PSY 101 Test 3 Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:27 PM on 12/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Altered States of Consciousness
-A condition of awareness distinctly different in quality or pattern from waking consciousness.
--Distinct shifts happen in our perceptions, emotions, memories, time sense, thoughts, feelings of self-control, and suggestibility.
--Used for pleasure or escape from reality
--They can increase endorphin output.
--Better energy level, less physical discomfort
--Distinct shifts happen in our perceptions, emotions, memories, time sense, thoughts, feelings of self-control, and suggestibility.
--Used for pleasure or escape from reality
--They can increase endorphin output.
--Better energy level, less physical discomfort
2
New cards
Attributes of Altered States of Consciousness
-Since of time/space is lost when focusing on something
-Sense of psychological body/self is lost
-Mental chatter goes on constantly.
-Some activities where you step outside of time, you start processing things differently.
-Four common attributes:
--Time/space
--Physical body
--Psychological self
--Mental chatter
-Sense of psychological body/self is lost
-Mental chatter goes on constantly.
-Some activities where you step outside of time, you start processing things differently.
-Four common attributes:
--Time/space
--Physical body
--Psychological self
--Mental chatter
3
New cards
Are Altered States Universal?
Yes, they are a universal human characteristic.
4
New cards
Are all Altered States Created Equal?
No
5
New cards
Meditation
-Mental exercise used for producing relaxation or heightened awareness.
-Identified as an altered state of consciousness.
Seeks to stop the movement of the psyche.
-Focused, directed activity.
-In general, meditation heightens awareness and produces relaxation by interrupting the typical flow of thoughts, worries, and analysis. People who use meditation to reduce stress often report less daily physical tension and anxiety. Brain scans (such as PET and fMRI) reveal changes in brain activity during meditation, including the frontal lobes, suggesting that it may be a distinct state of consciousness.
-Alpha waves will be present.
-Identified as an altered state of consciousness.
Seeks to stop the movement of the psyche.
-Focused, directed activity.
-In general, meditation heightens awareness and produces relaxation by interrupting the typical flow of thoughts, worries, and analysis. People who use meditation to reduce stress often report less daily physical tension and anxiety. Brain scans (such as PET and fMRI) reveal changes in brain activity during meditation, including the frontal lobes, suggesting that it may be a distinct state of consciousness.
-Alpha waves will be present.
6
New cards
Mindfulness meditation
Mental exercise based on widening attention to become aware of everything experienced at any given moment.
7
New cards
Concentrative meditation
Mental exercise based on attending to a single object or thought.
8
New cards
Relaxation response
The pattern of internal bodily changes that occurs at times of relaxation.
9
New cards
Hypnosis
-An altered state of consciousness characterized by narrow detention and increased suggestibility.
--Seeks to stop the movement of the psyche.
Alpha and beta waves alternate (There is no specific identifiable brainwave.)
--Conscious psyche gets in the way of being convinced to do/stop doing something. Ex; Quitting smoking
---All techniques encourage a person to:
1. focus attention on what is being said,
2. relax and feel tired,
3. “let go” and accept suggestions easily, and
4. use a vivid imagination
--Seeks to stop the movement of the psyche.
Alpha and beta waves alternate (There is no specific identifiable brainwave.)
--Conscious psyche gets in the way of being convinced to do/stop doing something. Ex; Quitting smoking
---All techniques encourage a person to:
1. focus attention on what is being said,
2. relax and feel tired,
3. “let go” and accept suggestions easily, and
4. use a vivid imagination
10
New cards
Hidden observer
A detached part of the hypnotized person’s awareness that silently watches events.
11
New cards
Religion
All cultures and most religions recognize and accept some alterations of consciousness. However, the meaning given to these states varies greatly—from signs of “madness” and “possession” by spirits to life-enhancing breakthroughs. Thus, cultural conditioning greatly affects what altered states we recognize, seek, consider normal, and attain.
12
New cards
Brain waves
Recordings of changes in electrical activity in the brain.
13
New cards
Beta waves
Small, fast brain waves associated with being awake and alert.
14
New cards
Alpha waves
Large, slow brain waves associated with relaxation and falling asleep.
