sources of ionizing radiation
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
What is “ionization”?
It is the gain or loss of an electron from the outer shell of an atom
Ex: when an external force, such as x-ray, kicks one one electron out of the outer shell and leaves the neutral atom with missing one electron
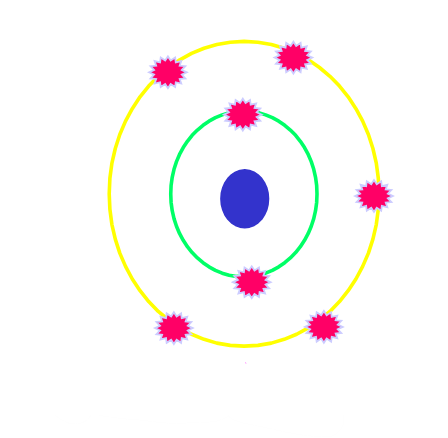
What is an “ion pair”?
ion pair is the combination of the ionized atom and the electron that was ejected from its outer shell
ion pair is unbalanced
Natural Radiation
3 mSv/year or 300 mrem/year
cosmic rays: sun & stars
Terrestrial radiation: uranium, thorium, radon (the largest source of the rest of radiation). All of these 3mSv/year
Internally deposited radionuclides: potassium 40. Can be found in vegetables. Anything that is planted
Artificial radiation: 3..1 mSv/year
Medical/Dental X-rays: 3 mSv/year or 300 mrem/year
Nuclear Energy Plants effect very small
Consumer items: exit signs, smoke detectors, camping lanterns, airport surveillance systems. All of that is 0.1 mSv/year
NCRP?
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement