BSC360: Exam 2 Information
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
In vitro
experiments performed with cellular structures or tissues in a test tube
Outside the organism
Ex: cell culture: the process of growing cells isolated from an organism in a cell culture dish
Need:
Medium that contains essential nutrients and is at physiological pH
Humidity
Physiological temperature
Growth factors
Adherent cells
Cells that have to attach to a solid surface; most animal cells
Suspension cells
cells that can float around solution; bacteria, yeast, and some animal cells
Primary Cells
cells isolated from tissues
Can be cultured in dishes for several generations
Limited life span
Grows in a monolayer
Contact inhibition: stop dividing when cell contact each other
Cell lines
derived from GMO cells; isolated from tumor tissues
Transformed cells; immortalized
Grow indefinitely
Rapid growth rate
Lost contact inhibition
Tumor morphology
In vivo
experiments conducted in living organisms
Ex: clinical trial, drug testing
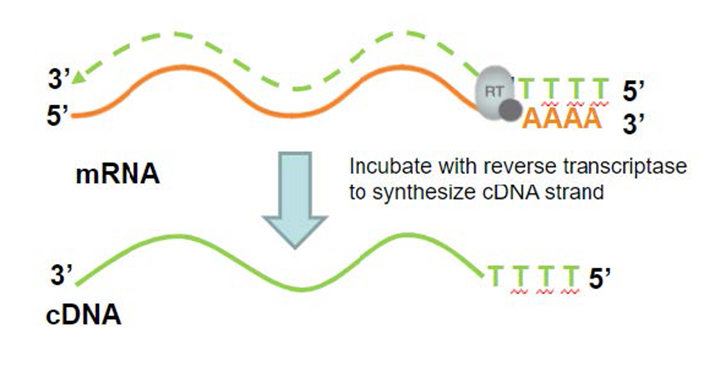
Reverse Transcription
uses the enzyme reverse transcriptase to make DNA from an RNA template
mRNA is pureed from cells of interest
poly -T primer binds to poly-A tail of mRNA; makes it DS
Reverse transcriptase needs DS nucleotide to bind and begin transcription
Reverse transcriptase uses mRNA template to make cRNA
RNA is partially degraded by RNases
DNA polymerase needs DS nucleotide to bind and begin transcription
DNA polymerase uses cDNA strand as a template to make DS cDNA
Result: complementary DNA strand containing DNA copy of mRNA
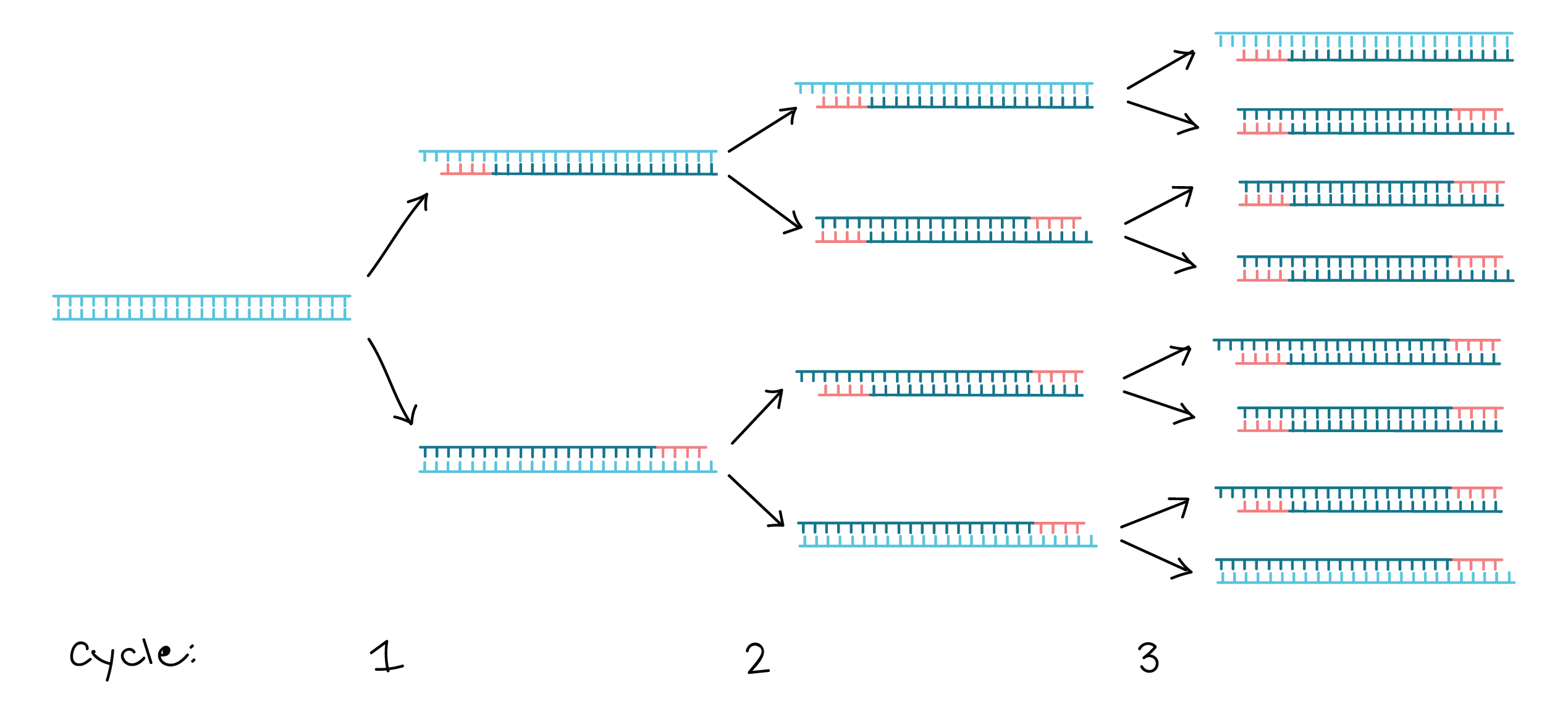
