HumanA&P 6: Integumentary System
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Integumentary System
Anatomy of the skin
Functions of Skin
Accessory Structures
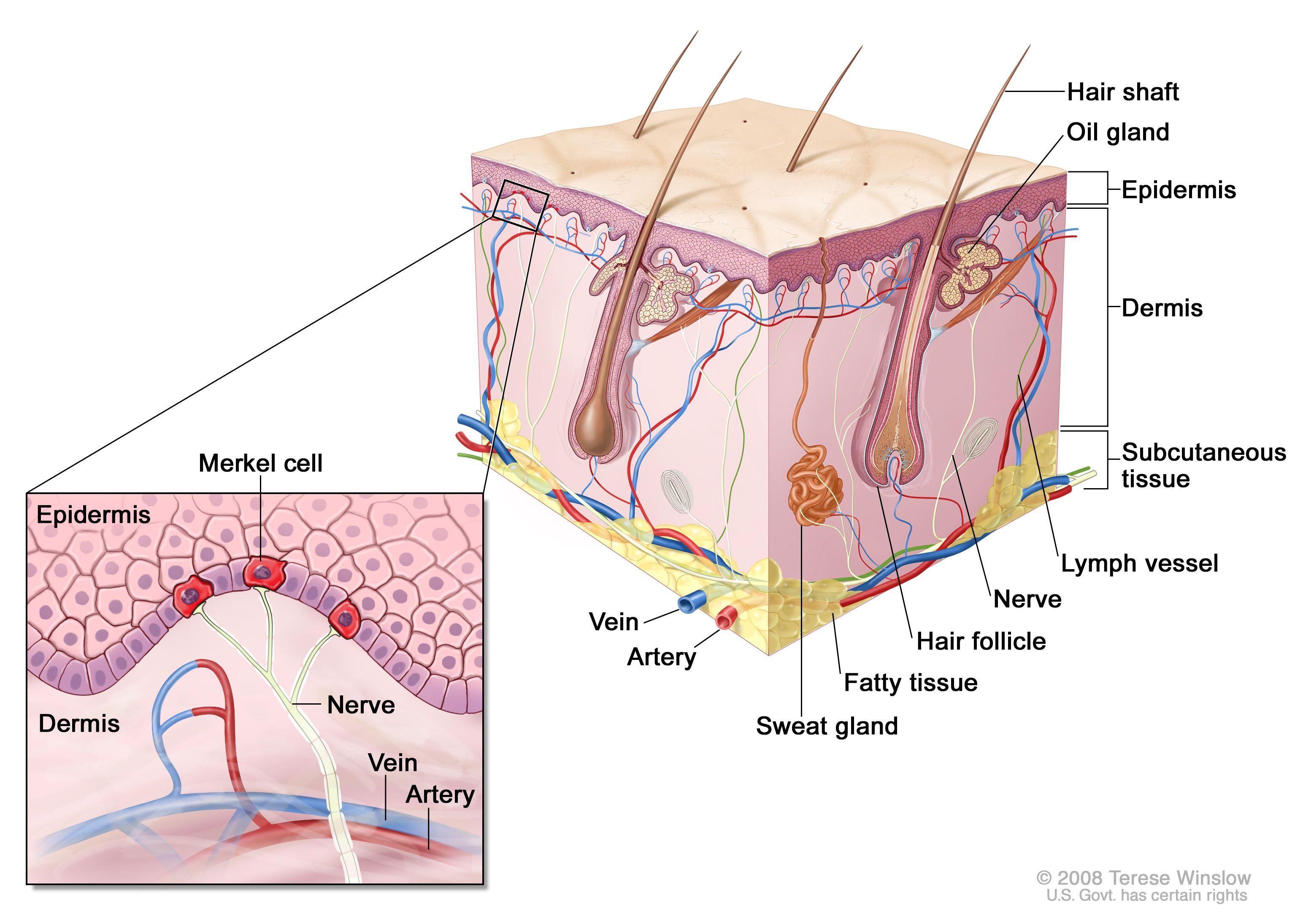
Skin
Largest organ
16% total body weight
1.5-2m²
2 Major Components:
Cutaneous Membrane
Accessory Structures
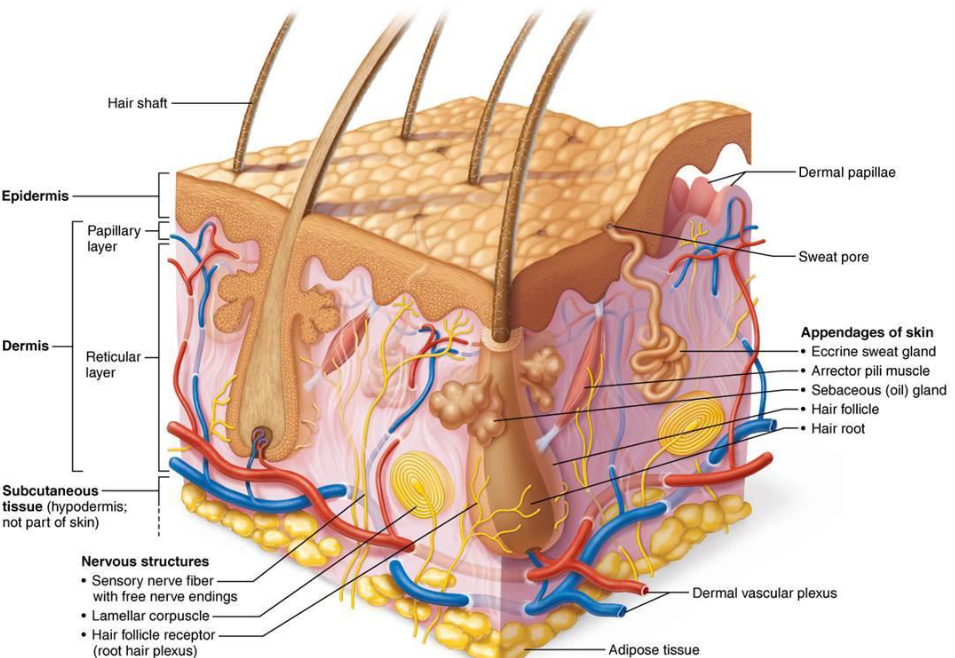
Skin Structure
Epidermis: Superficial region
Consists of epithelial tissue, avascular
Dermis: Underlines epidermis
Mostly fibrous connective tissue, vascular
Hypodermis: superficial fascia
Subcutaneous layer
Mostly adipose tissue
Anchors skin to underlying structures
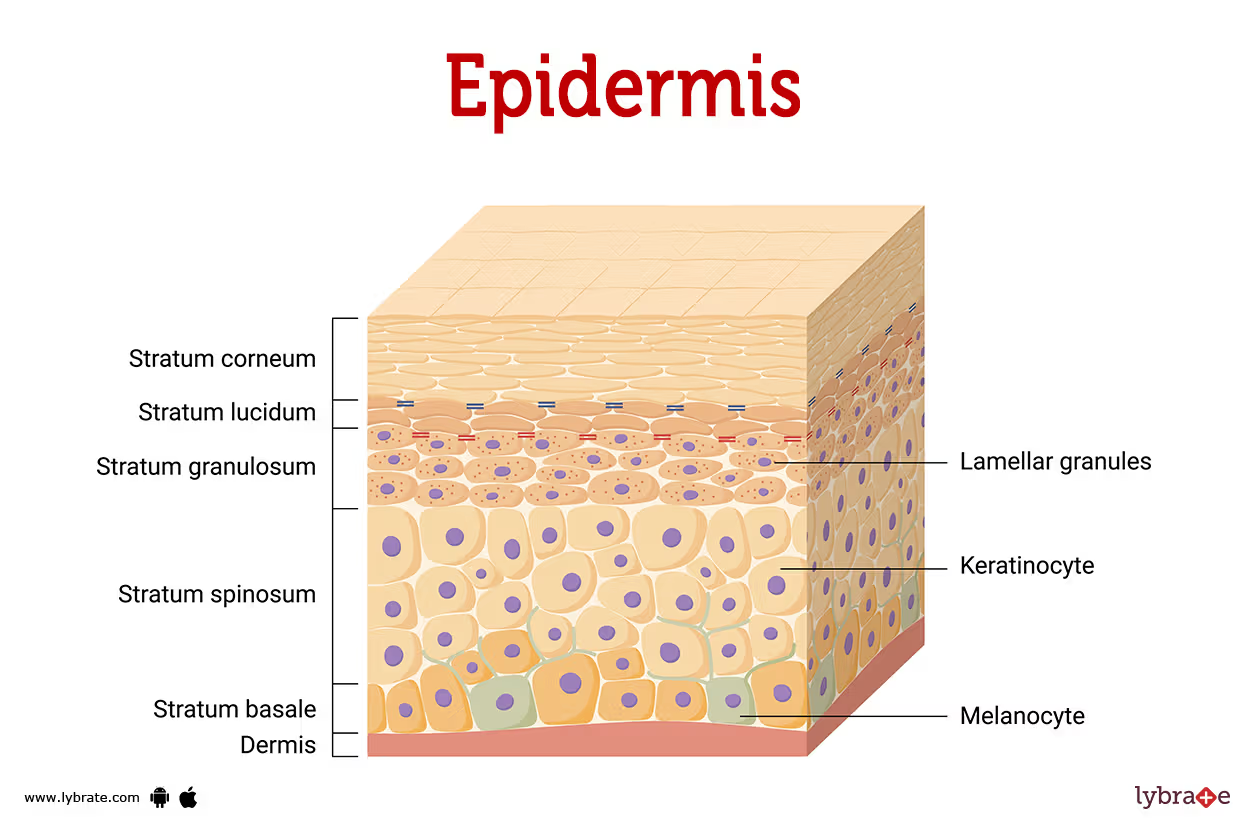
4 Cells of the Epidermis
Keratinocytes ~90%
Melanocytes ~8%
Dendritic (Langherhans) 1-2%
Tactile (Merkel) <1%
Keratinocytes
~90% of epidermis
Stratified squamous epithelium
Produce keratin
Tightly connected by desmosomes
Millions slough off every day
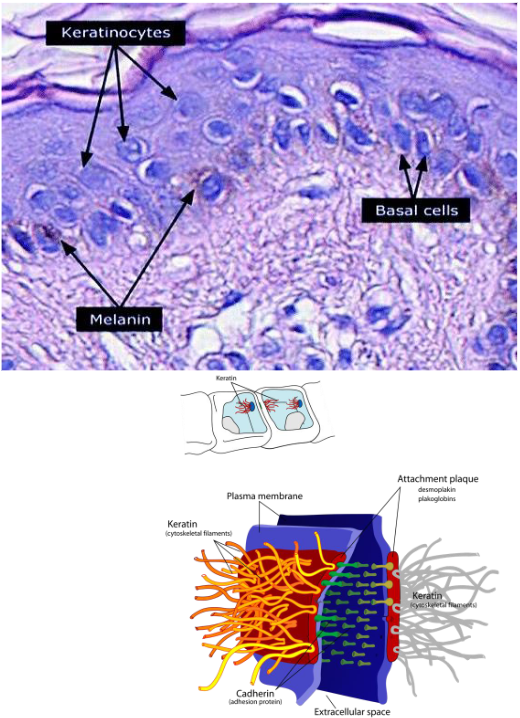
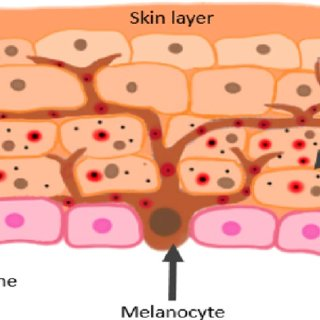
Melanocytes
~8% of epidermis
Located in deepest epidermis
Produce melanin packaged into melanosomes
Transfers to keratinocytes, protects from UV
Dendritic (Langherhans) Cells
~1-2% of epidermis
Star-shaped macrophages that patrol deep epidermis
Key activators of the immune system
