefs
34
New cards
The latitude of acceptance is…
Self perception
35
New cards
The latitude of rejection is…
Cognitive dissonance
36
New cards
What are the three main types of behavioural request?
Foot in the door/door in the face/low ball
37
New cards
Foot in the door stats
53% more likely to accept large request after smaller request 22%
38
New cards
What is sunk cost fallacy?
Person is reluctant to give up on something when they have put so much effort into it
39
New cards
Yale Attitude Change Approach says people are persuaded based on three things
Source/message/audience
40
New cards
What attributes of the source of the message are important for attitude change?
Credibility/appearance/similarity
41
New cards
What attributes of the message itself is important?
One or two sided/Fact vs feeling
42
New cards
What is protection motivation theory?
Based on threat appraisal and coping appraisal/response is dependent on personal threat
43
New cards
What is the dual process models of persuasion?
Central and peripheral route
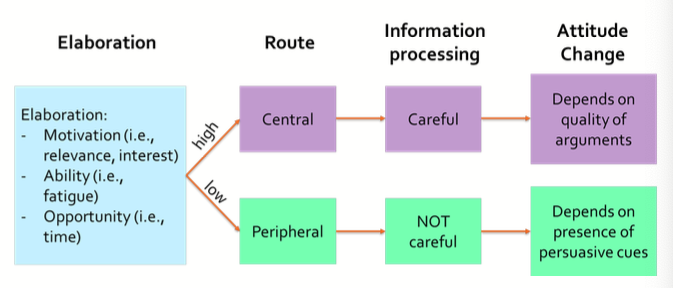
44
New cards
What is social influence?
How people affect each other
45
New cards
What is conformity?
Change in beliefs, opinions and behaviours as result of pressure from others
46
New cards
What is compliance?
Responding favourably to explicit request by another
47
New cards
What is obedience?
Submitting to demands of another person in authority
48
New cards
What is automatic mimicry?
Copying those around us in a spontaneous and automatic sense
49
New cards
What is ideomotor action?
Merely thinking about an action makes it more likely
50
New cards
What was Sherif’s auto kinetic effect experiment?
Visual illusion where light appears to move/converge on a group norm
51
New cards
What is informational social influence?
Ambiguous situation leads us to look to others for guidance
52
New cards
What did Neighbors et al 2007 find about misperceived social norms?
Students tend to overestimate descriptive norms for student drinking
53
New cards
What was Asch’s conformity experiment?
Match line to line of same length
54
New cards
Asch’s experiment stats
75% gave at least 1 incorrect answer/37% of all responses were conforming
55
New cards
What is normative social influence?
Conform to social norms to avoid social sanctions
56
New cards
What is the difference between normative VS informational social influence?
Norm=fulfil others expectations/Informational=conformity under acceptance of evidence about reality which has been provided by others
57
New cards
What kind of factors are situational?
Group size/group unanimity/expertise and status
58
New cards
In order to influence the majority, the minority needs to have a..
Consistent and unanimous response
59
New cards
What is psychological reactance?
Motivational state that resists social influence
60
New cards
What is prosocial behaviour?
Behaviour that has positive social consequences and contributes to the physical or psychological well-being of another person. Voluntary and has the intention of helping others
61
New cards
What is helping behaviour?
Intentional and benefits another living being in the group
62
New cards
What is altruism?
Act that benefits another rather than oneself
63
New cards
What six factors are people prosocial because of?
Personal/situational/evolutionary/social and biological/cognitive/consequences of receiving help
64
New cards
What is the diffusion of responsibility?
Someone else will help
65
New cards
What is audience inhibition?
Don’t want to look stupid in front of others
66
New cards
What is self attribution?
Act in a way that aligns with self concept
67
New cards
What is the scrooge effect?
Morality salience increases prosocial behaviour
68
New cards
What is an example of bystander effect?
Kitty Genovese
69
New cards
Mutualism
Benefiting from interactions
70
New cards
What is reciprocal altruism?
Help someone for something in return
71
New cards
What are some direct ways of socially influencing others?
Instructions/reinforcement/conditioning
72
New cards
What are some indirect ways of socially influencing others?
Modelling/vicarious learning
73
New cards
What is a bio-social account of attitude change?
Misattribution of state
74
New cards
What is the bystander calculus model?
Number of bystanders present that will encourage other to help
75
New cards
What are two evolutionary accounts of prosocial behaviour?
Survival of kin/reciprocal altruism
76
New cards
What are 4 social accounts for prosocial behaviour?
Told to do so/rewarding/social norms/own egos
77
New cards
What is Latané and Darley’s cognitive model of prosodical behaviour?
Attend/interpret/assume responsibility/decide
78
New cards
Why are people aggressive?
Personal/situation/evolutionary/social and biosocial/cognitive
79
New cards
What personal factors explain why people are aggressive?
Hormones/personality/gender/alcohol
80
New cards
What situational factors make people aggressive?
Physical environment/cultural norms
81
New cards
What role does crowd bating play in aggression?
Situational/deindividuation/dehumanisation
82
New cards
What evolutionary explanations of aggressions are there?
Psychodynamic theory/ethology/evolutionary social psych
83
New cards
What is the bio-social explanation for aggression?
Arousal + context
84
New cards
What is the frustration-aggression hypothesis?
Frustrating event leads to aggression
85
New cards
What is the catharsis hypothesis?
Way to let of steam or release frustration
86
New cards
What is the excitation transfer model?
Learnt aggressive behaviour+arousal+individuals interpretation of arousal state
87
New cards
What is the general aggression model?
Model that considers the social, cognitive, personality, developmental and biological factors
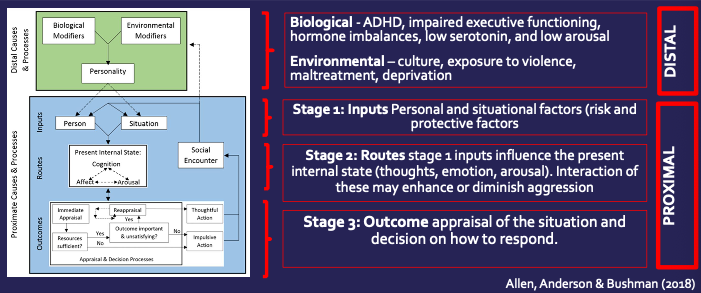
88
New cards
What is the I3 model of aggression?
Affective, behavioural and cognitive
89
New cards
Values come from…
Genes/family/childhood/culture
90
New cards
What is the bleed over effect?
Adjacent values in the value circle
91
New cards
What is the seesaw effect?
Opposite value is negatively effected
92
New cards
What is hypothesis deprivation?
research method that involves temporarily removing or altering a variable in order to test its effect on the outcome of an experiment or study.
93
New cards
What is SVS self report methods?
List of values/rate how important on scale of 1-7
94
New cards
What is a PVQ report method?
Describe a person and ppt identifies which description they align with most on scale of 1-6
95
New cards
Parent who value what trait are most successful at transmitting their values to their children?
Self-transcendence
96
New cards
Values represent what…?
Broad life goals
97
New cards
Values are organised in a circle of….
Motivational conflicts and compatibilities
98
New cards
What are examples of objective cultural variables?
Buildings, music, language…
99
New cards
What are examples of subjective cultural variables?
Norms/values…
100
New cards
When was the birth of anthropology?
End of 19th century