U.S. History Assessment #7 - The Cold War (Topic 2)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Dwight Eisenhower
Party?
Career (know it generally)
What did he want? (2)
How did he hope to achieve this? (2)
Republican (President, 1952-1960)
Career: Military officer, Supreme Allied Commander during World War Two responsible for planning Operation Torch and the D-Day invasion
Worldview: Wanted to deter Soviet Expansion/likelihood of war between the two nations through
Buildup of nuclear arsenals
Fostering of anti-communist alliances
The Soviet Possession of Nuclear Weapons
What did the US do to try to get the upper hand?
What did the USSR do in turn to that?
What did these events show?
The U.S. monopoly on nuclear weapons ended in 1949 when the USSR successfully tested an atomic bomb
The advice coming out of NSC-68 is that the United States now needed to seek a new weapons advantage against the USSR
The US decides it needs to invent an even more powerful weapon
The US invents the hydrogen bomb which is 1,000 times more powerful than the atomic bomb BUT the Soviets develop their own hydrogen bomb in 1953 *showed difficulties in gaining the upper hand*
The Soviet Possession of Nuclear Weapons
What was the significance of the series of events/events?
What did this mean for the people? (3)
What did this cause the creation of?
This creates Mutually Assured Destruction: both nations possess large nuclear stockpiles
National and local governments prepared citizens for a Soviet nuclear attack on the US
Citizens built fallout shelters
Cities + school practiced building evacuations + drills
Construction of the Eisenhower Interstate System
41,000 miles of highway connected US cities
Highways served as a means to evacuate cities during a potential nuclear attack
The Space Race
What started it?
[1957] the USSR used its first ICBM to launch Sputnik (first satellite into space)
The Space Race
What did the US do in return? (3)
There was now a missile gap + the US has fallen behind, so the US
Increasing nuclear weapons production
Passing the National Defense Education Act in 1958 to promote math, science, and technology education and to fund university research
Creating the National Aeronautics & Space Administration (NASA) in 1958
John F. Kennedy
What party?
Main context about him?
What were his ideals? (2)
Democrat
First young, Catholic president & assassinated in his 3rd term, born in MA, served in WWII, rep for MA, senator for MA
Ideals:
Foreign affairs: Soviet Union confrontations → rather than using containment, he wanted to talk and negotiate with the USSR
In promoting the vision of America, cost is not an issue, America is the best
Key Cold War Events of the Kennedy Presidency (4)
Bay of Pigs Invasion 1961
Construction of the Berlin Wall 1961
Cuban Missile Crisis 1962
Nuclear Test Ban Treaty 1963
Bay of Pigs Invasion 1961
Context/US thoughts
Communist Fidel Castro came to Cuba + was supported by the Soviets who were growing expansionist policies and were gaining a foothold in Latin America
US felt threatened bc Cuba is close to Florida
Bay of Pigs Invasion 1961
What does the US do about their opinion + how did it end?
Kennedy decides to push Castro communism + Soviets out of Cuba through CIA missions
CIA recruits Cuban exiles in Florida to launch a coup against Castro → it fails
Bay of Pigs Invasion 1961
Signifigance?
How does it impact Kennedy’s opinions domestically?
Significance:
Cuba will become a new center of confrontation between the US & USSR (Soviet’s intensify their commitment to the country + US fear/anxiety over Cuba intensifies)
Castro remains in power
Kennedy becomes skeptical of CIA covert operations + his military advisors
Construction of the Berlin Wall 1961
What were the vibes of West vs. East Germany/Berlin?
Who created the wall and why?