Tactile (Merkel) Cells
<1% of epidermis
Sensory receptors that sense touch & pressure
5 Layers of the Epidermis
Stratum Basale
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Corneum
Before Signing, Get Legal Counsel
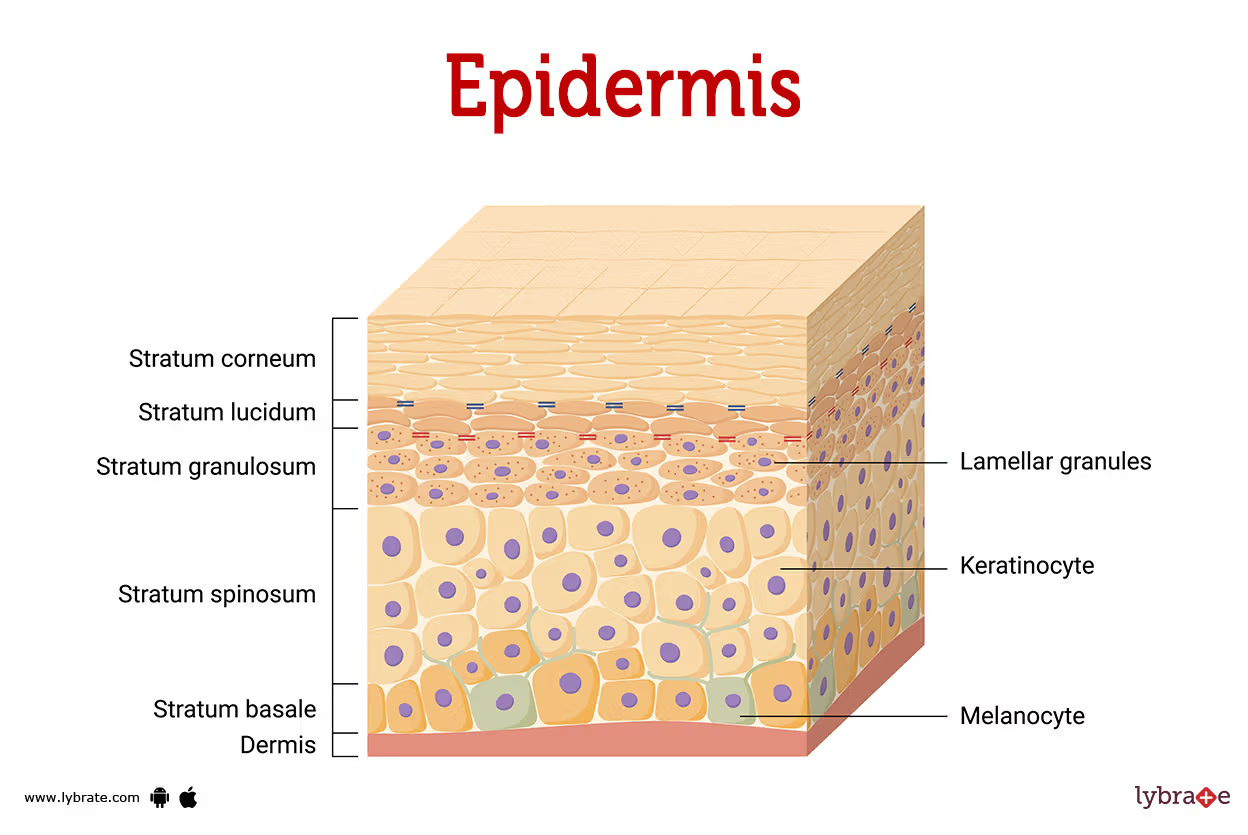
Stratum Basale
Deepest epidermal layer
Cuboidal or columnar keratinocytes & stem cells
1 row of stem cells
AKA stratum germinativum
10-25% composed of melanocytes
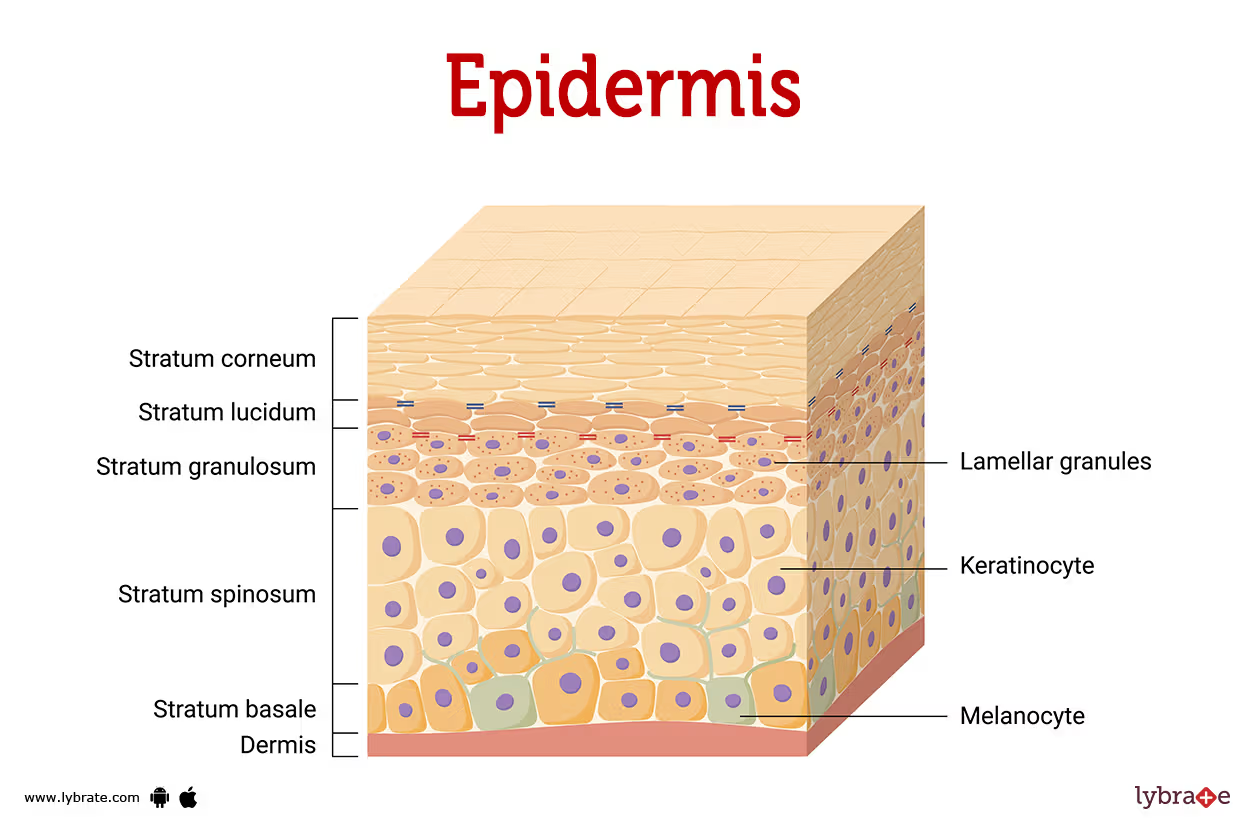
Stratum Spinosum
2nd deepest epidermal layer
8-10 layers of cells that produce coarser keratin
Contain intermediate prekeratin filaments
Allows resistance to tension & pulling
Spikey keratinocytes called “prickle cells”
Abundant melanosomes & dendritic cells
Stratum Granulosum
3rd deepest epidermal layer
4-6 cells thick
Cell appearance changes:
Flatten
Keratinization begins
Accumulate lamellar granules
Cells above this layer die
To far from dermal capillaries
Lamellar Granules
Water resistant glycolipid that slows water loss
Stratum Lucidum
2nd most superficial epidermal layer
Only in thick skin
Thin, translucent band of 2-3 rows of clear, flat dead keratinocytes

Stratum Corneum (horny layer)
Most superficial epidermal layer
20-30 rows of flat dead keratinocytes
¾ of dermal thickness