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Amplification of small parts of DNA in a test tube
Uses DNA polymerases found in thermophilic bacteria bc of its ability to survive high heat needed to denature protein
Exponential reaction: initial copy becomes template for other DNA segments
DNA is heated to melting temperature-> breaks hydrogen bonds between strands and allows them to separate
Becomes SS
Sample is cooled just enough to allow primers to bind to their specific complementary section of DNA
DNA synthesis:
Sample is heated to the working temperature of DNA polymerase
Polymerase binds to the DNA primer complex and synthesis of a new DNA strand
PCR rxn continues-> by third cycle you have DNA that is only from your area of interest
DNA segment becomes predom further in the cycle
The cycle runs 30x times
Fluorophore
molecule with fluorescent chemical that emits wavelengths when light hits it
absorbs light energy→ light absorpotion excitation of electrons ->the fluorophore re-emits the absorbed light energy at a larger wavelength upon the electrons return to their basic state
DAPI
DNA dye that is exicted by 354 nM (UV LIght) and emits a blue light
Phalloidin
dye Toxin that binds to actin filaments; Can be conjugated to fluorescent dye
Phosphatidylserine
Most abundant negatively charged phospholipid
In healthy cells: found only on the cytosol side
If on the extracellular side-> signal for apoptosis
Phosphatidylcholine
Most abundant phospholipid in eukarytoes
Most commonly found on the extracellular side on the membrane
Sphingomyelin
Regulator of cholesterol distribution within membranes
Involved in cholesterol homeostasis
