Higher Chemistry - Unit 2 - Nature's Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
Last updated 10:06 AM on 4/28/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
What are carbon - carbon single bonds described as?
saturated
2
New cards
What is the test for a saturated and unsaturated compound?
• Saturated compounds do not decolourise bromine solution \n • Unsaturated compounds decolourise bromine solution quickly.
3
New cards
What are the 3 alcohol classifications
primary, secondary or tertiary
4
New cards
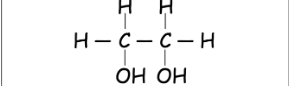
What is a Primary Alcohol
1 carbon directly attached to \n the carbon with the –OH bond
5
New cards
What is a secondary alcohol
2 carbons directly attached to \n the carbon with the –OH bond
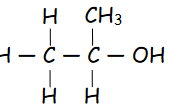
6
New cards
What is a tertiary alcohol?
3 carbons directly attached to \n the carbon with the –OH bond
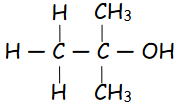
7
New cards
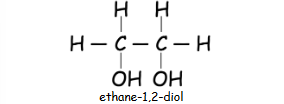
What are alcohols with two hydroxyl groups called??
diols
8
New cards
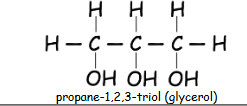
What is an alcohol with 3 hydroxyl groups called?
triols
9
New cards
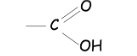
What is a carboxylic acid?
a molecule containing the carboxyl functional group
10
New cards
Metal oxide + carboxylic acid reacts to give ……
Metal hydroxide + carboxylic acid reacts to give……
Metal hydroxide + carboxylic acid reacts to give……
salt + water
11
New cards
Metal carbonate + carboxylic acid reacts to give……..
salt + water + carbon dioxide
12
New cards
How to name salts?
First name of the salt, Second name of the acid
13
New cards
Sodium oxide + methanoic acid reacts to give…….
sodium methanoate + water
14
New cards
Calcium carbonate + propanoic acid reacts to give….
calcium propanoate + water + carbon dioxide
15
New cards
How is an ester identified?
from the ester link
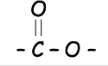
16
New cards
What are esters useful for?
Flavourings, Fragrances and Non-polar industrial solvents. Also have a sweet/fruity smell
17
New cards
How are esters formed?
From the condensation reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
18
New cards
What is formed if esters undergo hydrolysis?
an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
19
New cards
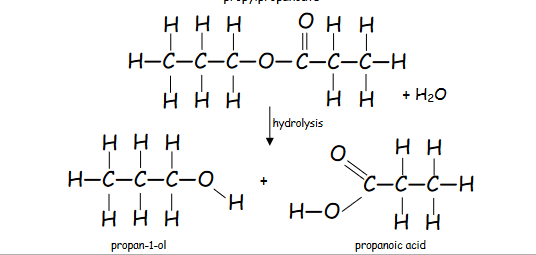
How is an ester broken down?
Ester ----Hydrolysis-----Alcohol + Carboxylic acid
20
New cards
What are edible fats and edible oils formed from??
Condensation reaction between carboxylic acids and glycerol
21
New cards
What does oxidation in carbons result in?
increase in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio
22
New cards
What does reduction in carbons result in?
a decrease in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio
23
New cards
Oxidation of a primary alcohol
Primary alcohol ----OXIDATION--- Aldehyde-----OXIDATION---- Carboxylic Acid
24
New cards
Oxidation of a Secondary Alcohol
Secondary Alcohol-----==OXIDATION==---Ketone
25
New cards
Oxidation in tertiary alcohols process
No oxidation.
26
New cards
What is oxidation in hot copper II oxide reaction?
black to brown
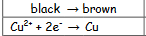
27
New cards
What is acidified dichromate solutions reaction when oxidised?
orange to green
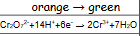
28
New cards
What is benedict/Fehlings solutions reaction when oxidised?
blue to brick end
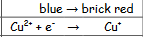
29
New cards
What is tollen reagents reaction
colourless to silver mirror
30
New cards
What two molecules contain the carbonyl functional group?
Aldehyde and Ketone
31
New cards
What is the aldehyde name ending and structure?
\-al

32
New cards
What is the ketone name ending and structure?
\-one
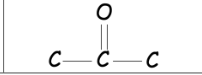
33
New cards
What gives food a rancid flavour
Oxygen from the air causes the oxidation of food giving edible oil foods a rancid flavour
34
New cards
what happens when fats and oils when oxidised?
they become rancid
35
New cards
How are soaps produced?
Alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils
36
New cards
what happens to soaps in 'hard' water?
form a scum
37
New cards
what's the difference between soaps and detergents?
detergents are synthetic products made from crude oil and soaps are made from natural fats
38
New cards
what happens when an enzymes is denatured
it permanently/irreversibly changes shape
39
New cards
what are the oxidising agents for alcohols?
acidified potassium dichromate (orange → green) , hot copper (II) oxide (black → brown)
40
New cards
What are antioxidants?
molecules that prevent unwanted oxidation
41
New cards
what are terpenes?
Unsaturated compounds formed by joining together isoprene
42
New cards
what is UV?
a high energy form of light, present in sunlight
43
New cards
what chemical reactions does UV light cause in skin?
production of vitamin D, sunburn, tanning and ageing of the skin
44
New cards