PBSI 330: Exam 1 Prep
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is personality?
Someone's usual pattern of Affect, Behavior, and Cognition (ABC)

How can personality be shaped?
Genetics
Parents
Peers
Birth Order
Culture

What are the different ways a personality can be observed?
1. Social Interaction
2. Social Media Use
3. Choice of product brand + Features
4. Offices + Bedrooms
5. Physical Appearance + Mannerisms

How can situation affect personality?
It is a Dynamic Interaction between personality and situations

Person-Situation Debate
Person = the view that stable personality traits predict behavior
Situation = the view that a situation is much more important + personality does not matter

S-Data?
Self-Report Data - a person's OWN evaluation of their personality

S-Data Pros + Cons?
Pros - Large Information, Access, Definitional Truth
Cons - Bias, Error

Face Validity?
The degree to which an assessment appears to measure what it is intending to measure

I-Data?
Informant Data - judgments by informants (may be more accurate than S-Data)

I-Data Pros + Cons?
Pros - Real World, Common Sense
Cons - Limited info, lack of access, Error, Bias

L-Data?
Life-Data - verifiable, concrete, real-life facts that hold psychological significance (bank statements, school file, medical records, etc)

L-Data Pros + Cons
Pros - Objective + Verifiable, Intrinsic Importance, Psychological Relevancy
Cons - Multi-determination

B-Data?
Behavior-Data - gathered by observing a person or by recording themselves
What are Physiological Measures?
They give information on biological behavior
What are Behavior Experiments?
They represent real-life contexts that are difficult to observe directly and examine reactions

B-Data Pros + Cons?
Pros - Range of Contexts, Appearance of Objectivity
Cons - Difficult and Expensive, Uncertain Interpretations

Mixed Types of Data?
Data that doesn't always fit into one category (Ex: behavioroid)

Behavioroid
Where one reports what they WOULD do --> this is both S + B Data

Most prominent type of data in personality?
S-Data

Psychometrics?
Quality of Data
Generalizable?
The degree to which you can apply the results of your study to broader context
Measure of Error
Representing the degree of inaccuracy in a measurement. Less Error = More Reliable

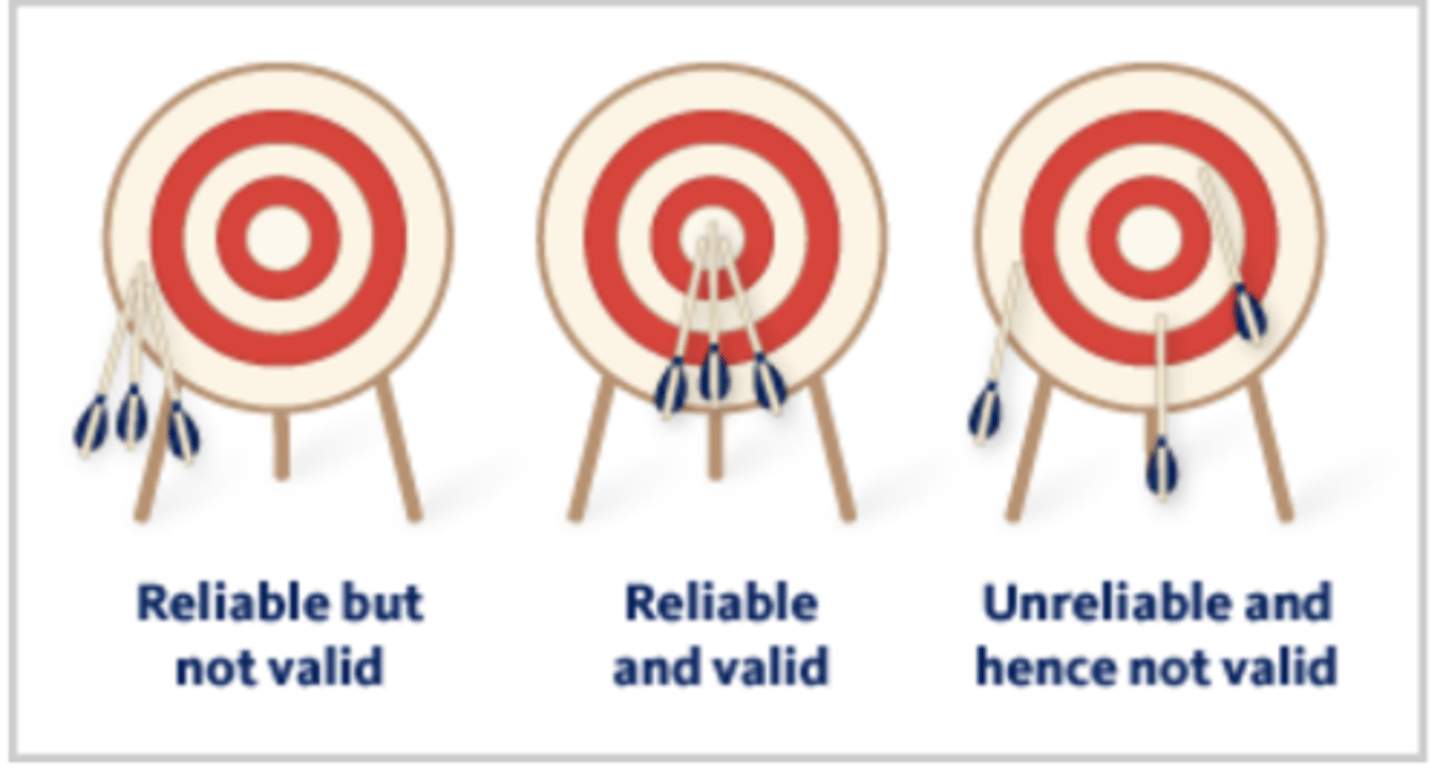
Validity
Is it measuring what it is supposed to?

What are Constructs?
Constructs cannot be seen BUT affect and help EXPLAIN things that are visible.
Construct Validity?
Developing (constructing:) a group of different measurements that yield more or less the same result
Reliability
When a measure is performing consistently

Internal Reliability
When all items on scale measure the same concept (Cronbachs Alpha)

Test-Retest Reliability
Taking a test at 2 different times produces similar results
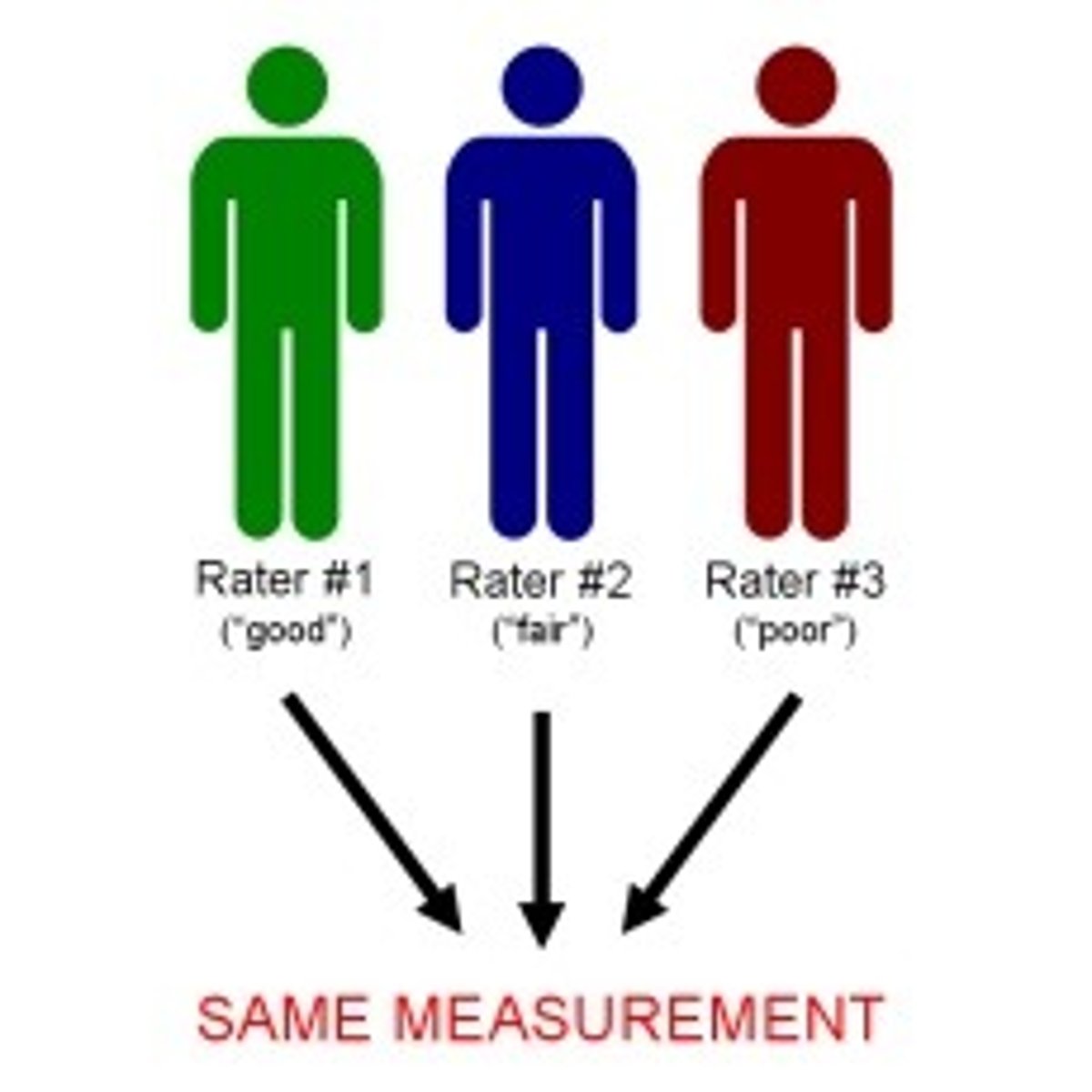
Intercoder / Interrater Reliability
Used when assessment involves writing samples or behaviors and indicates correlation between coder's ratings
Predictive Validity
The measure is related to a concrete behavior or outcome (can predict outcome)

Convergent Validity
The scale correlates with similar scales

Discriminant Validity
the scale doesn't correlate with unrelated scales
If a measure is Valid, it must be ________.
Reliable.
Barnum Effect?
People tendency to believe vague, positive statements about themselves.