Cell functions:
Protection
Prevent water loss
Barrier against biological, chemical & physical assaults

Apoptosis
Controlled cell death
Cells change by undergoing this process
Dead cells are dandruff
Humans can shed ~50,000 cells/minute
Psoriasis
Increased rate in cell division & sloughing (7-10 days)
Formation of New Epidermal Cells
Formed by cell division in stratum basale
~4-6 weeks from mitosis to sloughing
Keratinocytes moving superficially accumulate more keratin become less metabolically active
Epidermal Growth Factor
Allows basale keratinocytes to divide faster due to scrapes & burns
Dermis
Strong, flexible connective tissue
Cells:
fibroblasts
macrophages
mast cells
leukocytes
adipocytes
Contains nerves, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels
Hair follicles, oil glands, sweat glands
2 regions:
Papillary
Reticular
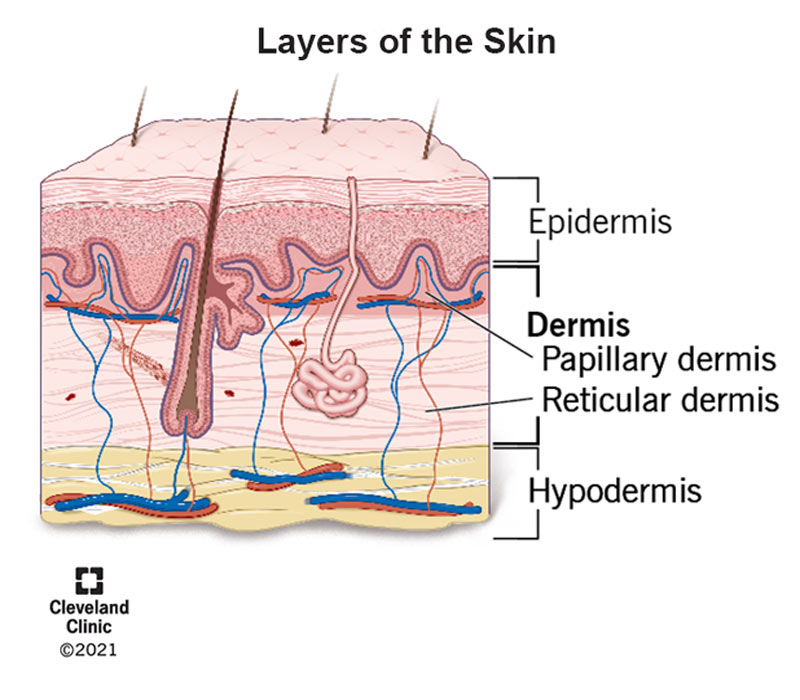
Papillary Layer
Superficial dermal layer
Composed of:
Areolar connective tissue
Collagen
Elastic fibers
Blood vessels
Dermal papillae
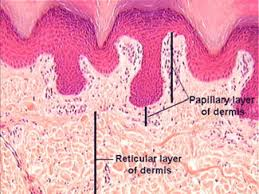
Dermal Papillae
Superficial region of dermis that sends fingerlike projections up into epidermis
Contains:
Capillary loops
Free nerve endings
Touch receptors
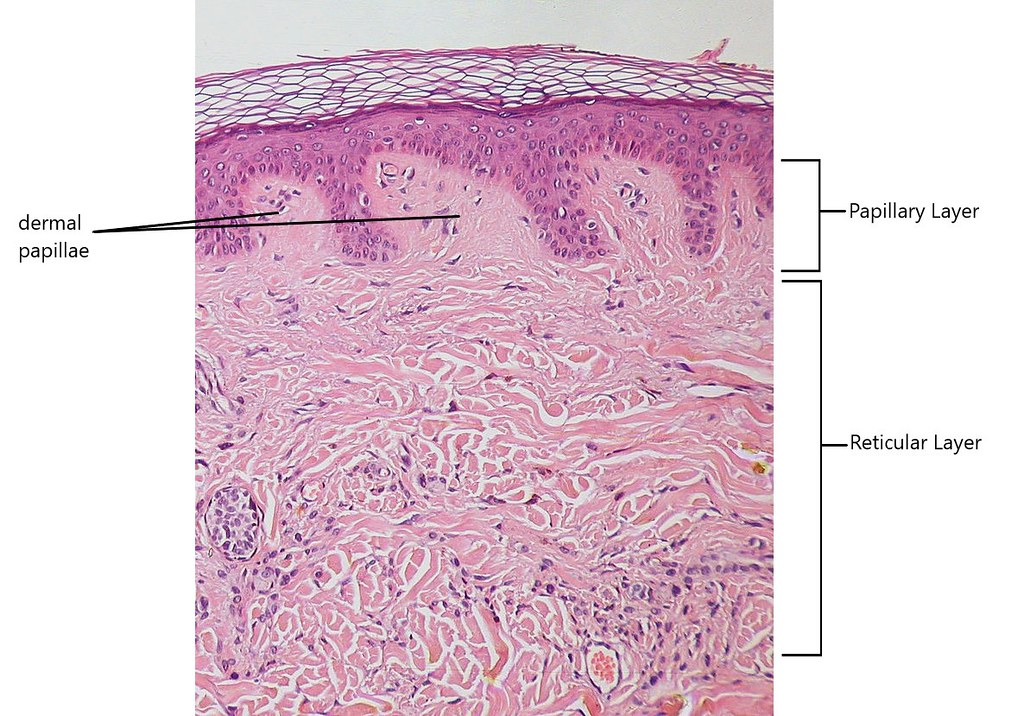