Phosphatidylethanolamine
Helps fold certain membrane proteins
Essential for mitochondrial respiratory complexes
Plays a role in autophagy (cell cycling)
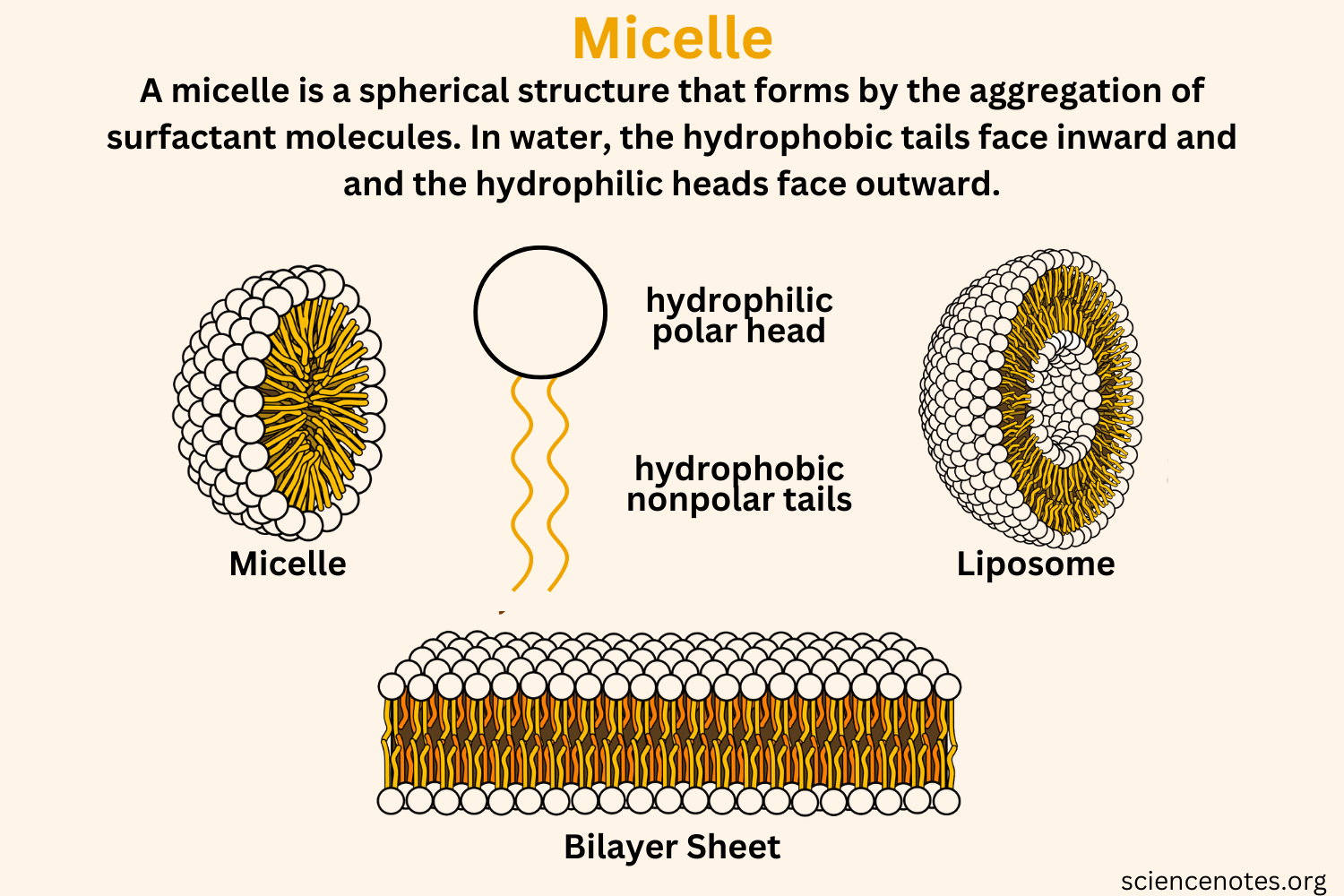
Micele
type of bilayer formation. Cosists of a core and a shell where hydrophobic end groups form the core and hydrophilic head groups form the outer shell
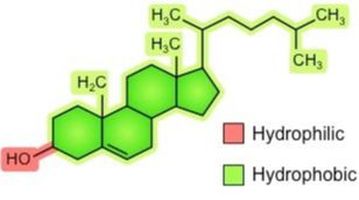
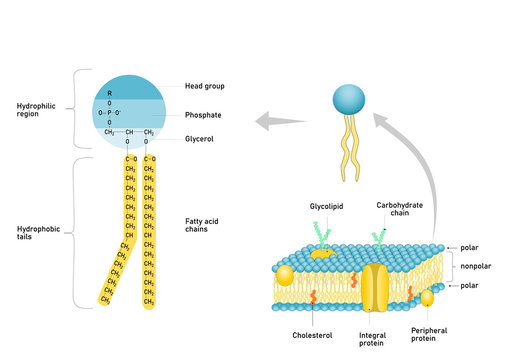
Cholesterol
Contains rings of hydrocarbon structures in the hydrophobic part
Hydrophilic part: hydroxyl group
Abundant in mammalian cells
Absent in prokaryotes
Affects the membrane permeability and mobility of other membrane lipids
Membrane lipid-> precursor of steroid hormones
Glycolipids
Sugar group in hydrophilic heads
Hydrophobic fatty acid tail
Found on the surface of all plasma membrane (non cytosolic side)
cold
temperature in bilayer that results in phospholipids pack in tighlty making membrane rigid and inflexible; gel like consistency
→ Cholestrol molecuels counteract this
hot
the temperature of phospholipids where are loosely packed making membrane flexible, un able to hold shape; fluid-like consistency
Cholesterol: holds phospholipids together stopping them from becoming loose: increases rigidity
unsatured fatty acid tails
kinks in their hydrocarbon tail
Harder to pack; increases fluidity
Harder to freeze
Creates small spaces for small molecules allowing certain small molecules to easily cross the membrane
organelles without membranes
Ribosome
Centrosome (structure that organizes mitotic fibers)
Cytoskeleton: microfilaments, microtubules
Phospholipids
