Biology I Lesson 3: Studying The Brain
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
True or False? Phrenology is the study of cerebral hemispheres in which a larger left hemisphere indicates that an individual is "left-brained." It is a methodology that is well-accepted in the scientific community.
False. Phrenology involved the studying of bumps on one's skull in determining the characteristics of an individual. It is an early method for studying the brain that has no scientific backing today.
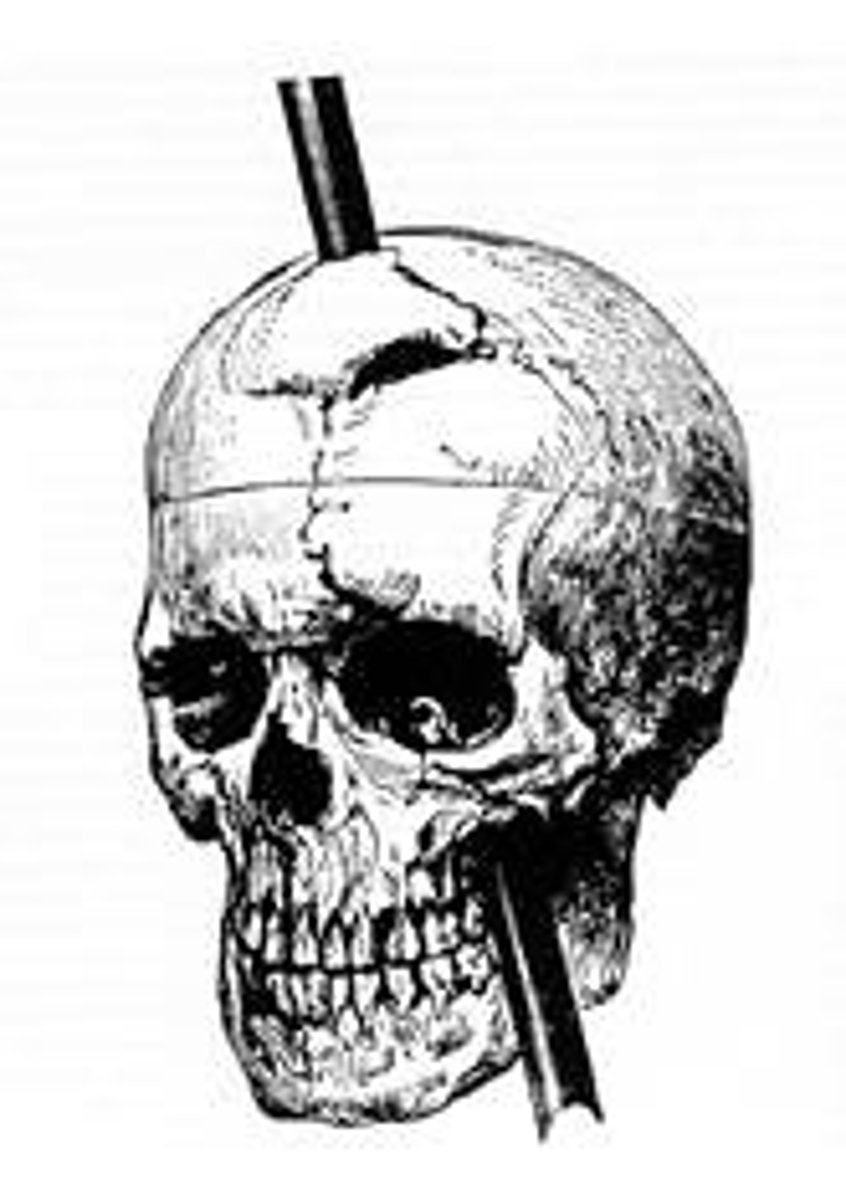
A railroad spike went through Phineas Gage's skull and brain. What was so significant about this event?
His behavior and emotional disposition changed dramatically. He was easily angered and more impulsive than before (due to damage to his Frontal Lobe). This revealed to scientists that certain areas of the brain must be responsible for certain functions.
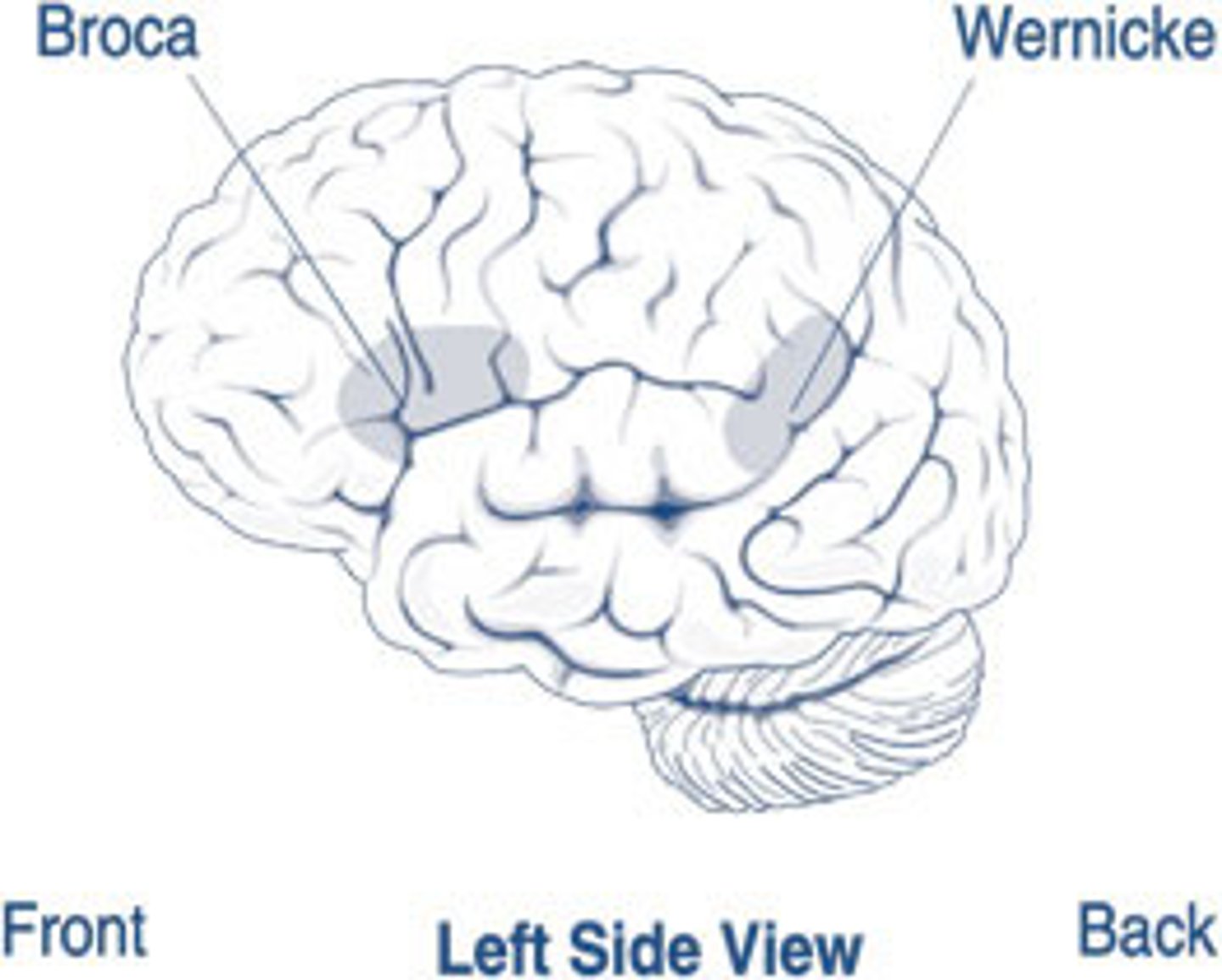
Paul Broca was a French anatomist, and performed many autopsies on former patients with serious speech impediments, sometimes unable to speak or only say one word chunks with long pauses, and found similar lesions in each. This area is now called Broca's Area and patient's with damage to this area are said to have Broca's Aphasia. Where in the brain is Broca's Area usually located?
(A) Right Frontal Lobe
(B) Left Frontal Lobe
(C) Right Parietal Loba
(D) Left Parietal Lobe
(B) Left Frontal Lobe
Broca's Area is usually located in the Left Frontal Lobe. The Left Hemisphere is responsible for language, and the Frontal Lobe contains the Motor Cortex, which would allow for the movement of muscles associated with the mouth. In some individuals, it is found in the Right Frontal Lobe, but this is less common.
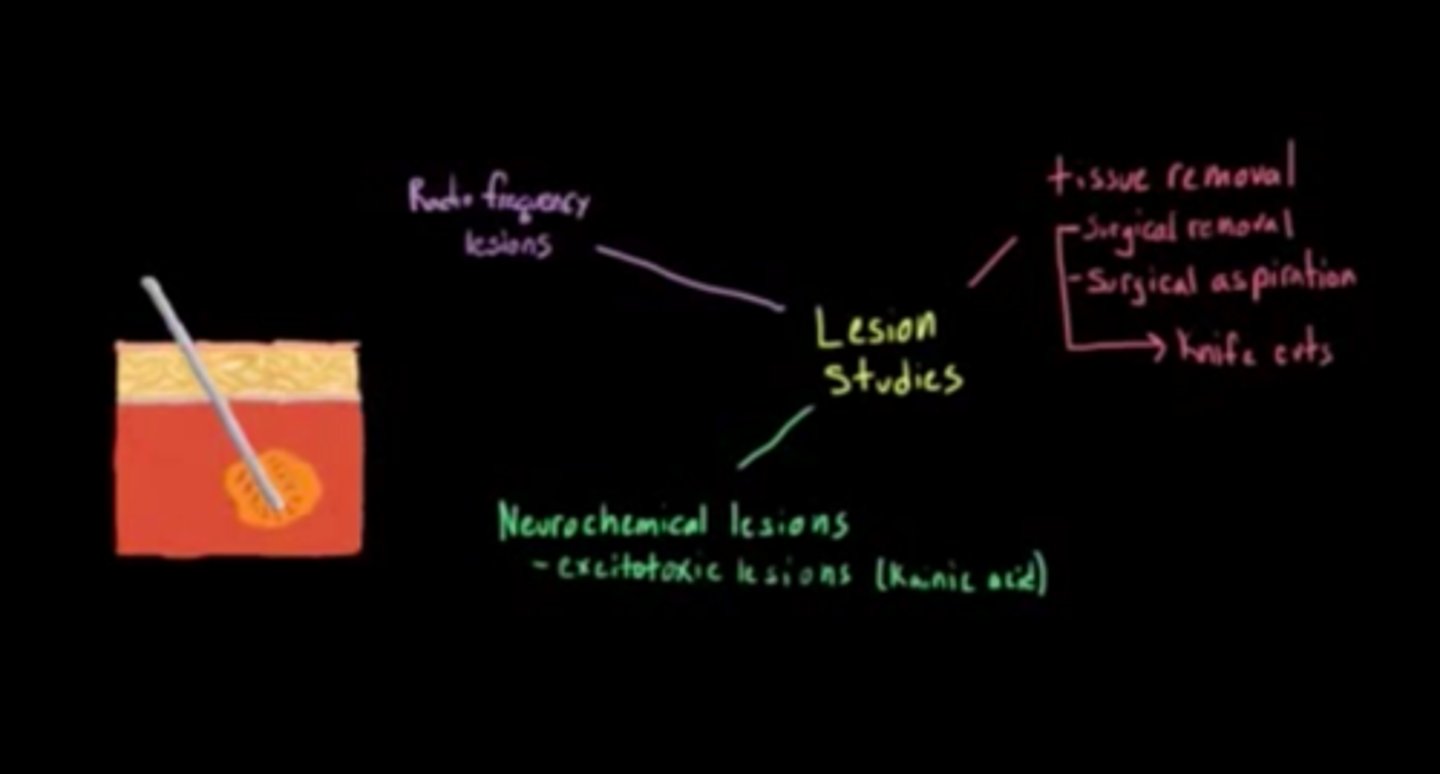
Which of the following lesion studies entail a temporary change in the brain?
I. Tissue Denaturing
II. Cryogenic Blockade
III. Neurochemical Lesions
(A) II only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II, and III
(A) II only
Only Cryogenic Blockades and some Neurochemical Lesions can cause changes in the brain for scientist to study the brain.
However, Neurochemical lesions tend to irreversibly damage or kill the affected cells, so only cryogenic blockades are temporary.
CRB In research, the FINER method is used to evaluate if a question is worth evaluating. Which of the following parts of FINER would be most related to determining methods used, like temporary brain changes when possible instead of permanent changes.?
(A) Interest
(B) Novel
(C) Ethical Principles
(D) Relevancy
(C) Ethical Principles
Whether these methods are really acceptable and the most appropriate would be evaluated as Ethical Principles.
Note that the F in FINER stands for Feasability.

CRB When talking about Ethics in medicine, people commonly refer to the four main tenants. Which of the following is NOT one of the four main tenants?
(A) Nonmaleficence
(B) Beneficence
(C) Compassion
(D) Justice
(C) Compassion
The four tenants of ethics in medicine are Nonmaleficence, Beneficence, Respect for Autonomy of the Patient, and Justice

CRB Nonmaleficence and Beneficence sound like one and the same. Compare the two.
Beneficence is the obligation to act in the patient's best interest, whereas Nonmaleficence is an obligation to avoid treatments that may cause more harm than good. There is a fine line between the two!

Compare Cortical Cooling and the Cryogenic Blockade.
Cortical Cooling and the Cryogenic Blockade refer to the same procedure, which involves using a Cryoloop to temporarily freeze a part of the brain, making it nonfunctional for the duration of the experiment.
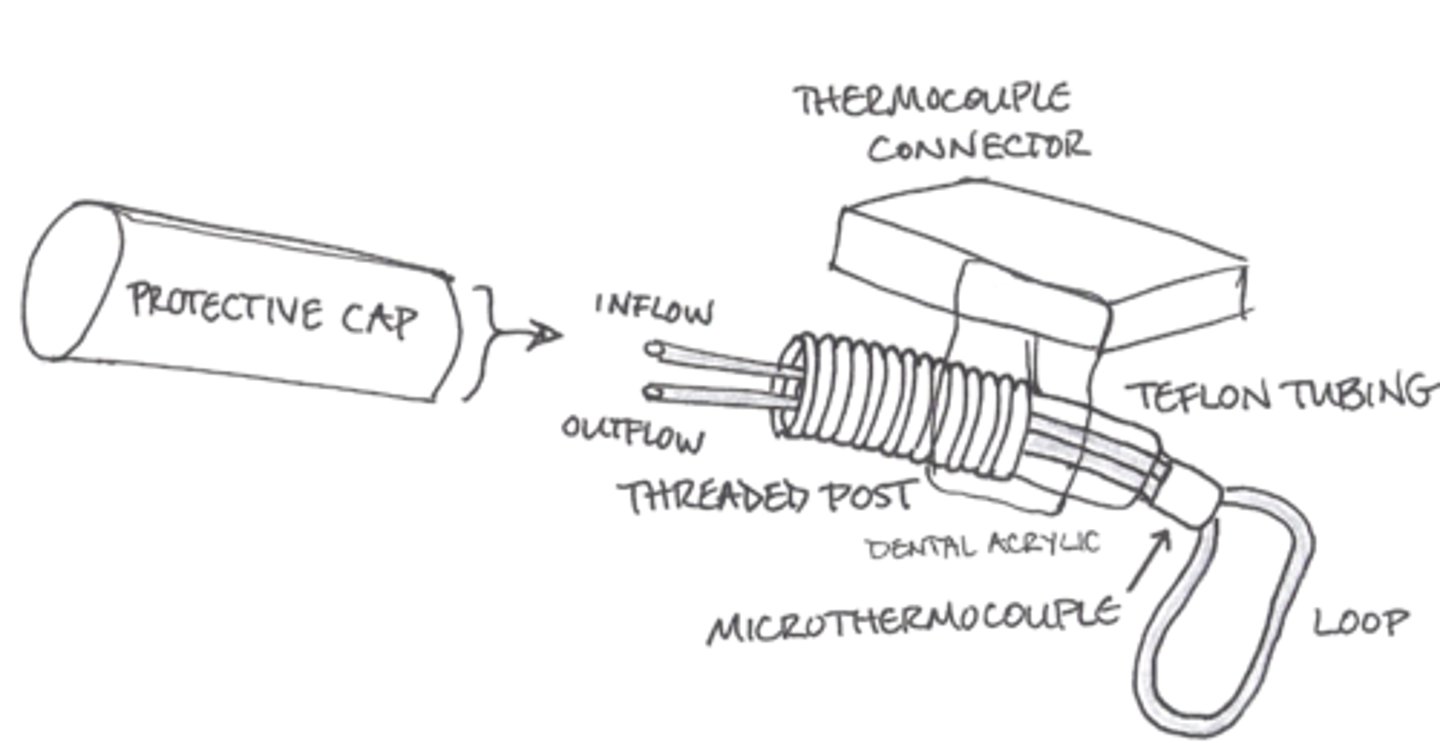
CRB Imagine that a devoutly religious family comes to your clinic. You recommend that the patient undergo an invasive treatment method like Cortical Cooling, but the family insists that no invasive procedures can be done on the live human body, or else it risks the soul forever. Which tenet of medical ethics demands that you follow the patients' wishes here?
(A) Beneficence
(B) Nonmaleficence
(C) Autonomy
(D) Justice
(C) Autonomy
Autonomy states that we have a responsibility to respect our patients' decisions and choices about their own healthcare.

CRB Think of an example where Justice, the need for equal distribution of goods and services where needed, could come into play at a low-budget clinic.
A low-budget clinic may have less resources, like maybe only a limited amount of their best anesthetic. Justice would be an issue if the clinic were saving the best of their resources for people with better insurance coverage or some other external factor, instead of strictly based on the patients' needs.

Sam has a brain tumor. To destroy the tumor, wire insulated everywhere except at the very tip is inserted into the brain. What term best describes this procedure?
(A) Tissue Removal
(B) Neurochemical lesion
(C) Cryogenic Blockade
(D) Radio Frequency Lesions
(D) Radio Frequency Lesions
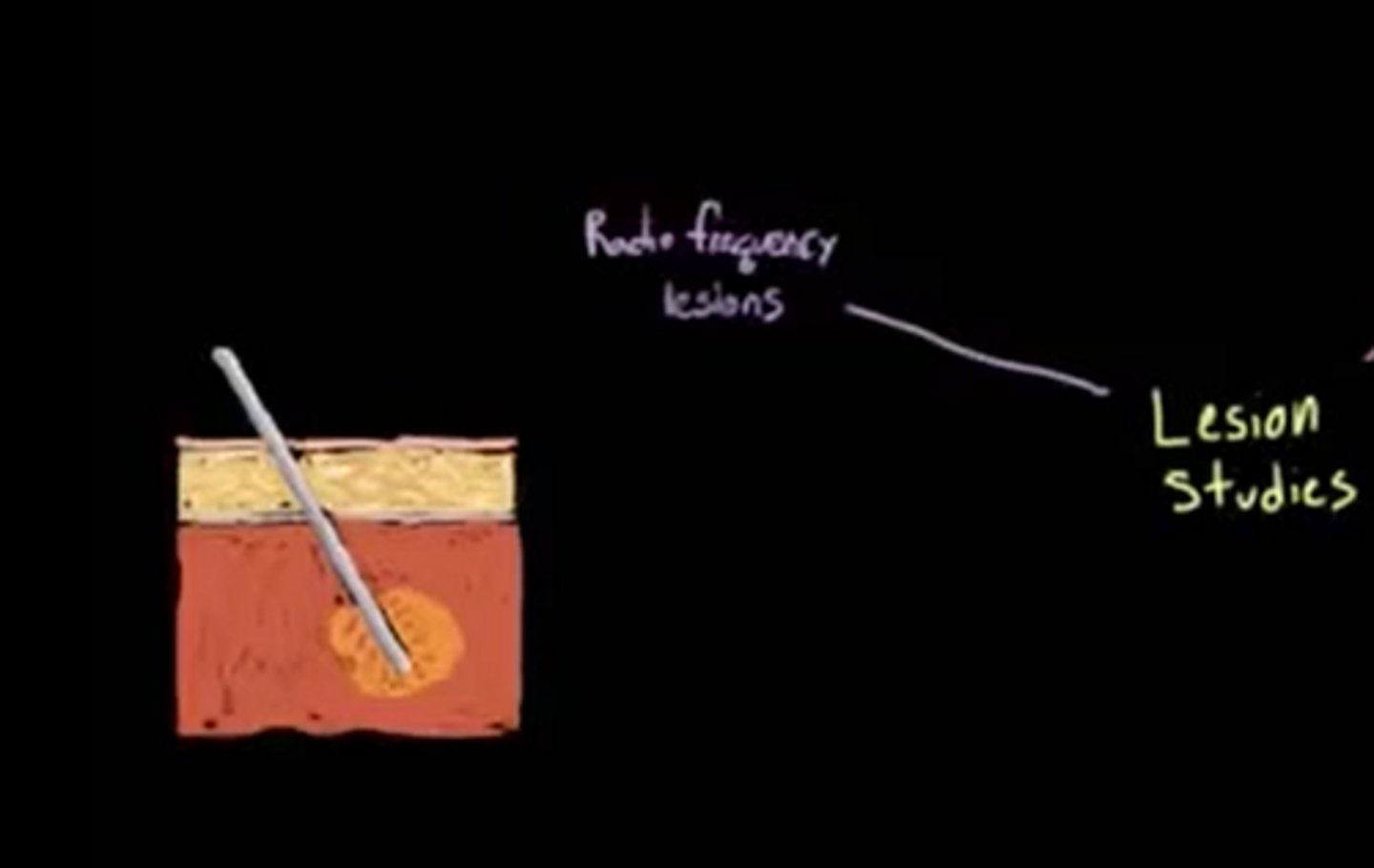
A researcher uses the Radio Frequency Lesion technique to destroy an area of the Temporal Lobe. The researcher notices that the subject's vision is severely affected. Why might this be the case?
