Organic Chemistry 2 ACS Final
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
How can an aldehyde be protected?
Using a diol and H+
What does permanganate do? (KMnO4, NaOH)
Oxidizes aldehydes and primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
How can an acetal (being used as a protecting group) be hydrolyzed back to it's original form?
H2O and H+ and heat
At what frequency is an OH or NH bond in IR spec?
3400
At what frequency is a CH (sp3) bond in IR spec?
3000-2850
At what frequency is a CH (sp2) bond in IR spec?
3100-3000
At what frequency is a CH (sp) bond in IR spec?
3300
At what frequency is a C-C triple bond or C-N triple bond in IR spec?
2100
At what frequency is C=O bond in IR spec?
1700
At what frequency is a C=C bond or aromatic C-C bond in IR spec?
1600
At what frequency is an aromatic C-C bond in IR spec?
1500
At what frequency is carboxylic acid in IR spec?
1720 + a strong and broad band at 2500-3300
At what frequency is an amide bond in IR spec?
two medium strength bands around 3400 + the carbonyl band below 1700
At what frequency is an sp3 C atom in a proton NMR spec?
1
At what frequency is a C atom attached to a pi system in a proton NMR?
2
At what frequency is a C atom attached to an O atom in a proton NMR?
3-4
At what frequency is an sp2 C atom in a proton NMR?
5-6
At what frequency is an aromatic C atom in a proton NMR?
7-8
At what frequency is an aldehyde C atom in a proton NMR?
10
At what frequency is a carboxylic O atom in a proton NMR?
11-12
At what ppm is an sp3 alkyl C atom in carbon NMR?
10-30
At what ppm is an sp3 C atom attached to O, N, or X in carbon NMR?
50-70
At what ppm is an sp C atom in carbon NMR?
75-90
At what ppm is an sp2 C atom in carbon NMR?
100-150
At what ppm is an ester, amide, or carboxyl C=O in a carbon NMR?
160-180
AT what ppm is an aldehyde or ketone C=O in a carbon NMR?
190-200
What are examples of oxidizing agents?
Chromium (VI) reagents like CrO3, K2Cr2O7, K2CrO4; and a manganese (VII) reagent (KMnO4).
Chromium reagents = acidic conditions
Manganese reagent = basic conditions
Which anhydrous chromium (VI) reagents can stop oxidation of primary alcohols at the aldehyde stage?
CrO3--2 pyridine (chromium trioxide-pyridine complex), PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate) and PDC (pyridinium dichromate)
In oxidative cleavage reactions, what reagents will cleave vicinal diols, alkenes, and methyl ketones?
Vicinal diols = HIO4 (periodic acid)
Alkenes = ozone
Methyl ketones = alkaline solutions of the halogens (haloform reaction)
In oxidative addition products of alkenes and alkynes, which reagents can be used?
Cold, alkaline permanganate, osmium tetroxide and proxy acids.
Chromic acid is an oxidizing reagent that
does not oxidize ketones; but it can oxidize C-C double bonds.
How are reductions of carbonyl compounds usually done?
complex metal hydrides
How are reductions of alkenes usually done?
Catalytic hydrogenation
How are reductions of alkynes usually done?
Catalytic hydrogenation or alkali metals in ammonia (dissolving metal reductions)
What can react with alcohols to produce a ketone?
PCC (converts primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones; doesn't affect C=C bonds.
What can react with secondary alcohols to give ketones?
KMnO4, NaOH. But it can also react with double bonds.
What are the two types of free-radical reactions?
substitution and addition.
How can the free-radical addition reaction of
1. HBr + alkene + peroxides
2. the polymerization of alkenes or dienes
be initiated?
heat, peroxides, or UV light
What is the trend in stability for organic radicals/carbocations?
allylic/benzylic > 3 alkyl > 2 alkyl > 1 alkyl > methyl > vinylic/aryl
*Allylic and benzylic radicals are especially easy to generate because of the stabilization caused by resonance.
* when formed in a ring, the C+ will form preferentially to the C that can be stabilized by resonance.
What conditions will usually indicate a radical reaction?