Papillary Layer in Thick Skin
Dermal papillae lie on top of dermal ridges, give rise to epidermal ridges
Collectively ridges are called friction ridges
enhance gripping ability
Contribute to sense of touch
Sweat pores in ridges leave unique finger prints
Dermis Reticular Layer
Deep dermal layer
~80% of dermal thickness
Consists of coarse, dense fibrous connective tissue
Elastic fibers
Collagen fibers
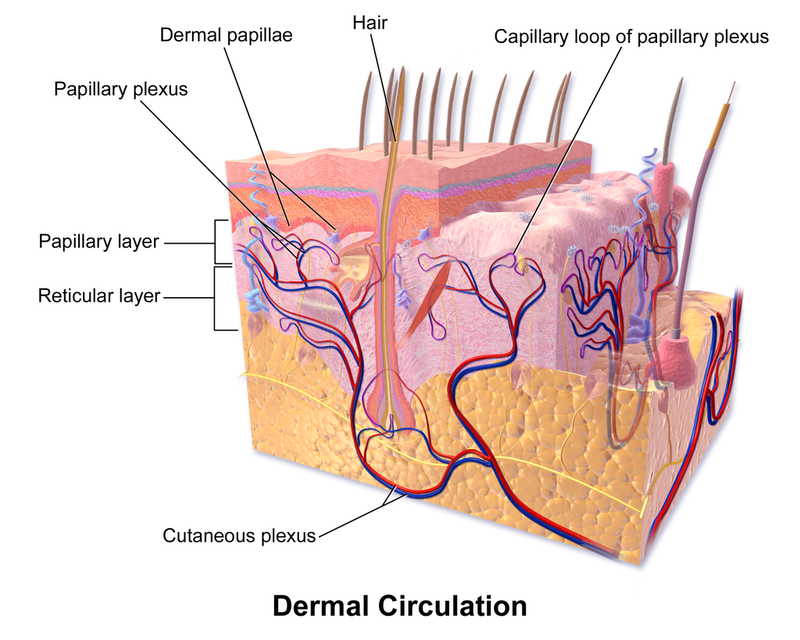
Cutaneous plexus
Extracellular matrix contains pockets of adipose cells
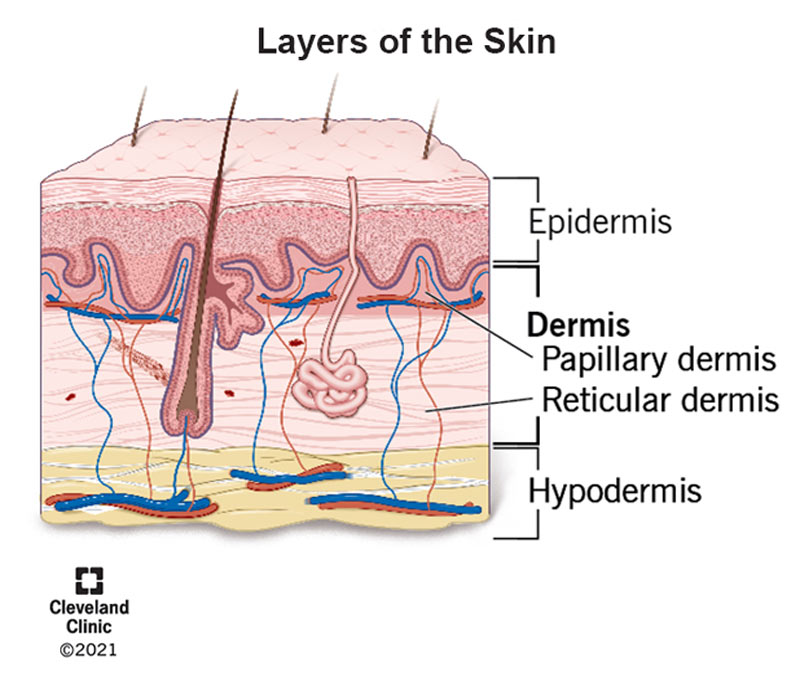
Cutaneous Plexus
Network of blood vessels between reticular layer and hypodermis
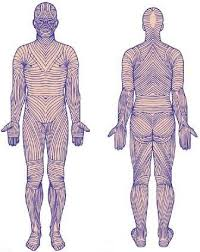
Cleavage (Tension) Lines
Collagen fibers in reticular layer running parallel to skin surface
Externally invisible
Indicate direction skin is most stretch resistant
Surgeons make incisions parallel so they heal more readily
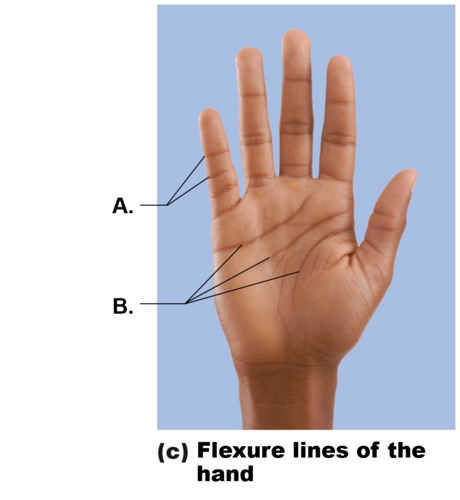
Flexure Lines
Dermal folds in reticular layer at or near joints
Dermis is secured to deeper structures
Skin’s inability to slide easily for joint movement causes creases
Striae
Extreme stretching of skin causing dermal tears leaves striae
Acute, short-term traumas can cause blisters
3 Pigments that Contribute to Skin Colour