Radio Frequency Lesions don't just destroy neurons in that specific brain area, but they also destroy any neurons that are passing through. Perhaps, some of the neurons passing through the damaged area are heading to or from the Occipital Lobe.
CRB When actually researching the effects of Radio Frequency Lesions, researchers wanted to verify this technique was causing the damage to nearby areas. Hill's Criteria may have been used to make sure that this was a causal relationship and not just a correlation. Which of the following is NOT one of Hill's Criteria?
(A) Temporality - whether the Lesion occurred before or after the symptoms' onset.
(B) Consistency - whether this relationship is seen in multiple patients.
(C) Anonymity - whether the people evaluating the experiment are biased or not.
(D) Plausibility - whether there is a reasonable way that the Lesion could have caused the symptoms.
(C) Anonymity - whether the people evaluating the experiment are biased or not.
Other examples of Hill's Criteria include:
- The strength of the relationship
- Any dose-response relationship
- Consideration of Alternative explanations
- Whether it was an Experiment or Correlational study
- Specificity
- Coherence - whether the new data and hypothesis align with other current knowledge.

Tim's temporal lobe is removed by a physician. What term best describes this procedure? Which sensory function will he lose?
(A) Tissue Removal
(B) Neurochemical lesion
(C) Cryogenic Blockade
(D) Radio Frequency Lesions
(A) Tissue Removal
Tim will not be able to hear if you remove his temporal lobe.
Dr. Al and his lab are working towards finding a cure for Parkinson's Disease. To aid them, they have modeled Parkinson's disease in the animals of their lab by targetting and destroying the dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra using 6-Hydroxydopamine. What term best describes this procedure?
(A) Tissue Removal
(B) Neurochemical lesion
(C) Cryogenic Blockade
(D) Radio Frequency Lesions
(B) Neurochemical lesion
This type of lesion study gives a lot of control, by destroying the cell bodies and very specific populations of neurons within specific areas of the brain.
Which of the following tests of studying the brain tell us about the brain structure?
I. CT Scans
II. MRI
III. EEG
(A) II Only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(B) I and II only
CT Scans and MRIs tell us information about the structure of the brain, whereas EEGs tell us information about the functions of the brain.
Which of the following tests for studying the brain tell us information about the function of the brain?
I. CT Scans & MRI
II. EEG & MEG
III. fMRI & PET
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) II & III only
(D) I & II only
(C) II & III only
Both EEG & MEG tell us about the brain function. In addition, fMRI & PET do the same with the added bonus of telling us about the brain structure as well as function.
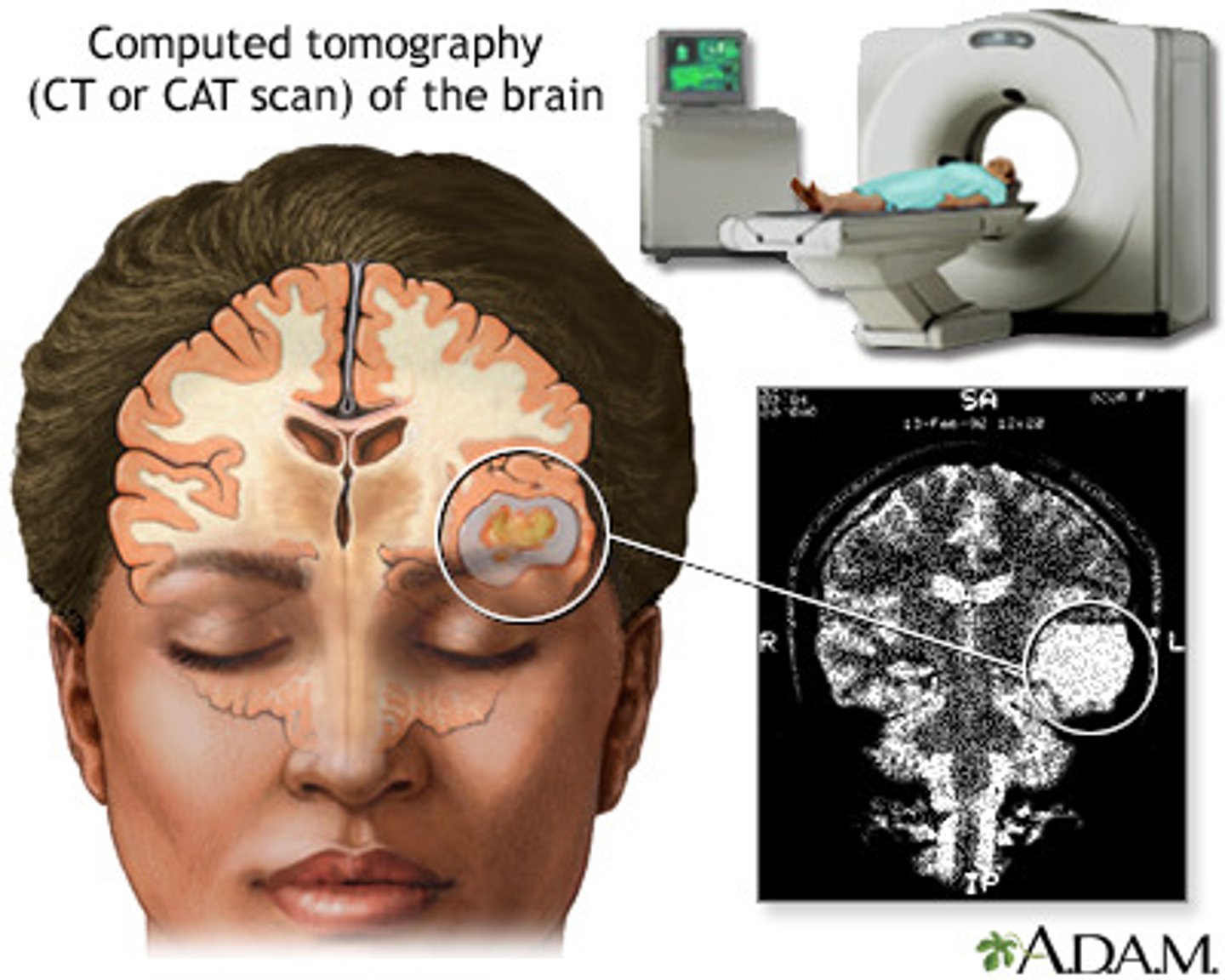
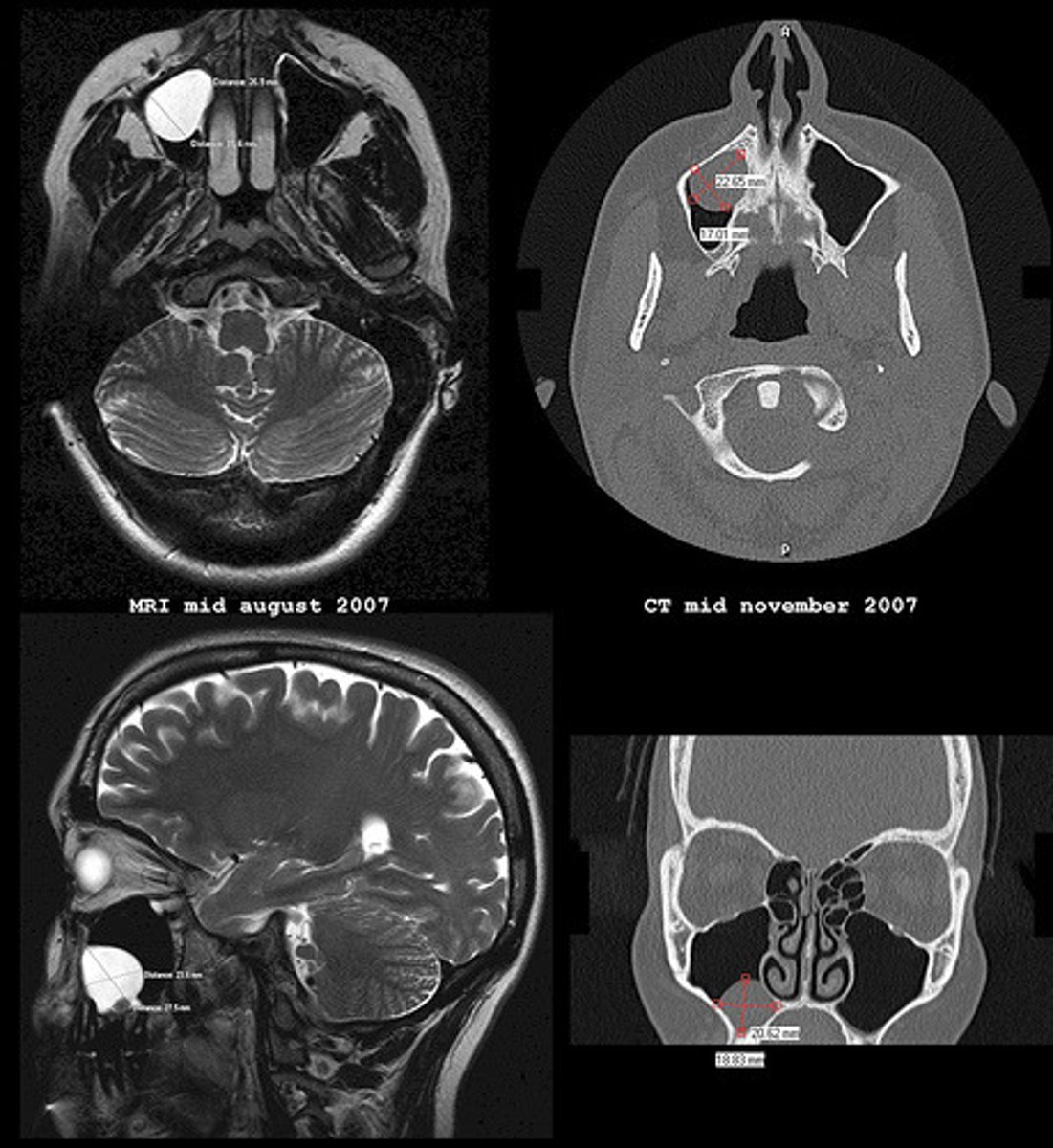
Which of the following techniques entails using X-rays to create a detailed image of the brain?
(A) PET scans
(B) MRI
(C) CT Scans
(D) EEG
(C) CT Scans
CT Scans use X-rays to create a detailed image of the brain.
CT Scans can provide us with which of the following information?
I. Which brain areas are currently active
II. Which brain areas are currently bleeding
III. Which brain areas are currently damaged
(A) I and II Only
(B) I and III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) II and III Only
CT Scans provide us with structural information such as which brain areas are damaged or bleeding. They cannot provide us with functional data such as which brain areas are currently active. You'd want to use an fMRI for that.
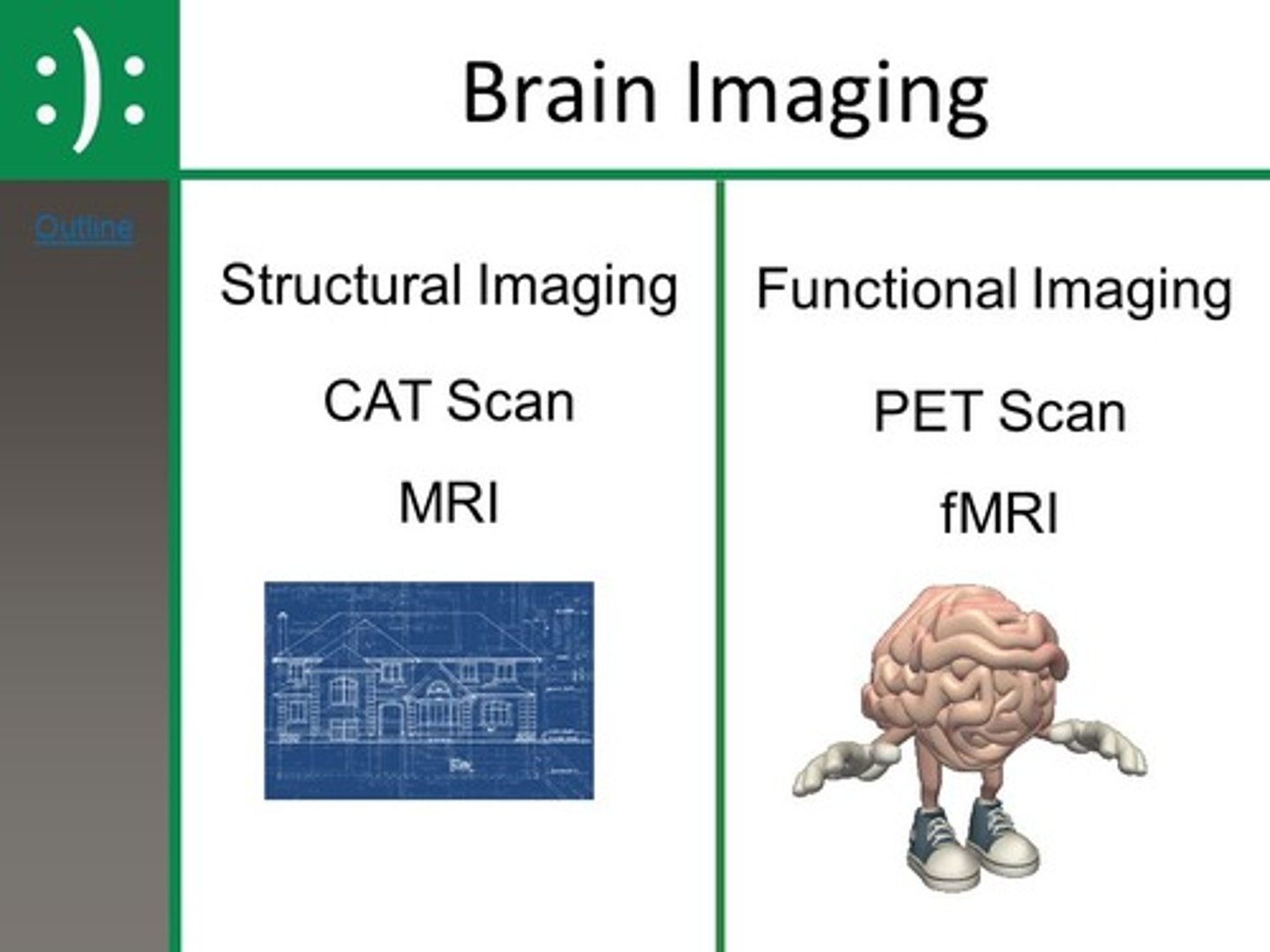
Compare a CT Scan with MRI.
CAT (CT) scans use X rays while MRI's use radio waves to create an image.
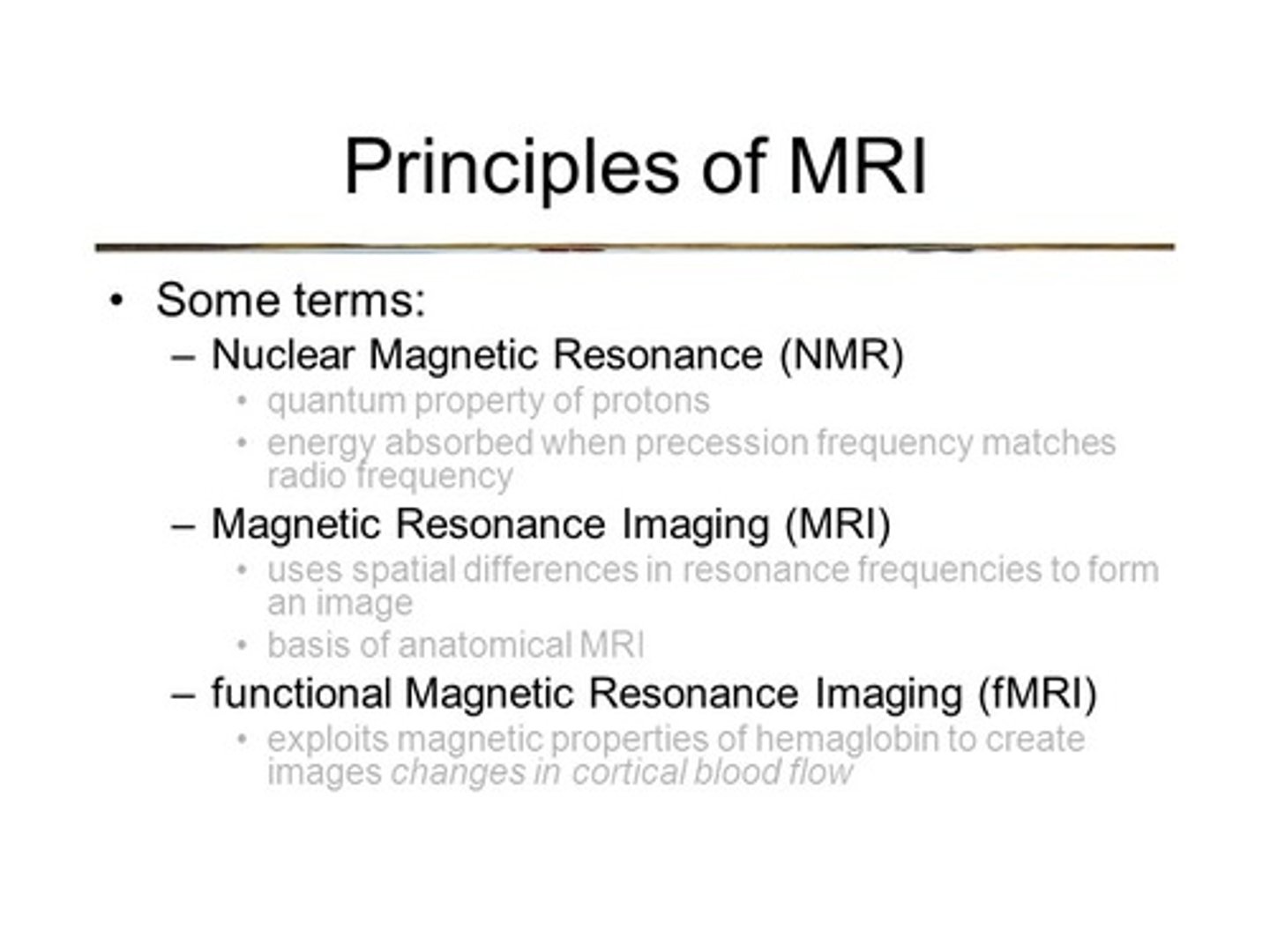
MRI is most similar to what technique used in Organic Chemistry?
(A) Mass Spectroscopy
(B) NMR
(C) Distillation
(D) Extraction
(B) NMR
Both NMR and MRI rely on using a magnetic field to orient protons in a certain direction.