AIBN (a radical initiator), peroxides, UV light, or high temps (300-500 C)
Groups that reduce electron density of a ring by resonance or induction will
cause the ring to be less reactive than benzene
Groups that increase the electron density of the ring by resonance or induction will
be more reactive than benzene
Electron-donating groups cause the electron density to increase at the
ortho (next to) and para (opposite) positions. Causes electrophiles to prefer to attack at those positions
Electron withdrawing groups cause electron density to be reduced at the
ortho and para position more than at the meta position. Causes electrophiles to prefer to attack at the meta position.
What has the greatest influence on electron density of an aromatic ring?
Resonance
What increases electron density in an aromatic ring?
Groups that have an atom with non bonded electrons
What reduces electron density?
groups that have multiple bonds to an atom more electronegative than carbon
What are the two distinct pathways for nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
Addition-elimination and elimination-addition.
What is the addition-elimination mechanism?
1. aromatic ring accepts a pair of electrons from a nucleophile to make an anionic intermediate. Must have a strong EWG, like a nitro (NO2) group to stabilize the anion.
2. Elimination of a leaving group. H- is a very poor leaving group, so the nucleophile must add at the site of a good leaving group. Often it is a halogen.
What is the elimination-addition mechanism?
1. strong base initiates an elimination to make a very reactive benzene
2. rapidly undergoes nucleophilic addition
What is a nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
a good leaving group, at least one electron withdrawing groups that are oath or para to the leaving group. More EWG's = greater reactivity toward nucleophiles. Not as common as addition-elimination because three things are required (strong nucleophile, good leaving group, and one ore more oath hydrogen atoms).
What is an important difference between the two nucleophilic substitution mechanisms?
The site of attachment of the nucleophile.
Addition-elimination = nucleophile attaches to the site of the leaving group
Elimination-addition = nucleophile attaches either at site of leaving group or site of oath hydrogen atom.
In tautomerization, the beta-dicarbonyl compound may favor
the enol tautomer instead of the keto form
What are the hot spots for reactivity in aldehydes and ketones?
1. The carbonyl carbon atom, which is subject to addition reactions by nucleophiles
2. The alpha-carbon atom can be deprotonated, converting it into a nucleophile
A hydrogen atom on an sp3 carbon atom that is alpha to a carbonyl group is
30 orders of magnitude more acidic than normal, due to resonance.
What effect do strong bases have on alkoxide ions?
Quantitatively convert simple carbonyl compounds tiny their enolates.
What are examples of strong bases?
LDA, NaH
What can happen to an alpha carbon atom?
It can be halogenated or alkylated.
What is the aldol reaction?
The nucleophilic alpha-carbon atom of one aldehyde can attack the carbonyl carbon atom of another aldehyde molecule in a dimerization reaction.
*Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones (steric and electronic)
What is the Claisen condensation?
The alcohol portion of an ester can be displaced in a nucleophilic substitution reaction by the alpha-carbon atom.
How can the product of a reaction with aldehydes, ketones, esters, nitriles, nitralkanes, and beta-dicarbonyl be predicted?
1. Write the formula for the anion of the component with the most acidic alpha-hydrogen atom.
2. Write the formula for the product that would form following attack on the carbonyl group of the other component (either addition or substitution)
In what conditions can enols act as nucleophiles?
With very reactive electrophiles like halogens or protonated carbonyl groups.
What is formed when nucleophiles bond with carbonyl carbon atoms?
a tetrahedral intermediate due to the sp3 hybridized carbon atom.
What is nucleophilic acyl substitution?
A nucleophile attacks at the carbonyl carbon, pushing the electron in the double bond onto the oxygen. The tetrahedral intermediate is typical of these reactions. When the lone pair on oxygen reforms the double bond, a leaving group leaves
*These are subject to acid catalysis.
**Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen atom increases the electrophilic character of the carbonyl carbon atom.
***Stereochemistry is retained.
****in basic conditions, a carboxylic acid is formed. The OH is immediately deprotonated.
Protonation of a poor leaving group
increases its tendency to dissociate
If the nucleophile is a weak base in nucleophilic addition,
the nucleophilic addition is reversible; the relative stabilities will be affected by the increased strain of the tetrahedral intermediate, compared to the prior sp2 structure.
What is the effect of electron-releasing groups attached to the carbonyl group?
a diminished positive charge on the carbon atom.
