(4) Adaptations of Marine Organisms to Environmental Changes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Organismal response
Organisms react to environmental variations throughout life.
Adaptive responses
Responses include behavioral, physiological, and biochemical changes.
Acclimation
Adjustment of physiology to new environmental conditions.
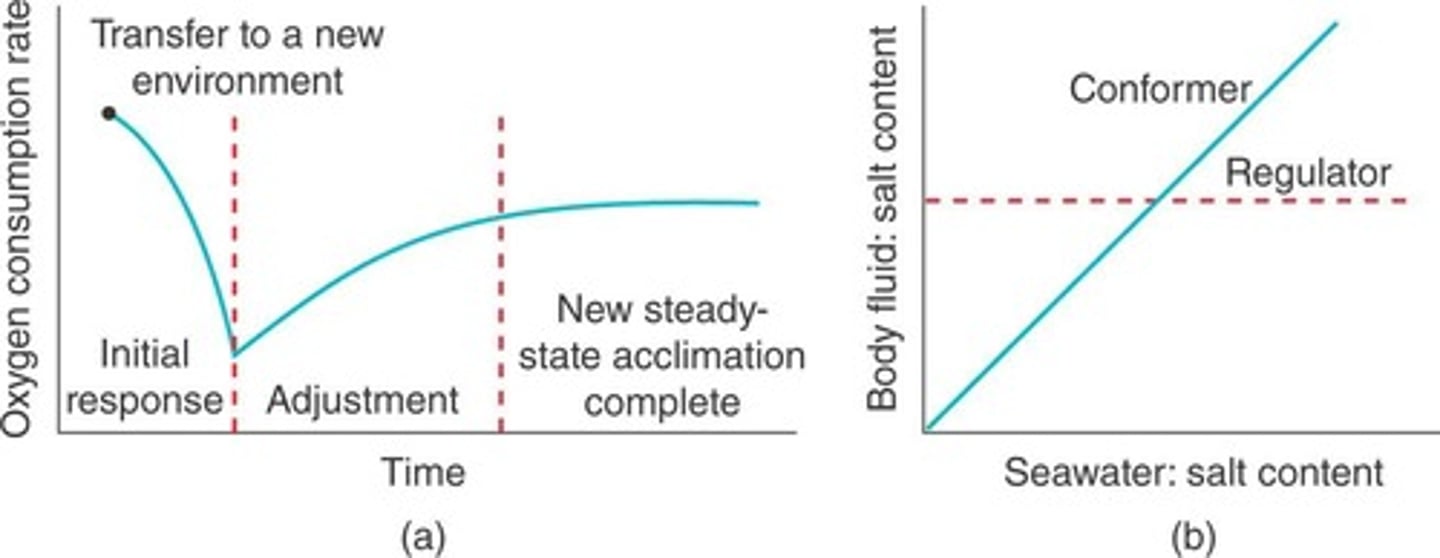
Regulators
Maintain constant internal parameters despite external changes.
Conformers
Allow internal parameters to fluctuate with external conditions.
Homeotherms
Organisms that regulate body temperature above ambient.
Poikilotherms
Organisms conform to external temperatures.
Heat loss
Most heat lost through skin conduction.
Convective heat loss
Heat loss via warm blood contact with body surface.
Insulation
Methods like fur or blubber reduce heat loss.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels to conserve heat.
Countercurrent heat exchange
Heat transfer between arteries and veins.
