Zoo-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 6: Cell Reproduction
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
reproduction
basic characteristic of production of new life
cell division
underlying all forms of reproduction; reproduction of cells
single cell
has a double function: maintain itself and participate in the entire life of the organism
cell division in single-celled animals
results in the reproductiom of the whole organism
cell division in multicellular organisms
results in the development of the organism by the formation of additional cells
perpetuate one’s kind
primary purpose of reproduction
cellular reproduction
for repair of worn-out tissues; for growth and development of the body of an organism
amitosis
nucleus divides into two halves without the formation of spindle fibers; two daughter cells do not have the same number of chromosomes; occurs in some protozoans, especially the ciliates and suctorians
mitosis
typical cell division; consists of an equal division of nuclear materials (karyokinesis) followed by division of the cell body (cytokinesis) in such a fashion that each of the two daughter cells receive exactly the same number of chromosomes that the parent cell
karyokinesis
equal division of nuclear materials; chromosomes segregate to separate poles of the cell
cytokinesis
division of the cell body; division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells due to the formation of a new cell membrane
interphase; prophase; metaphase; anaphase; telophase
different stages in mitosis
early; middle; late stages
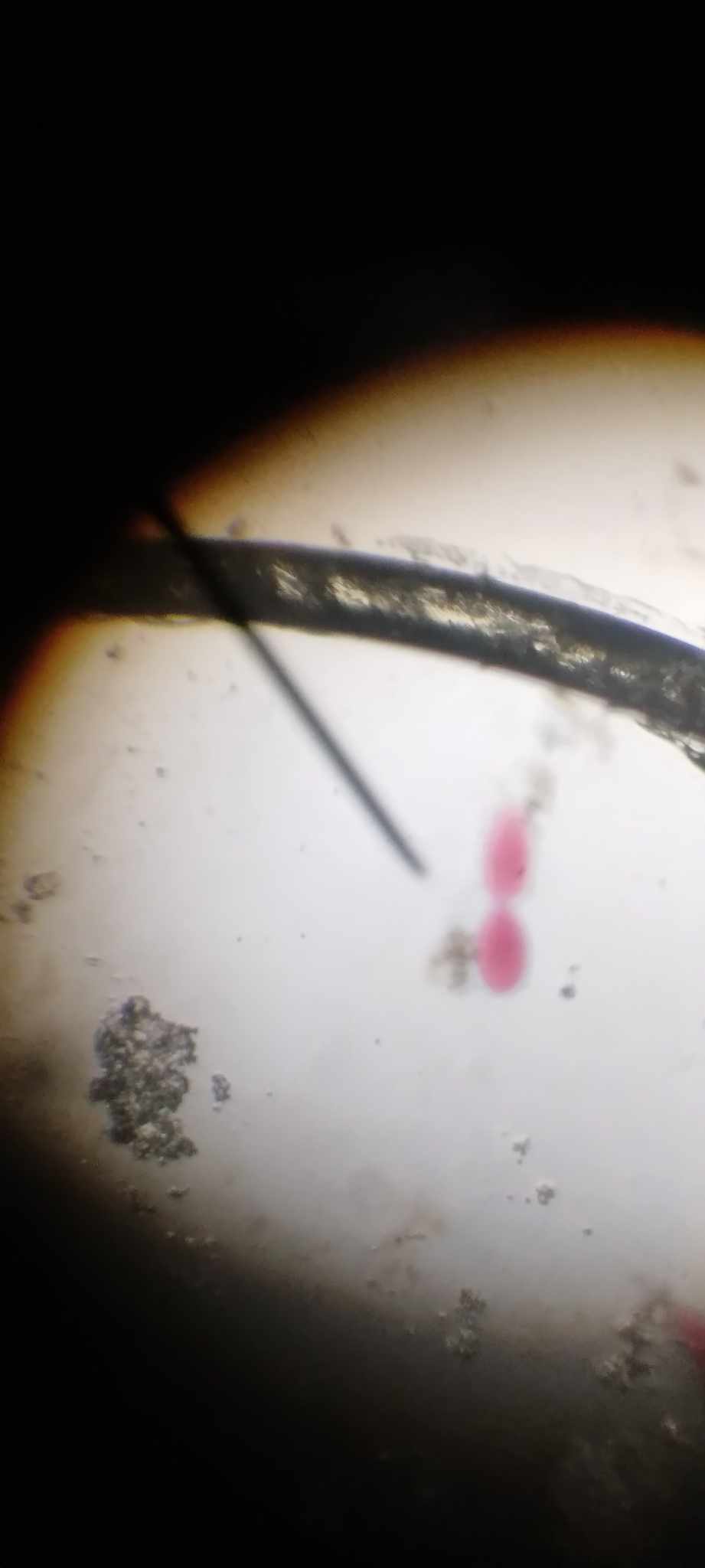
3 stages of transverse/binary fission
binary fission
type of asexual reproduction in which an organism replicates its DNA and divides in half, producing two identical daughter cells
early stage - binary fission
macro-nuclei/micro-nuclei elongate;
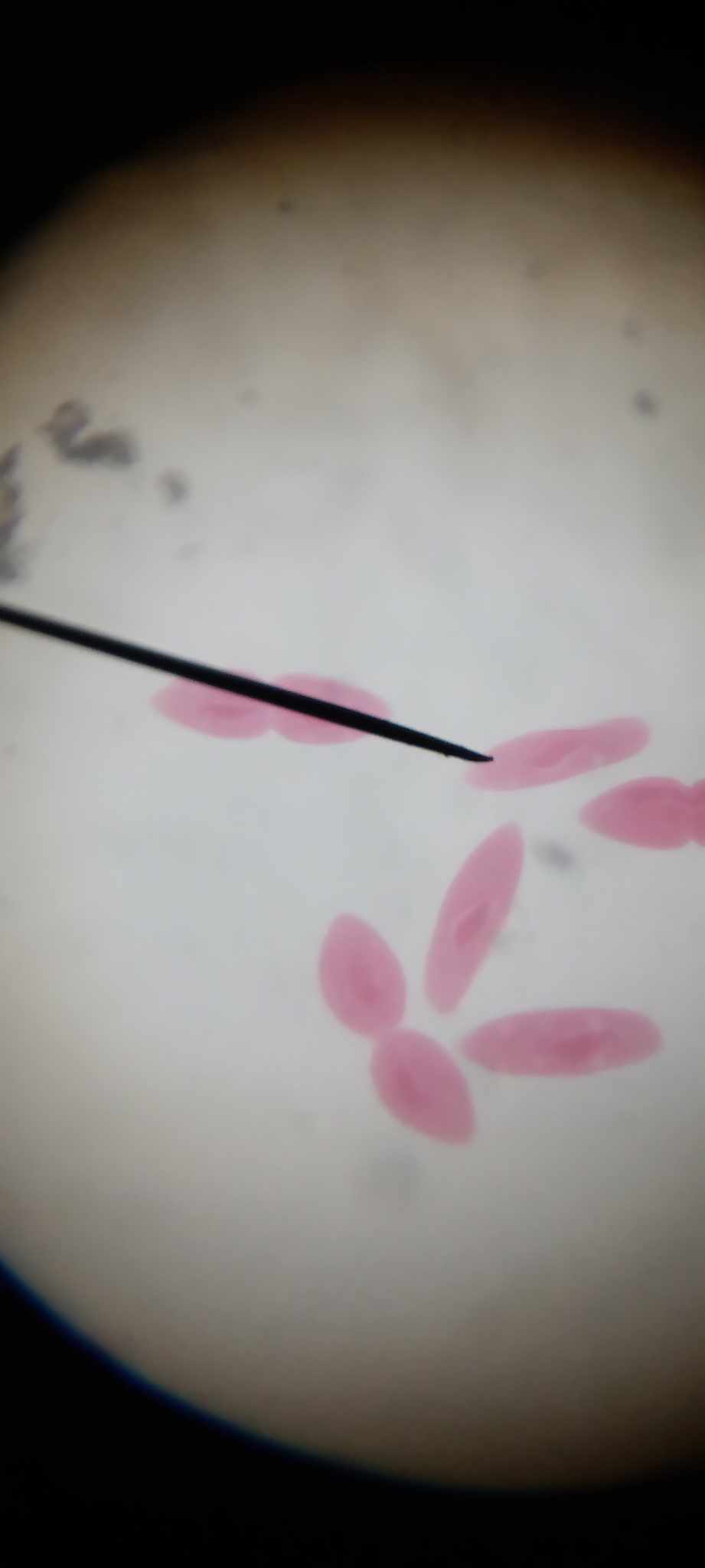
middle stage - binary fission
deepening of indentation and constriction around the middle of the individual plane at right angles to the animal’s longitudinal axis