What is Factor Analysis?
A statistics technique that identifies groups of things that seem to have something in common.
Steps of Factor Analysis -->
1. Generate long list of items
2. Administer the items to people
3. Analyze w/ factor analysis
4. Consider what they have in common and group the together w/ a name
What is the Case Method?
CLOSELY studying a particular event or person to find out as much as possible

Case Method Advantages + Disadvantages
Advantage - Describes whole person/event, illuminates disasters, deals w/ common event/people
Disadvantage - unknown generalizability

Experimental Study?
It tests differences between groups to determine if the differences are larger than would be expected by chance
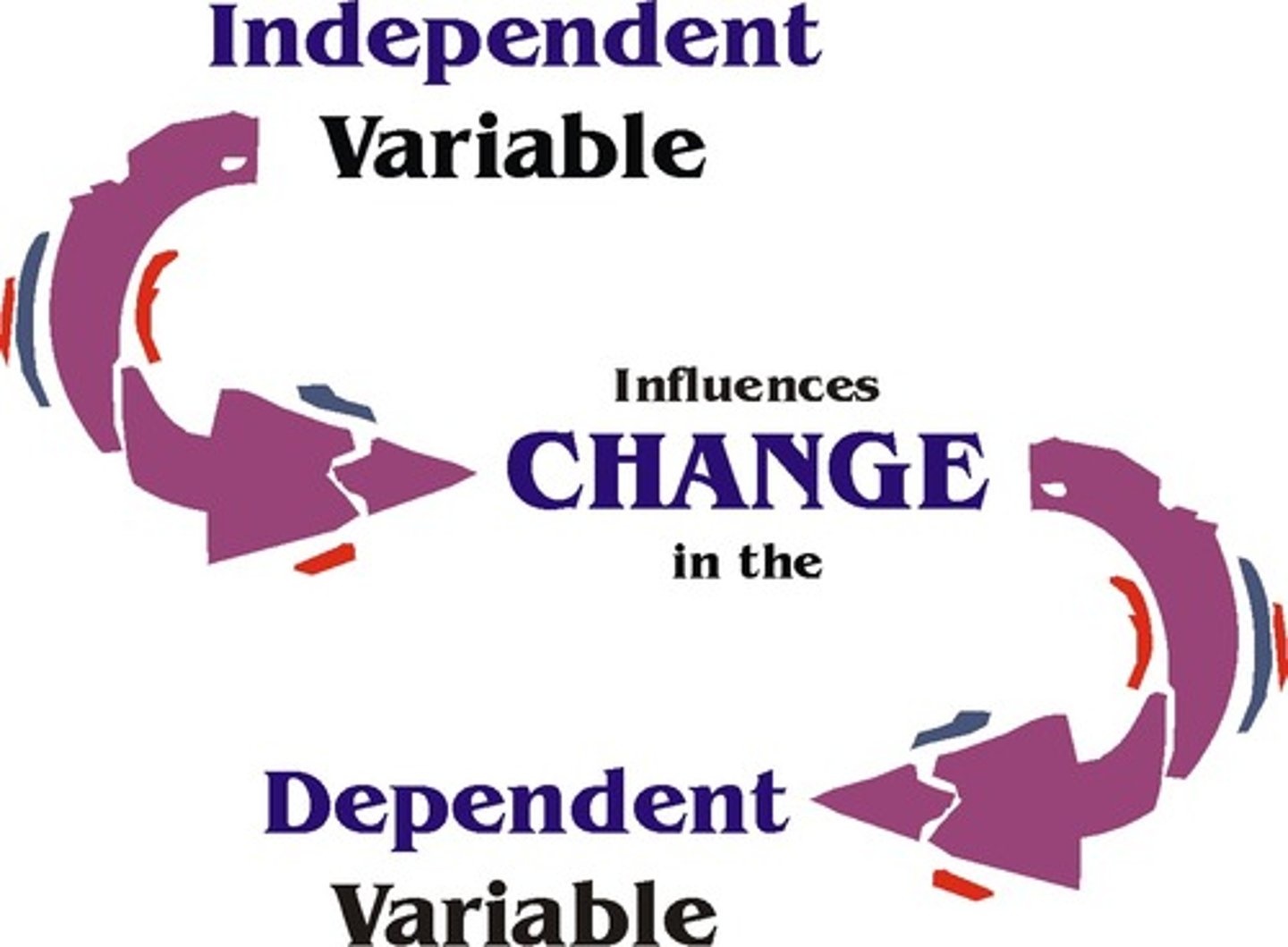
Independent variable
Imposed by Experimenter

