Chemistry 12 + 6.1
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
How to find the significant figures of concentrations and ps?
Right side of the decimal
How to find the pH of strong acids?
How to find [H3O+] with pH?
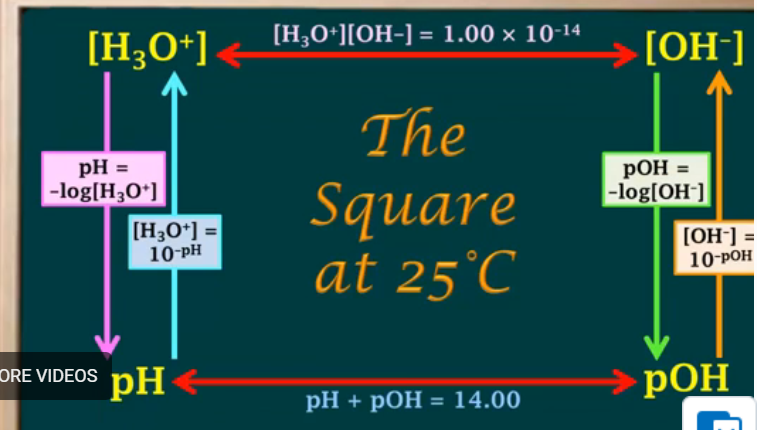
pH = -log[H3O+]
[H3O+] = 10-pH
Find pH:
0.00367M
0.14M
6.5219M
12M
Find [H3O+]:
pH = 2.61
pH = 5.3
pH = 8.419
pH = 6.0000
2.435
0.85
0.8144
1.079
2.46×10-3
5.0×10-6
3.811×10-9
1.000×10-6
What happens to pH when [H3O+] increases largely?
pH decreases slightly.
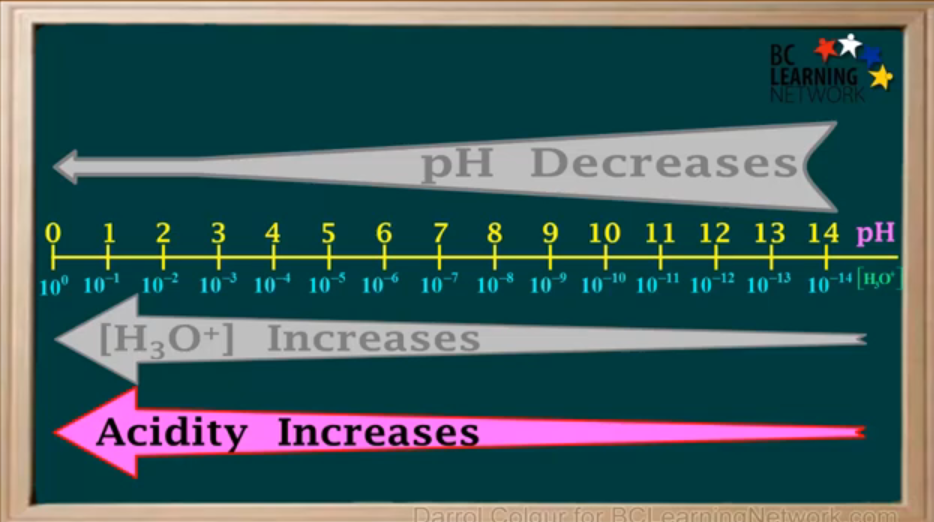
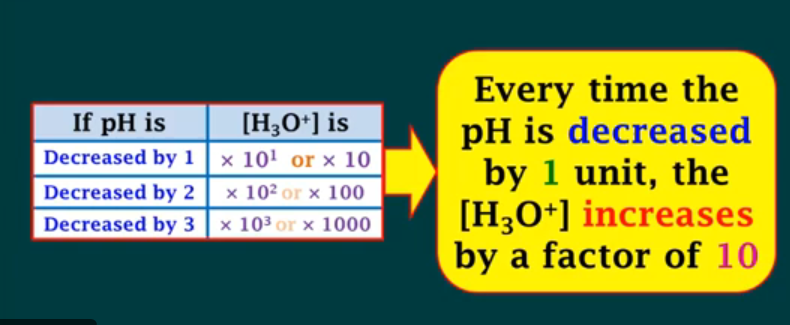
Everytime the pH is decreased by 1, the [H3O+] increases by
a factor of 10.
How much more acidic is A?
A —→ pH = 3
B —→ pH = 12
A is 109 more acidic than B.

Answer in mL.
1300mL

How to find the pOH of strong bases?
How to find [OH-] with pOH?
pOH = -log[OH-]
[OH-] = 10-pOH
Find the concentration of NaOH if pOH IS 0.815.
0.153M
Find the concentration of Sr(OH)2 if pOH is 1.319.
0.0240M
Formulas for pKw:
-log(Kw)
pH + pOH = pKw
Formula for pH and pOH at 25 degrees:
pH = 14 - pOH
pOH = 14 - pH



Percent ionization of strong acids?
Percent ionization of weak acids?
100%
less than 100%
What are steps that must be added to find pH for weak acids?
Ka and I.C.E chart.
Formula for % ionization:
% = ([H3O+] / [acid]initial) x 100
0.25M CH3COOH
a) pH?
b)% ionization
a) 2.674
b) 0.85%
[H3O+] of Nitrous Acid.
0.021M
0.200M of CHCl2COOH has pH of 1.13.
Find Ka:
4.4×10-2
500mL of H2C2O4 has pH of 1.095. Find the initial moles of H2C2O4.
0.095 mol
What is Kb?
Base ionization constant (equilibrium for bases).
What is hydrolosis?
Adding water.
Find Kb of F-
2.9×10-11
What must you do when looking for Kb in amphiprotic species?
Use Ka when species is at the RIGHT SIDE of the table.
Kb of HPO42-
1.6×10-7
Find pH of NaNO2
8.4
0.25M of weak base B- has a pH of 12.481.
a) Kb of base B-?
b) What is B-?
a) 4.2×10-3
b) HO2-
Kb of (CH3)2NH is 5.1×10-4 and the pH is 11.9435.
What is the initial [(CH3)2NH]?
0.16
[H+] of monoprotic strong acid
[H+] of diprotic strong acid
1.0M of monoprotic strong acid (like HCl) = 1.0M H+
1.0M of diprotic strong acid (like H2SO4) = 2.0M H+
a) Find the % dissociation of 2.4 M HNO3
and
b) what is the pH of the solution?
a) Because it is a strong acid the % dissociation is 100%. The molarity is irrelevent in this case.
b) The [H3O+] is 2.4M. This means the pH is:
pH = -log[H3O+]
pH = -log[2.4]
pH = -0.38
a) Find the % dissociation of 0.48 M H2S
and
b) what is the pH of the solution?
Ka | = | [HS- ][ H+]/[H2S ] |
9.1x10-8 | = | x2/0.48 |
x | = | (( 9.1x10-8)(0.48))0.5 |
x | = | 2.1x10-4 |
% dissociation | = | (2.1x10-4/0.48) x 100 |
% dissociation | = | 0.044 % |
b) The pH is given by the following:
The [ H3O+] is 2.1x10-4 M.
pH = -log[H3O+]
pH = -log[2.1x10-4]
pH = 3.68
Formula for ionization of water:
2H2O(l) + heat ←→ H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Heat increase in ionization of water:
shift?
concentration?
Kw?
pH?
pOH?
pKw?
acidic, basic, neutral?
shift right.
concentrations of hydronium and hydroxide increase at the same rate. (remain equal)
Kw increases
pH decreases
pOH decreases
pKw decreases
water remains neutral
Kw and pKw when:
Temperature > 25
Temperature < 25
Kw > 1.00×10-14 and pKw < 14
Kw < 1.00×10-14 and pKw > 14
At 20 degrees, Kw is 6.81×10-15
a) [H3O+]?
b) pH?
c) [OH-]?
d) pOH?
a) 8.25×10-8
b) 7.084
c) 8.25×10-8
d) 7.084
pH of pure water is 6.63
a) Kw
b) Temperature higher or lower than 25?
a) 5.5×10-14
b) Temperature > 25
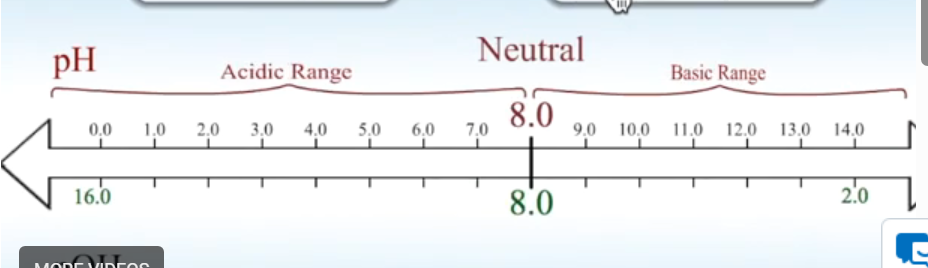
Draw pH diagram for 25 degrees.
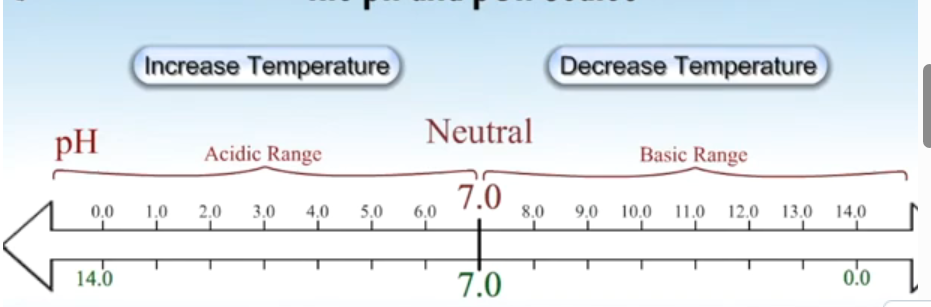
Draw pH diagram for higher than 25 degrees.
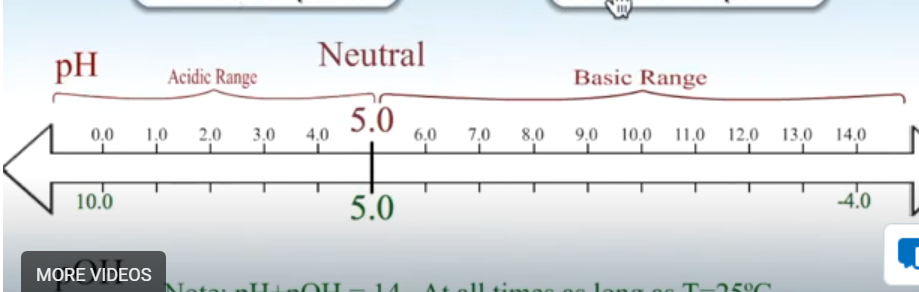
Draw pH diagram for lower than 25 degrees.
The [H3O+] of pure water at 0.0°C is 4.4 x 10-8M.
What is the pH of the solution?
What is the [OH-]?
Is the solution acidic, basic or neutral?
Calculate the pKw.
pH = -log[4.4 x 10-8] Therefore: pH = 7.36
Since the water is pure, [OH-] = [H+] = 4.4 x 10-8
Since [OH-] = [H+], the water remains neutral.
pKw = pH + pOH = 7.36 + 7.36 = 14.72
What is pure distilled water?
Water that has been purified by boiling it into steam and then condensing the steam back into liquid.
What is pure distilled water altered by?
Contaminants, which cause the pH to change and water to be no longer pure.
What is air made of?
True or False? It is easy to prevent air from contaminating.
Air is made up of several gases.
False. It is hard to prevent air from contaminating.
Describe solubility of Oxygen (O2), Nitrogen (N2), and Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
Oxygen and nitrogen dissolve in water but have little effect on pH.
Carbon dioxide has high solubility in water, which allows a sequence of reactions to occur.
