BIO 101 Chapter 3A Obj jc
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
3 Components of the Cell Theory
Cells are the fundamental unit of life
Organisms are made up of one or more cells
Cells come from pre existing cells
Magnification
Enlarging the size of an image
Resolution
Clarity of an image
Total Light Microscope Magnification
1,000x
Total Electron Microscope Magnification
100,000x.
Scanning Electron Microscope
Bounces electrons off the surface of cells for surface imaging
Transmission Electron Microscope
Sends electrons through a thin specimen for internal imaging
Smallest Observable Objects (Light Microscope)
Bacteria, Organelles, Small cells
Smallest Observable Objects (Electron Microscope)
Molecular details, Molecules, Atoms
Four Features Shared by All Cells
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm/Cytosol
DNA
Ribosomes
Why are most cells small
Maximize surface area to volume ratio
Why is the surface area to volume ratio so important?
So they can move materials in and out efficiently
Number of Cell Types
2
Prokaryotic
Eukaryotic
Number of Domains
3
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Bacteria & Archaea Characteristics
Prokaryotic
Unicellular
Eukarya Characteristics
Eukaryotic
Uni/multi
Prokaryotic Characteristics
Smaller
Not complex
No nucleus
No organelles
Eukaryotic Characteristics
Larger
More complex
Has nucleus
Has organelles
Anatomy of prokaryote
Label ts:
Flagellum
Capsule
Cell Wall
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm (the three shits below)
Ribosomes
Nucleoid with DNA
Cytosol
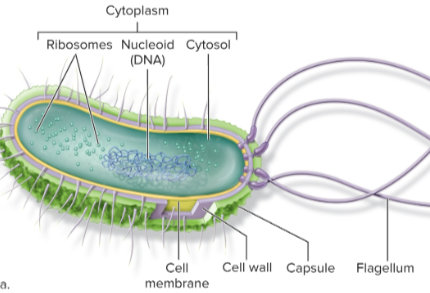
Flagellum Function
Movement
Cell Wall Function
Protection, prevent cell bursting
Nucleoid Function
Where DNA is located
DNA Function
Instructions for life/proteins
Capsule Function
Protection, stick to surfaces
Ribosomes Function
Protein synthesis
Cytosol Function
Liquid of cytoplasm, location of chemical reactions
Cell Membrane Function
Semi permeable membrane to control what comes in and out
Cytoplasm Function
Site of most cellular functions and contents
Nucleus Function
Stores DNA
Lysosome Function
Break down waste, digest food
Peroxisomes Function
Detoxify the cell by breaking down toxins
Vesicles Function
Small sacs that transport materials
Cytoskeleton Function
Give shape and support, Cell’s skeleton
Nucleolus Function
Make ribosomes/rRna
Golgi Apparatus Function
Receive, Modify, Store, and Package proteins and lipids for transport
Mitochondria Function
Convert food into ATP through cellular respiration
Four structures/organelles that are unique to plants
Cell Wall
Chloroplast
Large Central Vacuole
Plasmodesmata
4 Phospholipid Components
Two fatty acids
Phosphate group
Glycerol
Choline
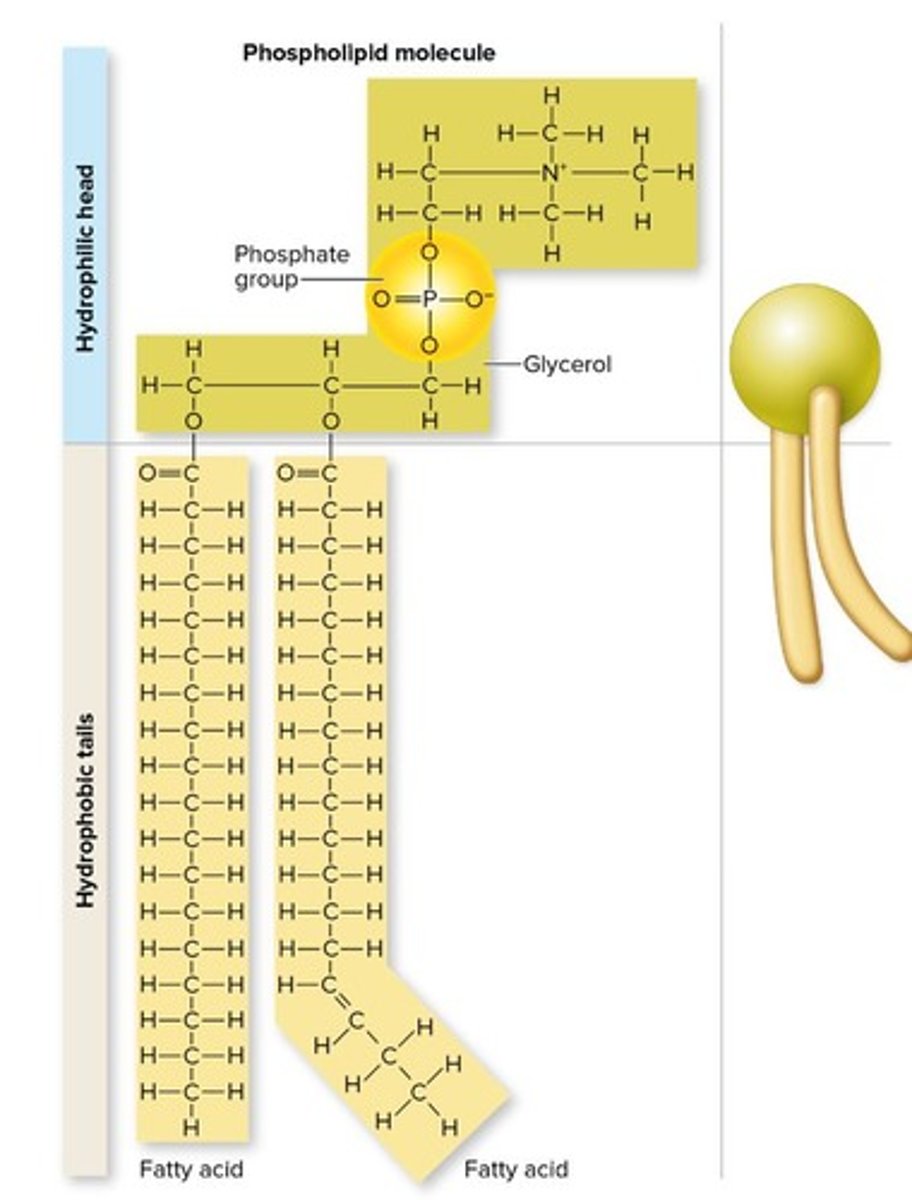
Chemical Properties of Phospholipid Head
Hydrophilic
Made of a phosphate group
Chemical Properties of Phospholipid Tail
Hydrophobic
Made of fatty acids
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid - Phospholipid bilayer acts like a fluid (substances can move in and out)
Mosaic - Phospholipid is made up of other parts/biomolecules
3 Types of Membrane Proteins
Transport protein
Receptor protein
Enzymes