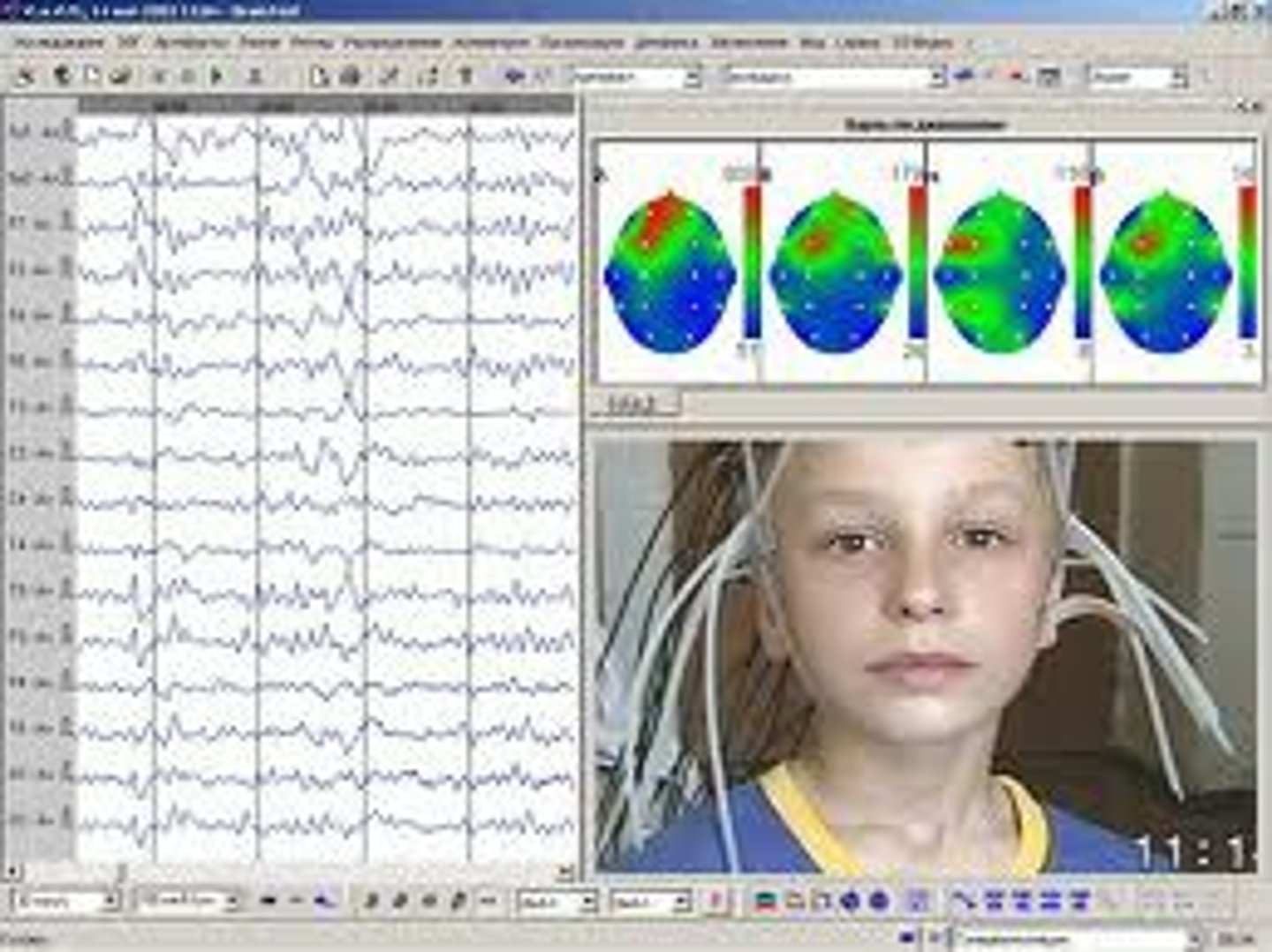
Mark has been having trouble sleeping at night. He goes into a sleep clinic to get evaluated. Which of the following tests will they use to evaluate his sleeping patterns?
(A) PET scans
(B) MRI
(C) CT Scans
(D) EEG
(D) EEG
While there is no picture of the brain associated with this, it records sleep patterns. In addition, it can also show if someone had a seizure and engaged in different cognitive tasks.
CRB When Mark went to get his sleeping patterns evaluated, the researchers noticed that Mark is a white male, and looked for other, additional specific symptoms based on his background and sleep issues. What would this be an example of?
(A) Selection Bias
(B) Lack-Of-Blinding Bias
(C) Detection Bias
(D) This is not bias
(C) Detection Bias
Detection bias comes from when professionals use their knowledge inconsistently. Here, the researcher knows that white males with sleep issues commonly suffer from other issues and specifically went out looking for those.
CRB Compare Bias and Confounding.
Both Bias and Confounding are issues that can skew results and conclusions.
Bias results from flaws while collecting data.
Confounding is an error during data analysis.
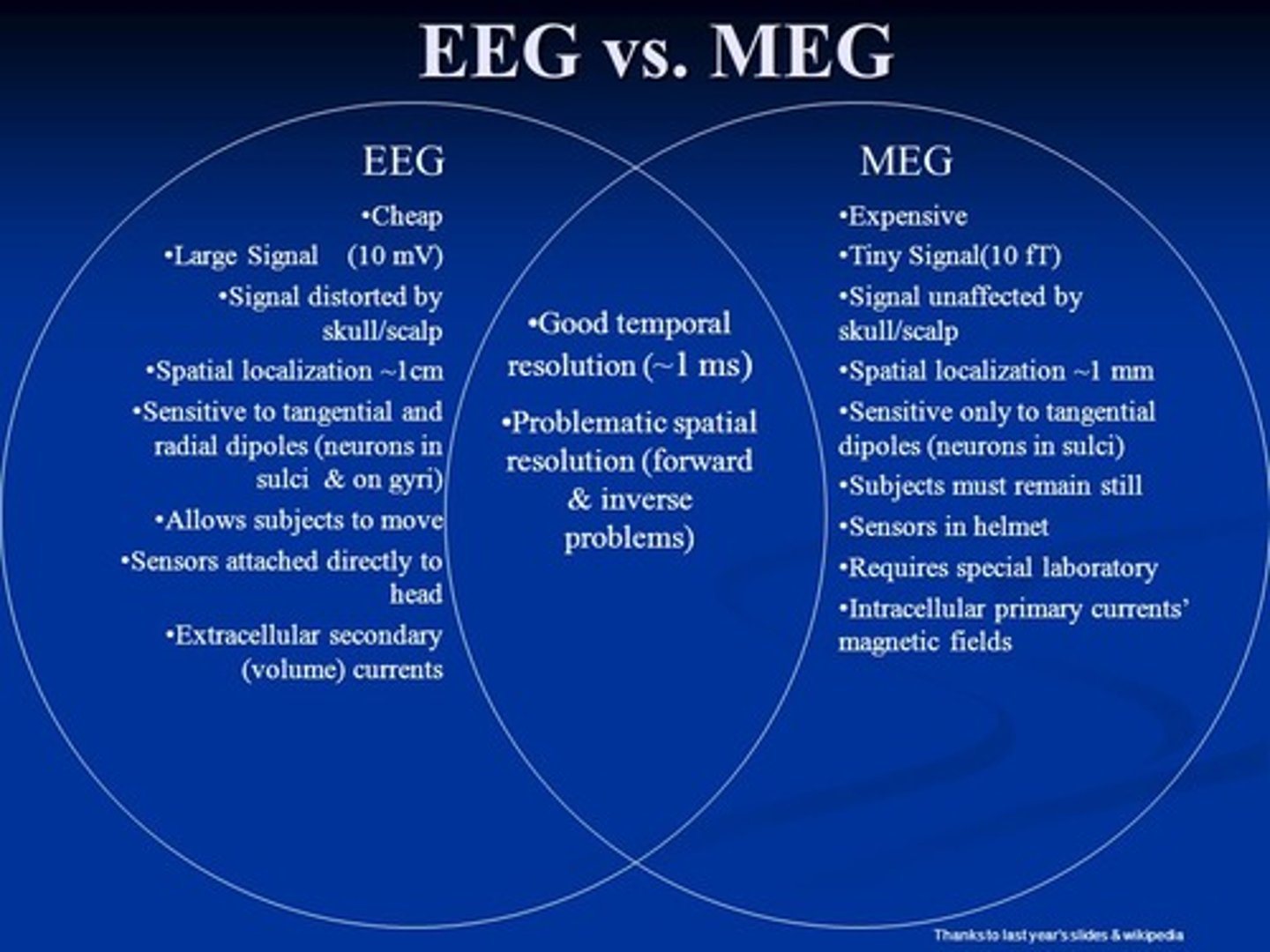
Between EEG & MEG, one has a better resolution, but also requires a lot of set up and a separate room, so it's usually not used as much. Which one is that?
MEG uses SQUIDS, which has a better resolution than EEG, but it also requires a lot of set up and a separate room. For this reason, EEG are used more often.
Jack is a participant in a research project, and is asked to drink radioactive glucose, which is then used to create a functional image of his brain. Which research technique is being utilized in this scenario?
(A) PET scans
(B) fMRI
(C) CT Scans
(D) EEG
(A) PET scans
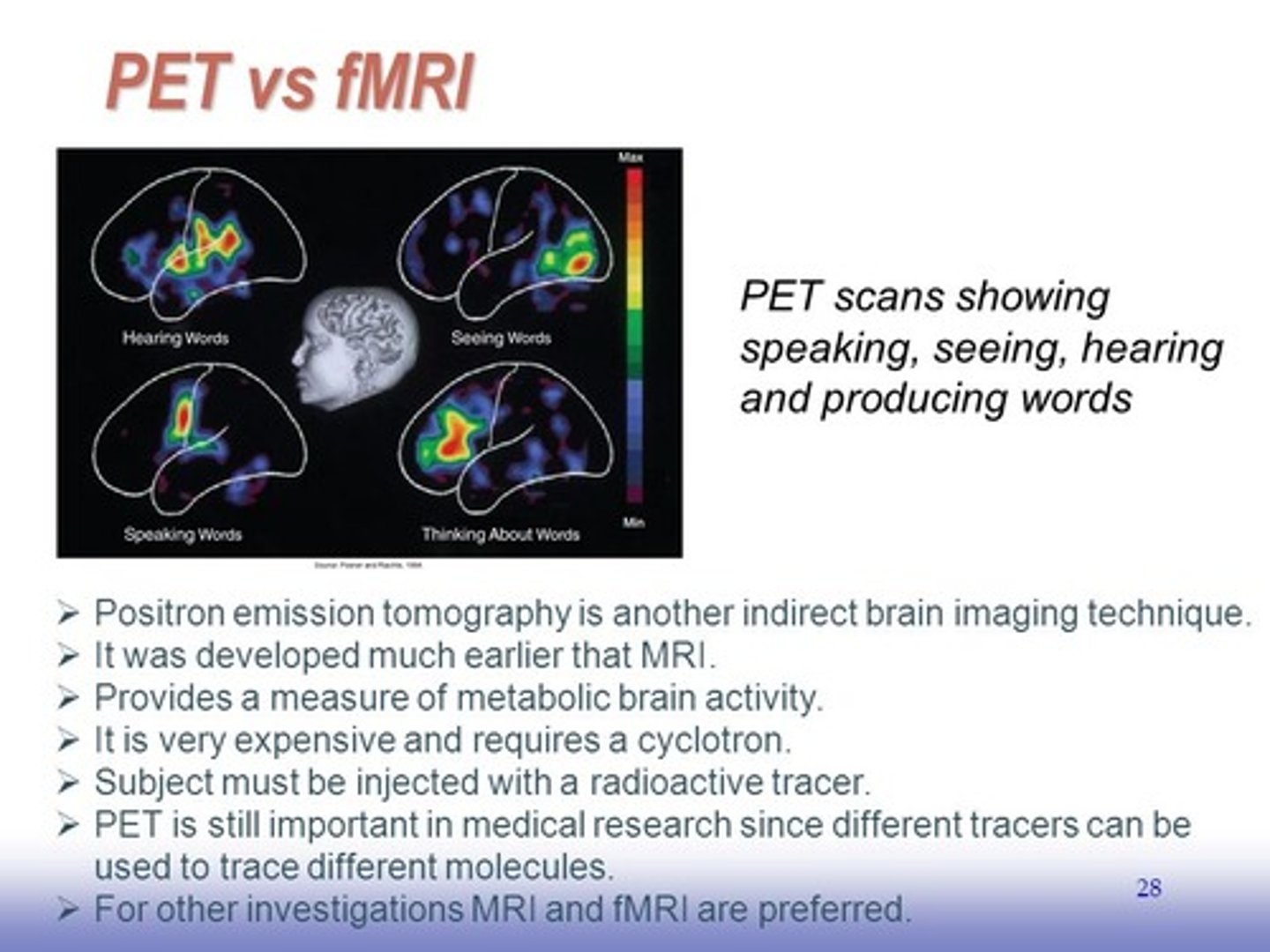
Which is used more commonly? fMRI or PET?
fMRI is less invasive and easier to set up. It is used very often.
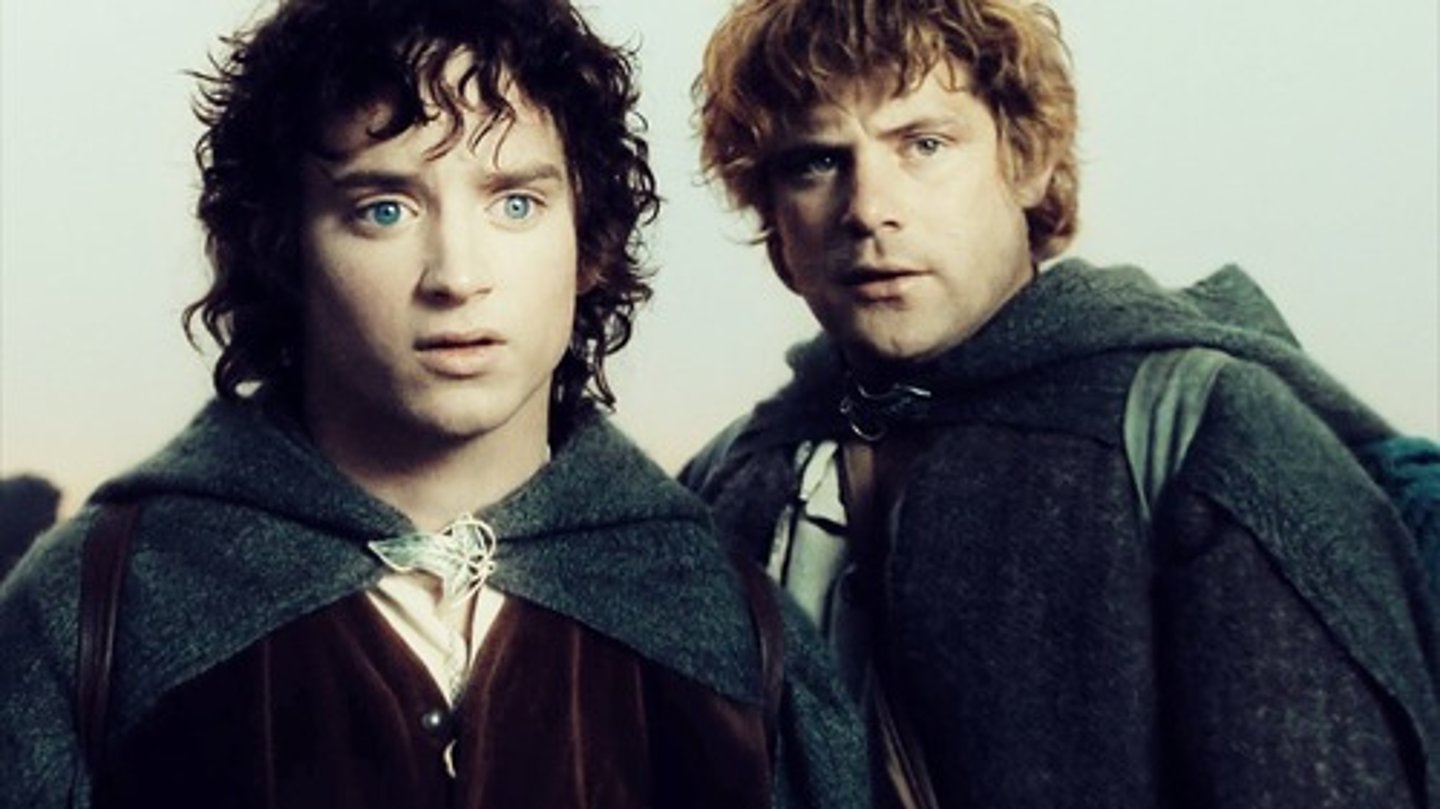
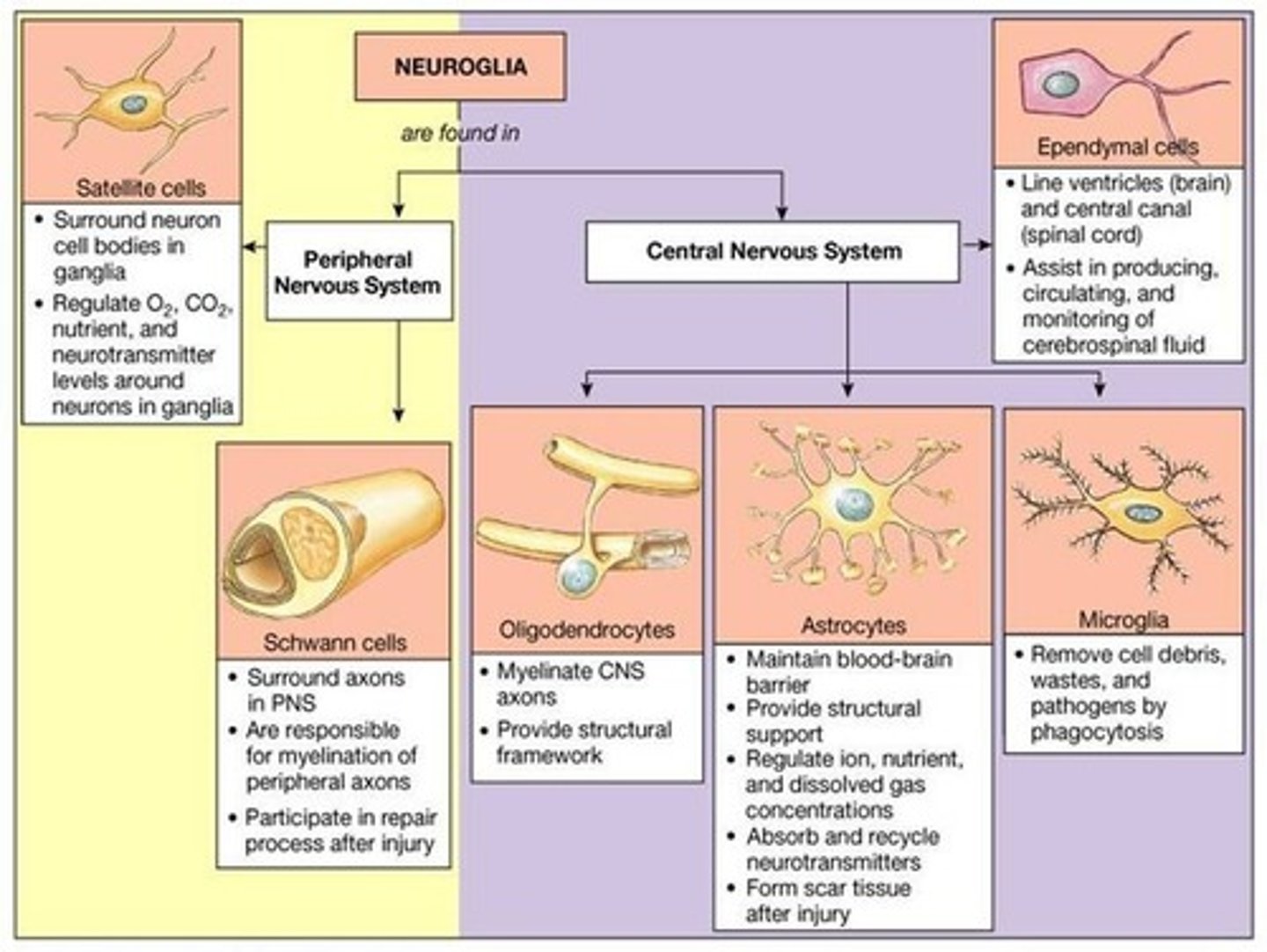
Compare the function of the two types of Neural Cells: Neurons vs. Glia?
Neurons transmit information (think Frodo). Glia function to support Neurons in doing their job (think Sam).