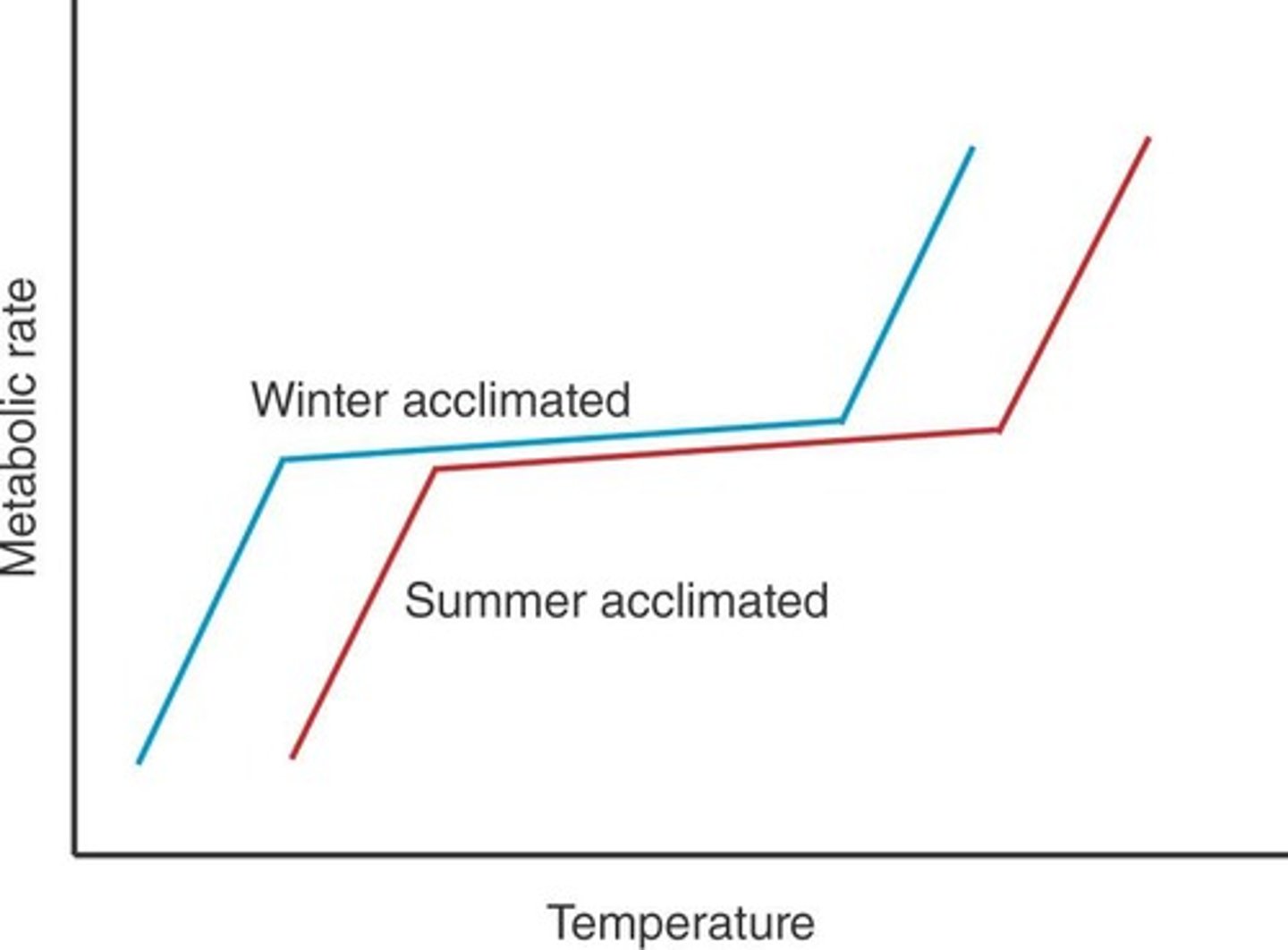
Metabolic rate
In poikilotherms, increases with temperature rise.
Heat shock proteins (HSP)
Proteins protect structure under high temperature stress.
Ubiquitin
Protein involved in degrading damaged proteins.
Freeze tolerance
Ability to survive freezing conditions without damage.
Antifreeze compounds
Substances preventing tissue freezing in fish.
Osmosis
Movement of water towards higher solute concentration.