15
New cards
Delta waves
High amplitude neural oscillations with a frequency between 0.5 and 4 hertz. Like other brain waves, they can be recorded with electroencephalography and are usually associated with the deep stage 3 of NREM sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, and aid in characterizing the depth of sleep.
16
New cards
Sleep stages
-Stages 1 and 2 are light sleep stages. Stages 3 and 4 are deep sleep stages.
-The first two cycles last about 90 minutes.
-Quality of sleep is important.
-Staying on artificial substances for extended periods of time is detrimental.
-Proper sleep and going through the stages help replenish the brain.
-The first two cycles last about 90 minutes.
-Quality of sleep is important.
-Staying on artificial substances for extended periods of time is detrimental.
-Proper sleep and going through the stages help replenish the brain.
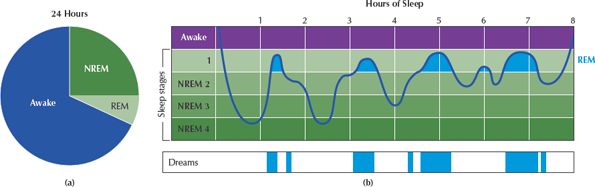
17
New cards
Sleep Stage 1
As you enter light sleep, your heart rate slows even more. Breathing becomes more irregular. The muscles of your body relax. This may trigger a reflex muscle twitch called a hypnic (HIP-nik: sleep) jerk. (This is quite normal, so have no fear about admitting to your friends that you fell asleep with a hypnic jerk.) In this stage, the EEG is made up mainly of small, irregular waves, with some alpha waves. Persons awakened at this time may or may not say that they were asleep.
18
New cards
Sleep Stage 2
As sleep deepens, body temperature drops further. Also, the EEG begins to include sleep spindles, which are short bursts of distinctive brain-wave activity generated by the thalamus. Sleep spindles may help prevent the sleeping brain from being aroused by external stimuli, thus marking the true boundary of sleep. Within a few minutes after spindles appear, most people will say they were asleep.
19
New cards
Sleep Stage 3
In this stage, very large and slow delta waves begin to appear. They signal a move to deeper slow-wave sleep and a further loss of consciousness.
20
New cards
Sleep Stage 4
Most people reach deep sleep (in this stage)—the deepest level of normal sleep—in about an hour. Brain waves from this stage are almost pure slow-wave delta, and the sleeper is in a state of oblivion. If a sleeper hears a loud noise during this stage, he or she will wake up in a state of confusion and may not remember the noise.
21
New cards
Electroencephalography
Device that records electrical activity in the brain.
22
New cards
REM (rapid eye movements)
-Swift eye movements during sleep.
-Rebounds more vigilantly than any of the other stages.
-Facilitates memory.
-Rebounds more vigilantly than any of the other stages.
-Facilitates memory.
23
New cards
REM Explanations
-Psychological - Psychoanalytic Explanation
-Biological/Physiological Explanation
-Biological/Physiological Explanation
24
New cards
Psychological - Psychoanalytic Explanation
Some feelings/emotions accumulate in us and are unexpressed. An outlet is needed for this, which will become a dream. This allows people to express fears/wishes/pleasures without any ramifications. Hidden messages in dreams are symbolic. This is necessary for all human’s psychological well-being. Dreams are deliberate, meaningful messages from our unconscious. This position is held by therapists.
25
New cards
Biological/Physiological Explanation
Based on brain functions. It is called the Activation-Synthesis. Random stimulation produces sleep stages/dreams. Dreams are usually meaningless.
26
New cards
REM sleep
-Stage of sleep marked by rapid eye movements, high-frequency brain waves, and dreaming.
-The brain is so active during REM sleep that it looks as if the person is awake.
-Because frontal areas of the cortex, which control higher mental abilities, are mostly shut down during REM sleep, the resulting dreams are more primitive and more bizarre than daytime thoughts.
-Newborns spend almost 50% of sleep in REM.
-REM-induced paralysis.
-Dreams/Nightmares happen in REM.
-Night terrors occur in stage 4.
-The brain is so active during REM sleep that it looks as if the person is awake.