Dependent Variable
Dependent on Independent Variable

Correlation Study?
It measures BOTH variables AS they occur naturally in a sample (no experimental groups)
What is Statistical Significance?
It is only S.S. when it only occurs less that 5% of the time
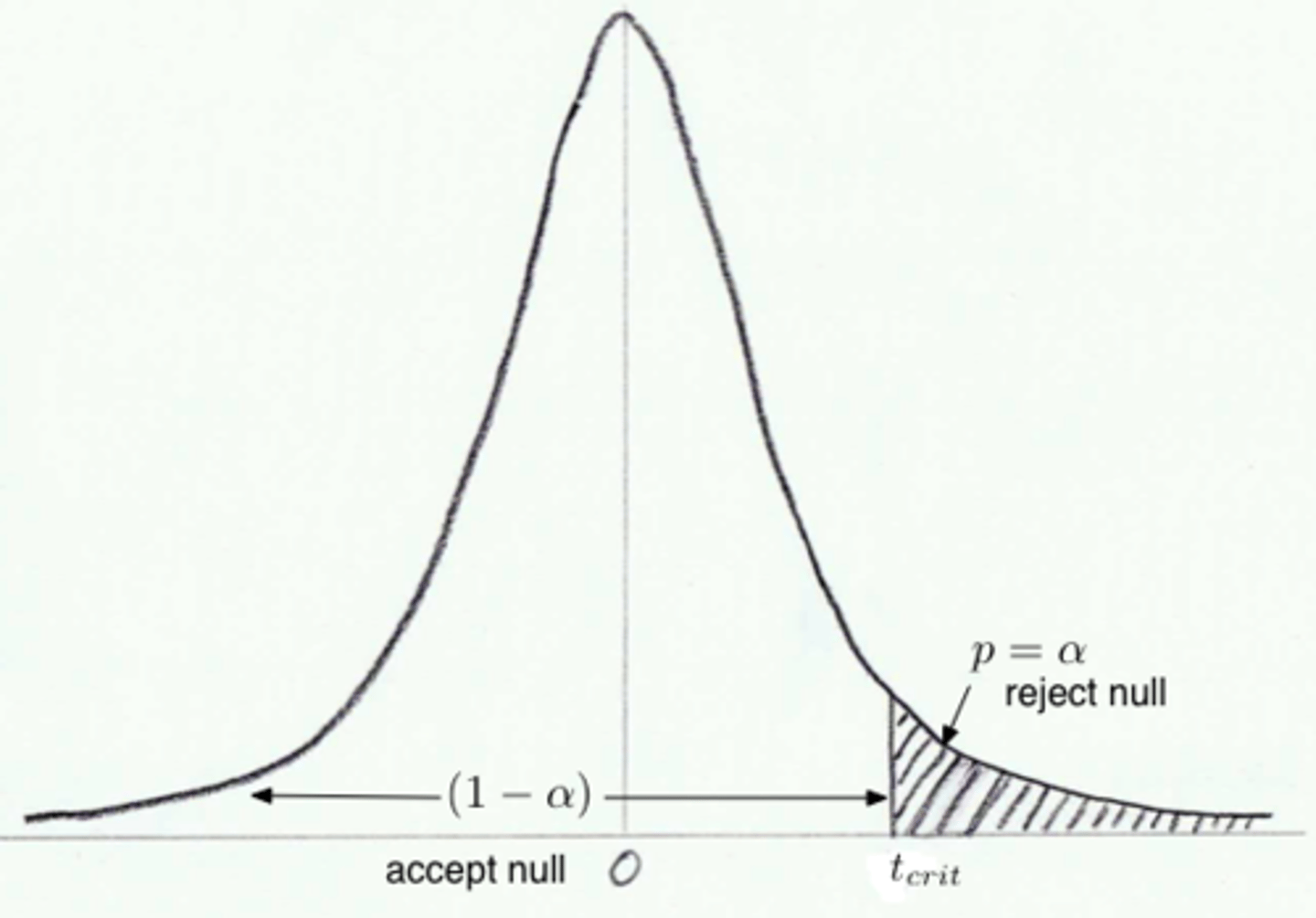
Null Hypothesis Significance Testing (NHST)
Determines the chance of getting the result if NOTHING were really going on
P-Level?
Probability of obtaining result
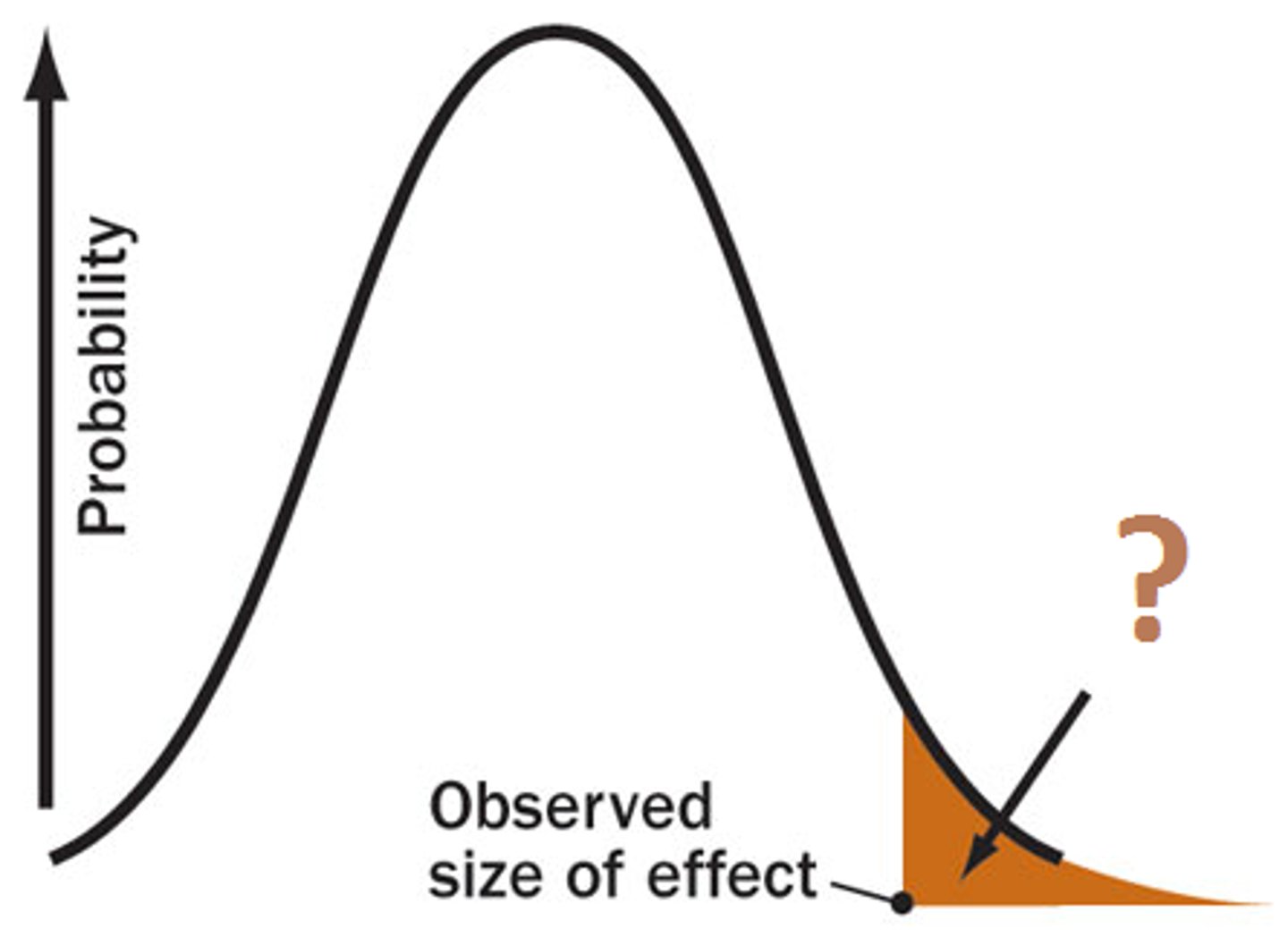
Effect Size?
The index of magnitude and strength of the relationship between variables
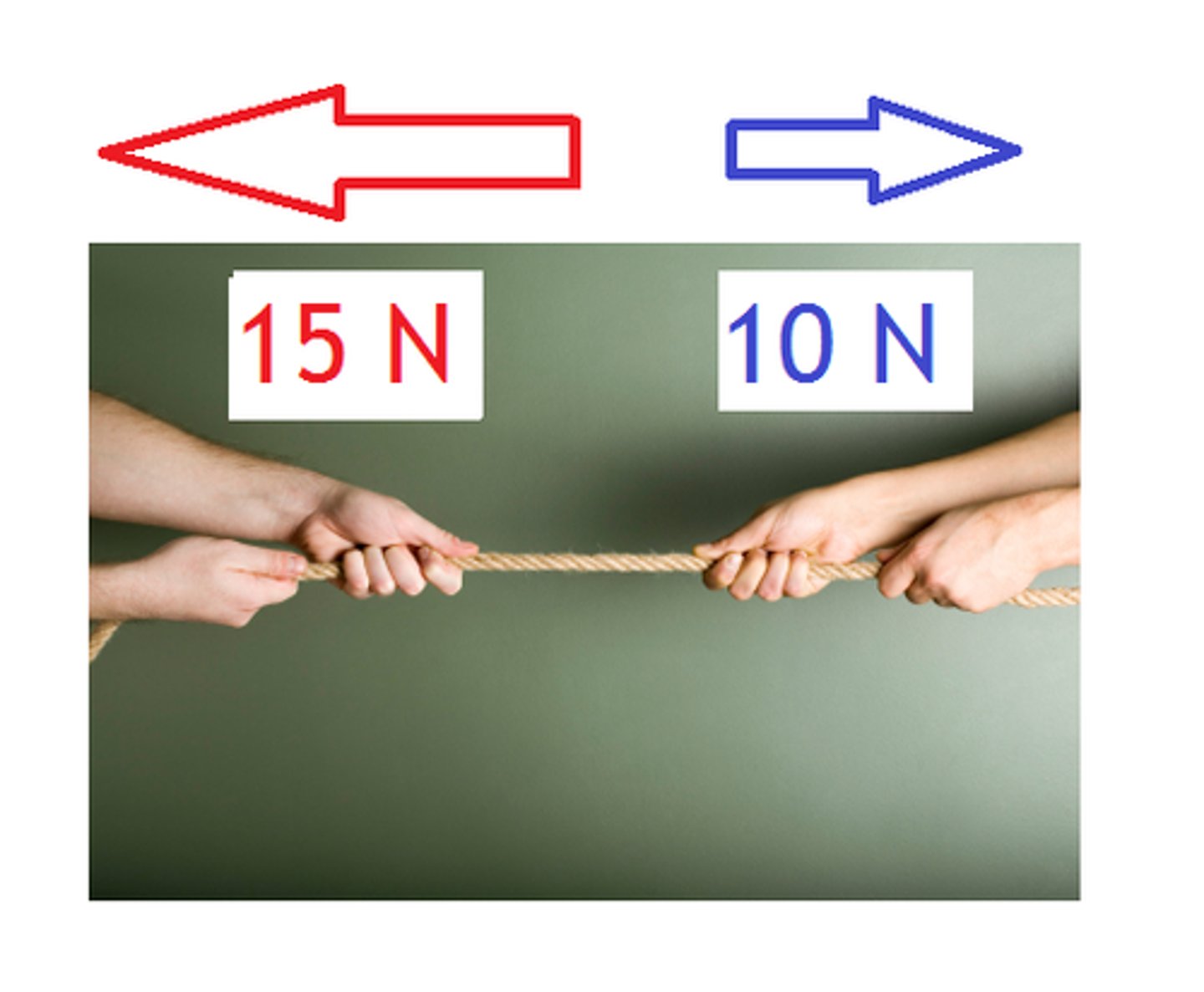
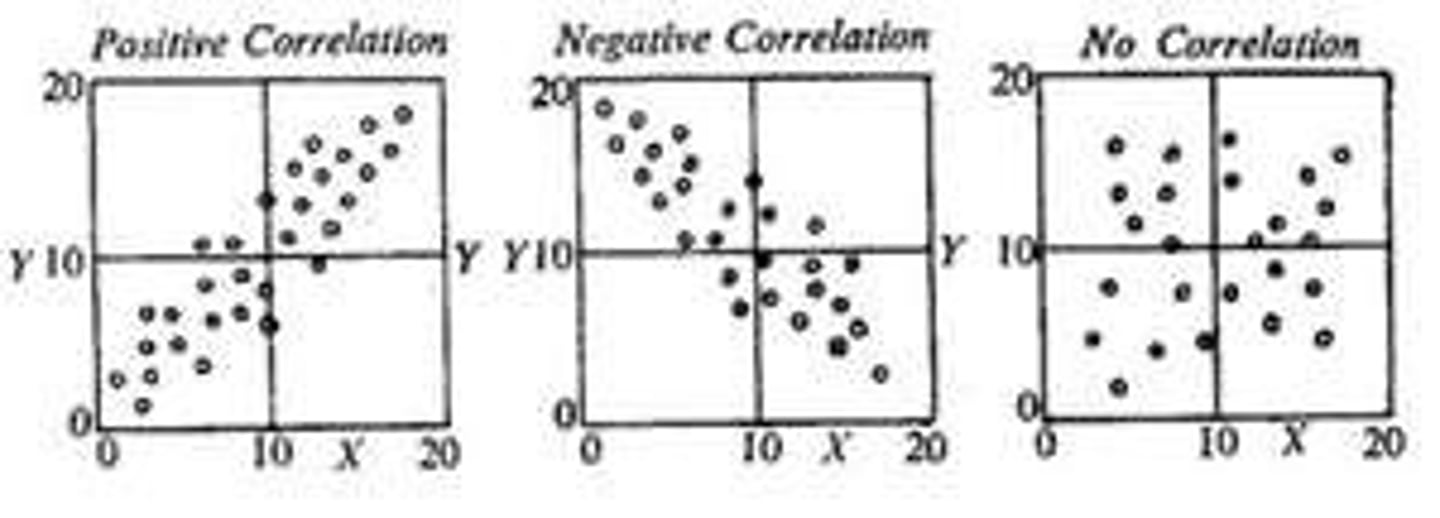
Positive Correlation VS Negative Correlation
Positive = / /
Negative = X
(between -1 & +1)
Null Correlation
p = 0, no linear relationship
What is Replication?
Finding the same results repeatedly with different people and labs