What is the sequence produced by Carbon Dioxide?
CO2 + H2O ←→ H2CO3
H2CO3 ←→ H3O+ + HCO3- (BICARBONATE ION)
What does the formation of H3O+ cause?
It causes rain water to have a pH of 5.8 to 6.2.
Why does the pH vary?
Because the solubility of CO2 changes as well as Kw when temperature changes.
Define acid rain.
Rain that is acidic.
Why does acid rain form?
Because of gases that dissolve in the rain water.
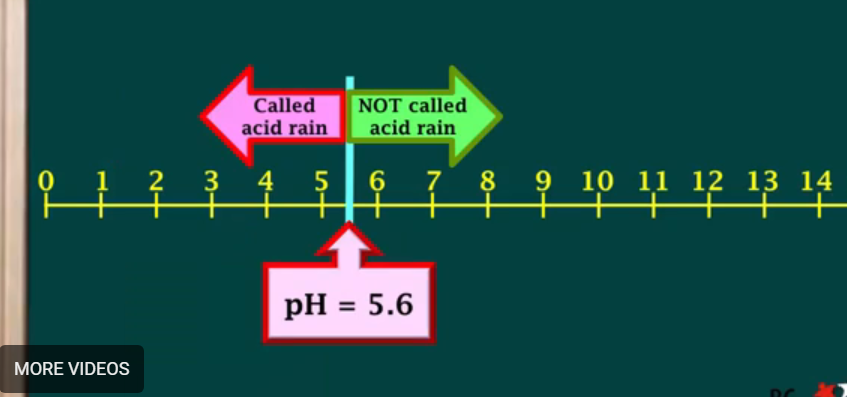
Why is rain naturally slightly acidic?
What pH do these reasons give to the rain?
Because of CO2 derived from animals breathing
Lesser extent: Chlorine from salt in sea
Those two give rain a pH of approximately 5.6.
How do fossil fuels contribute to acid rain?
When burned, fossil fuels get released in the air and combine with moisture to create acid rain.
pH of acid rain:
Precipitation with pH higher lower than 5.6.
Which gas is 70% of acid rain made up from?
What about the rest?
Where do those gases come from?
70% of acid rain is made from SO2
The rest comes from oxides of nitrogen (NO2, NO3, NOx)
Those gases come from burning fossil fuels (power stations and road transport)
70% of sulfur emmissions in North America come from…
70% of sulfur emmissions in North America come from burning electrical power plants and ore smelting.
40% of NOx is from _____________ and the rest is from ________________.
40% of NOx is from transportations and the rest is from fossil fuel and combustion.
What are mixtures of most fuels including coal and oil made of?
Many different hydrocarbons, some of which contain sulphur.
What will gardeners add to soil to lower the pH and why does it work?
Write down the steps.
Gardeners will add elemental Sulfur(S) to soil to lower the pH. This works because Sulfur is a acidic anhydride:
Step 1: | S(s) | + | O2(g) |  | SO2(g) |
Step 2: | SO2(g) | + | H2O(g) |  | H2SO3(g) |
Optional step 2: | SO2(g) | + | 1/2O2(g) |  | SO3(g) |
followed by: | SO3(g) | + | H2O(g) |  | H2SO4(g) |
What constitutes acid rain?
The “soup” made from H2SO3, H2SO4, HNO2, and HNO3.
Six natural things that contribute to acid rain:
Volcanic eruptions (SO2)
Gas from rotting vegetation
Lighting (produces nitric oxide)
Releases Al+3 ions from rock and soil (affects fish and plants)
Washes away nutrients important for trees and crops
Contaminates water
Two ways how lakes are protected from acid rain:
Moderate CO2 and HCO3 buffers (damages occurs when buffers get exceeded)
Rich in limestone, which neutralizes
What are effects of acid rain reversed by?
Absorption of CO2 from atmosphere.
List two environmental problems with acid rain and what they are affected by:
Fish (affected by acidified water)
Plant-grow (affected by acidified soil)
Minimum pH for it to be acid rain:


What is air made up of?