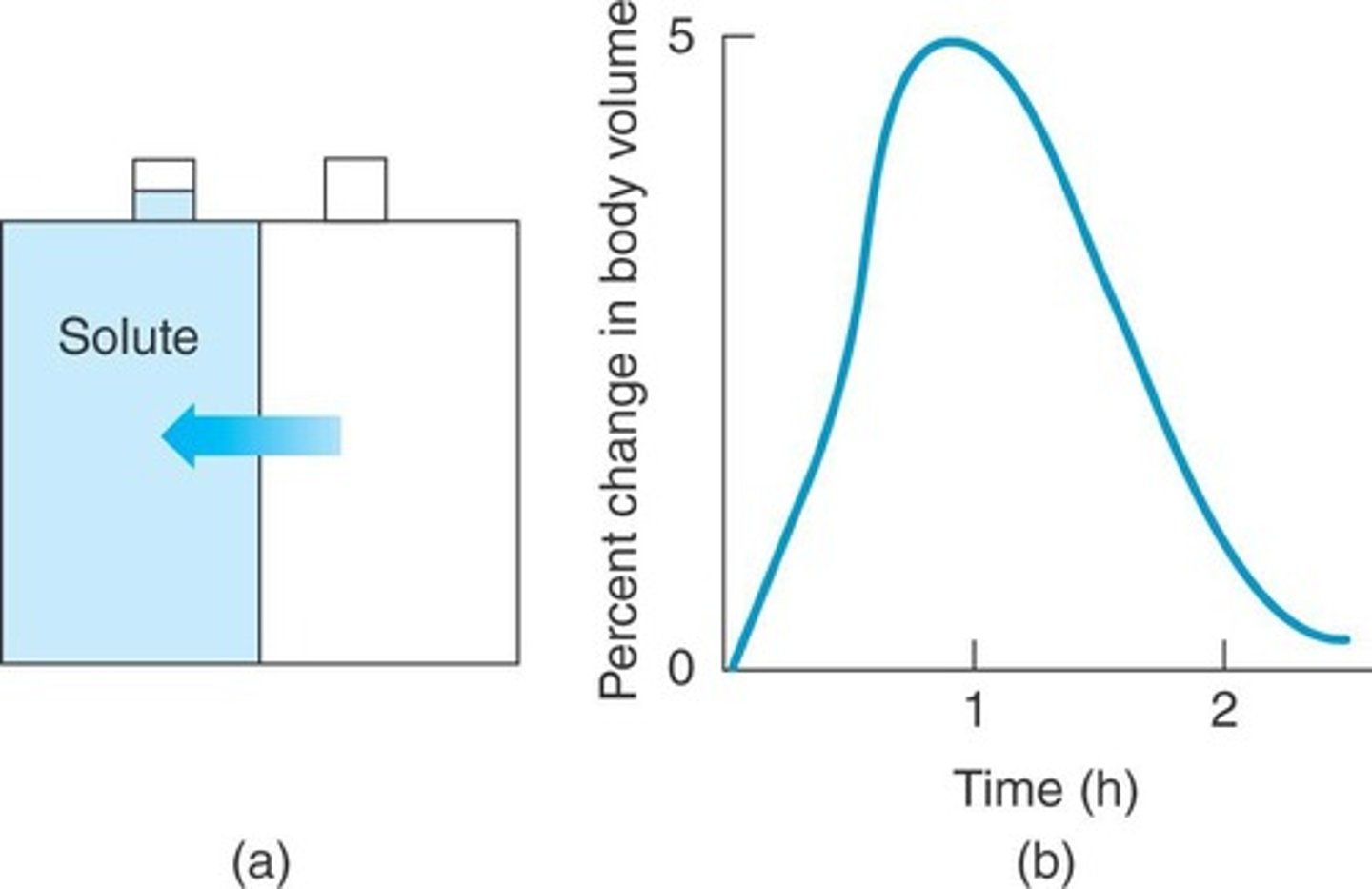
Osmoregulators
Organisms that maintain internal salt balance.
Active pumping
Mechanism to regulate internal salt concentrations.
Anaerobes
Organisms that do not require oxygen for metabolism.
Aerobes
Organisms that depend on oxygen for energy production.