-Because frontal areas of the cortex, which control higher mental abilities, are mostly shut down during REM sleep, the resulting dreams are more primitive and more bizarre than daytime thoughts.
-Newborns spend almost 50% of sleep in REM.
-REM-induced paralysis.
-Dreams/Nightmares happen in REM.
-Night terrors occur in stage 4.
27
New cards
Night Terror
-A state of panic during NREM sleep.
-A person suffers total panic and may hallucinate frightening dream images into the bedroom. An attack may last 15 or 20 minutes. When it is over, the person awakens drenched in sweat but only vaguely remembers the terror. Because sleep terrors occur during NREM sleep (when the body is not immobilized), victims may sit up, scream, get out of bed, or run around the room. Victims remember little afterward.
-Although sleep terrors are more common in childhood, they are not uncommon in adulthood.
-Extreme fear reactions.
-Age of onset generally appears between the ages of 2 and 4.
-The frequency of occurrence is variable.
-Not necessarily tied to any one disorder or trait.
-Sleeping in another place and being overtired are two leading causes.
-A person suffers total panic and may hallucinate frightening dream images into the bedroom. An attack may last 15 or 20 minutes. When it is over, the person awakens drenched in sweat but only vaguely remembers the terror. Because sleep terrors occur during NREM sleep (when the body is not immobilized), victims may sit up, scream, get out of bed, or run around the room. Victims remember little afterward.
-Although sleep terrors are more common in childhood, they are not uncommon in adulthood.
-Extreme fear reactions.
-Age of onset generally appears between the ages of 2 and 4.
-The frequency of occurrence is variable.
-Not necessarily tied to any one disorder or trait.
-Sleeping in another place and being overtired are two leading causes.
28
New cards
non-REM (NREM) sleep
-Non-rapid eye movement sleep characteristic of sleep stages 1, 2, 3, and 4.
-Slow-wave sleep early in the night brings overall brain activation levels back down, allowing a fresh approach to the next day.
-As slow-wave sleep reduces overall activation in the brain, less important experiences may fade away and be forgotten. If you wake up feeling clearer about what you studied the previous night, it might be because your brain doesn’t “sweat the small stuff!”
-Slow-wave sleep early in the night brings overall brain activation levels back down, allowing a fresh approach to the next day.
-As slow-wave sleep reduces overall activation in the brain, less important experiences may fade away and be forgotten. If you wake up feeling clearer about what you studied the previous night, it might be because your brain doesn’t “sweat the small stuff!”
29
New cards
Sleepwalking
-Occurs in deep sleep in stages 3 or 4.
-Age of onset generally appears between the ages of 2 and 4.
-Sleepwalkers are highly suggestible.
-Age of onset generally appears between the ages of 2 and 4.
-Sleepwalkers are highly suggestible.
30
New cards
REM Deprivation
People are awakened whenever they enter REM sleep, or, in comparison conditions, whenever they enter NREM sleep. Leads to REM rebounds.
31
New cards
REM Rebound
The occurrence of extra rapid eye movement sleep following REM sleep deprivation.
32
New cards
Sleep Deprivation Psychosis
When the absence of sleep causes a disconnection from reality that can present as hallucinations or delusional thinking—is a known effect of severe, prolonged sleep deprivation.
33
New cards
Memory
The value of more REM sleep, then, may be that it helps us sort and retain important memories, especially memories about strategies for solving problems. They can make a neurological footprint in the brain. Ideas can come from immersing yourself in dreams and understanding the problem/task at hand.
34
New cards
Lucid Dream
A type of dream in which the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming while dreaming. During a lucid dream, the dreamer may gain some amount of control over the dream characters, narrative, or environment; however, this is not actually necessary for a dream to be described as lucid. The frontal lobe is still active.
35
New cards
Environmental Stimuli
-Things that happen in the environment that elicit a response or reaction from a person.
--Things that happen in the environment can influence dreams.
--Things that happen in the environment can influence dreams.
36
New cards
Insomnia
-Difficulty in getting to sleep or staying asleep (such as frequent nighttime awakenings or waking too early).
-Most cases are psychological in nature.
-Most cases are psychological in nature.