78% nitrogen
21% oxygen
1% other gases
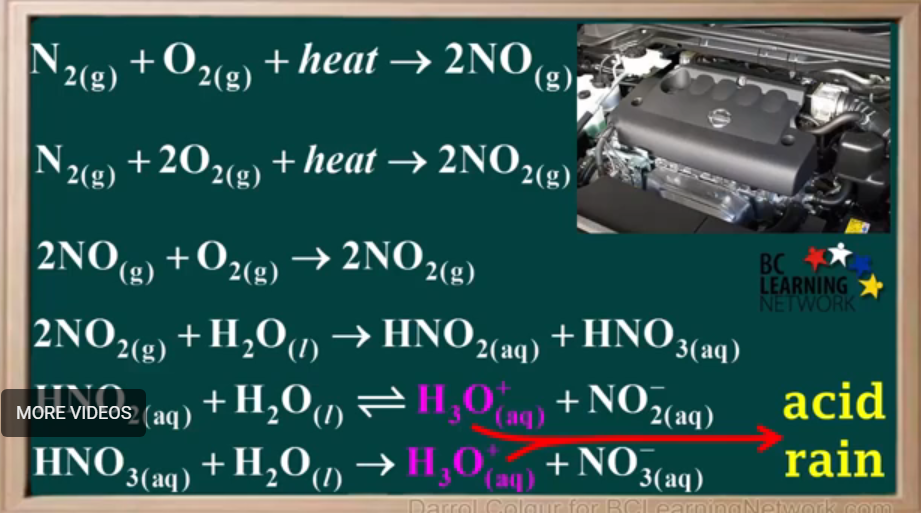
Write the equations that occur when automobile is heated:
What is produce when fossil fuels burn?
Write the equation:
Sulfur
S(s) + O2(g) —→ SO2(g)
Two major equation that occur when ores are roasted in smelters:
In the next question, state what happens to some of this SO2


;)
What does acid rain do to rocks and soils?
Leaches out minerals out of them.
What does acid rain do to metal and stone structures?
Damages them, especially when made from limestone.
What does acid rain do to ancient building and structures?
Destroys them.
Do the nations that cause the acid rain problem suffer from it?
No, acid rain falls far from where it was created, which means that other nations suffer from the consequences.
Acid rain and health.
People’s health suffers from acid rain because of contaminated water and chemicals from leached soil and rock.
Six ways of getting rid of pollution:
Public awareness
New technologies
Non-polluting energy sources
Modernized, non-polluting, industrial processes
International cooperation
Reclaiming SO2 that is emitted from smelting and using it to produce sulfuric acid instead of being released into the environment.
What is an anhydride? Its resulting compound?
A compound that had the water removed from it. Resulting compound is an oxide.
Acid acidic anhydride of H2SO4:
H2SO4 —→ H2O + SO3(g)
Base basic anhydride of 2NaOH:
2NaOH —→ H2O + Na2O(g)
How to increase pH of anhydride?
Add lime (CaO) because lime is a basic anhydride.
CaO(s) + H2O —→ Ca(OH)2(aq)
How to decrease pH of anhydride?
Add sulfur (S) because sulfur is an acidic anhydride.
S(s) + O2(g) —→ SO2(g)
SO2(g) + H2O(g) —→ H2SO3(g)
SO3(g) + H2O(g) —→ H2SO4(g)
What do metallic oxides form?
Basic Anhydrides
What do non-metallic oxides form?
Acidic Anhydrides
Vehicles that burn fossil fuels:
all contain…
emit…
result in…
all contain Sulfur
emit some SO2(g) and SO3(g)
result in Acid Rain
What is the anhydride of H2CO3?
Subtract 2 H's and 1 O atom from the formula to leave CO2.
What is the anhydride of Ba(OH)2?
Extract two H's and 1 O to leave BaO.
What is the result if N2O3 gas is bubbled through water?
Add one water molecule to the anhydride to produce H2N2O4.
This looks strange but if you are creative you will see that you can simplify by dividing by two, to produce two molecules of the weak acid HNO2.