How can you make research more dependable?
1. More people
2. Disclose Everything
3. Share your Data
4. Report false studies

What is Publication Bias?
Studies with STRONG results tend to be more likely published

P-Hacking?
Hacking around your data until you find the necessary degree of statistical significance that would allow publishing (publish-hacking)

Open Science?
Set of practices intended to move research closer to the ideals science was founded on
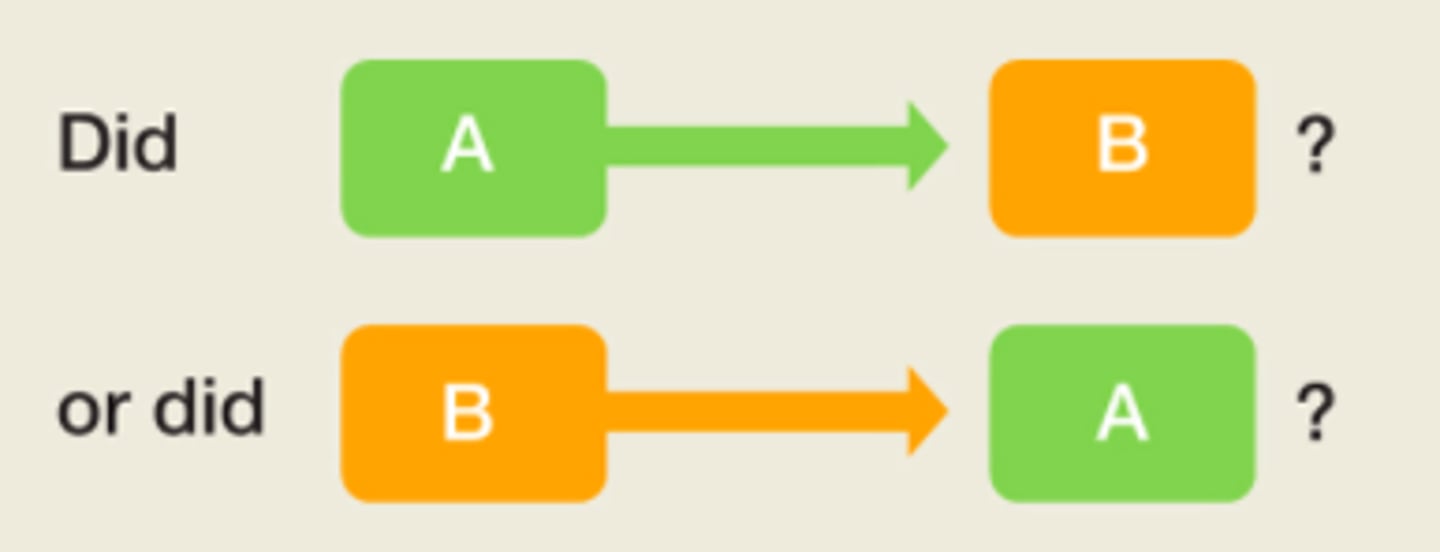
Causality
When you need to move beyond correlation studies
Ethics in Research includes:
1. Informed Consent
2. IRBs guidelines
3. Truthful reporting

Statistical Power?
Having enough observations or people in a study to reliably detect an effect

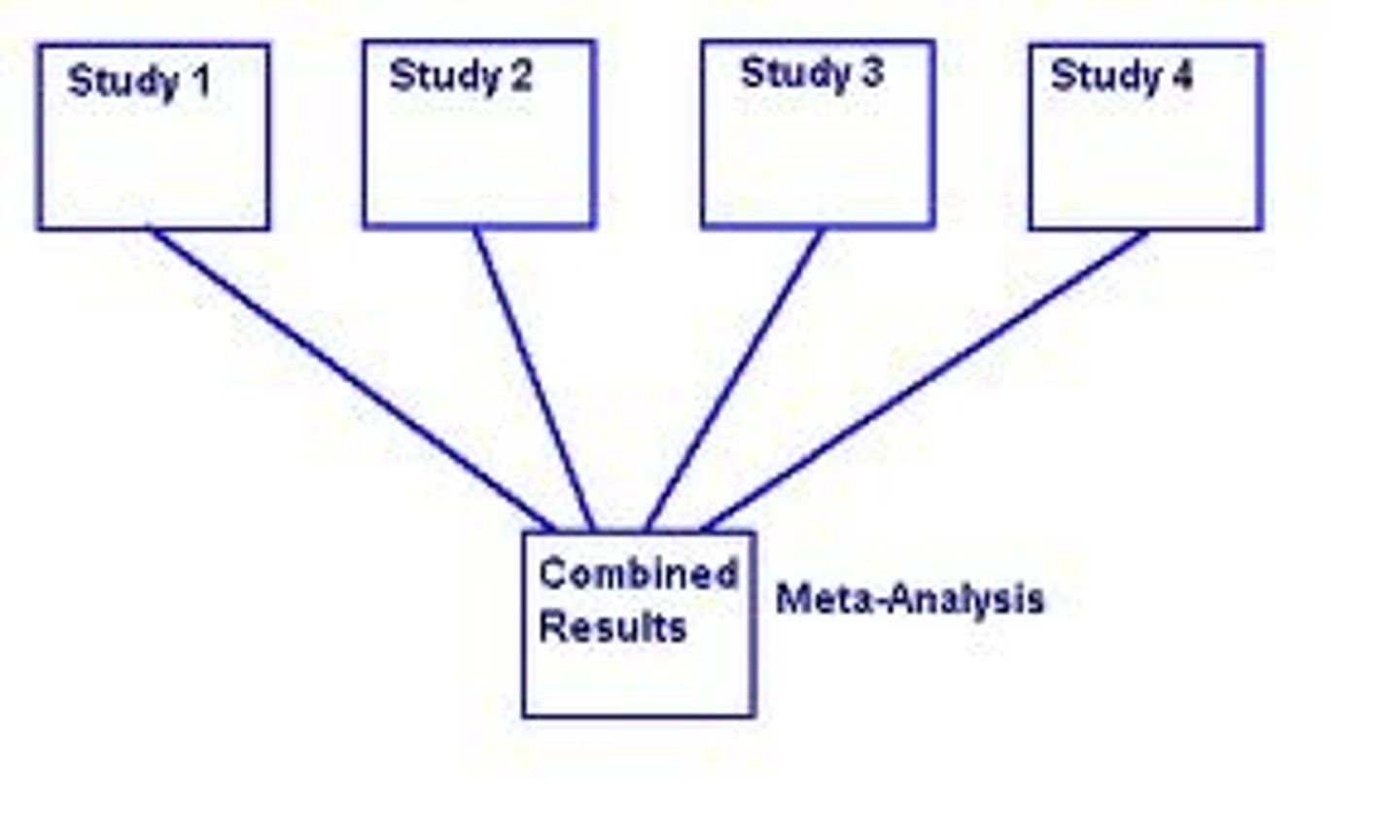
Meta-Analysis
A study of studies that statistically analyzes all of the results together
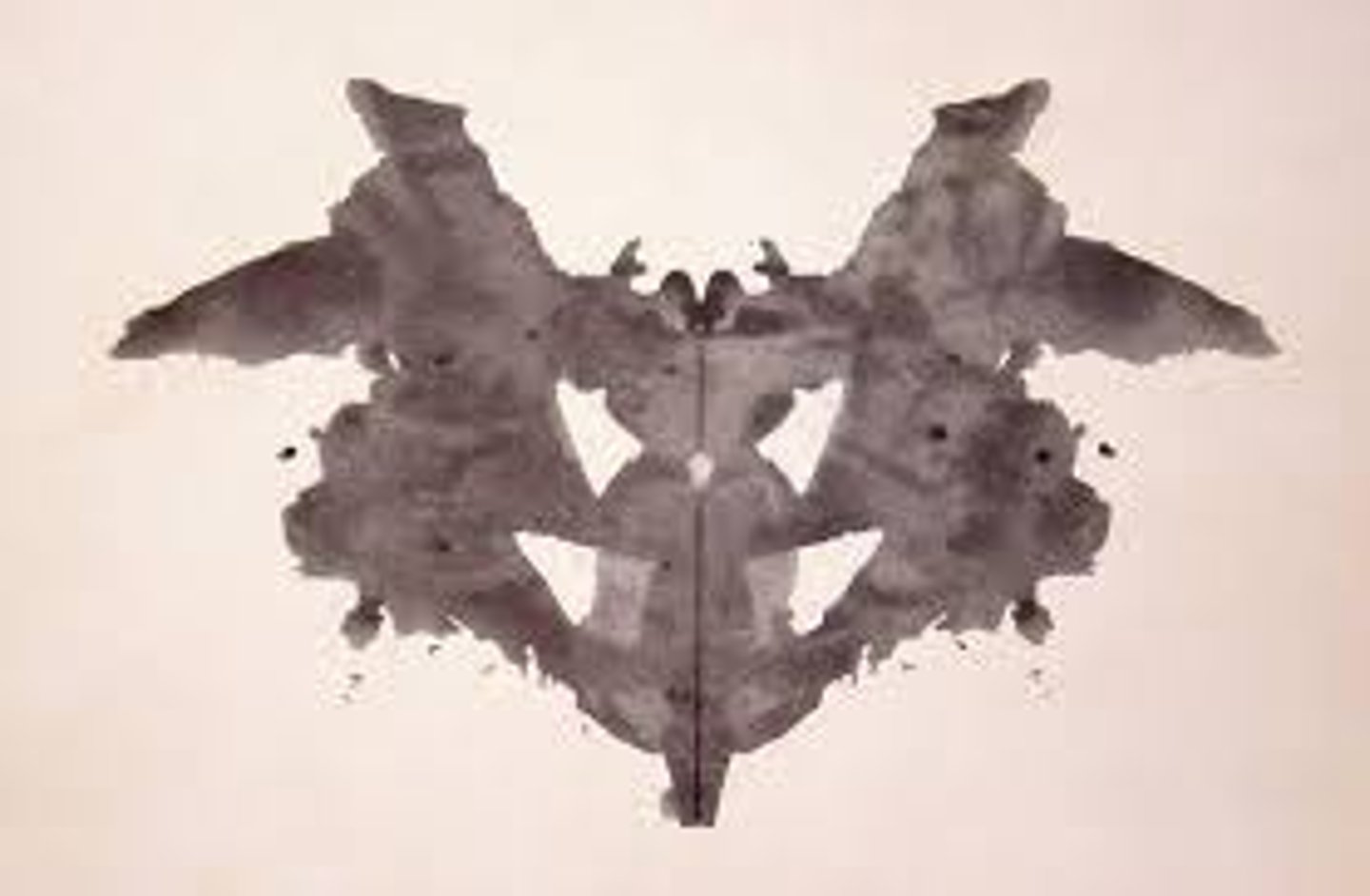
Projective Tests?
tests designed to reveal inner aspects of individuals' personalities by analysis of their responses to a standard series of ambiguous stimuli; the person may/may not be aware of their inner process
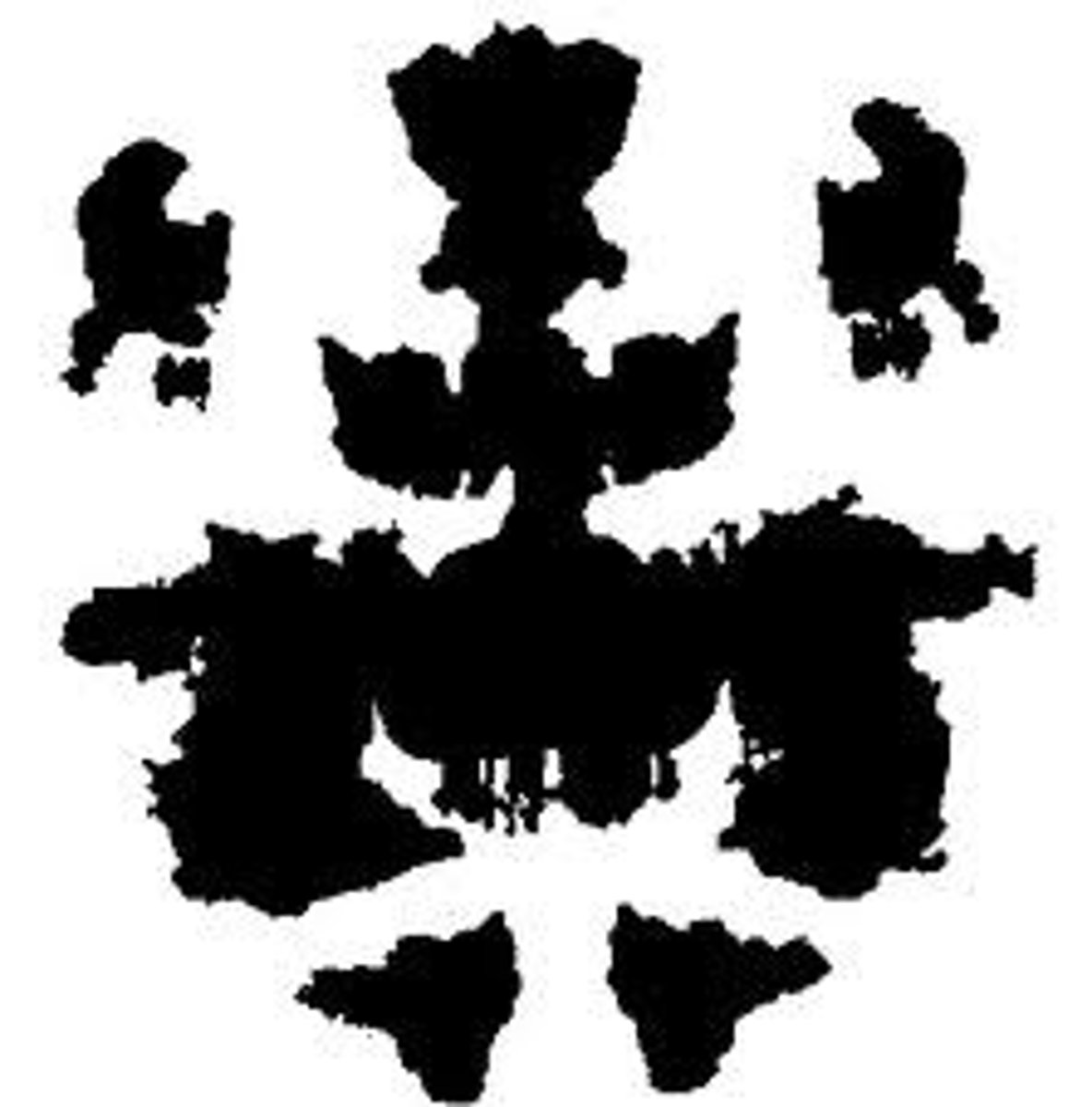