37
New cards
Approaches for treating insomnia
1. Stimulus control
2. Sleep restriction
3. Paradoxical intention
4. Relaxation
5. Exercise
6. Food intake
7. Stimulant avoidance
2. Sleep restriction
3. Paradoxical intention
4. Relaxation
5. Exercise
6. Food intake
7. Stimulant avoidance
38
New cards
Stimulus control
Insisting on a regular schedule helps establish a firm body rhythm, greatly improving sleep. This is best achieved by exercising stimulus control, which refers to linking a response with specific stimuli. It is important to get up and go to sleep at the same time each day, including weekends. In addition, insomniacs should avoid doing anything but sleeping when they are in bed. They are not to study, eat, watch television, read, pay the bills, worry, or even think in bed. (Lovemaking is okay, however.) In this way, only sleeping and relaxation become associated with going to bed at specific times.
39
New cards
Sleep restriction
Even if an entire night’s sleep is missed, it is important not to sleep late in the morning, nap more than an hour, sleep during the evening, or go to bed early the following night. Instead, restricting sleep to normal bedtime hours avoids fragmentation sleep rhythms.
40
New cards
Paradoxical intention
Another helpful approach is to remove the pressures of trying to go to sleep. Instead, the goal becomes trying to keep the eyes open (in the dark) and stay awake as long as possible. This allows sleep to come unexpectedly and lowers performance anxiety.
41
New cards
Relaxation
Some insomniacs lower their arousal before sleep by using a physical or mental strategy for relaxing, such as progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, or blotting out worries with calming images. It also is helpful to schedule time in the early evening to write down worries or concerns and plan what to do about them the next day in order to set them aside before going to bed.
42
New cards
Exercise
Strenuous exercise during the day promotes sleep. However, exercise within three to six hours of sleep is helpful only if it is very light.
43
New cards
Food intake
What you eat can affect how easily you get to sleep. Eating starchy foods increases the amount of tryptophan (TRIP-tuh-fan: an amino acid) reaching the brain. More tryptophan, in turn, increases the amount of serotonin in the brain, which is associated with relaxation, a positive mood, and sleepiness. Thus, to promote sleep, try eating a starchy snack, such as bread, pasta, or dry cereal. If you really want to drop the bomb on insomnia, try eating a baked potato (which may be the world’s largest sleeping pill!).
44
New cards
Stimulant avoidance
Stimulants, such as coffee and cigarettes, should be avoided. It also is worth remembering that alcohol, although not a stimulant, impairs sleep quality.
45
New cards
Drug-dependency insomnia
Sleep loss caused by withdrawal from sleeping pills.
46
New cards
Narcolepsy
-Sudden, irresistible, daytime sleep attacks that may last anywhere from a few minutes to a half-hour. Victims may fall asleep while standing, talking, or even driving. Victims go into REM.
--Triggered by an intense emotional response.
--Triggered by an intense emotional response.
47
New cards
Stimulants
Used to ward off daytime sleep attacks.
48
New cards
Types of Stimulants
-Amphetamines
-Cocaine
-MDMA
-Caffeine
-Nicotine
-Cocaine
-MDMA
-Caffeine
-Nicotine
49
New cards
Amphetamines
Synthetic stimulants. Some common street names for them are speed, bennies, dexies, amp, and uppers. These drugs were once widely prescribed for weight loss or depression. Today, the main instrumental medical use of them is to treat childhood hyperactivity and overdoses of depressant drugs. Illicit use of them is widespread, however, including among people seeking to stay awake and by those who rationalize that such drugs can improve mental or physical performance.
50
New cards
Cocaine
Also known as coke, snow, blow, snuff, and flake is a powerful central nervous system stimulant extracted from the leaves of the coca plant. It produces feelings of alertness, euphoria, well-being, power, boundless energy, and pleasure.
51
New cards
MDMA
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine; also known as ecstasy or molly) also is chemically similar to amphetamine. While it is technically a stimulant, it is sometimes classified as a hallucinogen since it can produce hallucinations. It also produces a rush of energy, and users say it makes them feel closer to others and heightens sensory experiences.