Phosphate group with hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic Fatty Acid Tails:
Can be unsaturated: results in a kink in the tail
Asymmetrically distributed into two leaflets of the bilayer
Most abundant membrane lipids
Fluid Mosiac Model
dynamic and flexible structure of membranes made up of proteins, phsoplipids, glycolipids and cholestrol
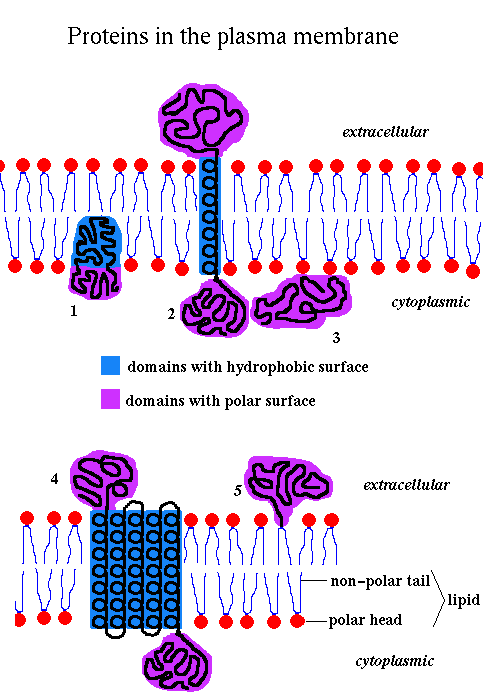
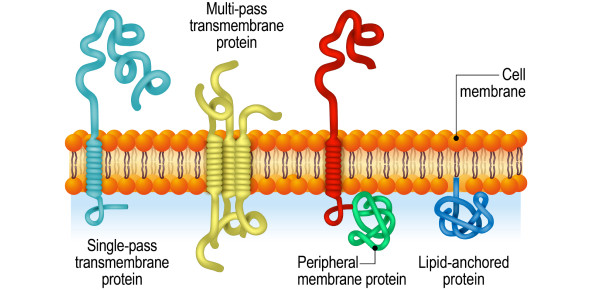
Transmembrane proteins
types of integral protein
Span the lipid bilayer by alpha helical segments
ThreForms: alpha-helical proteins, and beta barrels with hydrophobic side chains
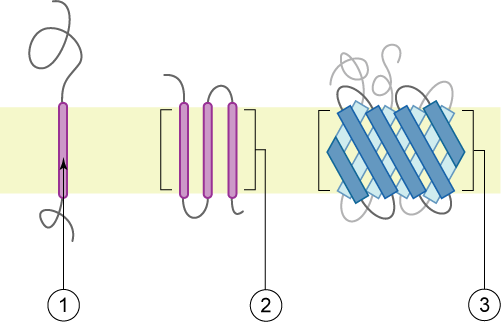
Monolayer associated
protein located almost entirely in the cytosol
→ amphipathic helix is snug in the bilayer
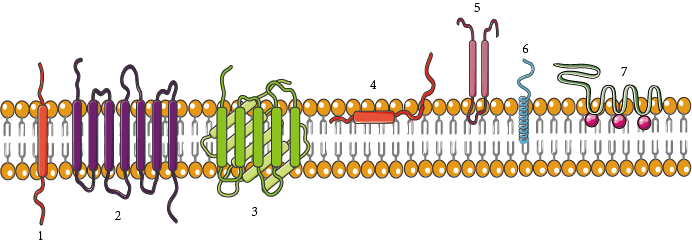
Lipid anchored proteins
Linked to one or more lipid molecules through different covalent bonds
Protein itself does not enter the bilayer
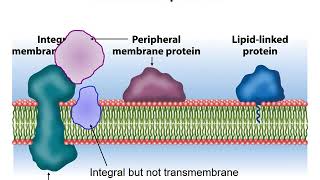
Peripheral Proteins
proteins that do not interact directly with the lipid bilayer
Associate with the membrane by interaction w/ transmembrane proteins or hydrophilic heads of lipids
Locaized at either side of the bilayer
mRNA
type of rNa that carries the nucleotide sequence that is used as the recipe for protein translation
rRNA
type of RNA that is resposbnible for ribosome cataylticc activty and function
tRNA
type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome for addition into the growing polypeptide chain
siRNA and miRNA
RNA that greulates protein translation by causing mRNA degradation
Wobble Hypothesis
a theory that states that the first two nucledtides of a codon are more important for tRNA binding during translation