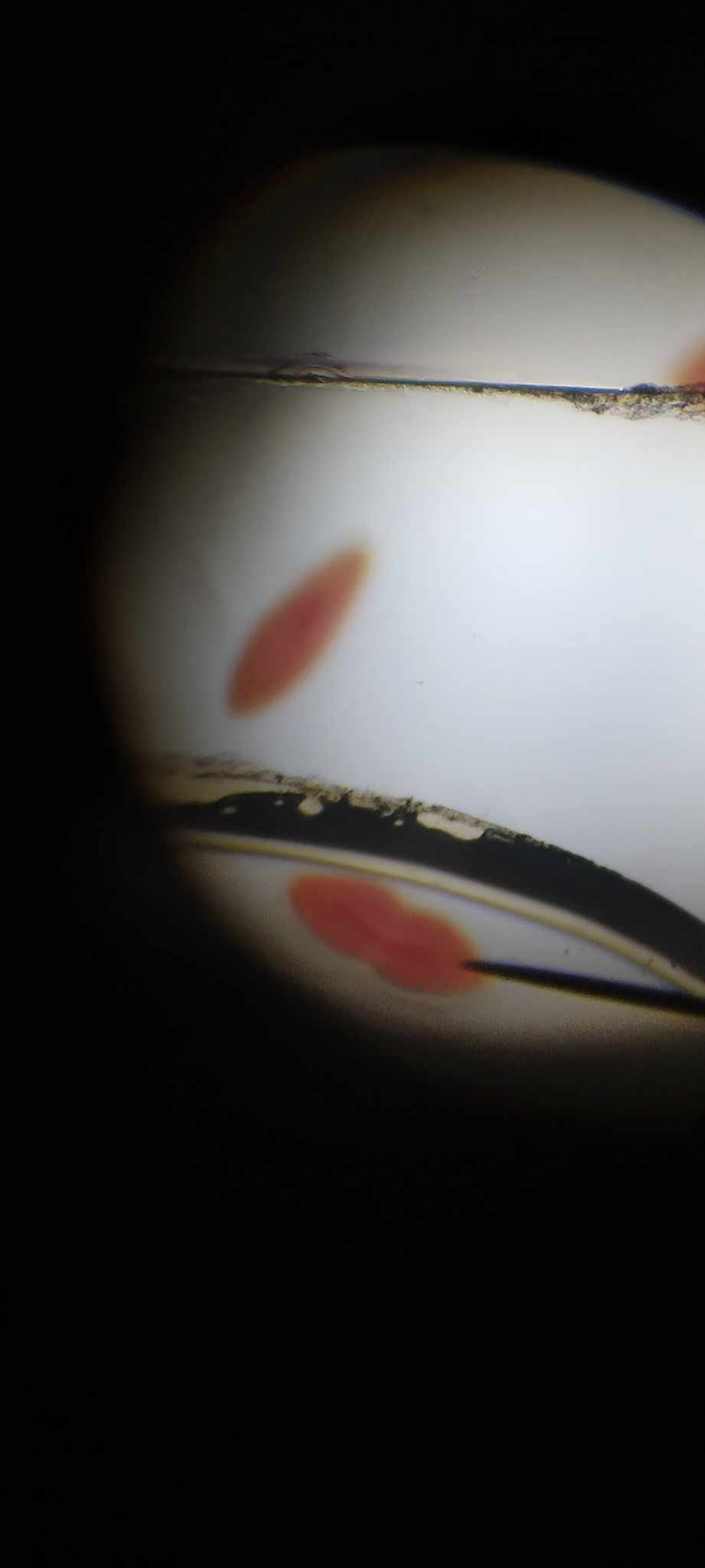
late stage - binary fission
the constructions deepen resulting in the pinching off of the animal into two daughter paramecia, each is half the size of the parent animal

interphase
aka resting cell stage; period between mitotic divisions; nucleus enlarges due to the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids, large molecules found in every nucleus, and duplication of each chromosome
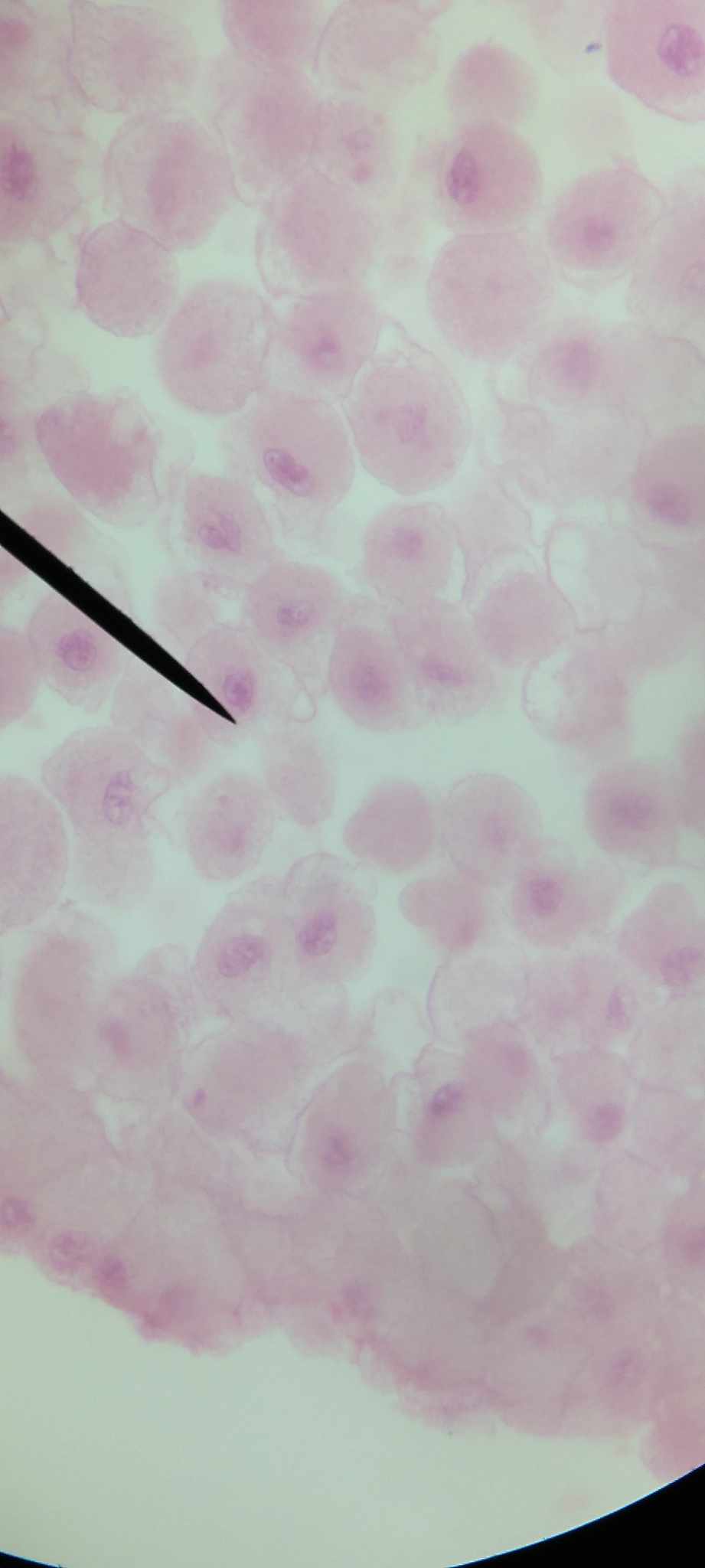
prophase