Rorschach Inkblot Test
though is not always hidden and mysterious

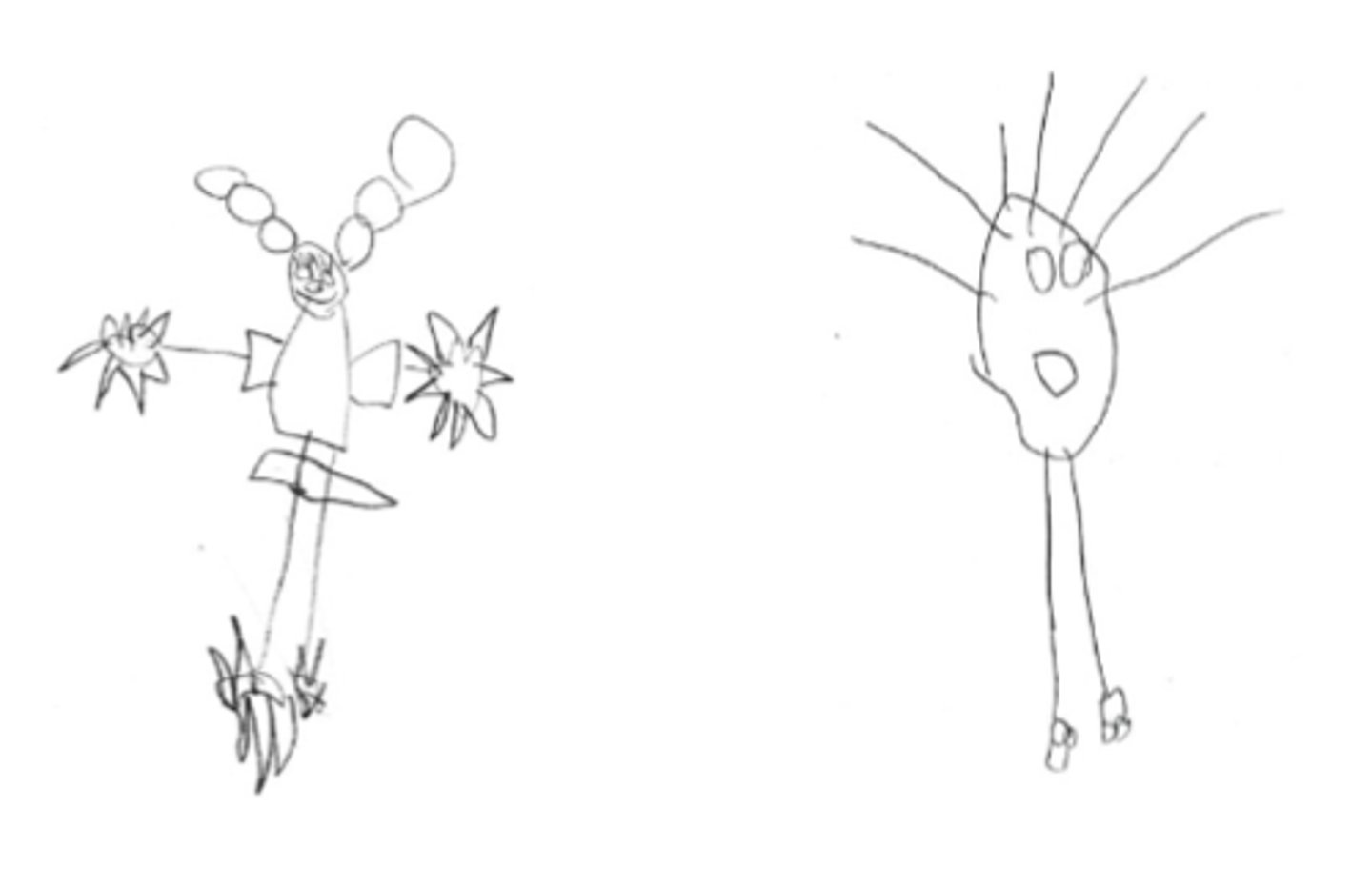
Draw-A-Person Test
Ask the subject to draw a person and study the omitted or exaggerated body parts.
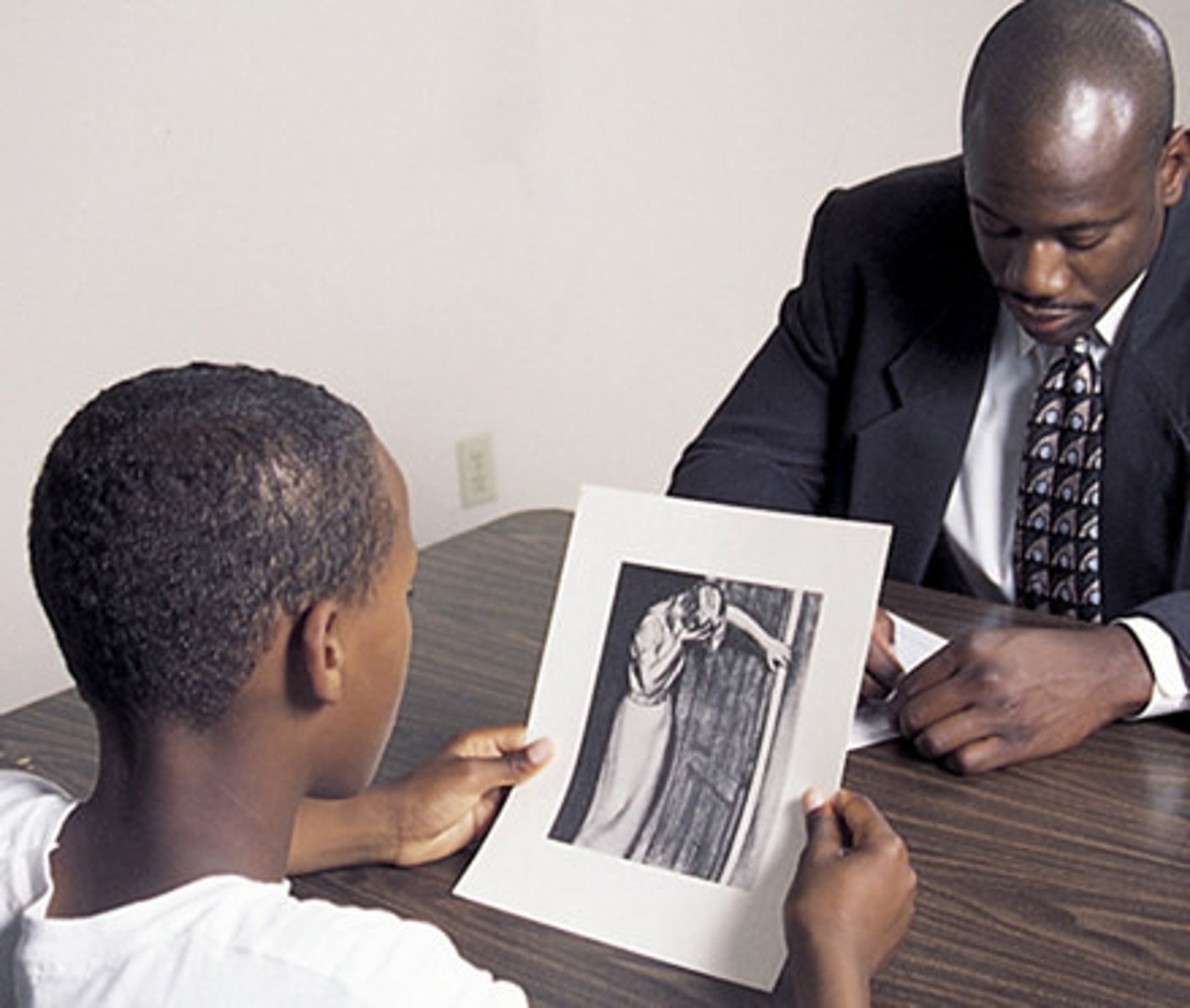
Thematic Apperception Test
used to assess motivational states, tell stories about drawings of people and ambiguous events

