11.0 Pulmonary oedema
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
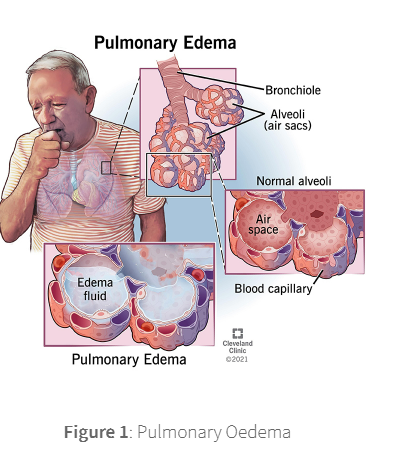
Pulmonary oedema is a condition where fluid builds up in the alveoli of the lungs, displacing air and reducing the amount of oxygen available.
Pulmonary oedema is defined as an abnormal accumulation of extravascular fluid in the lung parenchyma and disrupt normal gas exchange.
The two main types of pulmonary oedema are:
cardiogenic
noncardiogenic
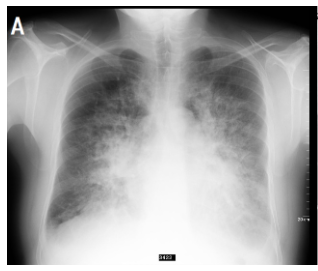
Cardiogenic: This occurs when the left side of the heart becomes ineffective and inefficient in pumping blood around the body. This results in a "back up" of blood through the pulmonary vein and into the lungs subsequently causing an increase in the pressure of the pulmonary capillaries, forcing extracellular fluid into the alveoli. Common causes include heart failure, myocardial infarction or valve disease.
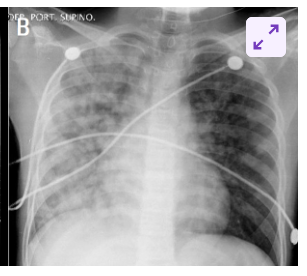
Noncardiogenic: This occurs when damage to the blood vessel walls results in increased production of extracellular fluid. Damage can occur due to infections (e.g., pneumonia, sepsis), toxins (e.g., smoke, chemicals) or exposure to high altitudes.
Progressively worsening dyspnoea, tachypnoea, and rales (or crackles) on examination with associated hypoxia are the clinical features common to both cardiogenic and noncardiogenic pulmonary oedema.
Cough with pink frothy sputum (haemoptysis) is suggestive of cardiogenic oedema as is the presence of murmurs, elevated jugular venous pressure and peripheral oedema.
In patients with non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema, the symptoms of infections such as fever, cough with expectoration, dyspnoea pointing to likely pneumonia, recent trauma, blood transfusions should be carefully assessed as these patients may progress to acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Auscultation remains the mainstay of bedside assessment in all patients with respiratory symptoms. More specifically, hearing of either fine or coarse crackles is crucial to determine the next steps in the management.
Fine crackles are heard in cardiogenic pulmonary oedema. They are exclusively heard in the inspiratory phase when the small airways, which were shut during expiration, open abruptly.
general symptoms
Trouble breathing, or shortness of breath
Wheezing or noisy breathing
Quick, shallow breathing
Trouble breathing while lying down
Pale or bluish skin
Sweating or feeling clammy
Swelling in the feet or ankles
Confusion