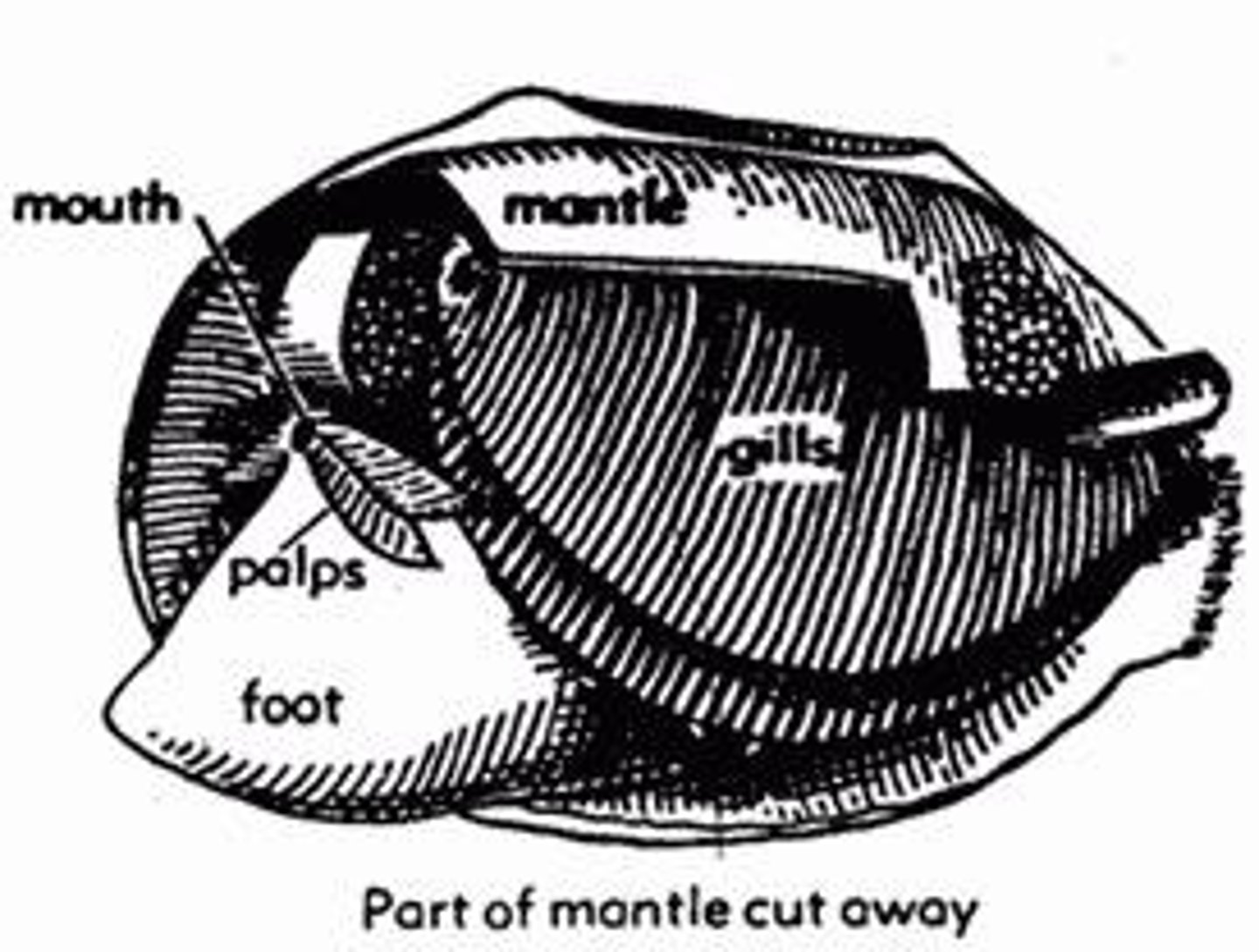
Oxygen uptake
Process of absorbing oxygen through diffusion or gills.
Oxygen-binding pigments
Molecules that increase oxygen transport capacity.
Photosynthesis
Process converting sunlight into energy by organisms.