What are the Pros and Cons of Personality Tests?
Pros - Breaking Ice, Skilled Clinicians may be able to use them
Cons - Validity is scarce, time + money, unclear interpretation, used inappropriately

What is the Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale?
used for Bias control in S-Date,
where you'd give extreme T or F questions to adjust for outliers
What is Multi-Method Assessment?
Using a bunch of different tests to understand someone more holistically

Single Trait Approach?
Examines behaviors associated with A trait.
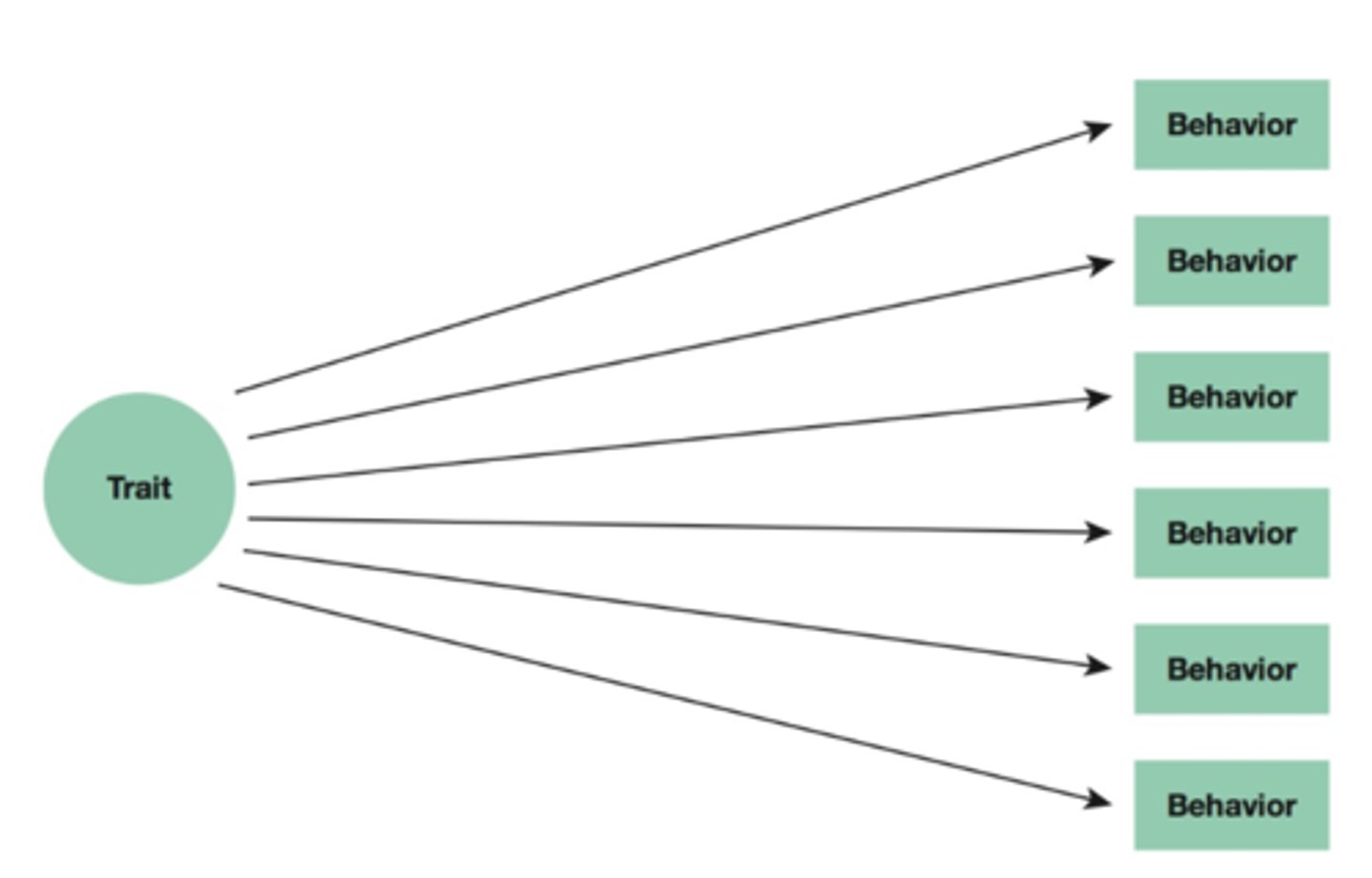
Many-Trait Approach?
Looks for traitS associated with a PARTICULAR behavior
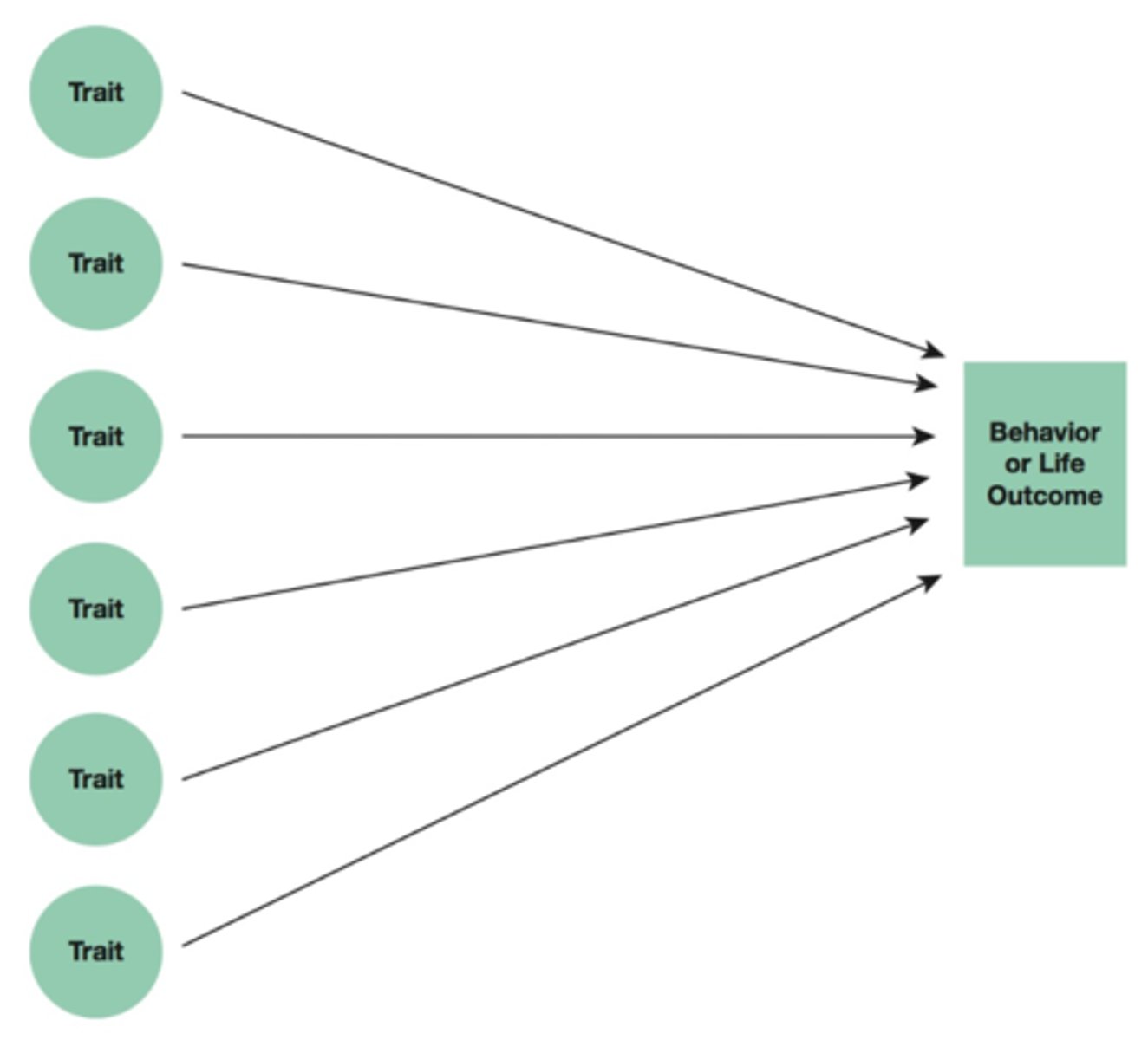
Essential-Trait Approach
Identifies which traits are MOST important
Typology Approach
Focuses on the patterns of traits that CHARACTERIZE a person