Melanin
Carotene
Hemoglobin
Melanin
Pigment that contributes to skin colour
Made in skin by melanocytes
Melanosomes sent to keratinocytes to shield from UV
2 Types:
Pheomelanin: reddish-yellow
Eumelanin: brownish-black
Carotene
Pigment that contributes to skin colour
Yellow-orange pigment
Palms & soles
Accumulates in stratum corneum & hypodermis
Vitamin A
Hemoglobin
Pigment that contributes to skin colour
Pinkish hue of fair skin is due to lower levels of melanin
More O² attached to hemoglobin, the redder the skin appears
9 Functions of Skin
Chemical Barrier
Physical Barrier
Biological Barrier
Protection
Body Temperature Regulation
Cutaneous Sensations
Metabolic Functions
Blood Resevoir
Excretion of Wastes
Functions of the Skin: Chemical Barrier
Secretes chemicals
Sweat: antimicrobial proteins
Sebum & defensins: kill bacteria
Acid mantle: low pH of skin slows bacterial multiplication
Melanin
Functions of the Skin: Physical Barrier
Flat, dead, keratinized cells of stratum corneum surrounded by glycolipids, block most water & water soluble substances
Some chemicals have limited penetration of skin
Lipid soluble
Plant oleoresins
Organic solvents
Salts of heavy metals
Drugs
Drug agents
Functions of the Skin: Biological Barrier