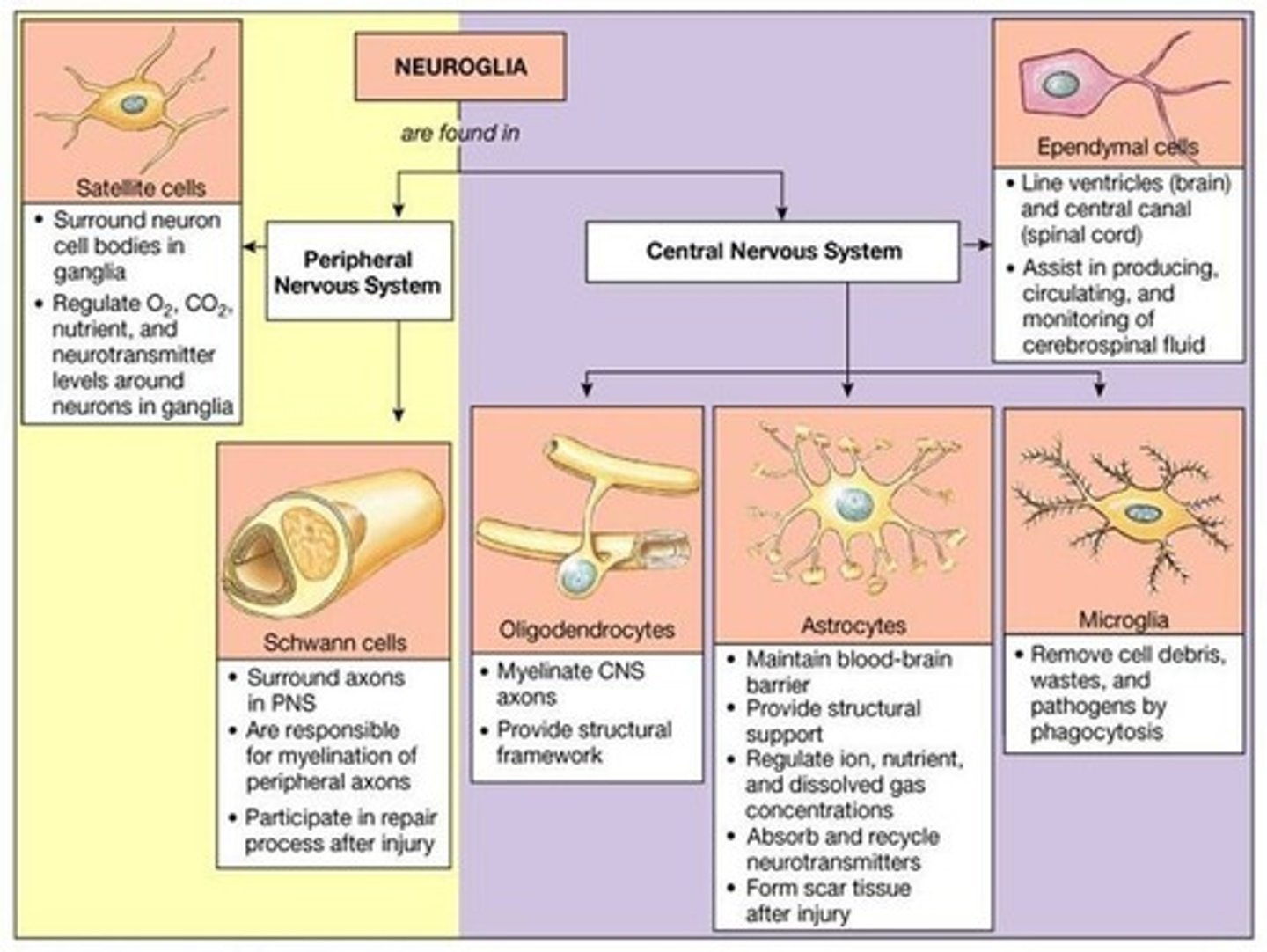
True or False? While neurons are located all over the CNS and PNS, the specific types of Glial Cells are only found in either the CNS or PNS.
True. Neurons are located throughout the CNS and PNS. Specific types of Glial cells are specific to either the CNS or PNS.
Match the Neuron & Glial cell location to the cells it was derived from.
(A) CNS
(B) PNS
(1) Neural Crest Cells
(2) Neural Stem Cells
(A) -- 2
(B) -- 1
Neurons and Glial cells in the CNS are derived from the neural stem cells, whereas in the PNS, they are derived from neural crest cells.
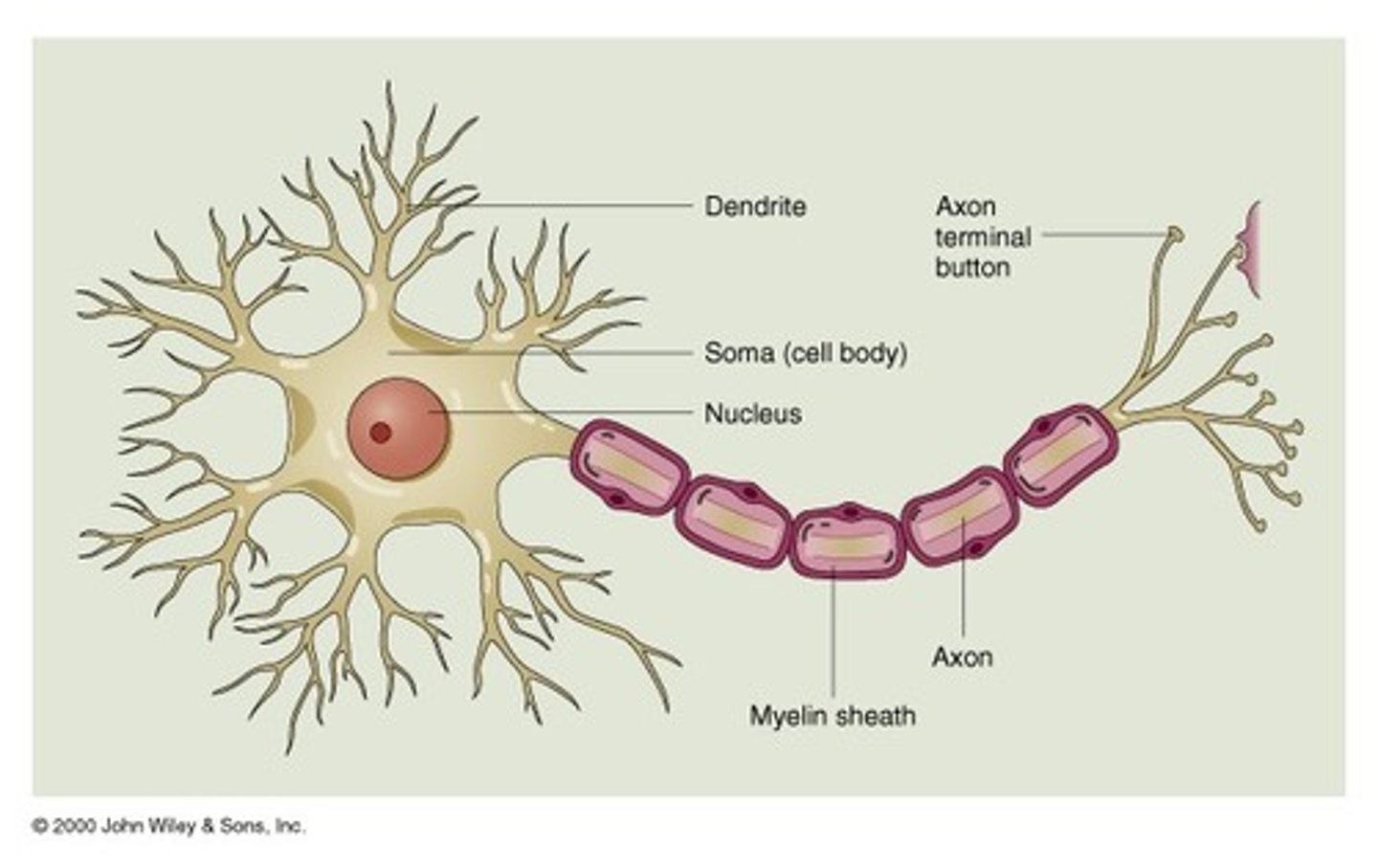
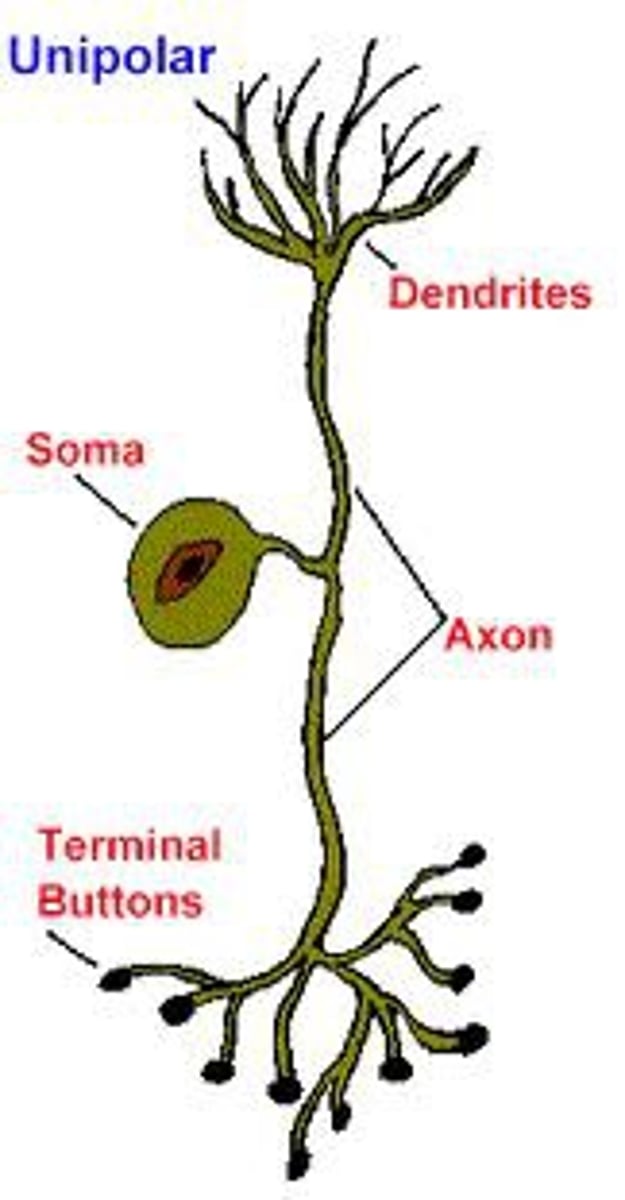
Match the parts of the neuron to their function:
(A) Axon
(B) Dendrites
(C) Soma
(D) Nodes of Ranvier
(E) Myelin Sheath
(1) Cell's life support center
(2) Receive messages from other cells
(3) Passes message away from cell body to other neurons
(4) Helps speed neural impulse
(5) Gaps between myelin sheath, help with conduction of nerve impulses
(A) -- 3
Axon -- Passes message away from cell body to other neurons
(B) -- 2
Dendrites -- Receive messages from other cells
(C) -- 1
Soma -- Cell's life support center
(D) -- 5
Nodes of Ranvier -- Gaps between myelin sheath, help conduction of nerve impulses
(E) -- 4
Myelin Sheath -- Helps speed neural impulse
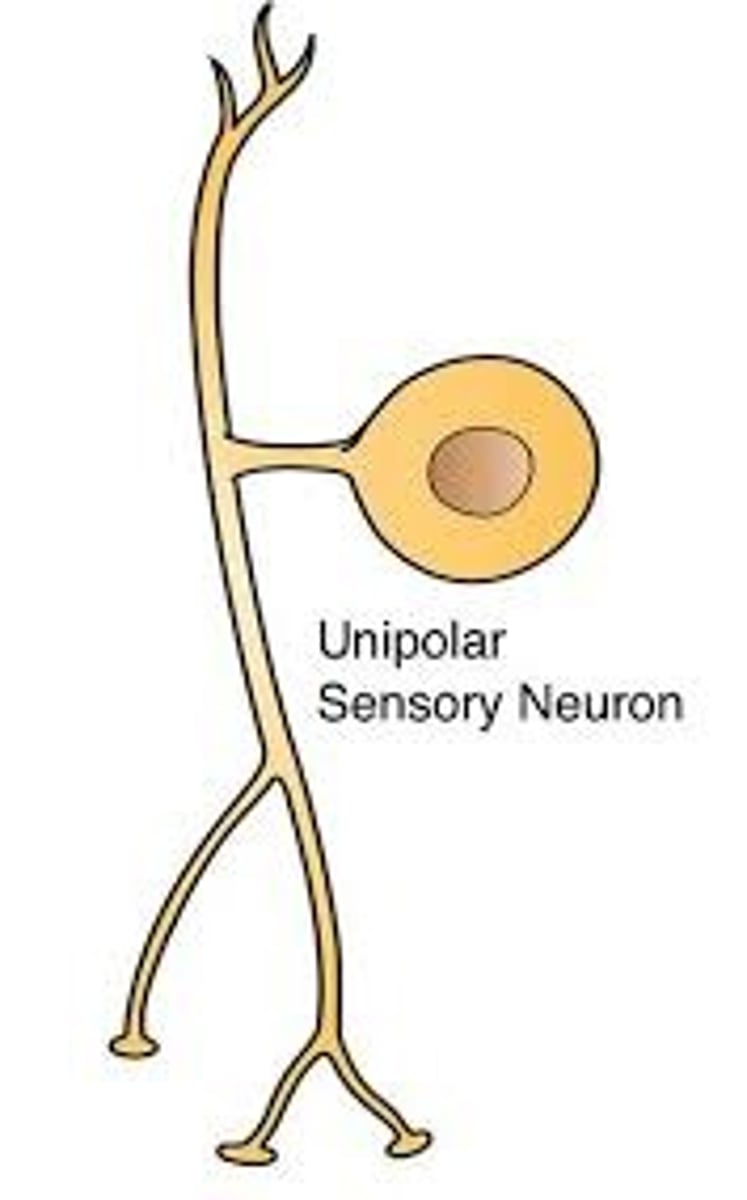
A unipolar neuron has ____ axon(s) projecting from the soma.
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Four
(A) One
A unipolar neuron has one axon projecting from the soma, and no dendrites, hence the name UNI-polar.
These are most common in humans during development.
A bipolar neuron has one axon projecting from it and one dendrite. What's the difference between a bipolar neuron and a multipolar neuron?
A multipolar neuron has multiple dendrites projecting from it.
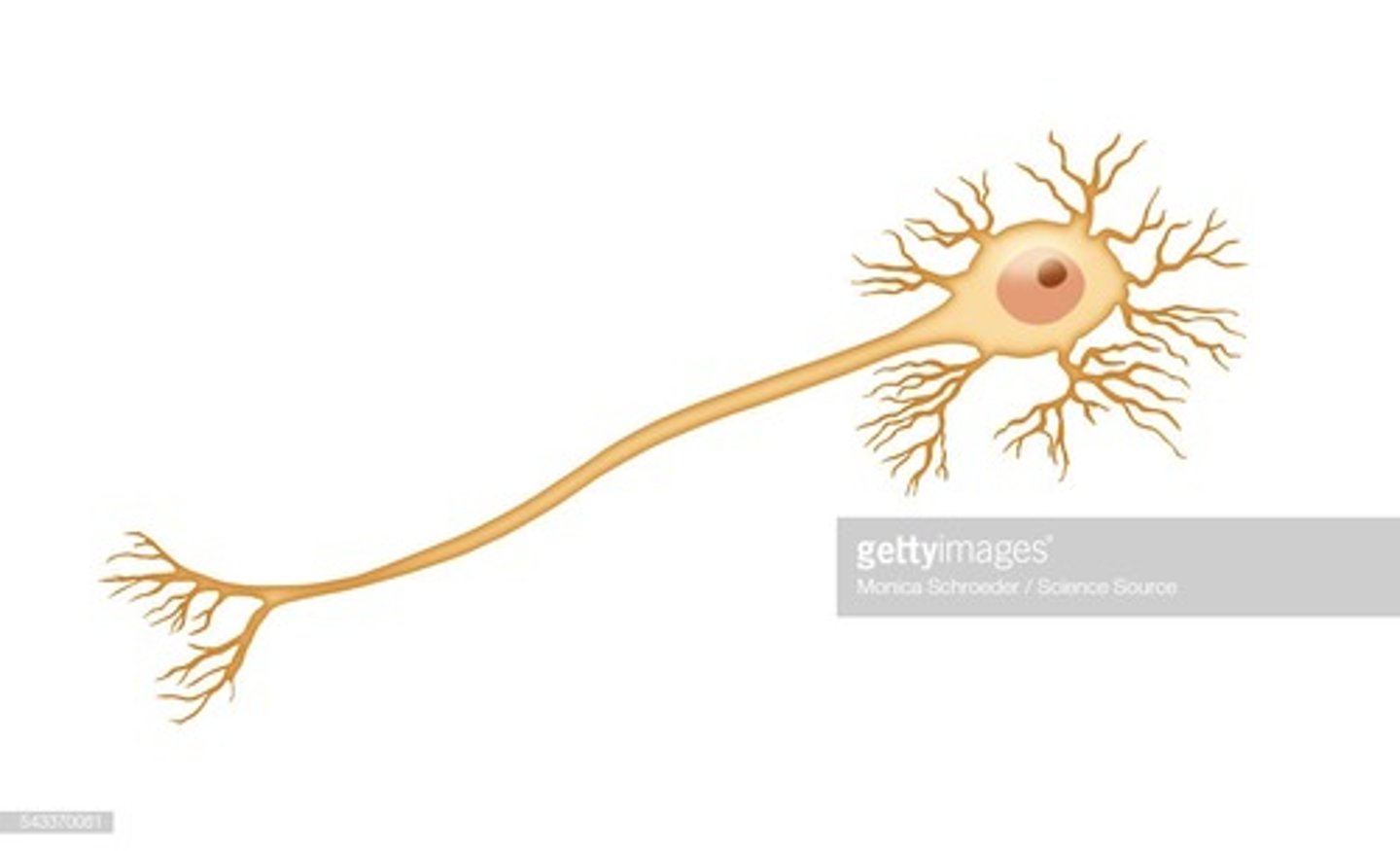
True or False? A pseudounipolar neuron contains an axon that splits into two branches, with one branch going to the periphery and the other going into the spinal cord.
True. A pseudounipolar neuron contains an axon that splits into two branches, with one branch going to the periphery and the other going into the spinal cord.
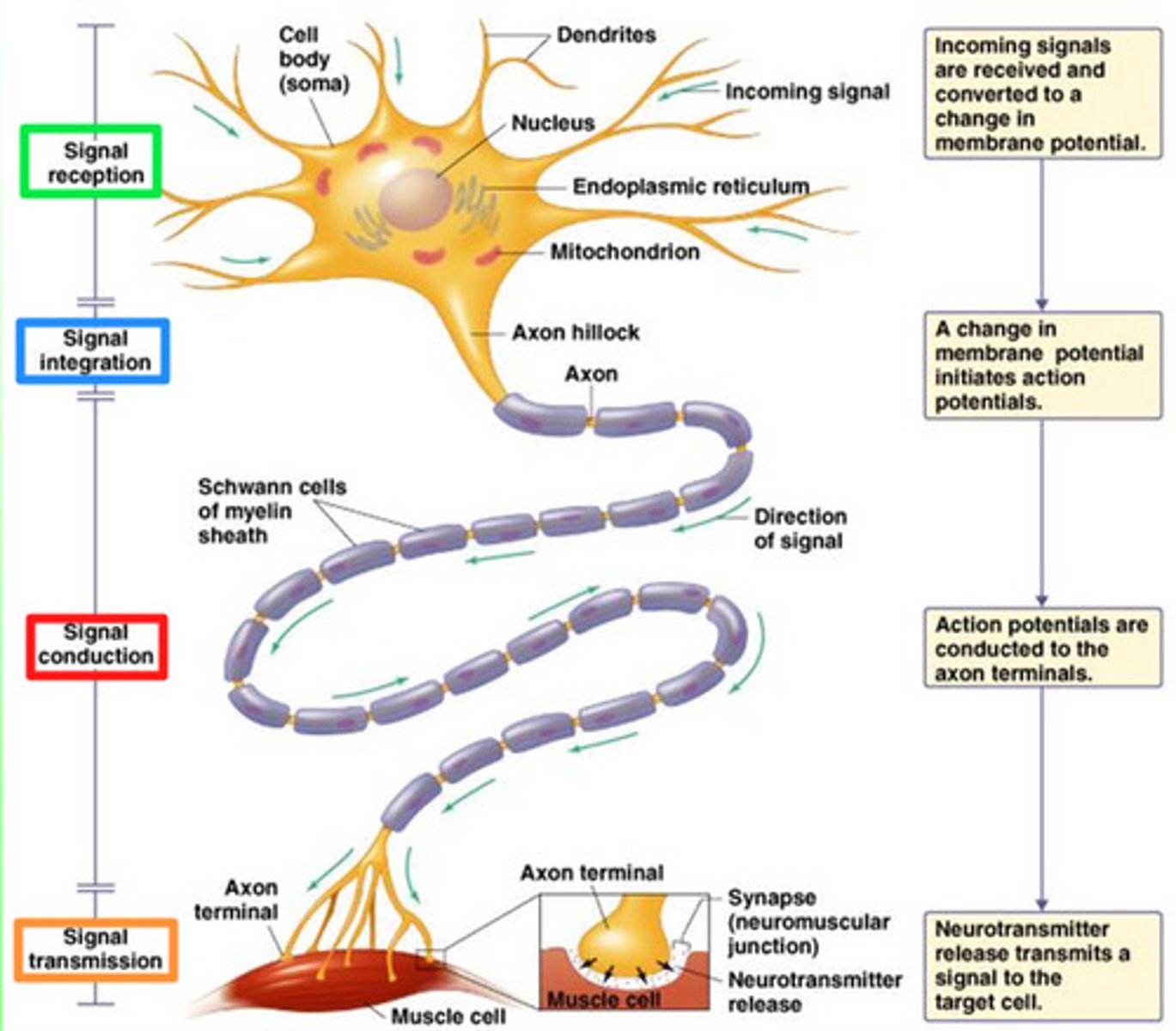
Put the following statements in order describing neuron function starting with a neuron at resting membrane potential.