Personality Traits?
Traits characterize what any person may do in any situation ON AVERAGE

Self Monitoring?
The ability to regulate behavior to accommodate social situations

High Self Monitoring and Low Self Monitoring = ?
High = Popular, Adaptable, Wish-washy, 2-faced
Low = Self-directed, Honest, Stubborn, Insensitive

California Q-Set?
Other raters express judgments of someone else's personality by sorting into 9 categories!
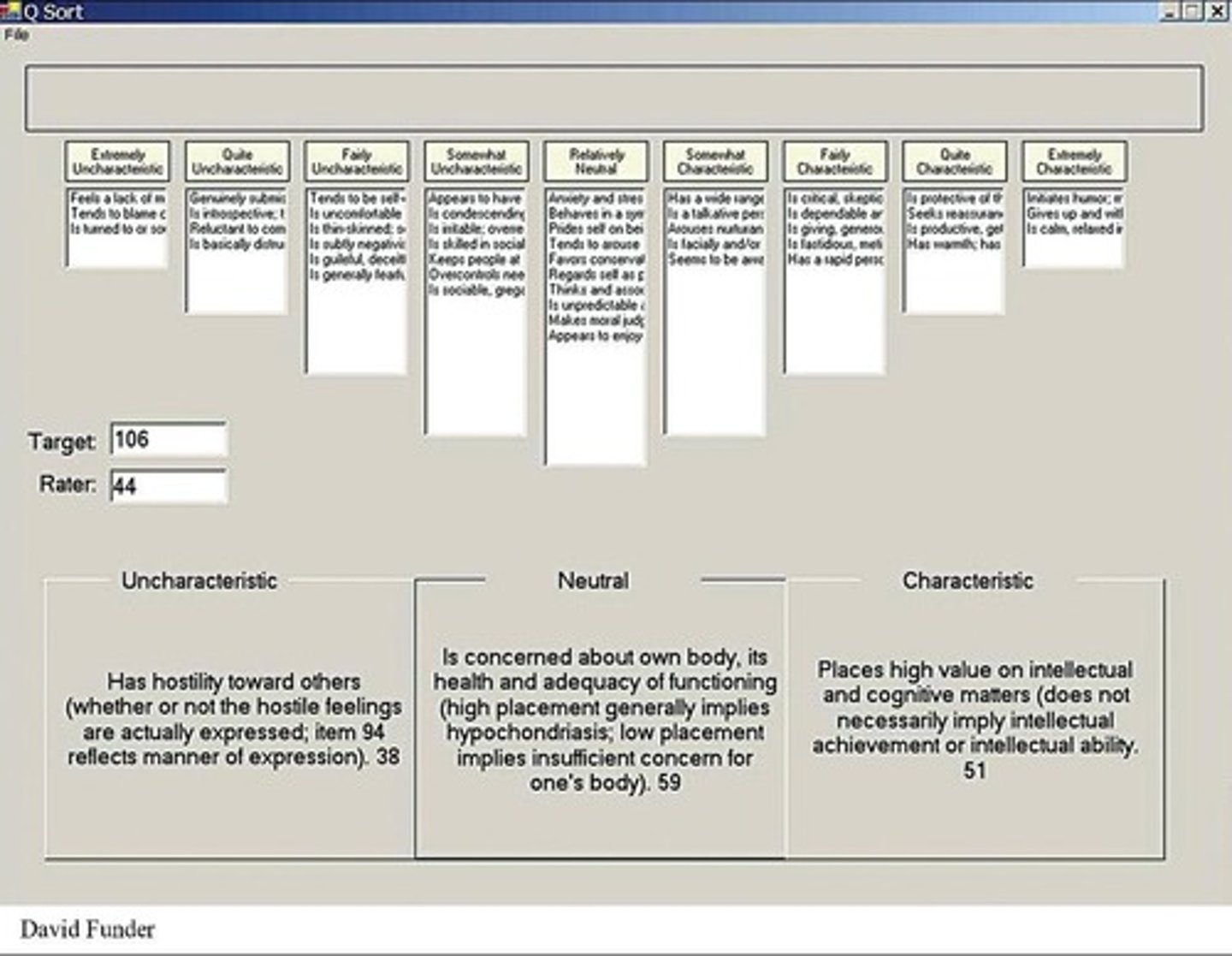
What type of Approach is the California Q Test?
Many-Trait Approach
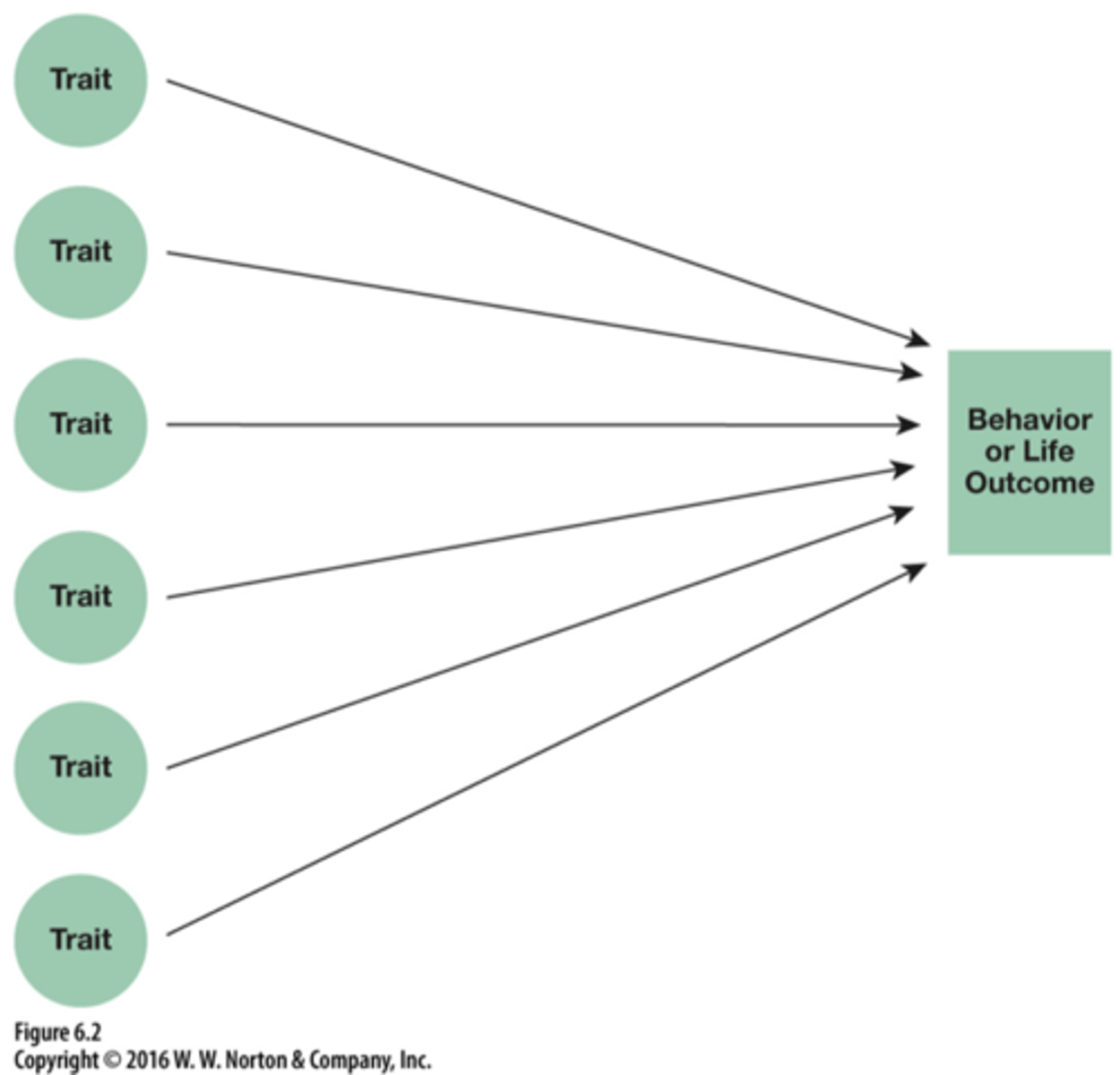
What is the Factor Analytic Approach?
Correlating EVERY measured variable with every other variable which reduces # of traits to only the important ones.
Examples of Factor Analytic Approach?
Cattell, Eysenck, and Tellegen (T.E.C.)
Lexical Hypothesis?
the important words throughout life have many words in many languages to describe them
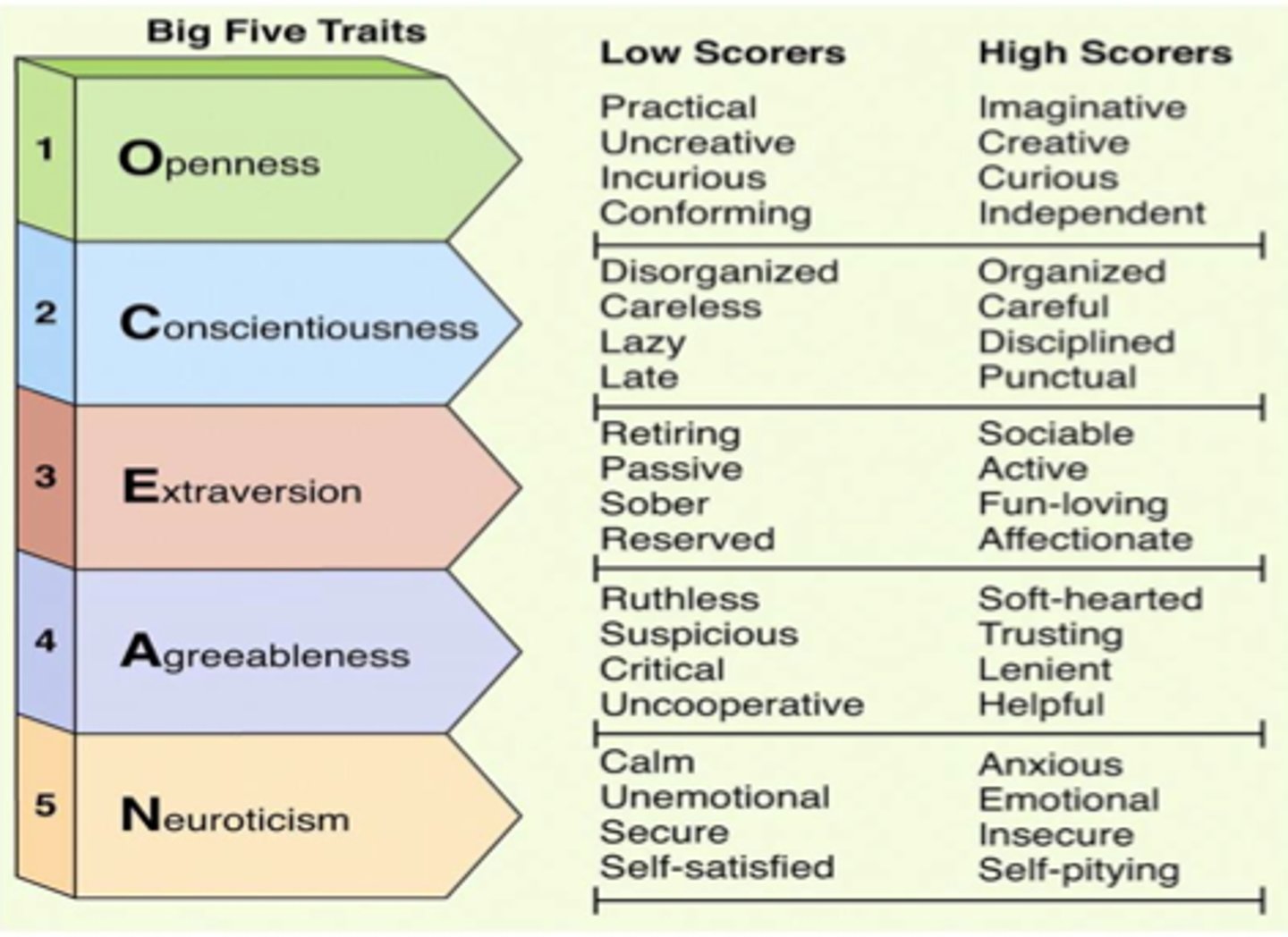
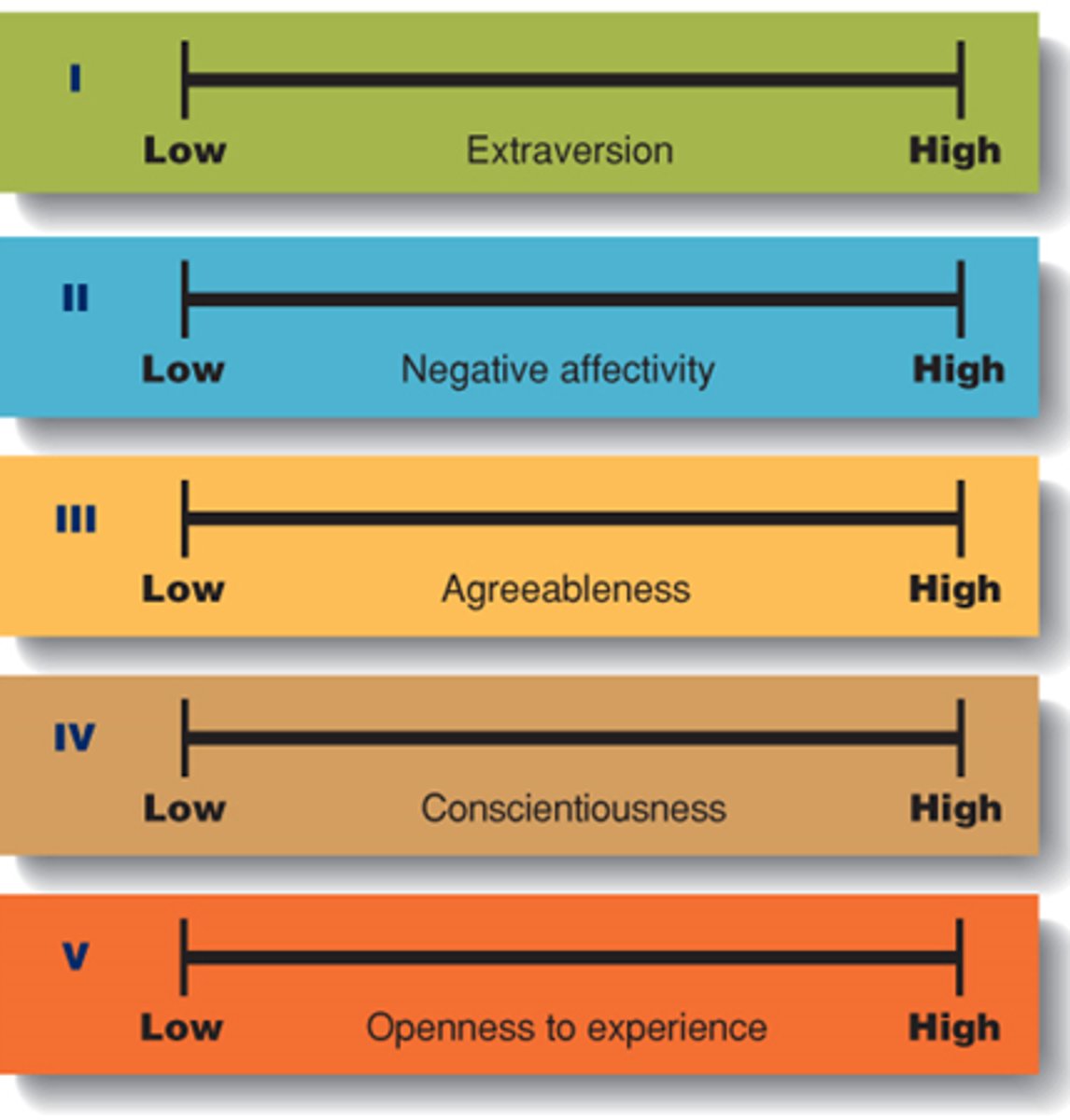
What type of approach is The Big Five?
Essential Approach
Stability?
(ego control) High in Agreeableness and Consciousness, Low in Neuroticism
Plasticity?
(Ego Resilience) High in Extraversion and Openness

What is Eyseneck's view of Extraversion?
Extraverts have more strong and negative reactions due to their craving for more extreme levels of stimuli, more susceptible to risky and dangerous activity

What type of approach is Eyseneck's hypothesis on Extraversion?
Single Approach

What are the controversies associated w/ Big Five?
"many attributes are not encompassed"
"honest/humility??"
"not sufficient for really UNDERSTANDING people"
Advantages and Criticisms of Myers Briggs?
Advantages - popular application
Criticisms - not useful for selection/predicting life outcomes, based on normally distributed scores, and not reliable (take the test twice and will likely get different answers)

Still learning (2)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!