chromosomes are coiling, shortening, and thickening; chromosomes are irregular threads and each is composed of two chromatids; nucleus disappears and nuclear membrane disintegrates
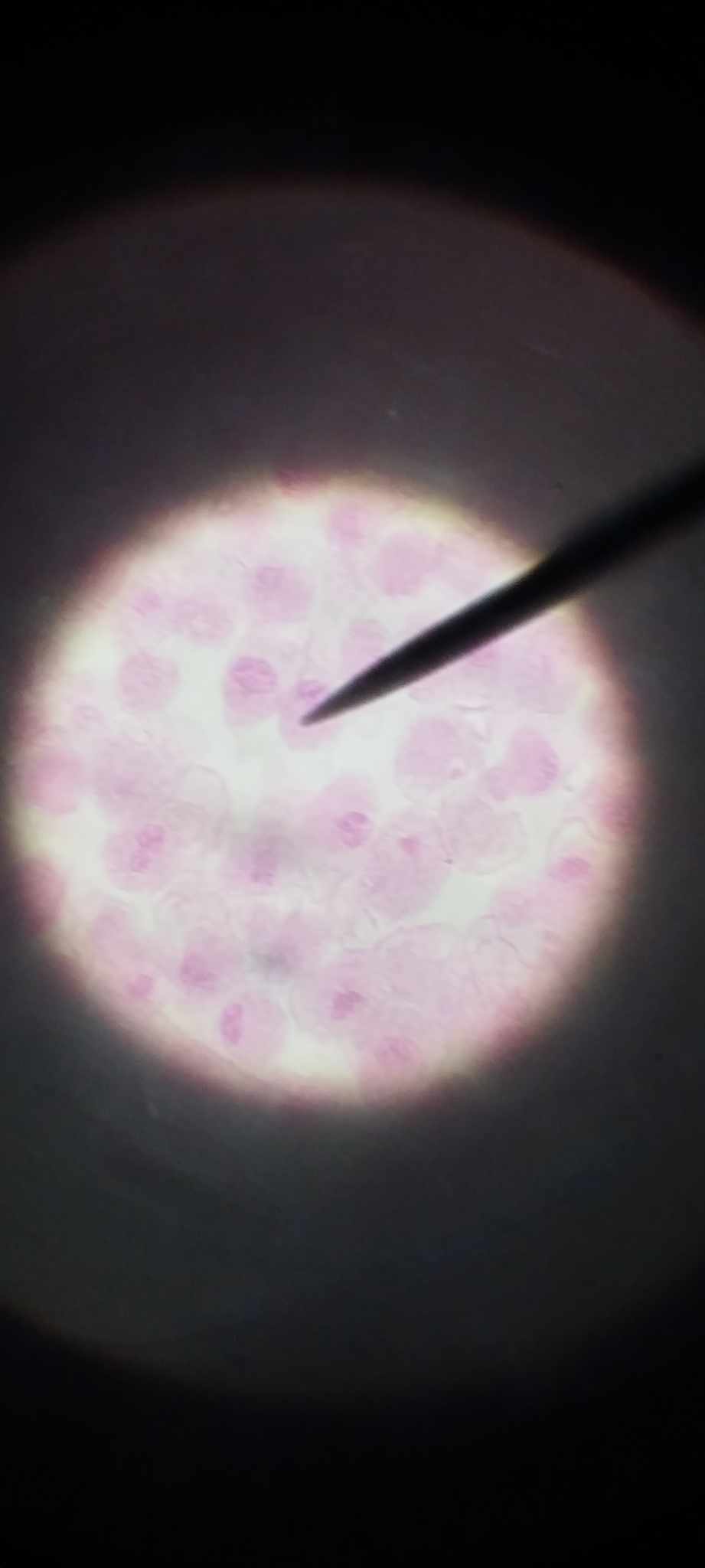
metaphase
chromosomes are aligned in the middle; spindle fibers extending from one centriolee (centrosomes) to the other; chromosomes are attached to some fibers by their centromeres
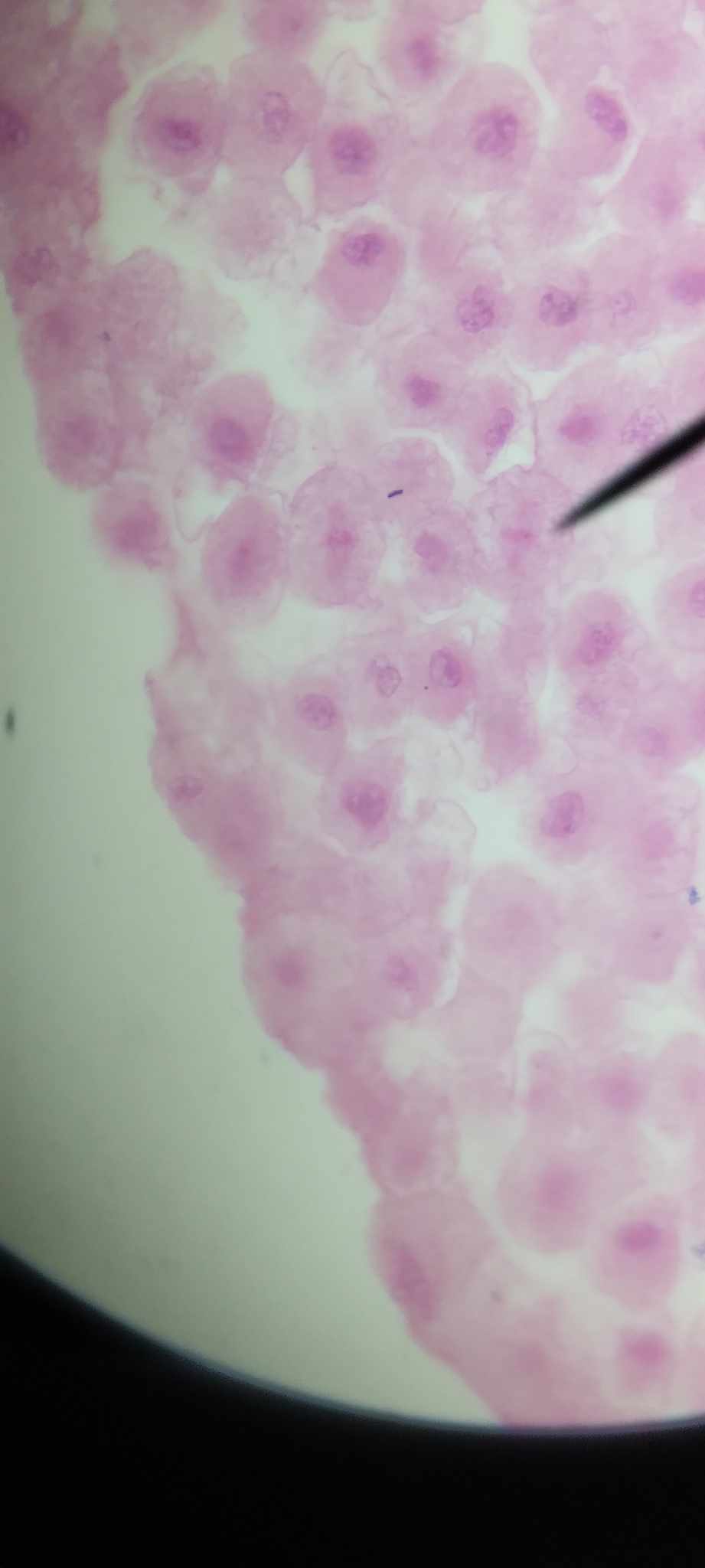
anaphase
sister chromatids of chromosomes separate and start moving towards opposite poles of the cell
