9-11 Palliative pain
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Explain the philosophies of palliative care and
the role of the team members
Describe causes and consequences of pain in
the palliative population
Discuss etiology and assessment of malignant
pain
Demonstrate how assessments are used in a
clinical setting
What is palliative care?
A specialized medical care that focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses. It aims to provide relief from symptoms, pain, and stress, while also addressing emotional, social, and spiritual needs ( holistic) Palliative care can be provided alongside curative treatment and is not limited to end-of-life care.
What did the Temel Study show?
Lung cancer patients into 2 groups
Proved that Palliative care improved QoL, Mood, Survival (by 3 more months)
When to consider palliative care
If you are not surprised if patient died in next year
If you are surprised if they passed in a year, may be an option if they are symptomatic
misconceptions of palliative care
Death imminent by everyone
Only those in C level of care go into ICU? (What public thinks)
palliative care is % communication
99
What does TPCU stand for?
% of pain syndromes can be controlled
85
sources of pain in palliative pts
Terminal - cancer
Pre existing pain condition - fibromyalgia, chronic pain, arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, migraine, sciatica
Pain is clinically sig symptom of cancer - what %?
59% of those receiving tx
64% of patients with advanced or metastatic disease
Causes of cancer pain
Invasion of tissue - nociceltive from somatic or visceral pain
Invasion of nerves
Paraneookastic phenomena
Altered nerve conduction
Indirectly - constipation, obstruction, fracture
Cancer pain from tx
Chemo - neuropathy
Radiation - burns, pain flare
Sx - infection, wound, phantom pain
Barriers to good pain control
Family
Compliance issues
Financial concern
Complaining to HCP
HCP
Skills, fear of addiction, reprimand, do not ID multidimensional pain or do not understand pain
Cancer pain is complex and involves TOTAL PAIN
Phys
Behaviour
Cognitive
Emotional
Spiritual
Interpersonal
Residual chronic cancer pain in survivors %
33 - 40
Reduces QoL
PPS palliative performance status
Assesses change in prognosis - better? Worse?
Mostly revolves around function and impact on daily activities
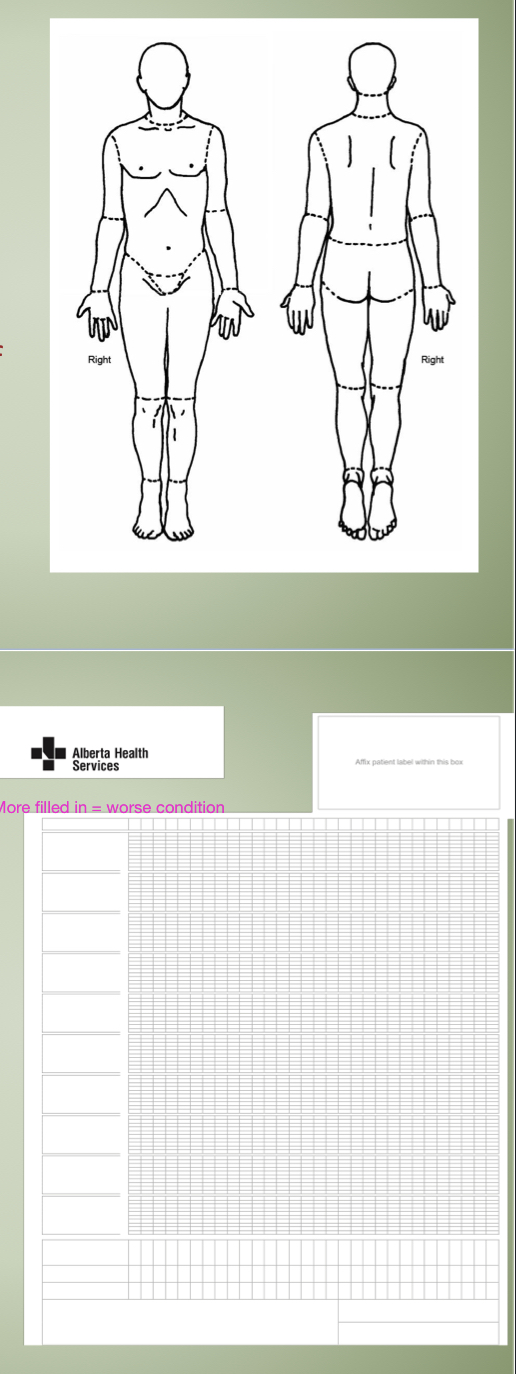
ESAS-r Graph
daily assessment of FEELINGS of patient - comes with a diagram of body and patient indicates what portion is affected by (condition) on a scale from 0-10
The symptoms are then plotted on a graph daily to visualize improvement/worsening
CAGE
Asses addictions
Cut down on addiction
Annoyed by criticism of your addiction?
Guilty feelings about addiction?
Eye-opener : use addiction method to get rid of addiction hangover or withdrawal
/4 (anything 2 or over is positive cage)
Folate is mini-mental state exam 1975
Cognition screen - free to use!
Other Assessments of cognitions
CAM (confusion assessment method)
Mini-Cog (clock drawing and memory)
BOMC (blessed orientation memory concentration test)
Executive function test
SLUMS or MOCA
ECS-CP
Edmonton Classification System for Cancer Pain
Addresses multi factorial approach
MOA of pain
Incident pain
Psych distress
Addictive behaviours
Cognitive function
N I P A C
What ECS-CP uses to identify different parts of pain
Mechanism of pain in ESC-CP

Incident pain in ESC-CP

Psychological distress in ECS-CP

Addictive Behaviour in ECS-CP

cognitive function in ECS-CP

What is Nx Ix Px Ax Ci
Unable to assess pain type, or if incident pain,
psychological or addictive components present because of cognitive impairment. (eg. Patient admitted in delirium)
What is No
no pain present, non-malignant pain only (eg. arthritis), or
no cancer diagnosis.
what is Ne Ii Pp Aa Co
Has neuropathic and incident pain. Psychological
component to pain expression and history of addictions.
What is Nc Ii Po Ao Co
Has nociceptive pain & incident pain, but no other pain
syndromes
Explain how cancer pain is managed based on
the WHO analgesic ladder
Discuss the analgesics used in malignant pain at
each step of the WHO analgesic ladder
Review the properties of methadone and identify
how this agent may be used in cancer pain
Describe adjuvant and non-pharmacologic
options available
Apply knowledge of assessments and analgesics
to patient case
Who ANALGESIC SCALE
1-3 mild (non opioid)
4-6 moderate (opioid + non opioid, adjuvant if needed
7-10 severe (opioid + non opioid, adjuvant anything that works)
Mild pain
Tylenol NSAIDs plus minus adjuvants
moderate pain
weak opioids (codiene, tramadol)
Adjuvants
severe pain opioids
morphine
Hydromorph
issue with step two of who analgesic ladder
Insufficient evidence to support/refute Step 2
opioids (eg. codeine) are superior to NSAIDS
Can be omitted in rapid progressing pain
Cancer pain medications (general info)
regular Rx analgesics ATC
Laxatives needed if opioid use
P.O. preferred
Why is P.O. preferred?
Cheap
Easiest admin
No specialized pharmacy
No risk of infection (unlike IV)
Less painful (unlike IV)
when is P.O. not achievable?
Malabsorption in gut
Short bowel, obstruction
NV
Pt is delirious or unresponsive
breakthrough pain is usually what % of TDD
10%
Tylenol 4g
Only use short term in healthy adults
Tylenol 3g
long term use in healthy adults (longer than 7 days)
Tylenol 2g or avoid
Heavy alcohol use, malnutrition, older, liver disease, interacting meds
Maybe avoid
Are NSAIDs are effective as weak opioids?
Yes
Usually for mild cancer pain
Bone pain efficacy is inconsistent
What adverse effects to look out for in Nsaids
elderly pop : GIB, kidneys
are opioids used only at end of life?
Increased survival - not shown to shorten life if used appropriately
opioids are sedating and they can’t drive
Sedating effects can be overcome over a few days (tolerance can be built)
Do opioid users get addicted easily?
Not if using appropriately - increases May be due to tolerance
If opioids started to early there are no more options at end of life?
Pain may not increase at end of life. can switch agents
Codiene is 1/10 as potent as morphine?
Yes
How is codiene metabolized
Via cyp2d6
Into morphine
Watch for genetic polymorphism
Max codiene dose
300-400mg
tramadol MOA
Weak opioid agonist and inhibitor of NE, agonist on 5HT reuptake
where is tramadol metabolized
Liver
maximum dose of tramadol
400-600mg qd
Tramadol interactions with medications and conditions
TCA and SSRI (seizure risk)
Seizure disorder, hepatic, renal impairment
what strong opioids are never used first line?
Fentanyl and methadone
Opioid AE that can gain tolerance PRUNS
Pruritus (histamine release)
Resp depression
Urinary symptoms (histamine)
Nausea
Sedation (histamine)
is fentanyl 100x stronger than morphine?
Yes
is fentanyl available orally?
NO - only patches, inj, SL, intranasal
Inj works quickly and short lasting - use 15 minutes prior to something that is painful
conversions of fentanyl patch (fyi?)
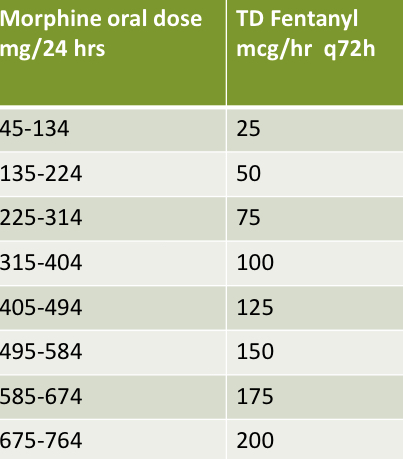
SL fentanyl
Can use inj SL by holding under tongue as long as possible
Expensive
methadone properties
SLAR
Synthetic
Lipophilic - gets to tissues well
Absorbed well orally (in GIT)
Rapid onset (2-3H)
Renal elimination of methadone is dependent on
Urine pH
NO ACCUMULATION IN RENAL FAILURE (so can use in renal failure)
what % is eliminated fecally?
60%
issue with dosing methadone
Unpredictable half-life (eliminated anywhere between 15 and 60 hours)
From this, can have a DELAYED OVERDOSE (ISSUE)
Why is methadone good in neuropathic pain?
useful in neuropathic pain without neurotoxicities
Works on
μ, k & δ (agonist)
NMDA antagonist
NE and 5HT reuptake
Pros of Methadone
Cheap
Good for neuropathic pain
Lower neurotoxicity due to NMDA antagonist
Metabolism of methadone
Cyp3a4
Cyp1a2
Cyp2d6
methadone and QTc interval
If in end of life - not concern
If not in end of life - concern because you can experience sudden death
Dose related especially in high doses (300-600mg qd)
Because of methadone’s unpredictable half life, can have unpredictable effect on QTc as well
what decreases Methadone?
Antiretrovirals: Nevirapine, Ritonavir
◦ Phenytoin ◦ Carbamazepine ◦ Dexamethasone ◦ Rifampin ◦ Spironolactone ◦ Alcohol/tobacco
what increases Methadone?
Cimetidine
◦ Omeprazole
◦ Ketoconazole
◦ Fluconazole
◦SSRI’s
◦ Verapamil
◦ Ciprofloxacin
◦ Macrolides
Who is on methadone therapy
highly tolerant to other agents
Neuropathic pain
For incomplete cross tolerance
Methadone as co analgesic
Low dose methadone can be used on top of reg opioid
May not get full benefit of methadone and if toxicity occurs hard to determine origin
Disadvantages of methadone
Unpredictable half life
QTc interval
Rectal and injectable not commercially available
Whenever naloxone is administered
Call ambulance
When patient is dying
Breathing rate will change - do not mistake for opioid toxicity, if opioid is reversed then they will die in a lot of pain
Gabapentin and Pregabalin
Must be tapered, cannot discontinue stat
Just use gut for tapering… no guide for it
Morphine and ketamine used together equals
Morphine and ketamine used together = methadone bc ketamine works as NMDA antagonist
Why is Effexor not used often for neuropathic pain?
Hard to d/c and has profound withdrawal effects like electric shocks
what antidepressants are not used anymore for neuropathic pain?
carbamazepine , valorous acid, phenytoin (all seizure meds)
why is dexamethasone CS of choice
6.7 times more potent than prednisone
Less mineralcorticosteoid effects like fluid retention
prednisolone causes less————- than dexamethasone
Proximal myopathy
when is taper needed for CS?
If taking longer than 2 weeks
risk of NSAID use with CS
Gastric ulceration
Buprenorphine in cancer
For chronic cancer pain
It is cheap and low potency
Ongoing research being done on it.
How to perform an opioid rotation
◦ Without methadone
◦ To methadone
LA opioids dosed Q12H or QD
CHOMT
Codiene
Hydro
Oxycodone
Morphine
Tramadol
What should not be titillated with in opioids
LA opioids
kadian is dosed
Every 24 hours
More addicting