Epidermis contains phagocytic cells
Engulf cells & activate immune system
Dermis contain macrophages
Activate immune system
DNA can absorb UV converting it to heat
Functions of the Skin: Temperature Regulation
Sweat glands produce ~ 500ml/day of insensible perspiration
In body temp rises, dilation of dermal vessels increase sweat gland activity to produce 12L of noticeable perspiration
In cold, they constrict
Functions of the Skin: Cutaneous Sensations
Cutaneous sensory receptors are part of the nervous system
Exteroceptors respond to stimuli outside the body
Free nerve endings sense painful stimuli
Functions of the Skin: Metabolic Functions
Synthesize vitamin D
Chemicals can disarm some carcinogens
Keratinocytes can activate some hormones
Collagenase aids natural turnover of collagen to prevent wrinkles
Functions of the Skin: Blood Reservoir & Excretion
Skin can cold up to ~5% of blood volume
Skin vessels can shunt blood to other organs
Can secrete limited amounts of nitrogenous wastes
Ammonia, urea, uric acids
Sweating causes salt & water loss
4 Accessory Structures
Hair
Nails
Sudoriferous Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Hair
Hairs(pili): flexible strands of dead, keratinized cells
Produced by hair follicles
Functions:
Prevent heat loss from scalp
Protects from sun
Senses light touch with root plexus
Anatomy
Shaft: extends above scalp
Root: area within scalp
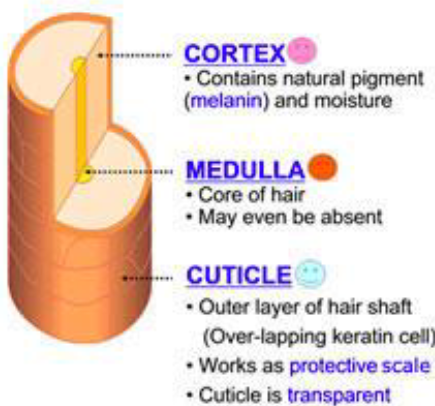
Structure of Hair
Medulla: central core of large cells
Cortex: several layers of flattened cells surrounding medulla
Cuticle: outer layer consisting of overlapping layers of single cells
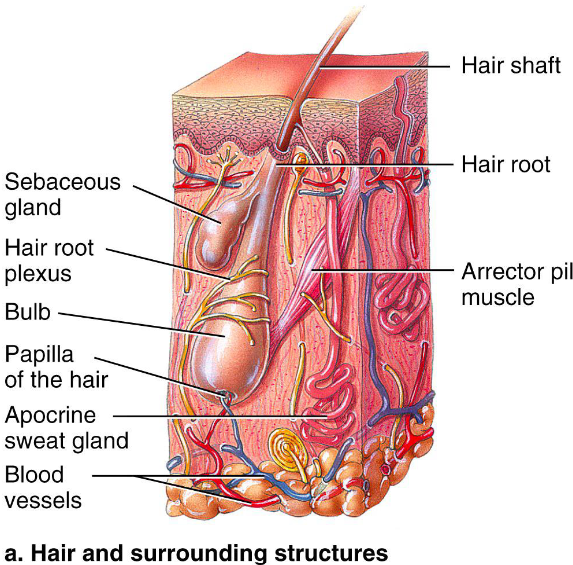
Structure of Hair Follicle
Hair bulb: expanded area at deep end of follicle
Follicle Receptor: sensory nerve endings that wrap around bulb
Hair Matrix: actively dividing area of bulb
Arrector Pili: small smooth muscle band attached
Hair papilla: dermal tissue containing knot of capillaries that supplies nutrient to grow hair
Hair Pigment
Made by melanocytes in follicles
Combinations of different melanins create colours
Black/brown = eumelanin
Red = pheomelanin
Blonde = a mix of low concentrations of eumelanin
and/or pheomelaninGray/white = melanin production decreases and air bubbles replace melanin in shaft
Types & Growth of Hair
Types of hair:
Lanugo Hair: downy fetal hair
Vellus Hair: fine body hair
Terminal Hair: coarse long hair
Follicles cycle between active & regressive phases
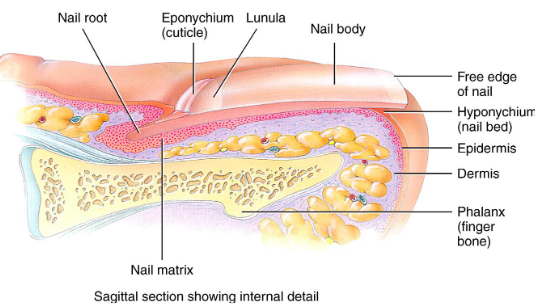
Nails
Scale-like modifications for epidermis that contain hard keratin