I. Information is fired down the axon.
II. Membrane potential at the trigger zone (Axon Hillock) surpasses the threshold potential.
III. Soma receives excitatory/inhibitory information via dendrites.
IV. Release of neurotransmitters.
(A) III > II > I > IV
(B) III > I > II > IV
(C) IV > II > I > III
(D) IV > I > II > III
(A) III > II > I > IV
The order is as follows: Soma receives excitatory/inhibitory information via dendrites > Membrane potential at trigger zone crosses threshold potential > Information fired down an axon > Release of molecules via neurotransmitters
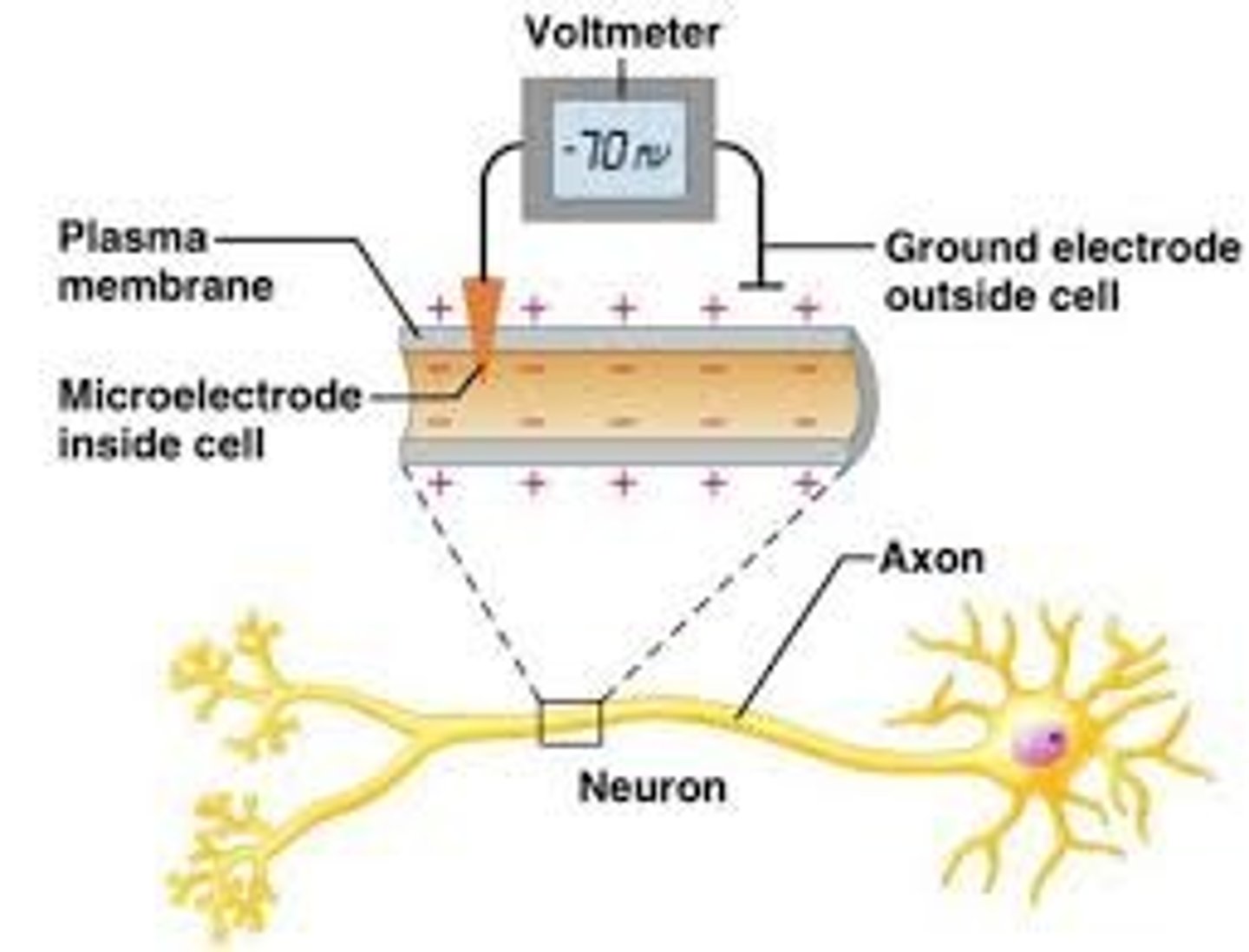
The resting membrane potential describes a neuron with a stable electrical charge difference across their cell membrane where the charge inside the cell is __________, and the charge outside the cell is ____________.
(A) Negative, Neutral
(B) Negative, Positive
(C) Positive, Neutral
(D) Positive, Negative
(B) Negative, Positive
The resting membrane potential describes a neuron with a stable electrical charge difference across their cell membrane where the charge inside the cell is negative, and the charge outside the cell is positive.
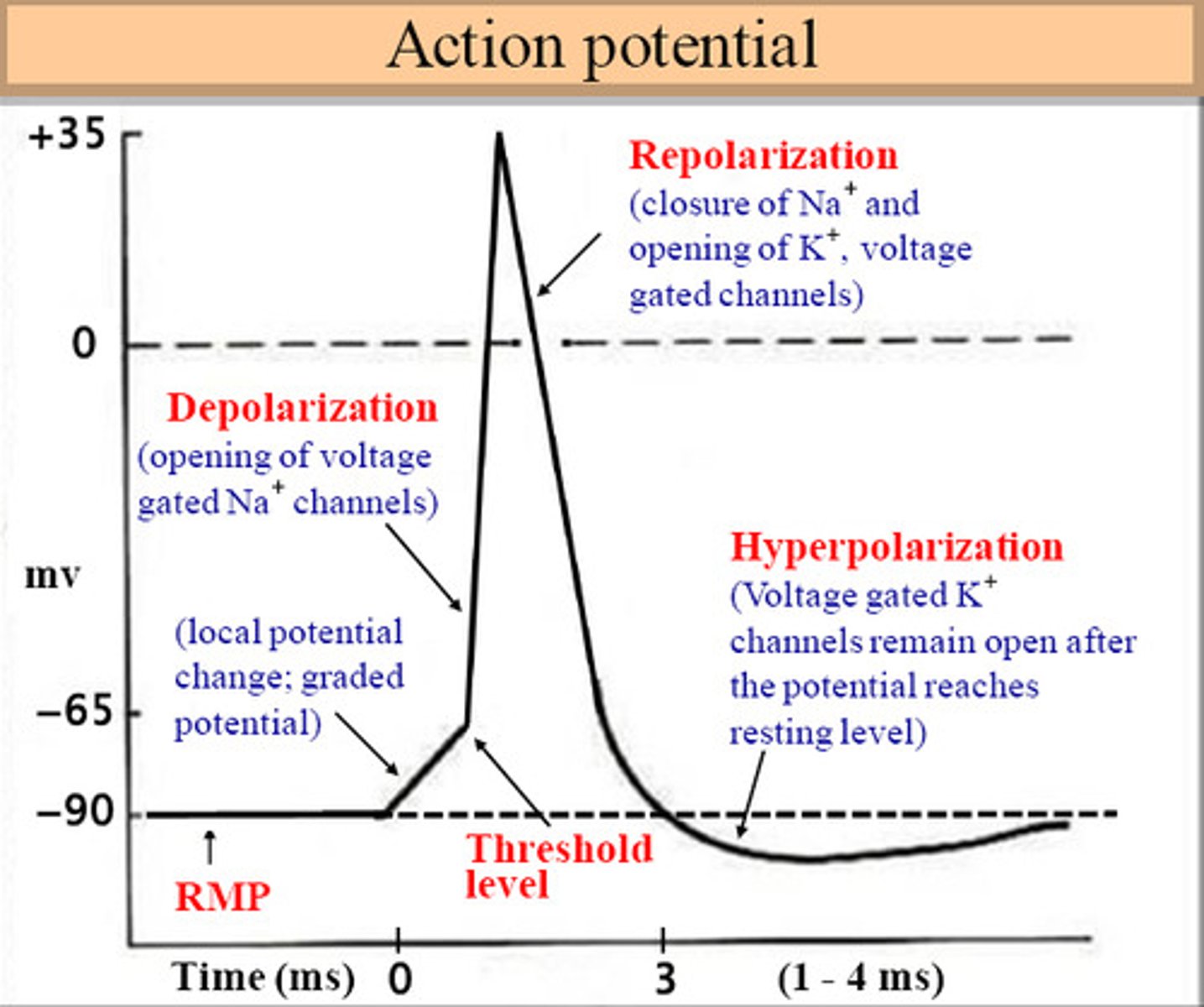
This type of potential's size and duration depends on the size and duration of inputs. Is this a graded potential or action potential?
Graded potential. An action potential is ALWAYS the same size and duration.
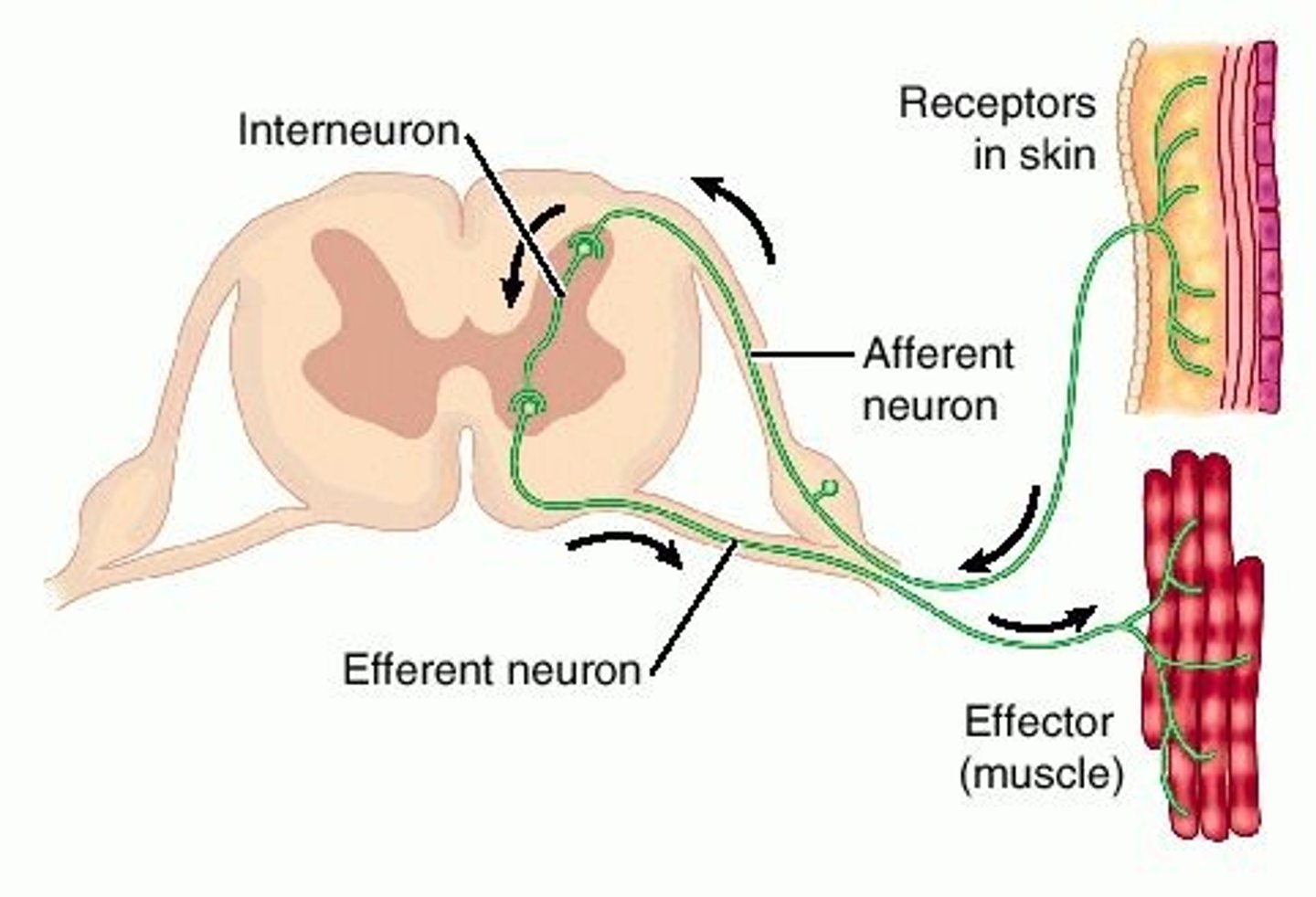
Describe the difference between afferent neurons and efferent neurons corresponding to the starting and ending locations of PNS & CNS.
Periphery --> CNS: Afferent Neuron
CNS --> Periphery: Efferent Neuron

Which of the following are Efferent Neurons?
I. Motor Neurons
II. Sensory Neurons
III. Autonomic Neurons
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) I and III Only
Motor and Autonomic Neurons are Efferent Neurons.
Sensory Neurons are Afferent Neurons.
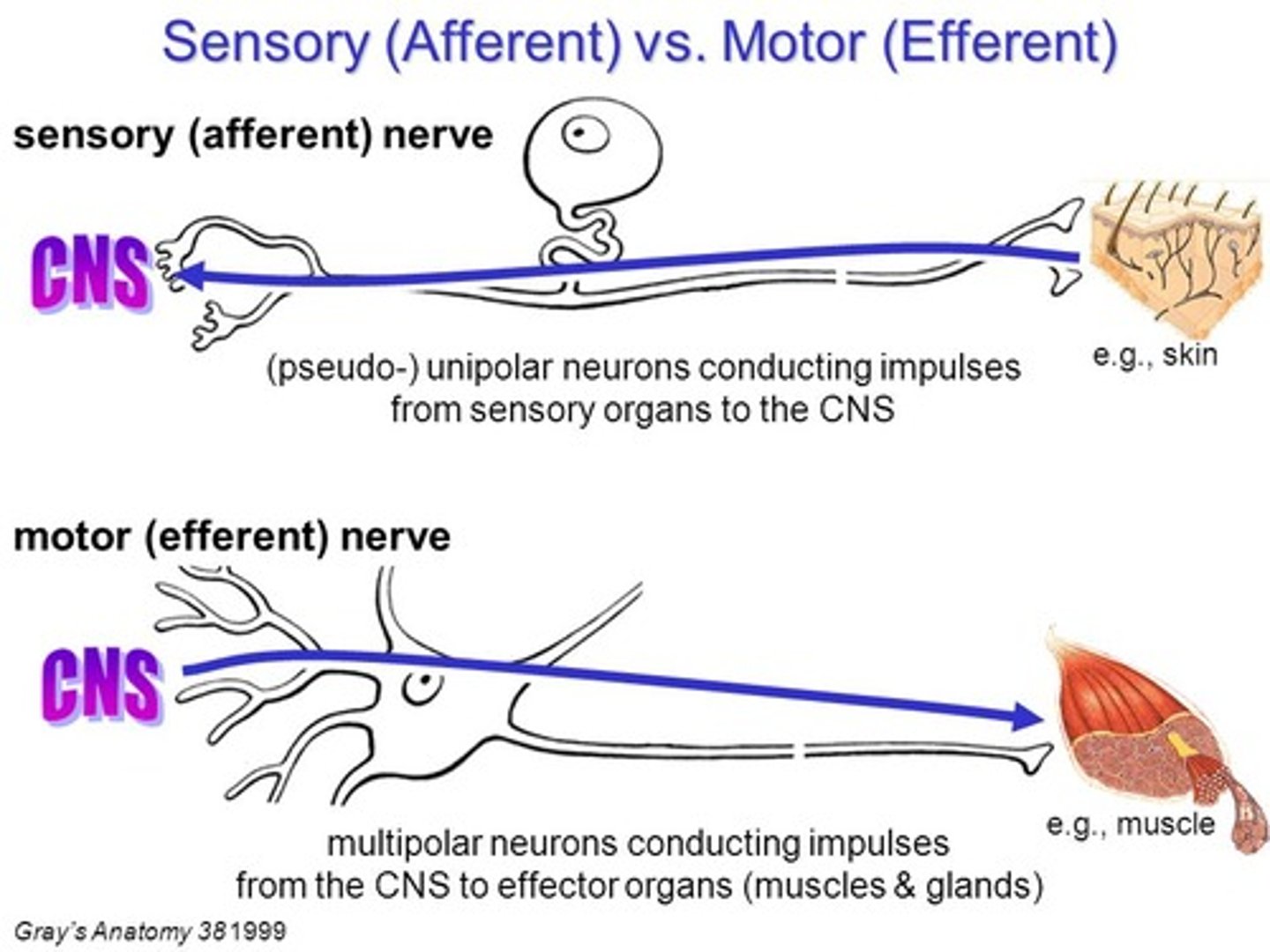
Efferent Motor Neurons control which of the following cell types?
I. Skeletal Muscle Cells
II. Smooth Muscle Cells
III. Cardiac Muscle Cells
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I, II, and III
(A) I only
Efferent motor neurons control skeletal muscle cells.
Efferent autonomic neurons control smooth and cardiac muscle cells.
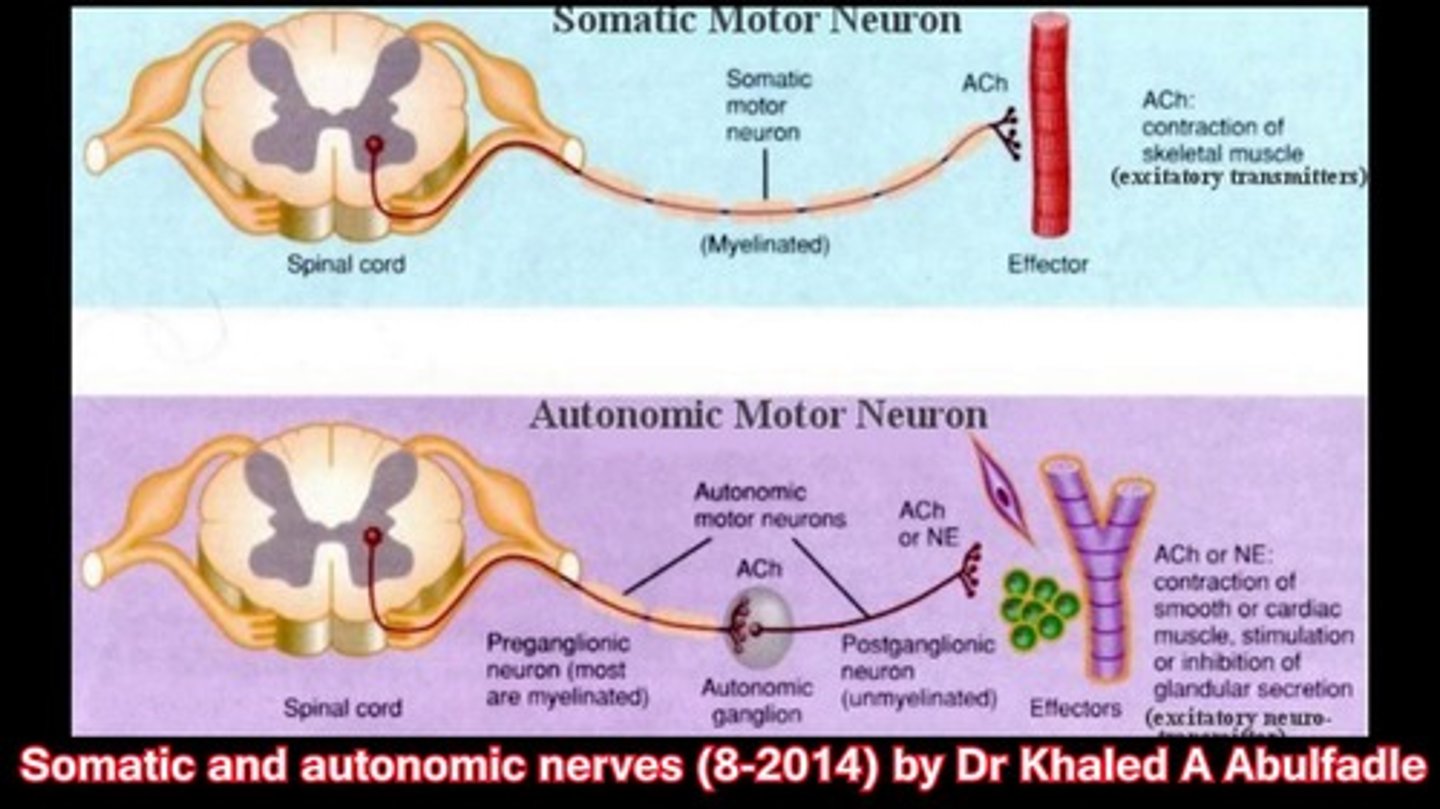
Efferent Autonomic Neurons control which of the following cell types?
I. Skeletal Muscle Cells
II. Smooth Muscle Cells
III. Cardiac Muscle Cells
(A) I Only
(B) II & III Only
(C) III Only
(D) I and III Only
(B) II & III Only
Efferent Autonomic Neurons control cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and gland cells.