ribosome
organelle not encoloded in a membrane
channel proteins
proteins that transport small hydrophilic molecules ions or H20, involved in passive transport, form a hydrophilic passage, and transport molecules down the concentration gradient
ex: K+ Channel
hypotonic, hypertonic
osomis is the transportaion of water across a semi[ermable membrane from a __________ solution to a ______ solution
Cholesterol
membrane lipid that does not contain a fatty acid tail
Passive Transport
With the concentration gradient - moving a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Active transport
Against the concentration gradient - moving a solute from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration
thylakoid membrane
where are the proteins of the elctron transport chain located in chloroplasts?
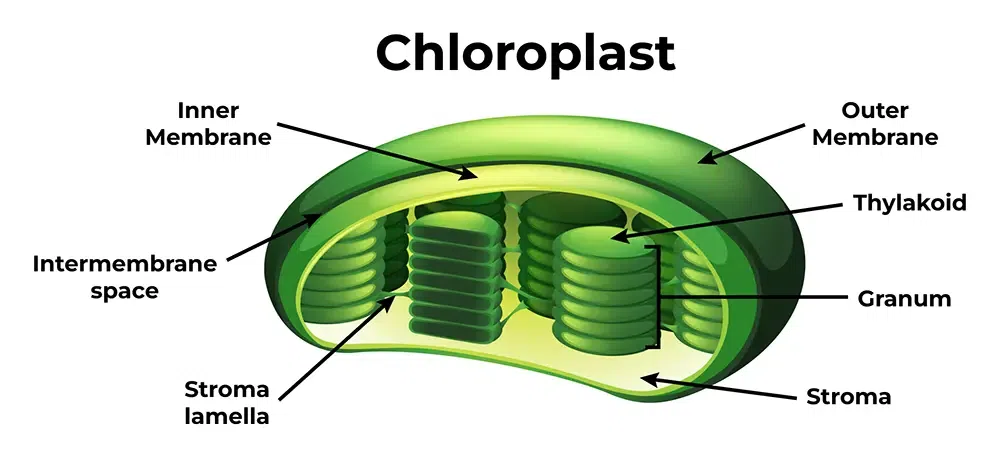
d. creates a H+ graident that ATP synthase uses to create ATP
what is true for all electron transport chains
a. cytochrome b6-f pumps H+ across the membrane that ATP synthase will utilize to create ATP
b. Water is a product of all electron transport chains
c. NADH is the high energy electron carrier
d. Creates a H+ gradient that ATP synthase uses to create ATP
stroma
light indepedent reactions produce sugar and occurs in the
ATP, NADPH, oxygen
light dependent reactions products
CO2, H20, and ATP
the oxidation of food molecules produces
c. ATP synthase inhbitor
Electron transport is coupled to ATP synthesis in mitochondria and in chloroplasts. Which of the following is likely to affect the coupling of electron transport to ATP synthesis in all these systems?