What is the effect of electron-withdrawing groups attached to a carbonyl group?
an intensified positive charge on the carbon atom.
In nucleophilic addition, if the nucleophile is a primary amine or a derivative of ammonia
the tetrahedral intermediate can lose water to form the C=N bond of an imine
In nucleophilic addition, if the nucleophile is a secondary amine
water can be lost from a C=C bond to form an examine.
By removing water in nucleophilic addition
the formation of acetals and imines can be favored. A reversal to the original reactant may be done in an aqueous acid solution
Aldehydes and ketones that are alpha,beta-unsaturated may go through
1,2-addition or 1,4-addition with nucleophiles.
*Kinetic product = 1,2-nucleophilic addition, forms faster, dominates if reaction stops before equilibrium is reached
*Thermodynamic product = 1,4-nucleophilic addition, forms slower, dominates if reaction continues to reach equilibrium
What conditions or reagents will typically give 1,2-addition?
Strongly basic nucleophiles like Grignard and organolithium and complex metal hydrides
What conditions or reagents will typically give 1,4-additions?
Weakly basic nucleophiles and organocuprates (R2CuLi)
What does NaBH4 do?
Reduces ketones and aldehydes to alcohols. Does not react with carboxylic acids, esters, or amides. But at room temperature it only reduces acyl chlorides to alcohols, due to the extreme electrophilicity.
What are some examples of concerted addition reactions?
Epoxidation, carbene additions, Diels-Alder reaction.
*Do not form intermediates
What 2 factors determine whether substitution or elimination will be the major product?
1. The substrate character (1, 2, 3). 1 = substitution and 3 = elimination. Sn2/E1 = faster on 1. Sn1/E1 = faster on 3
2. The type of base/nucleophile. Strong bases like alkoxides favor elimination of 2 or 3 substrates. Weak bases like alcohol and water favor substitution by Sn1/E1. Bulky bases = elimination, no matter the substrate.
What is the most common mechanistic step in organic chemistry?
Protonation
What makes the rate of substitution and elimination reactions increase?
A good leaving group. If a C+ is formed (Sn1/E1) its stability will affect rate (tertiary is better than primary)
What's a good polar protic solvent?
water, alcohol (Sn1/E1)
What's a good polar aprotic solvent?
DMSO, DMF (E2/Sn2)
How are isomers, constitutional isomers, stereoisomers, enantiomers, and diastereomers related?
Isomers, which are different compounds with the same molecular formula can be either
1. constitutional isomers (different connectivity) or
2. stereoisomers (same connectivity, different arrangement in space). Stereoisomers can be either
- enantiomers (nonsuperimposable mirror images) or
- diastereomers (stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other.
Optically active compounds are
single enantiomer mirror images.
What is the difference between conformations and configurations?
Conformations = different stereochemical representations of the same molecule
Configuration = different stereoisomers that interconvert by breaking and reforming bonds.
what are the two biggest factors influencing stability (and thus acidity and basicity)?
Resonance and induction (electronegativity)
What makes a good Lewis acid?
One that can accept a pair of electrons
What makes something aromatic?
Cyclic, planar, continuous pi system with 4n + 2 (where n is a whole number). These are very stable
When pyridine reacts with acid, it will attach
the most acidic portion. If all things are equal, the group attached to an alcohol will be deprotonated.