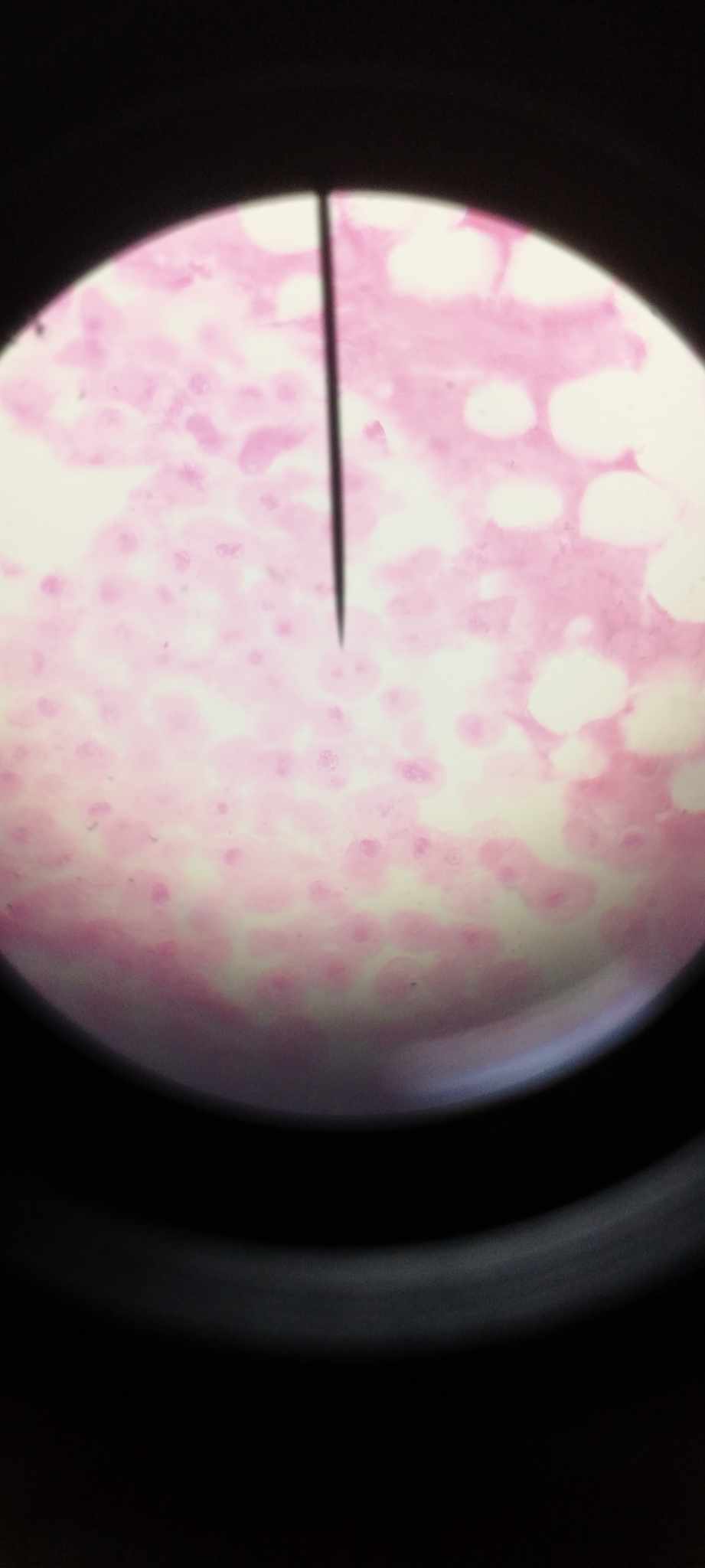
telophase
chromosomes reach the poles of the cells and begin to uncoil; new nuclear region formation; cleavage furrow deepens and divides cytoplasm into 2 cells
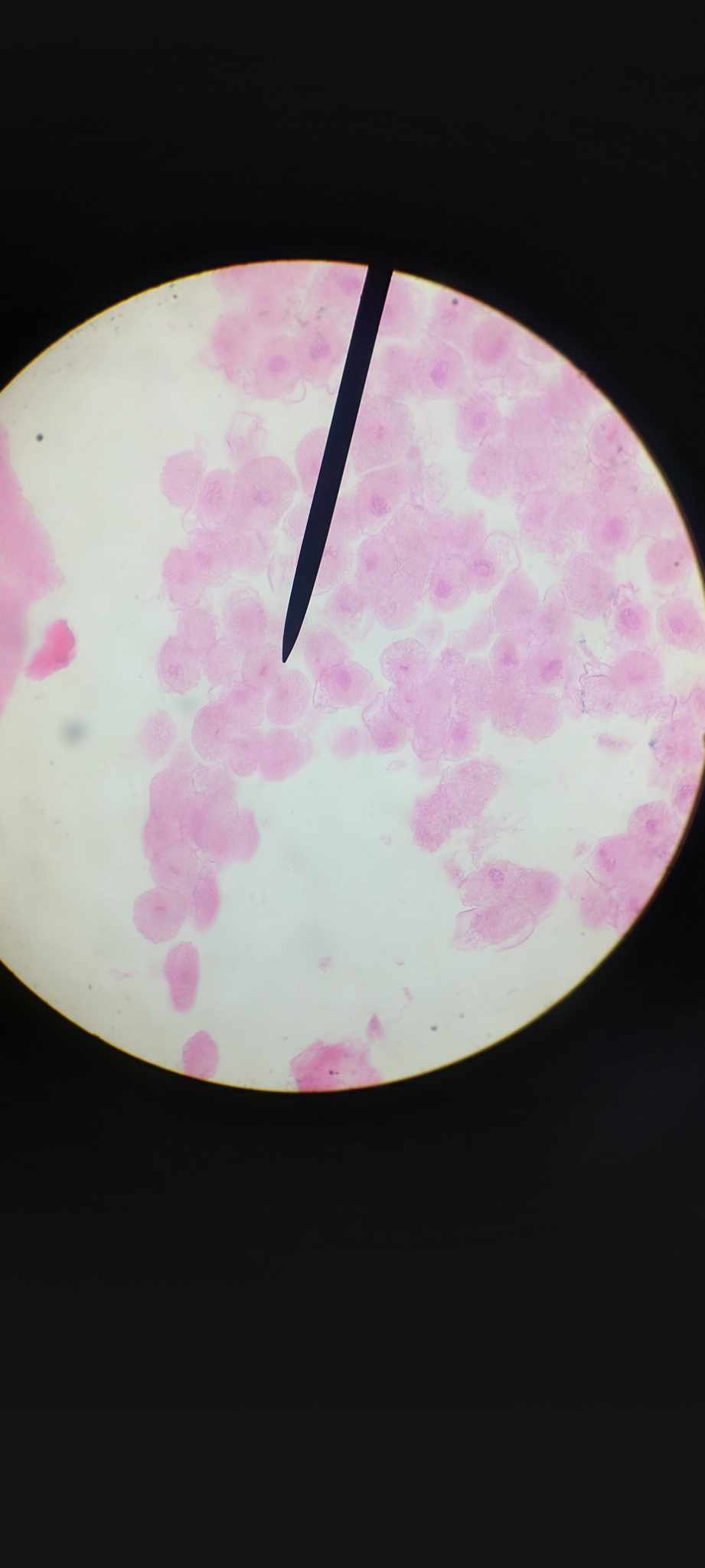
nucleolus
a spherical structure found in the cell's nucleus whose primary function is to produce and assemble the cell's ribosomes
chromosome
threadlike structures made of protein and a single molecule of DNA that serve to carry the genomic information from cell to cell
spindle fibers
responsible for organizing packages of DNA (chromosomes) on opposite ends of a cell to ensure that duplicated nuclei can divide into subsequent cells
centrosome
primary microtubule-organizing centre (MTOC) in animal cells; regulates cell motility, adhesion and polarity in interphase, and facilitates the organization of the spindle poles during mitosis
centriole
paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope; organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system