a. the absence of light
b. a potent inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase
c. ATP synthase inhibitor
d. the removal of oxygen
pyruvtae, ATP, NADH
final products of glycolysis
Transporter (carrier proteins)
Interacts with a molecule to be transported, like an enzyme interacting with its substrate
Confromational changes
UNIPORTER:
SYMPORTERS:
ANTIPORTERS:
partipates in passive transport
uses free energy released by the movement of one molecule down its cocnentration graident to power the movemnet of the other molecule aganist its concentration graident
UNIPORTER
type of transporter protein, single type of molecule moved down its concetrationg gradient
Bind site shifts from outside to inside positon
SYMPORTERS
type of transporter protein, two types of molecules in the same direction; coupled transporters
antiporters
type of transport protein, two types of molecules to opposite directions; coupled transporters
coupled transport
occurs in transport proteins (usally antiporters and symporters ) Uses free energy released by the movement of one molecule down its concentration gradient to power the movement of the other molecule against its concentration gradient
Pump transporter
type of transproter that partipates in active transport
ex: ATP powedered pumps (ATPases) that uses the enerfy from hydrolysis of ATP to pump out Na+
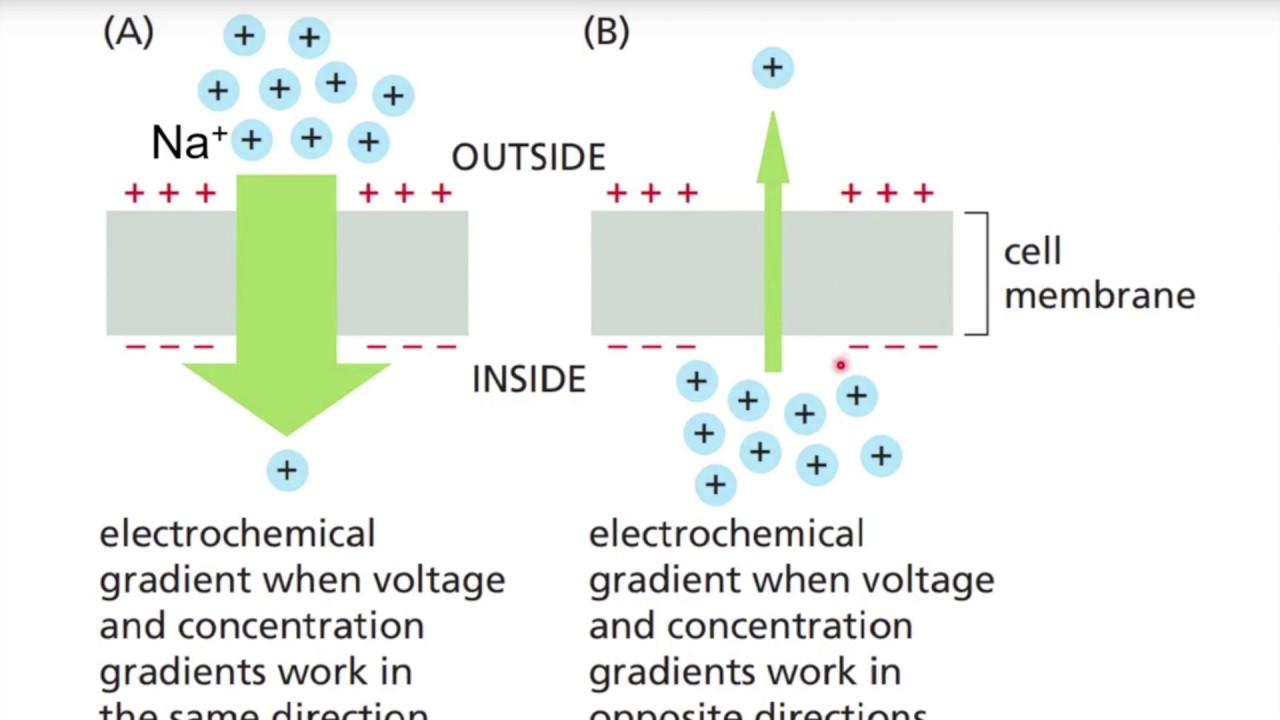
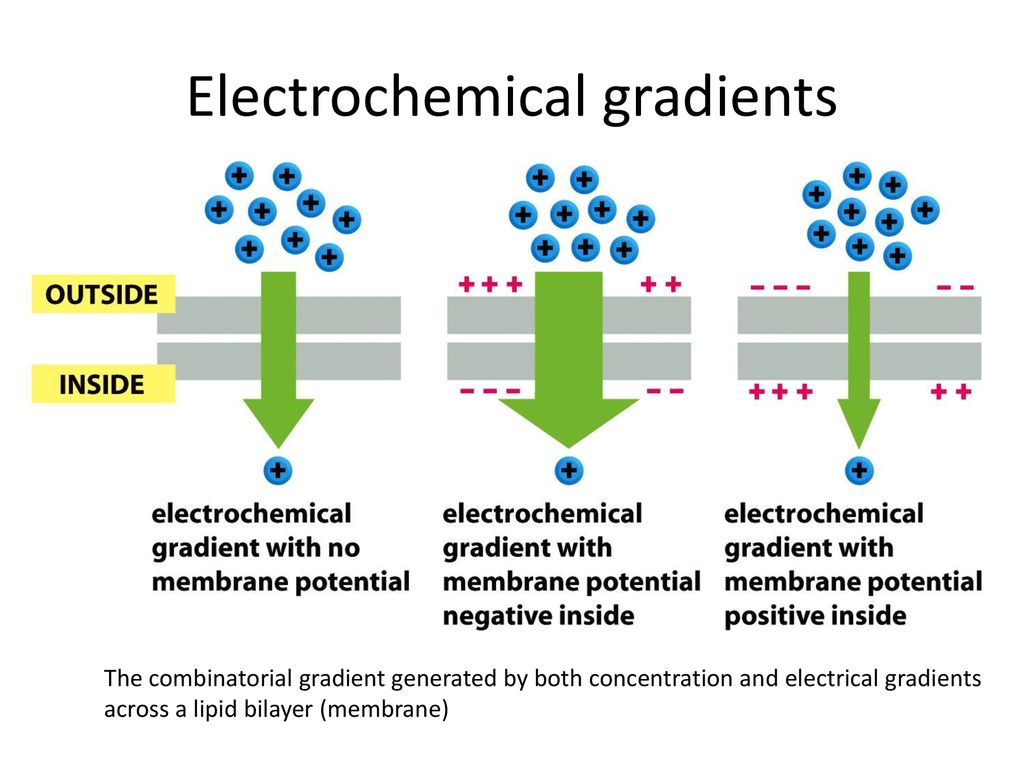
electrochemical gradient
the concentration gradient of the solute and a force from the memrabne potneital
Voltage and concentration work in opposite directions: Membrane potential makes transport of solute harder
polar and ions
what type of molecules require transport proteins to help them move across
cristae
inner membrane folds of the mitochondria that contains and organizes the elctront ransport chain and ATP synthase
→ carries out oxidative phsophoroylation
→ allows H+ graident formation by seperating matrix from inner membrane spave
3 NADPH, 1 GTP, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2 Released
net result of the citric acid cycle
Chemiosmosis
The movement of ions across a semipermeable memraben bound structure down their electrochemical gradient
occurs during oxidative phosphorylation H+ gradient drives ATP synthase to produce ATP:
ADP +Pi -> ATP,
32- 34 ATP, H2O
final products of the oxdiative phosphorlation
38
max amount of ATP that can be produced through cellular respiration with one glucose molecule
Acetyl CoA
pyruvate is converted into this molecule in the mitochondrial matrix
releases CO2 and converts NAD+ to NADH
cytosol
glycolysis occurs in what part of the cell
mitochondrial matrix
the citric acid cycle occurs in what part of the cell