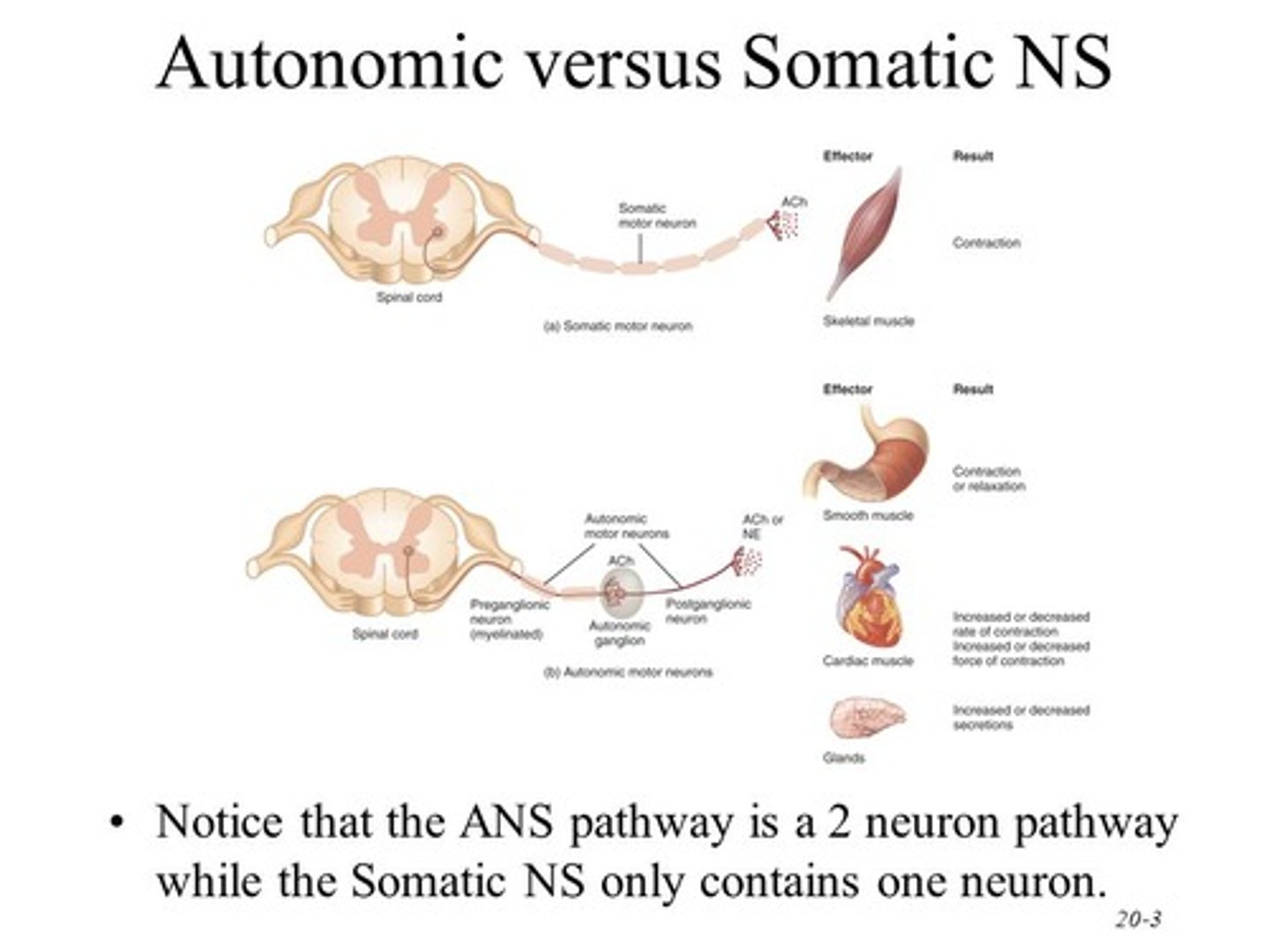
True or False? An interneuron is a neuron that transmits impulses from the CNS to the PNS.
False. An interneuron transmits impulses between other neurons within the CNS.
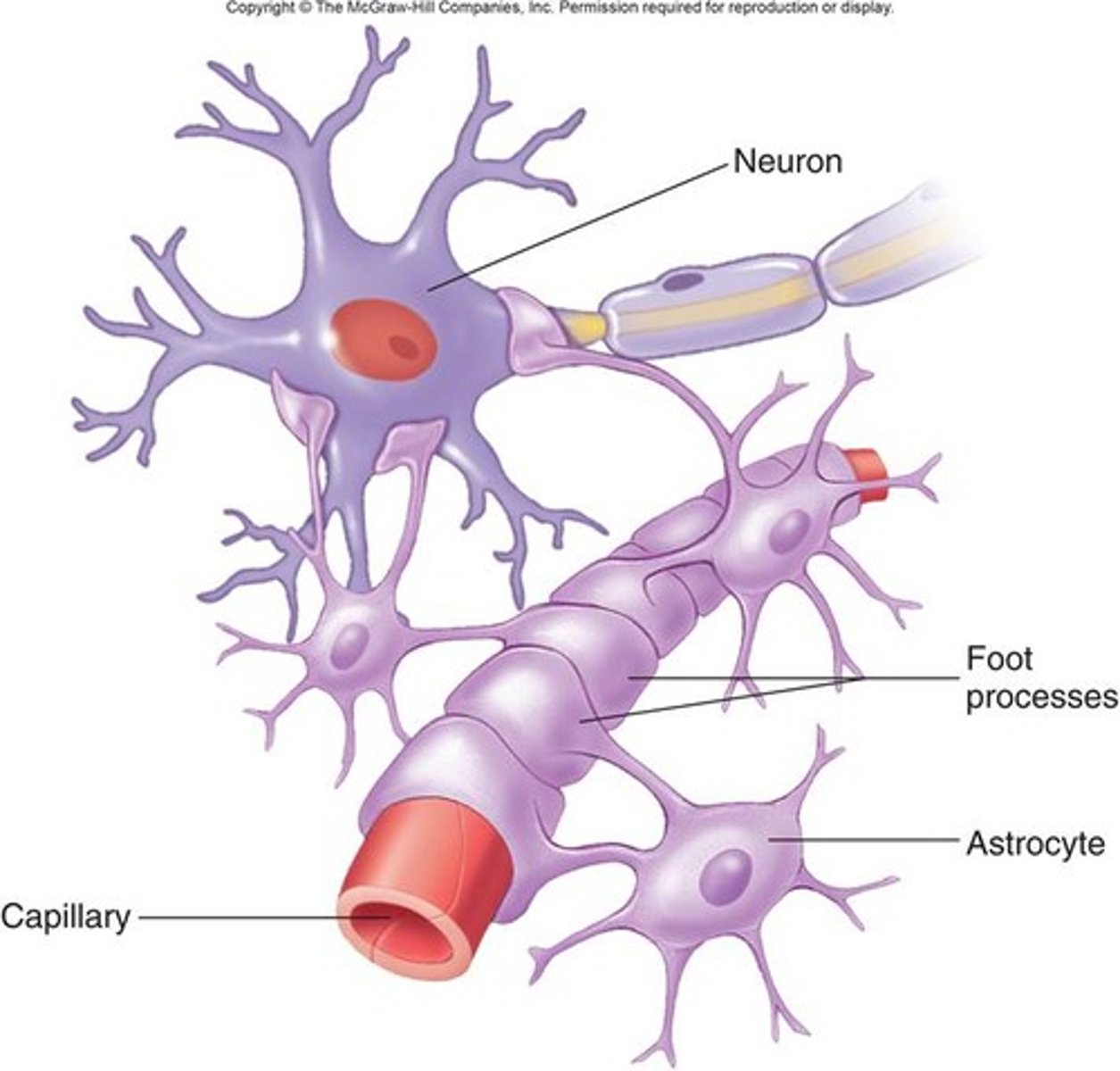
Astrocytes are glial cells derived from neural stem cells. Are they a part of the central nervous system or peripheral nervous system?
Astrocytes are part of the central nervous system.
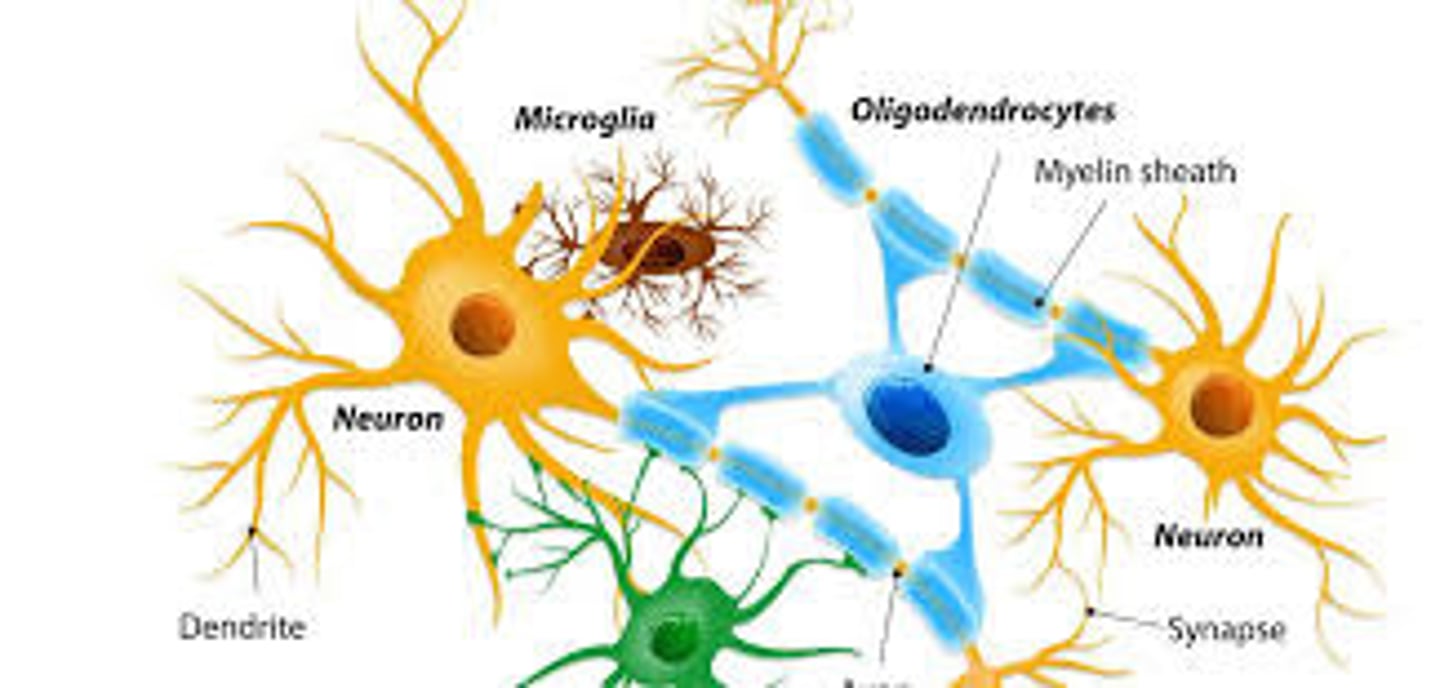
True or False? Astrocytes occupy a huge space of the central nervous system and form a majority of structure that makes up the brain and spinal cord.
True. Astrocytes occupy a huge space of the central nervous system and form a majority of structure that makes up the brain and spinal cord. This is also called a scaffold.
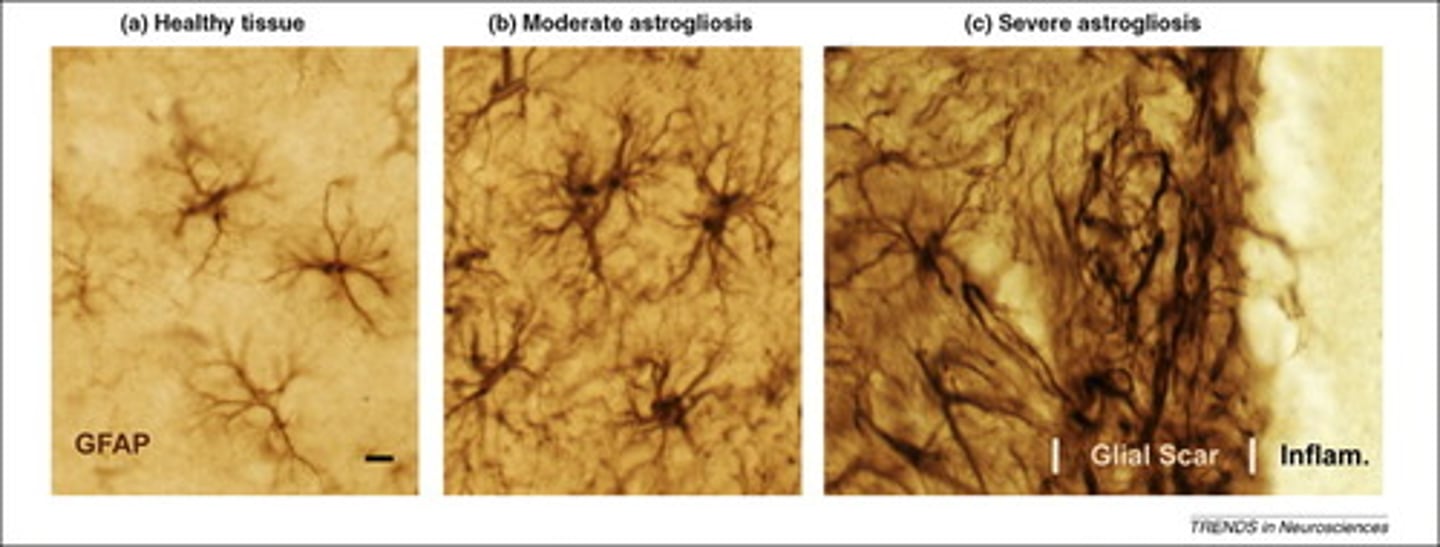
Astrocytes respond to any injury in the CNS. Which one of the following actions does NOT occur in the process of repairing the injury.
(A) Astrocytes grow to 10x their original size.
(B) Astrocytes migrate to the site of injury.
(C) Astrocytes' processes hypertrophy.
(D) Astrocytes form a thick tissue called a Glial Scar.
(A) Astrocytes grow to 10x their original size.
Astrocytes themselves do not grow bigger, they proliferate.
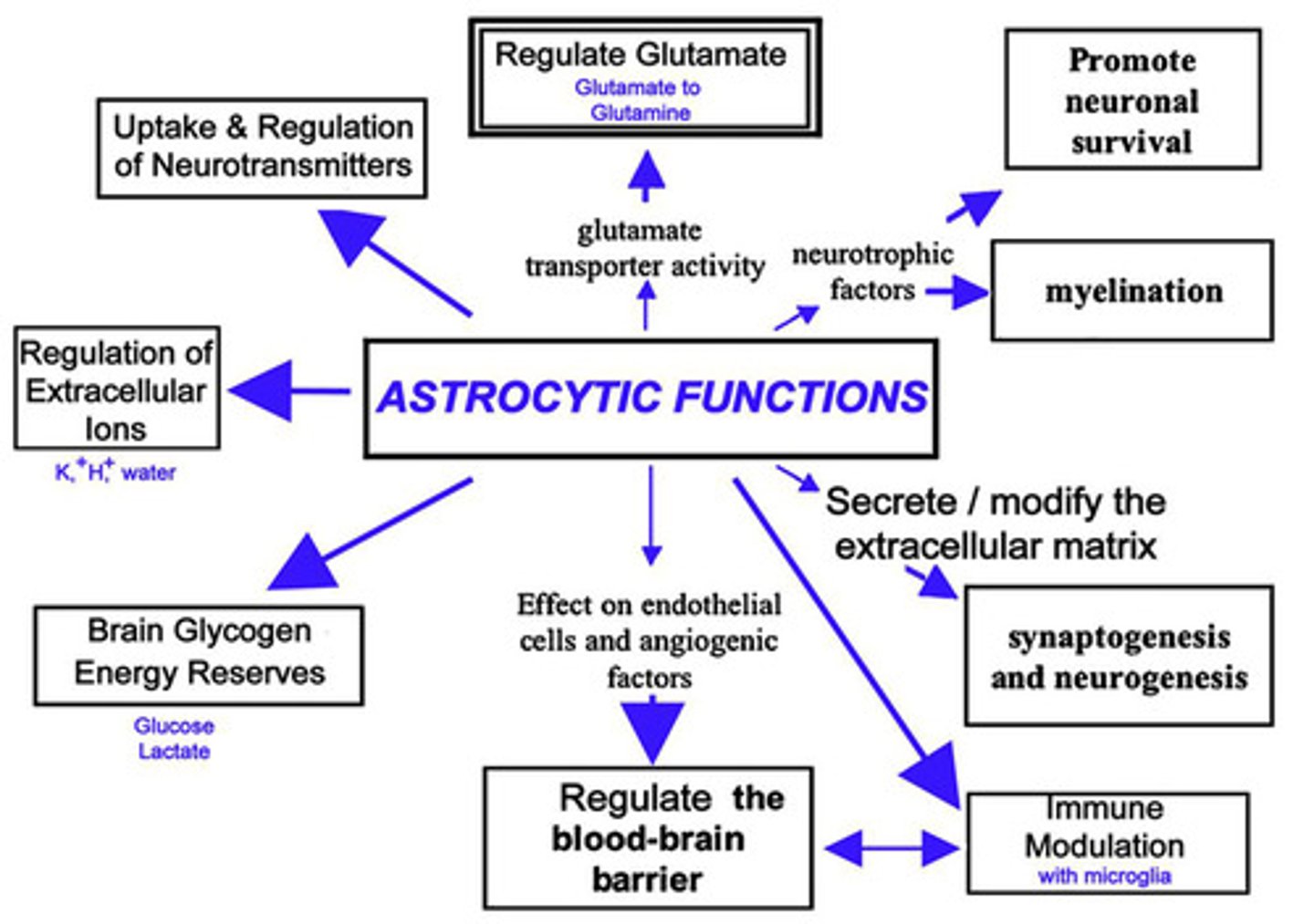
True or False? The central nervous system is unable to handle when things are off balance, so an increased amount of potassium ions will not be corrected and will cause neuron malfunction.
False. Astrocytes help maintain a constant homeostasis, especially by balancing the concentration of ions within and around neurons.
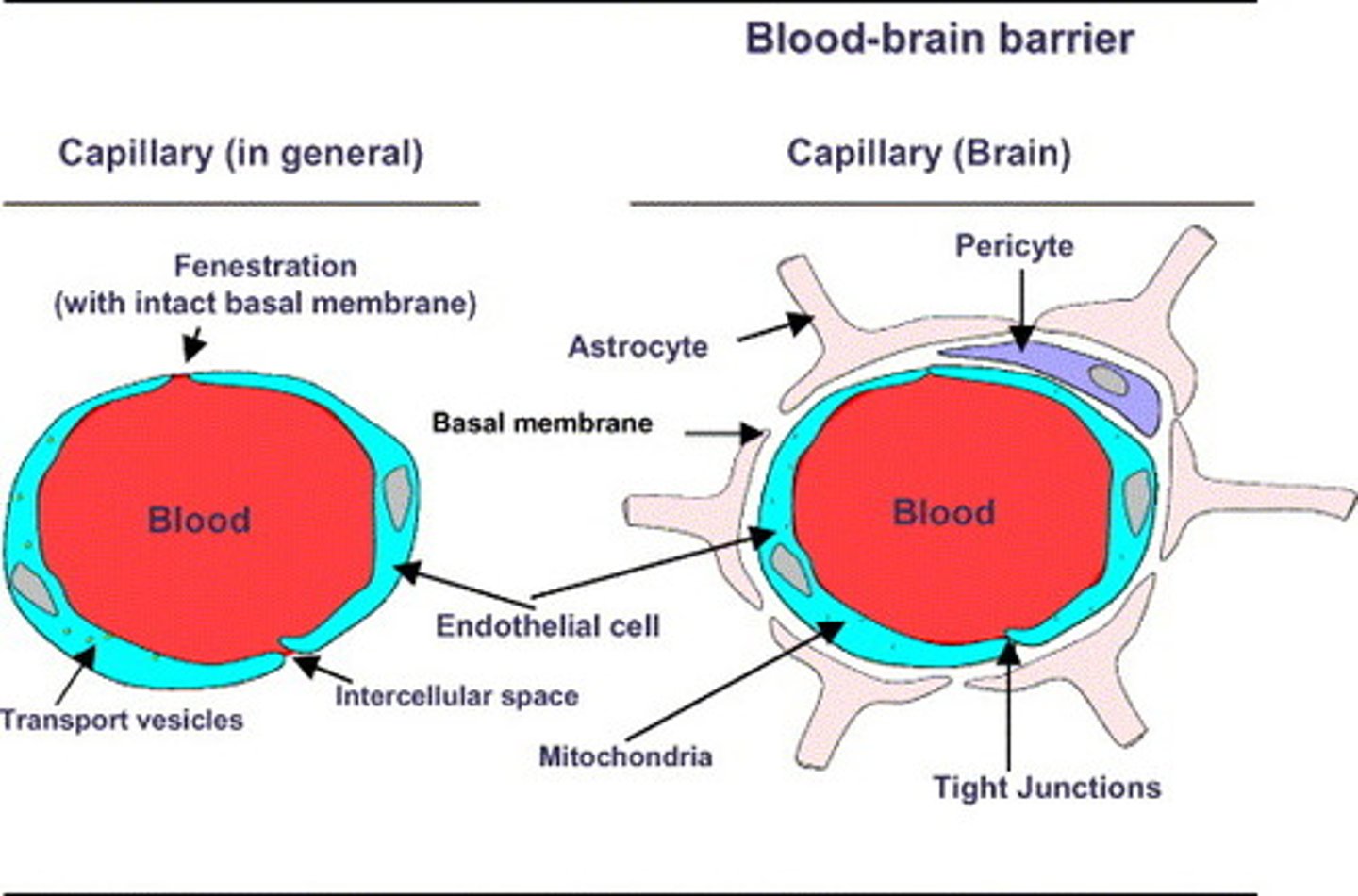
The end feet of Astrocyte processes are plastered over blood vessels of the blood brain barrier to prevent molecules from leaving the bloodstream and entering the brain, unless needed. Which molecule would most likely be prevented by the end feet from entering the brain?
