Tox Exam 3 - Drug Metabolism
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What catalyzes:
CH3 → C-OH
CYP
What catalyzes:
Phenyl → Phenol
OR
Phenyl → Epoxide Phenol
CYP
What catalyzes:
N-CH → [ N- C-OH ] → NH + O=<
What is the name of this intermediate?
CYP
Hemiacetal Intermediate
What catalyzes:
O-CH → [O-C-OH] → -OH + O=<
What is the name of this intermediate?
CYP
Hemiacetal Intermediate
What catalyzes:
S-CH → [S-C-OH] → -SH + O=<
What is the name of this intermediate?
CYP
Hemiacetal Intermediate
What catalyzes:
CH-Cl3 → O=Cl2
CYP
What catalyzes:
O=C-O- (ester) → COOH
CYP
What catalyzes:
CH-NH2 → C=O + NH3
CYP
What catalyzes:
-NH → -N-OH
CYP
What catalyzes:
-NH2 → -NH-OH
CYP OR FMO
What catalyzes:
-C-N-C- → C-NO-C
FMO
What catalyzes:
-SH → S-OH
FMO
What catalyzes:
-S- → S=O
FMO
What catalyzes:
CH2 - NH2 → O=<H + NH3 + H2O2
MAO
What catalyzes:
-OH → O=<H + NADH
ADH
What catalyzes:
O=<H → O=<OH + NADH
ALDH
What catalyzes:
Epoxide → Open epoxide with two OH groups
EH
What catalyzes:
O=< → OH<H
AKR/SDR

What catalyzes this picture:
UGT

What catalyzes this picture?
SULT

What catalyzes this picture?
GST

What catalyzes this picture?
NAT
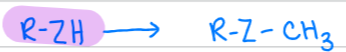
What catalyzes this picture?
Methyltransferase
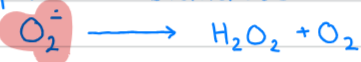
What catalyzes this picture?
Superoxide Dismutase

What catalyzes this picture?
Catalse

What catalyzes this picture?
Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx)
What is the cofactor for CYP
NADPH, O2, H+
What is the cofactor for FMO
NADPH, O2, H+
What is the cofactor for MAO
H2O, O2
What is the cofactor for ADH
NAD+
What is the cofactor for ALDH?
NAD+
What is the cofactor for AKR/SDR?
NADPH
What is the cofactor for EH?
H2O
What is the cofactor for UGT?
UDPGA
What is the cofactor for SULT?
PAPS
What is the cofactor for GST?
GSH
What is the cofactor for NAT?
Acetyl CoA
What is the cofactor for Methyltransferase?
SAM
What is the main organ for metabolism?
Liver
What is the general reaction for CYP?
RH + NADPH + H+ + O2 → ROH + NADP+ + H2O
In CYP1A3:
What is the individual subfamily?
What is the Gene family?
What is the subfamily?
Individual Subfamily = 3
Gene Family = 1
Subfamily = A
Where is CYP located?
ER
What is the significance of Acetaminophen and Imipramine when it comes to CYP metabolism?
They both have overlapping isoform metabolism, but imipramine has a different mechanism based on the catalyst
What is the major difference between CYP and FMO?
CYP requires Heme, whereas FMO does not
Phenobarbital and Carbamazepine are two major what for CYP?
Enzyme Inducers
Dihydroxybergamotin is found in grapefruit juice, what does this do to CYP?
It inhibits it.
Sort the following acronyms in order of Best at metabolizing to worst.
PM,IM,UM,EM
Which acronym represents the most common in population?
Which acronym(s) would you have to adjust the dose for? Up or down?
UM, EM, IM, PM
EM represents the most in population
UM and PM require dose adjustments. UM may mean a higher dose, PM may require a lower dose.