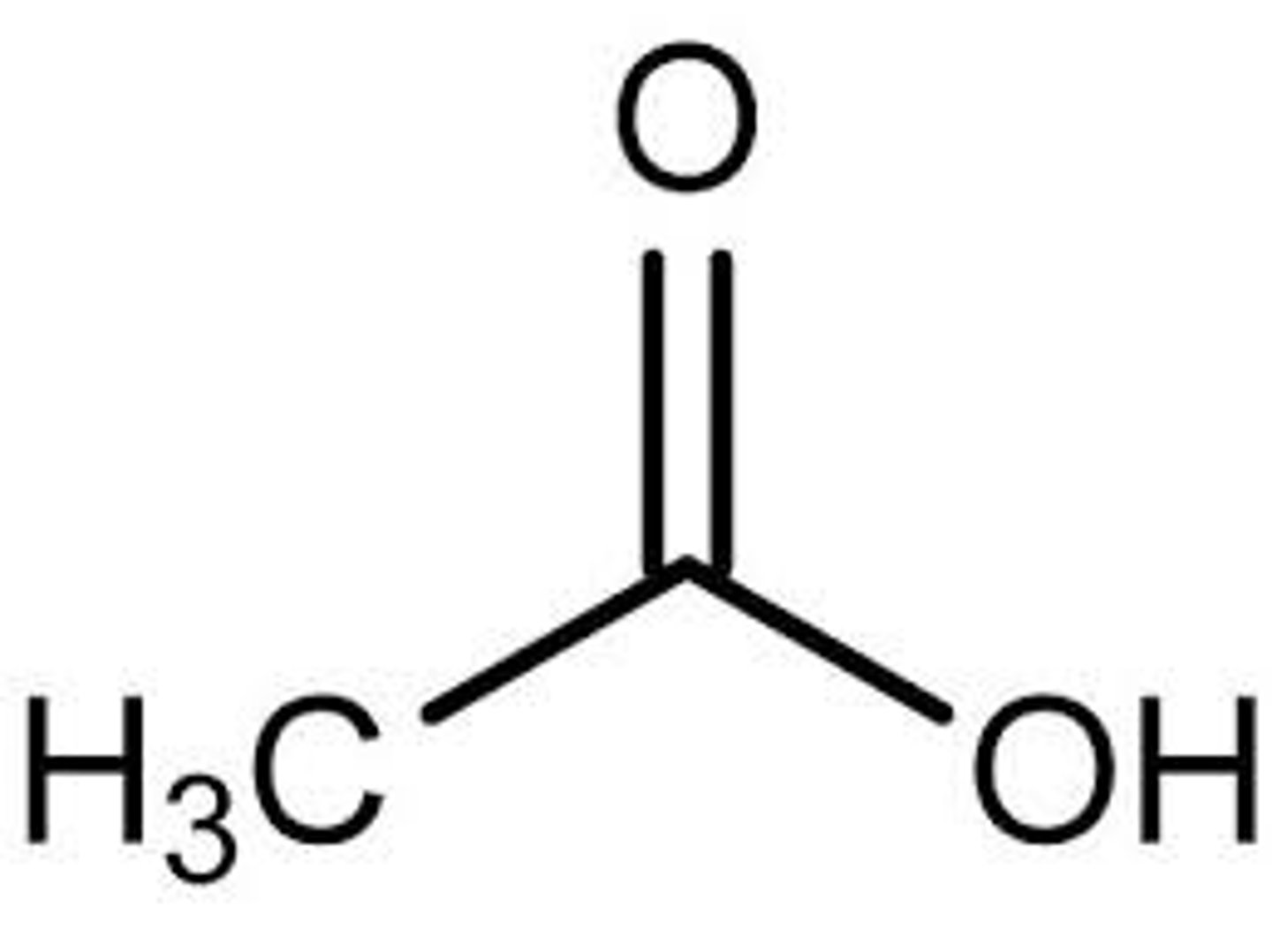
What does acetic acid look like?