(A) Glucose
(B) Ketones
(C) Sodium Ions
(D) Proteins
(D) Proteins
The blood-brain barrier will allow small molecules such as sugars and ions to pass through while preventing larger molecules such as proteins from entering the brain.
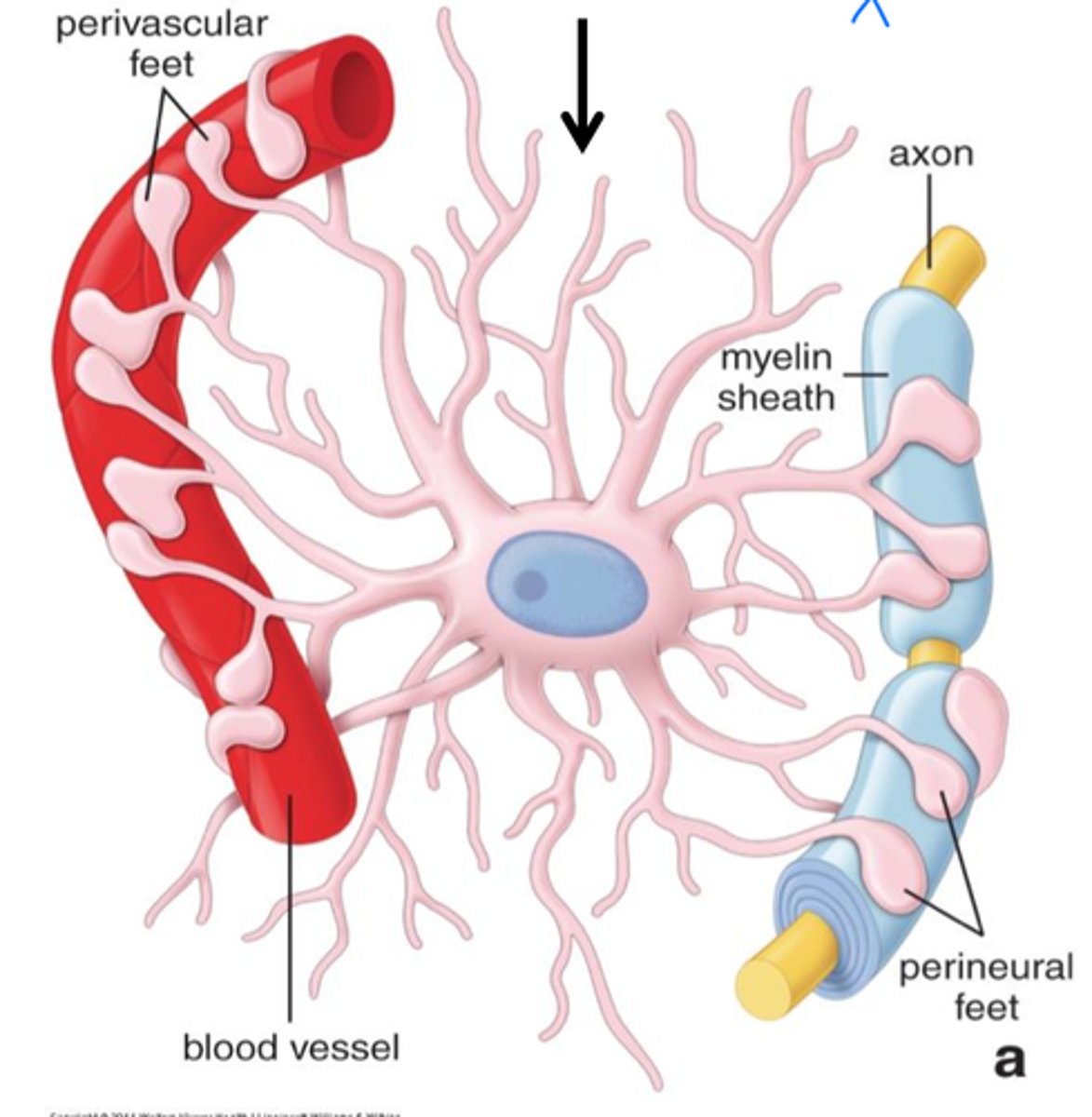
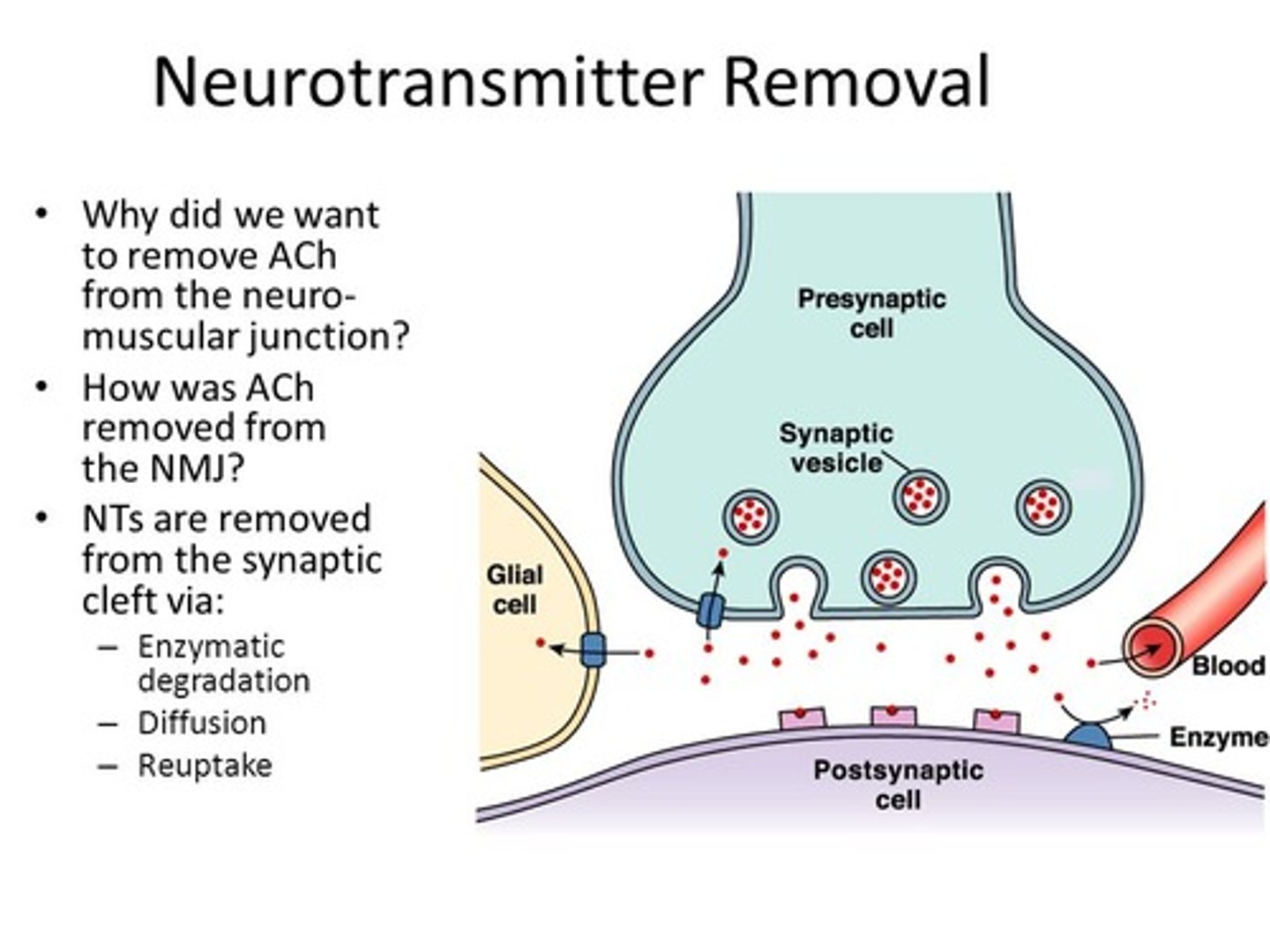
Astrocytes place their end feet of their processes all over synapses to help clear out synapses of neurotransmitters between neurons. Why is it important to clear out these synapses?
Neurons need to be able to turn on and off rapidly. If the neurotransmitters just lingered in the area, the synapse would just constantly be turned on.
Which of the following is not a function of Astrocytes?
(A) Scaffolding
(B) Glial Scar
(C) Homeostasis
(D) Spinal Cord Barrier
(D) Spinal Cord Barrier
This should be Blood Brain Barrier.
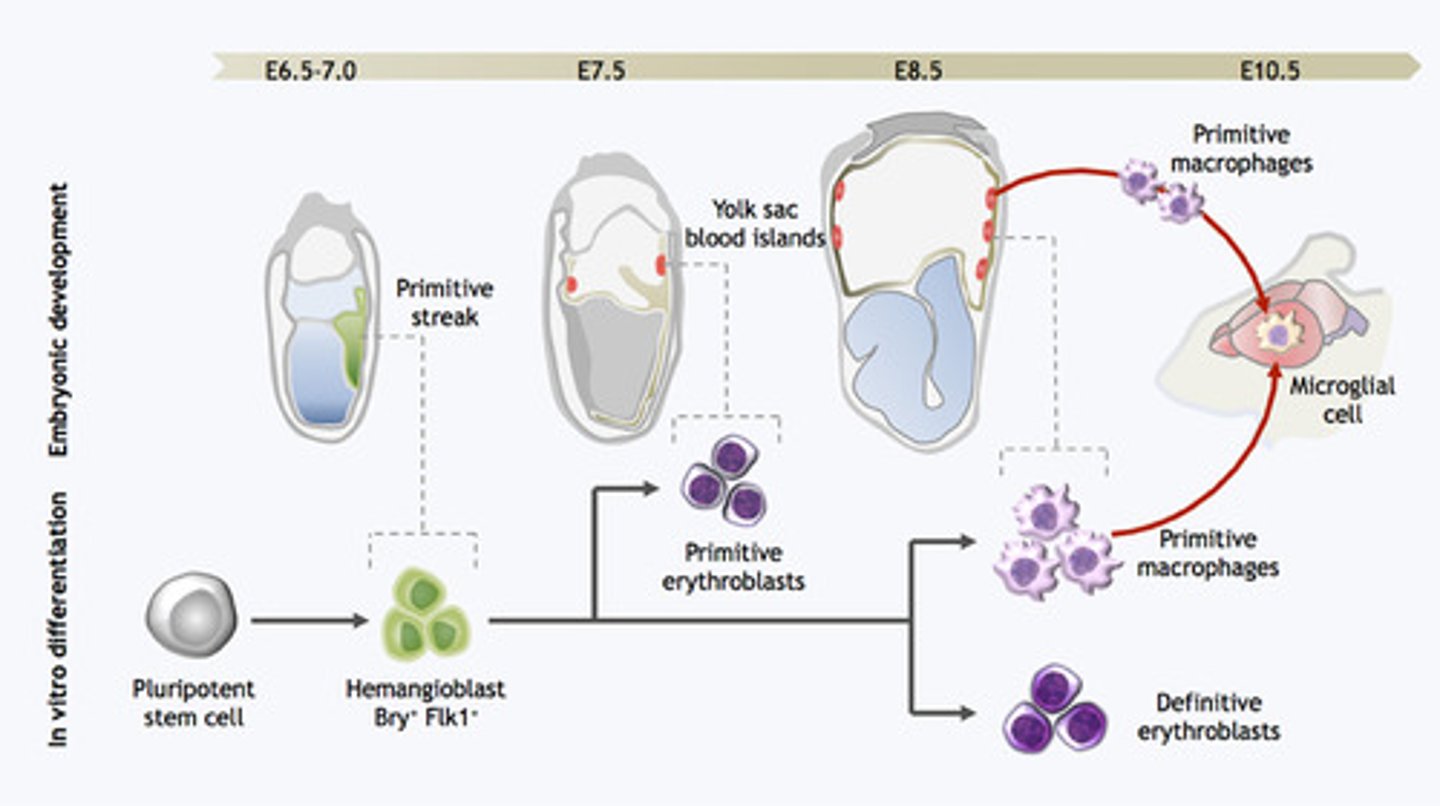
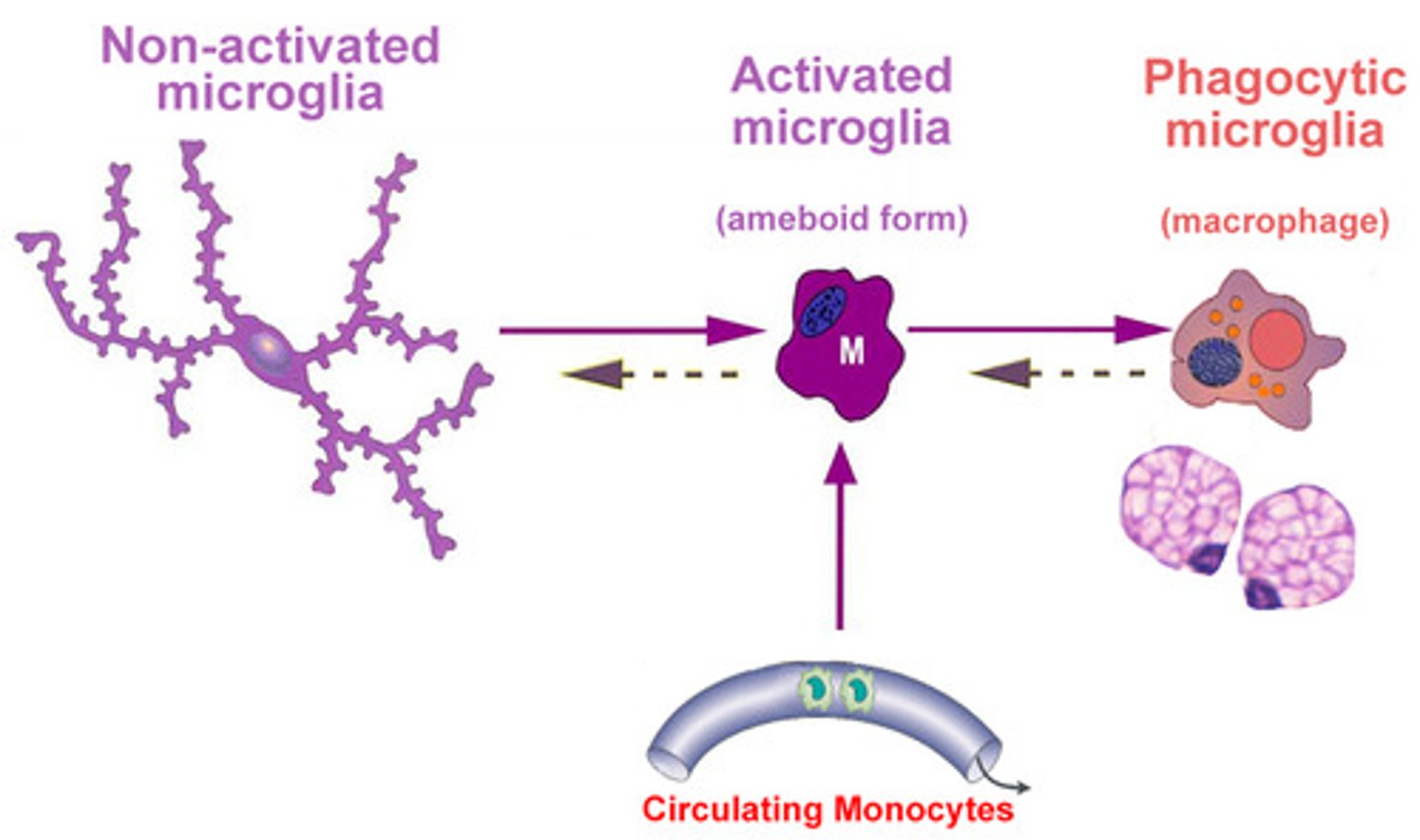
Most of the neural cells are derived from the ectoderm. What makes microglia different? What are these cells derived from?
Microglia are derived from circulating monocytes from the bone marrow that enter the central nervous system, so they are derived from the mesoderm.
Do active microglia or resting microglia have long processes projecting from the soma?
Resting microglia.
They are surveying the area looking for inflammation. Once they detect it, the processes retract into the soma, and the microglia becomes a blob-like structure.
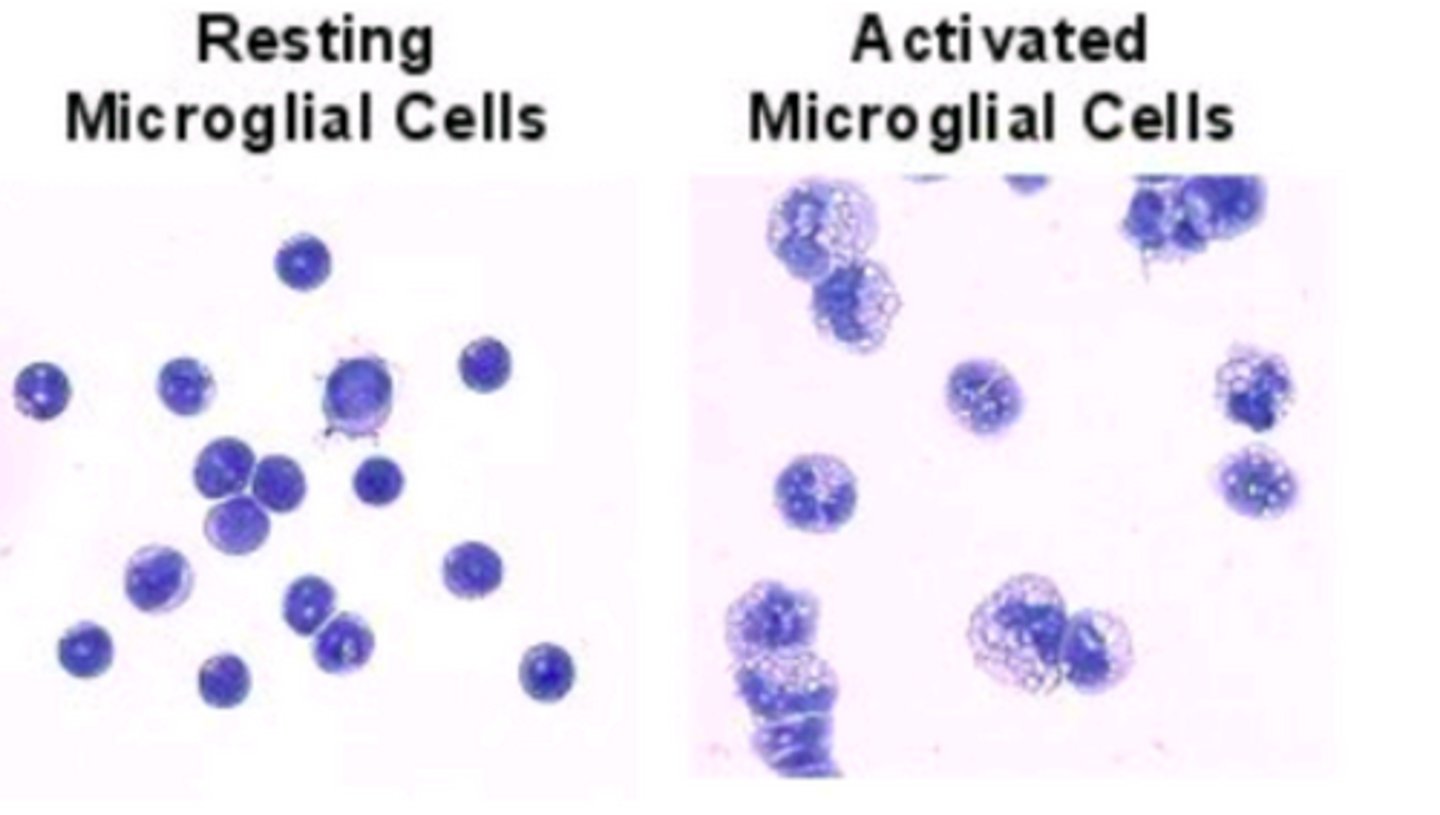
Active microglia or resting microglia can be analogous to a macrophage?