52
New cards
Caffeine
The most frequently used psychoactive drug in North America. (Goodnight, Seattle!) Many people have a hard time starting a day (or writing another paragraph) without a cup of coffee or tea because it suppresses drowsiness and increases alertness, especially when combined with sugar. Physically, it can cause sweating, talkativeness, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and hand tremors. It stimulates the brain by blocking chemicals that normally inhibit or slow nerve activity. Its effects become apparent with doses as small as 50 milligrams, the amount found in about one-half cup of brewed coffee.
53
New cards
Nicotine
A natural stimulant found mainly in tobacco, it is so toxic that it is sometimes used to kill insects! In large doses, it causes stomach pain, vomiting and diarrhea, cold sweats, dizziness, confusion, and muscle tremors. In very large doses, it may cause convulsions, respiratory failure, and death.
54
New cards
Depressants
While opioids, like heroin and morphine, may be more powerful, both as drugs of abuse and as painkillers, the most widely used depressants are alcohol, barbiturates, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), and benzodiazepine (ben-zoe-die-AZ-eh-peen) tranquilizers. Depressants are much alike in their effects. In fact, barbiturates and tranquilizers are sometimes referred to as “solid alcohol.”
55
New cards
Types of Depressants
-Opioids
-Barbiturates
-GHB
-Benzodiazepine tranquilizers
-Barbiturates
-GHB
-Benzodiazepine tranquilizers
56
New cards
Opioids
Raw opium, secreted by poppy seed pods, has been used for centuries to produce sleep and pain relief (Dikotter, Laamann, & Xun, 2008). For this reason, opium and the family of chemically related drugs, such as heroin (big H, dope, horse), morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and fentanyl, are now referred to as these.
57
New cards
Barbiturates
Sedative drugs that depress brain activity.
58
New cards
GHB
Also known as goop, scoop, max, and Georgia Home Boy is a central nervous system depressant that relaxes and sedates the body. Users describe its effects as similar to those of alcohol. Mild intoxication tends to produce euphoria, a desire to socialize, and a mild loss of inhibition. Its intoxicating effects typically last a few hours, depending on the dosage.
59
New cards
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers
Drugs that lower anxiety and reduce tension. Even at normal dosages, these drugs can cause drowsiness, shakiness, and confusion.
60
New cards
Stress
-An obstacle that’s going to force us to change the course of action. --You have to adjust or adapt.
-The more control of the situation you have, stress levels go down.
-Pressure or demand placed on an organism to adjust or adapt.
-Regardless of whether it is triggered by a pleasant or an unpleasant event, appraisals of threat generate a stress reaction that begins with the same autonomic nervous system (ANS) arousal that occurs during emotion.
-The more control of the situation you have, stress levels go down.
-Pressure or demand placed on an organism to adjust or adapt.
-Regardless of whether it is triggered by a pleasant or an unpleasant event, appraisals of threat generate a stress reaction that begins with the same autonomic nervous system (ANS) arousal that occurs during emotion.
61
New cards
Stressor
Specific condition or event that challenges or threatens a person.
62
New cards
Social Readjustment Ratings Scale (SRRS)
A scale that rates the impact of various life events on the likelihood of illness.
63
New cards
Life Change Units (LCUs)
Numerical values assigned to each life event that express their impact on stress.
64
New cards
0–150 LCUs
No significant problems
65
New cards
150–199 LCUs
Mild life crisis (33 percent chance of illness)
66
New cards
200–299 LCUs
Moderate life crisis (50 percent chance of illness)
67
New cards
300 or more LCUs
Major life crisis (80 percent chance of illness)
68
New cards
Life Events/Illness Risk
-You have a higher chance of illness or accident when your LCU total exceeds 300 points. Other stressful events—such as entering college, changing majors, or experiencing a breakup in a steady relationship—can affect the health of college students more specifically.
-Major life changes—both good and bad (and ugly)—can increase susceptibility to illness. These changes in our surroundings or routines require us to be on guard and ready to react. Over long periods, this can be quite stressful.
-Major life changes—both good and bad (and ugly)—can increase susceptibility to illness. These changes in our surroundings or routines require us to be on guard and ready to react. Over long periods, this can be quite stressful.