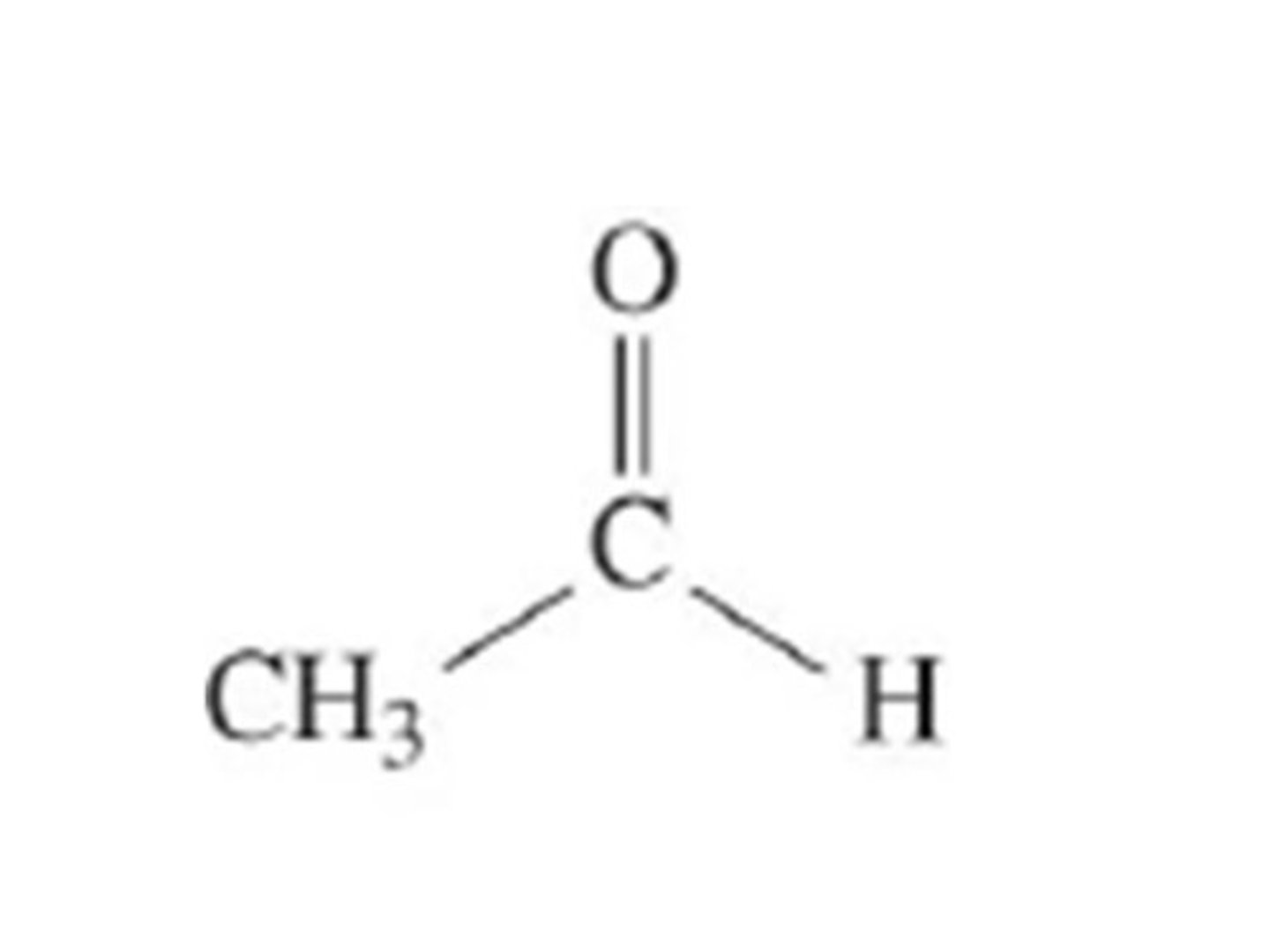
What does acetaldehyde look like?
What does LiAlH4 do?
IT is a strong reducing agent and will reduce an ester to two alcohols. In diethyl ether and followed by an acid workup, it will convert esters, carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides, aldehydes, and ketones into the corresponding alcohols. Similarly, it converts amide, nitro, nitrile, imine, oxime, and azide compounds into the amines
An intermediate in this reaction is an aldehyde intermediate.
What does KMnO4 do?
It is a strong oxidizing agent that converts alcohols or aldehydes into carboxylic acids.
What is an acyl?
An acid halide, anhydride, or ester
What is esterification?
a reaction of alcohol with an acid to produce an ester and water
What is saponification?
when fatty acids combine with an alkali solution made of bases and processed with water and heat
How does a Grignard reagent react with esters?
It reacts twice, first producing a ketone, then again (with another molecule of the reagent) to produce a tertiary alcohol.
What is the haloform reaction?
Converts methyl ketones (ketone with a methyl on the end) into carboxylic acids. Reagents = I2, Br2, or bleach (NaOCl), then a neutralizer.
FeBr3 + Br2 can react to create
Br+, a powerful electrophile. It can result in electrophilic substitution.
What is an activating group?
Any group that increases the electron density of the aromatic ring by resonance, making it more reactive.
What is a deactivating group?
Any group that decreases the electron density of the aromatic ring by resonance.