Protective cover for distal, dorsal surface of fingers/toes
Consists of:
free edge
nail plate: epidermis
root
nail folds
Eponychium
Hypochondrium
Nail Matrix: thickened portion of bed responsible for nail growth
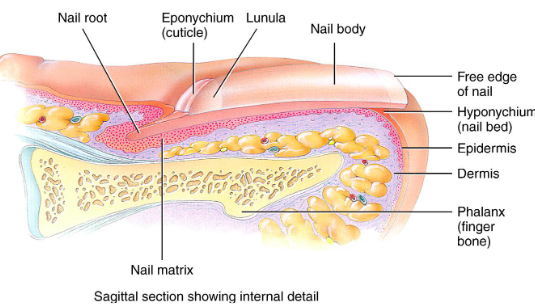
Eponychium
Nail fold that projects onto surface of nail body
Also called cuticle
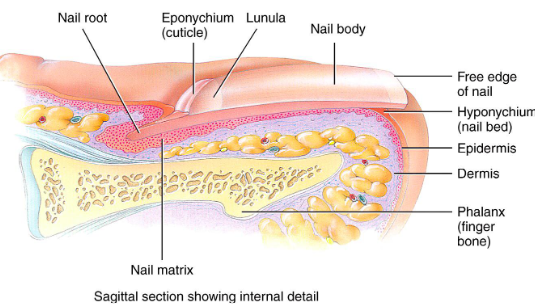
Hyponychium
Area under free edge of nail plate that accumulates dirt
Sweat Glands
Sudoriferous glands
All skin except nipples, external genitalia
3 million/person
2 types:
Eccrine
Apocrine
Contain myoepithelial cells
Contract upon nervous system stimulation to force sweat into ducts
Eccrine (Merocrine) Sweat Glands
Most numerous
Palms, soles, forehead
Thermoregulation
Secretes sweat
Apocrine Glands
Axillary & anogenital areas
Secrete viscous milky sweat that contains fatty substances and proteins
Larger than eccrine glands
Function at puberty
Modified apocrine glands:
Ceruminous glands: lining of ear canal, earwax
Mammary glands
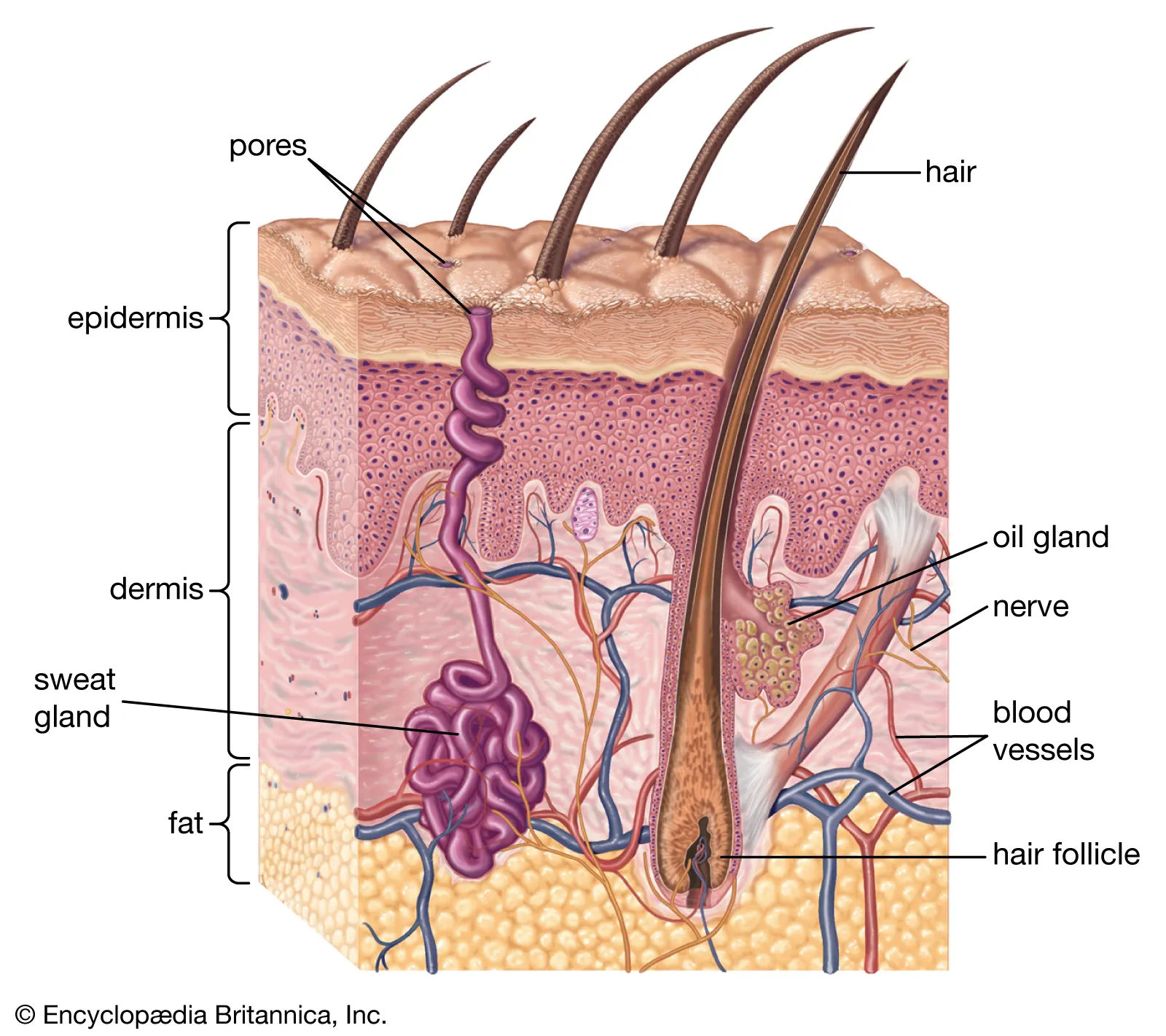
Sebaceous Glands
Secrete sebum
oily holocrine solution
bactericidal
Widely distributed except for palms, soles
Most develop from hair follicles/secrete into follicles
Inactive till puberty