Active Microglia. They will move to areas of inflammation and they're looking for bacteria or foreign cells that are causing an infection.
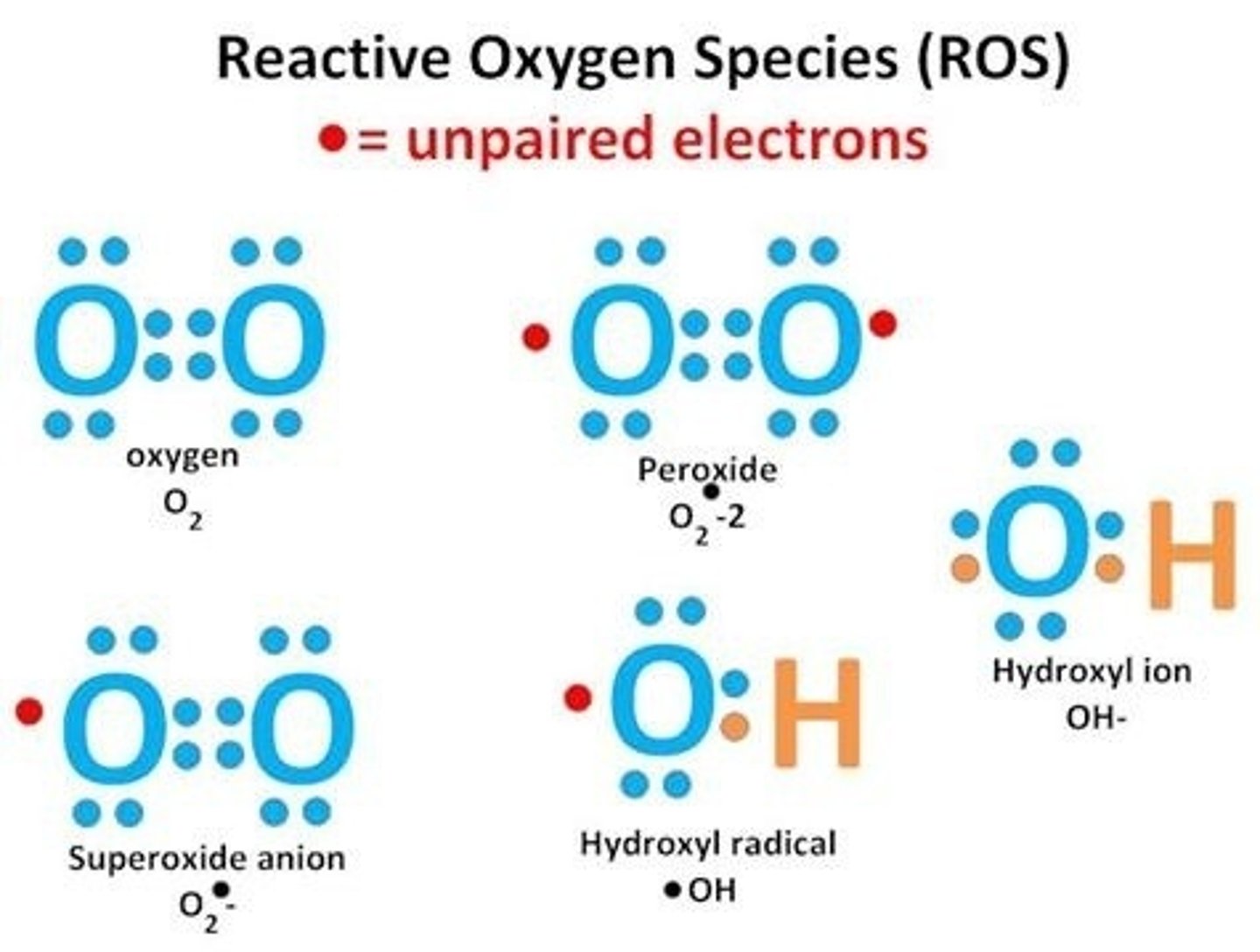
Which of the following will active microglia secrete in response to foreign cells?
(A) Macrophages
(B) Reactive Oxygen Species
(C) Lymphocytes
(D) Lactate
(B) Reactive Oxygen Species
Active microglia will secrete ROS substances to destroy foreign cells.
Which of the following is not a function of microglia?
(A) Secrete ROS
(B) Phagocytosis of debris
(C) Antigen presentation
(D) Homeostasis
(D) Homeostasis
Homeostasis is not a function of microglia. Rather, homeostasis is an important function of astrocytes.
The ependymal cells create a barrier between the cerebral spinal fluid and the interstitial fluid to limit the movement of large molecules between these spaces. Is this a strong barrier or a leaky barrier? Why is this useful for a physician or a researcher?
This is a leaky barrier. And it's important that it is as it allows us to gain information about what is going on within the tissues of the brain through taking a sample cerebrospinal fluid and analyzing it in a laboratory.
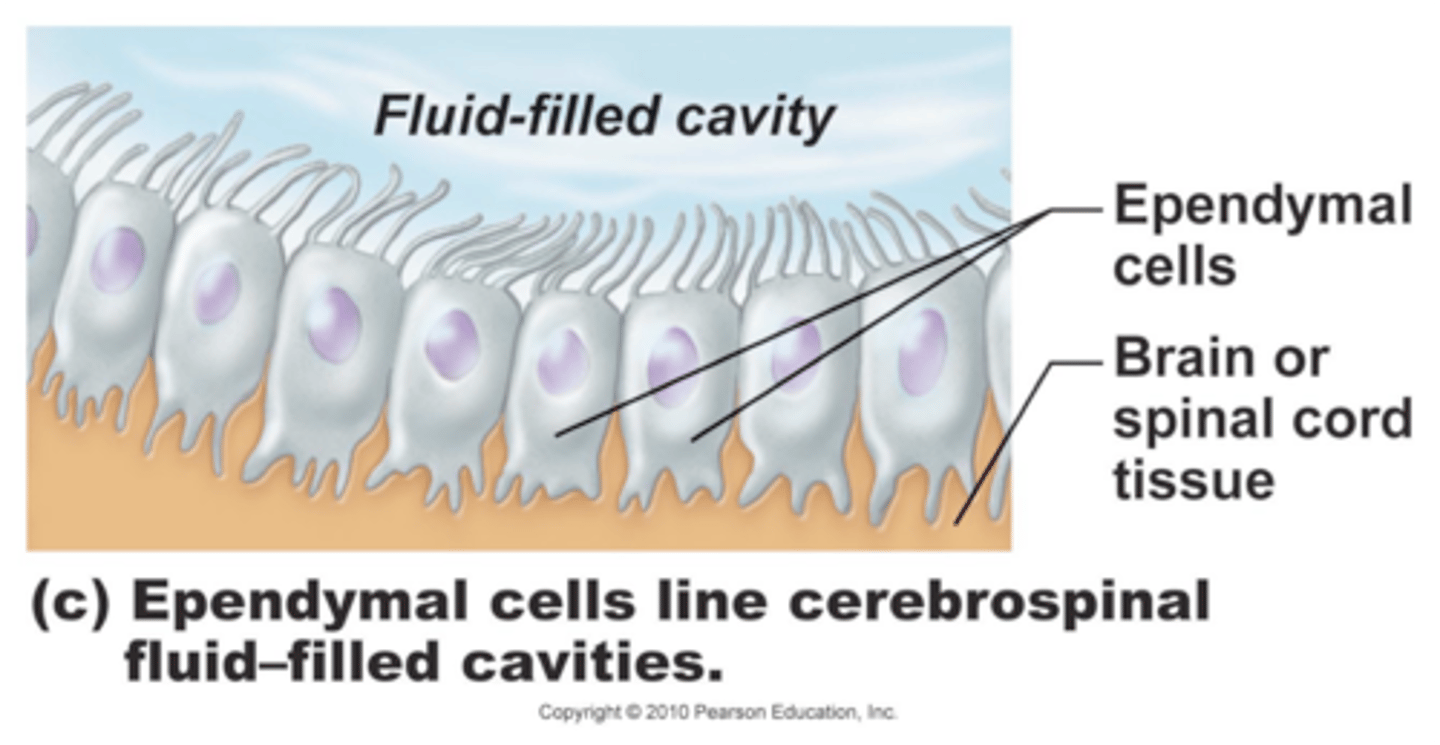
True or False? The two main functions of ependymal cells are to provide a barrier between cerebral spinal fluid and interstitial fluid and to secrete cerebral spinal fluid.
True. The two main functions of ependymal cells are to provide a barrier between cerebral spinal fluid and interstitial fluid and to secrete cerebral spinal fluid.
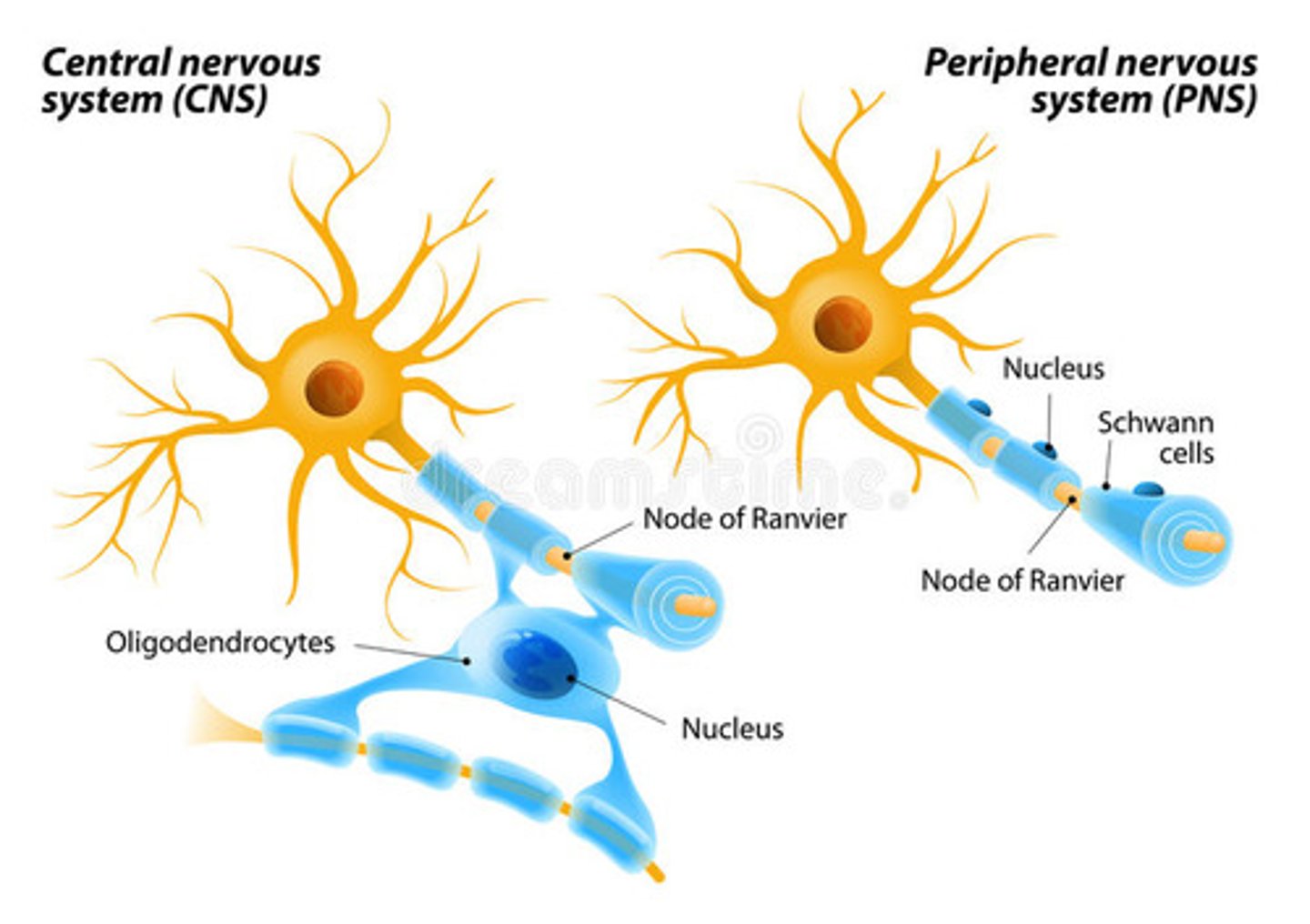
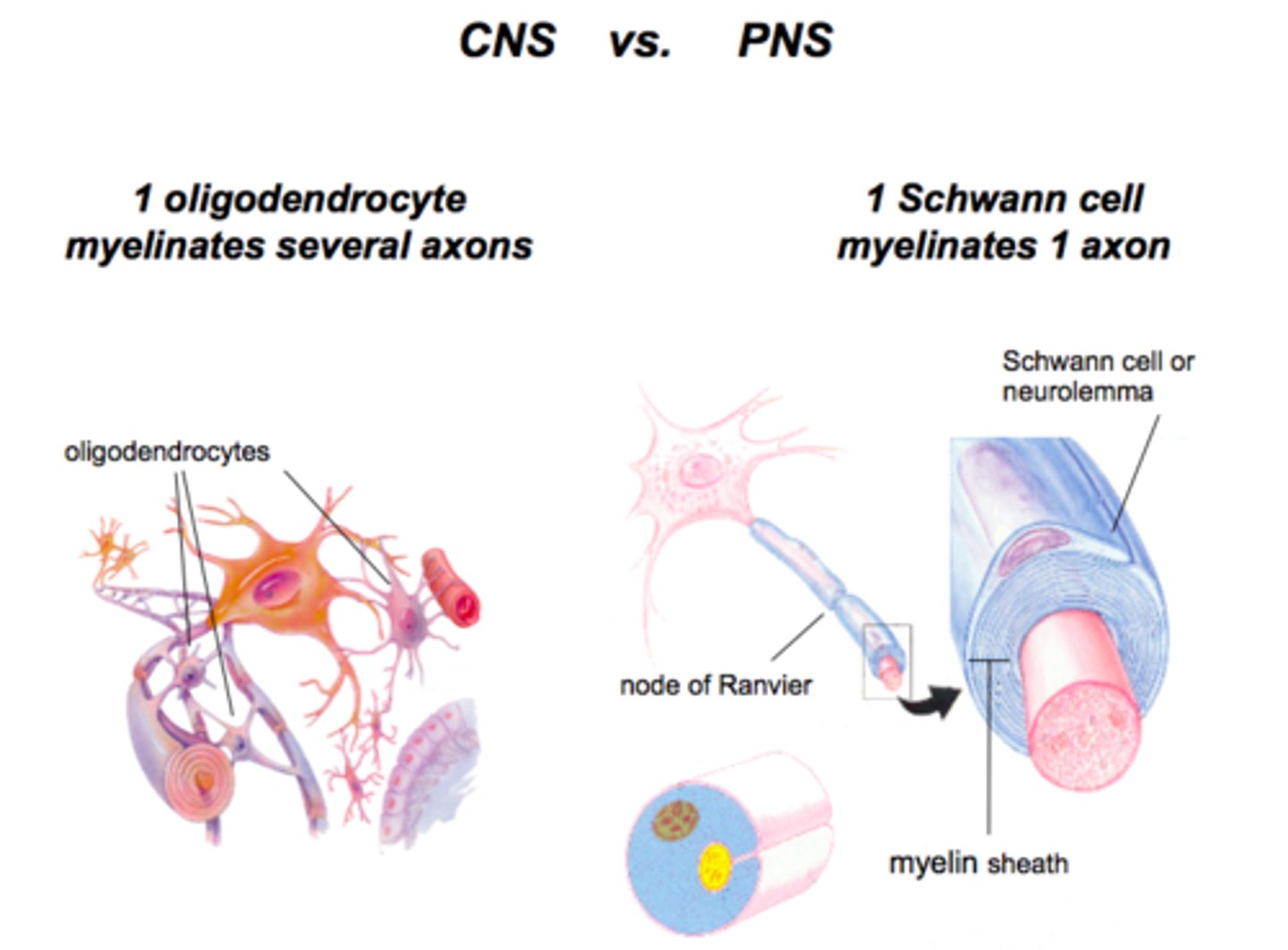
Each oligodendrocyte process forms one segment of myelin on an axon. Can oligodendrocytes myelinate only one axon or multiple axons? What about Schwann Cells?
Each oligodendrocyte can myelinate multiple axons.
Schwann cells produce myelin sheath for one axon only. In fact, it can only produce one segment of one axon.
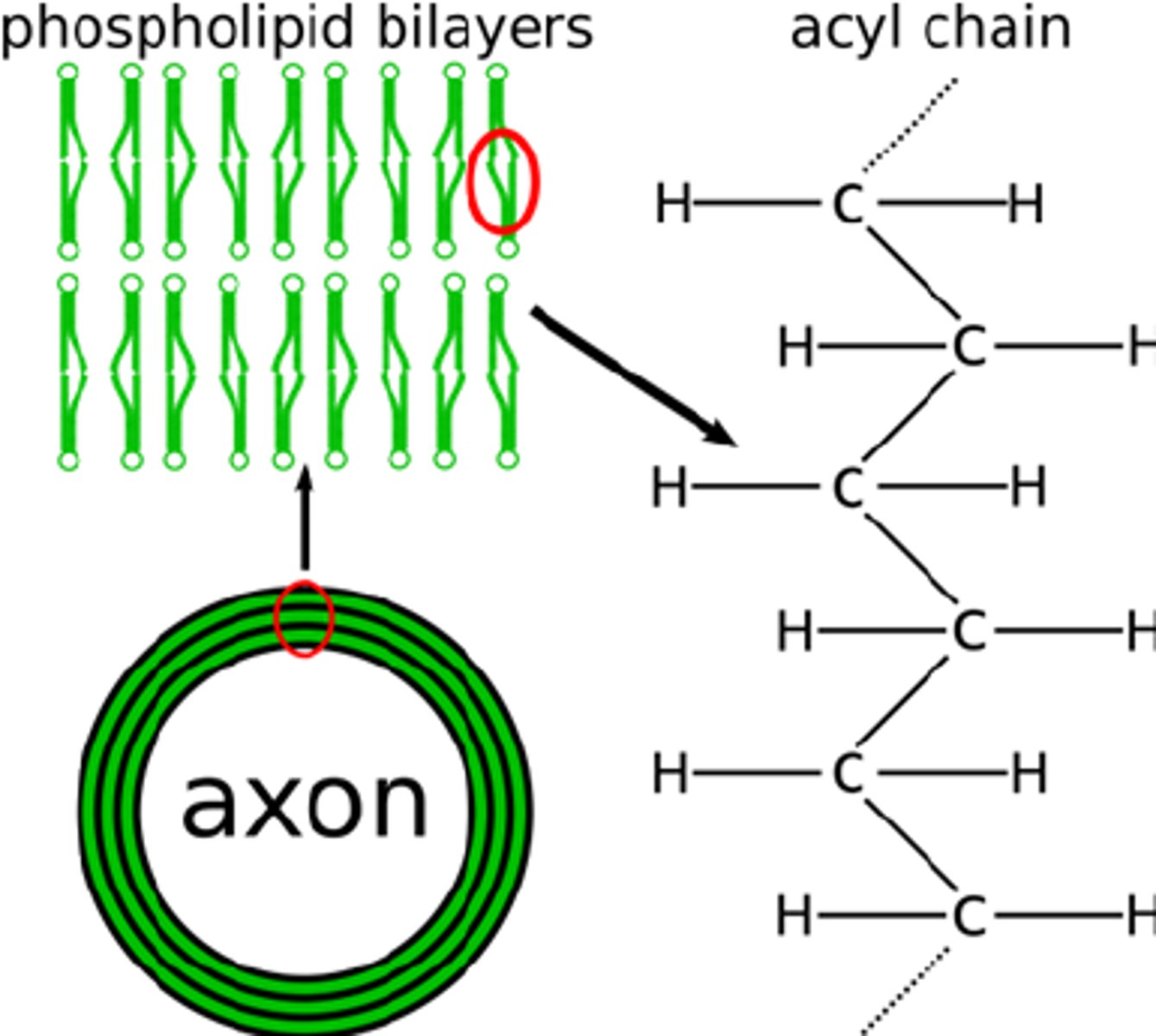
Myelin is rich in which substance?
(A) Carbohydrates
(B) Lipids
(C) Nucleic Acids
(D) All of the above
(B) Lipids
Myelin is rich in lipids
Match the type of glial cell to its location.
(A) Schwann Cells
(B) Oligodendrocytes
(1) Peripheral Nervous System
(2) Central Nervous System
(A) -- 1
Schwann Cells -- Peripheral Nervous System
(B) -- 2
Oligodendrocytes -- Central Nervous System