After the creation of West and East Germany, the two countries developed very differently → people began moving from East Berlin to West Berlin
West G/B = economic growth + prosperity
East G/B = economic stagnation, shortages of food, currency is weak
Stalin controls East Germany, thus, everywhere surrounding West Berlin, he ends up building a wall which stopped immigration → anyone that wanted to pass through would be shot
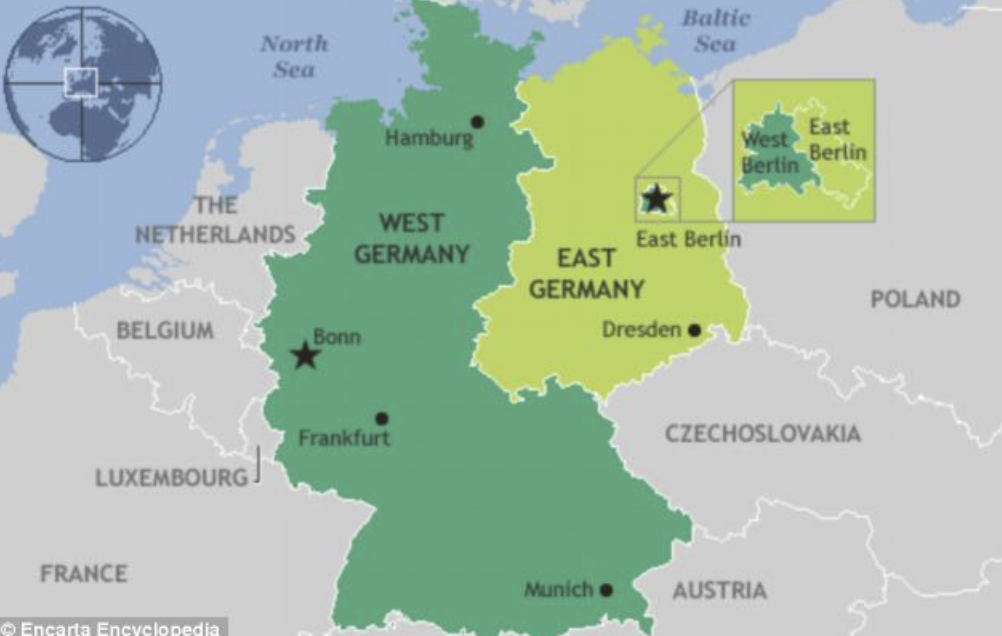
Construction of the Berlin Wall 1961
Signifigance?
The wall is a sign to Kennedy that maybe Kruchev is not as violant and crazy as he thinks → the wall shows that they’re not expanding + he is okay with communist boundaries
Cuban Missile Crisis 1962
What started this
US efforts + Soviet fight backs (2)
What started it:
Americans found out that the Soviets build launch-pads for nuclear missiles on Cuba + are sending boats with missiles to Cuba
US efforts + Soviet fight backs
US blockades Cuba → Soviets ignore blockade
US threatens invasion of Cuba + try to use a spy plan → Soviets shoot down US spy plane
Cuban Missile Crisis 1962
How did it end?
What actions were made? (3)
Signifigance
Secret communications between Khrushchev and Kennedy resolve it
Actions
Missiles are removed from Cuba, missiles are removed from Italy and Turkey (US public is not told the last part)
Moscow-Washington Hotline is established
Significance: Soviets + US come close to fighting (the closest they ever will)
Nuclear Test Ban Treaty 1963
What did it entail?
What caused this?
US + USSR agreed to stop all test detonation of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, space, and under water (underground testing is still permitted)
Kenney + Khurshchev realizes they had come dangerously close to nuclear war
Kennedy’s American University Speech (3)
Bombs can only destroy and never create
To think that peace isn’t real is a defeatest belief → if we think this that means we think that war is inevitable
Stockpiling weapons instills fear
Lyndon Johnson
What party
What impacted his foreign policy actions a lot
Democrat, committed to containment
Foreign policy actions were shaped by his personality: needed to appear masculine + tried to appear “tough on communism”
The Cold War in Asia
What was the US thinking?
Why were they thinking this? (2)
There was a fear that communism would spread rapidly throughout Asia
Mao and the CCP came to power in China in 1949
Kim Il Sung came to power in North Korea
Domino Theory: Theory held by the US that communism would spread out of China
Communism needed to be contained in Asia
Vietnam: Background
After Korea, the next flare-up of communism in Asia was in Vietnam → Vietnam was a French colony from mid-1800s to 1954
France ousted after defeat by the Vietnamese in the First Indochina War in 1954
[1954] The Geneva Peace Accords provided for the temporary partition of Vietnam at the 17th parallel
North Vietnam: communist regime, supported by the USSR and the PRC, led by of Ho Chi Minh.
South Vietnam: Republican government, led by President Ngo Dinh Diem.
US involvement: Truman = $ to the French, Eisenhower = props up Diem (South Vietnamese authoritarian), Kennedy = Sends military advisors