69
New cards
Psychosomatic
Mind-induced physical illness.
70
New cards
Psych
Mind
71
New cards
Soma
Body
72
New cards
Psychosomatic Disorders
Illnesses in which psychological factors contribute to bodily damage or to damaging changes in bodily functioning.
73
New cards
Type A
Type A people are hard driving, ambitious, highly competitive, achievement oriented, and striving. Type A people believe that with enough effort they can overcome any obstacle, and they push themselves accordingly. Perhaps the most telltale signs of a Type A personality are time urgency and chronic anger or hostility. Type As hurry from one activity to another, racing the clock in self-imposed urgency. As they do, they feel a constant sense of frustration and anger. In an eight-year follow-up, these researchers found that the rate of heart disease among Type As was more than twice that found among Type Bs.
-Cardiac personality
-Ambitious/industrious/driven
-Friedman and Rosenbaum
-Competitive
-Impatient/intolerant
-Aggressive
-Achievement
-Like to win
-Egocentric
-Anger
-Hostile
-Cardiac personality
-Ambitious/industrious/driven
-Friedman and Rosenbaum
-Competitive
-Impatient/intolerant
-Aggressive
-Achievement
-Like to win
-Egocentric
-Anger
-Hostile
74
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
Three-stage model of stress response, consisting of alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
75
New cards
Hans Selye
Observed, “To be totally without stress is to be dead.” That’s because stress is the pressure or demand placed on an organism to adjust or adapt. Unpleasant events such as work pressures, marital problems, or financial woes are naturally stressful. But so are travel, sports, a new job, rock climbing, dating, and other positive activities. Even if you aren’t a thrill seeker, a healthy lifestyle may include a fair amount of eustress (good stress). Activities that provoke “good stress” are usually challenging, rewarding, and energizing. He came up with the general adaptation syndrome (GAS).
76
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) Stages
1. Alarm Reaction
2. Stage of Resistance
3. Stage of Exhaustion
2. Stage of Resistance
3. Stage of Exhaustion
77
New cards
Alarm Reaction
The first stage of the general adaptation syndrome, during which body resources are mobilized to cope with a stressor.
78
New cards
Stage of Resistance
-The second stage of the general adaptation syndrome, during which the body's adjustments to stress stabilize, but at a high physical cost.
--The first stage of psychosomatic illness
--The first stage of psychosomatic illness
79
New cards
Stage of Exhaustion
The third stage of the general adaptation syndrome, at which time the body’s resources are exhausted and serious health consequences occur.
80
New cards
Some of the typical signs or symptoms of impending exhaustion include the following:
-Emotional signs
-Behavioral signs
-Physical signs
-Behavioral signs
-Physical signs
81
New cards
Emotional signs
Anxiety, apathy, irritability, mental fatigue; excessive worry about illness
82
New cards
Behavioral signs
Avoidance of responsibilities and relationships, extreme or self-destructive behavior, self-neglect, poor judgment
83
New cards
Physical signs
Frequent illness, exhaustion, overuse of medicines, physical ailments and complaints
84
New cards
Hardy Personality
-A personality style associated with superior stress resistance.
-Salvatore Maddi came up with this.
-Salvatore Maddi came up with this.
85
New cards
Hardy Personality Criteria
1. They had a sense of personal commitment to self, work, family, and other stabilizing values.
2. They felt that they had control over their lives and their work.
3. They had a tendency to see life as a series of challenges rather than as a series of threats or problems.
2. They felt that they had control over their lives and their work.
3. They had a tendency to see life as a series of challenges rather than as a series of threats or problems.
86
New cards
Positive Psychology
The study of human strengths, virtues, and effective functioning. Optimism and positive emotions are both closely connected to feelings of subjective well-being, which occur when people are generally satisfied with their lives, have frequent positive emotions, and relatively few negative emotions.
87
New cards
Social Support
Close, positive relationships with other people. Facilitates good health and morale. People with close, supportive relationships have better immune responses and better health. Apparently, support from family, friends, and even pets serve as a buffer to cushion the impact of stressful events.
88
New cards
Learned Helplessness
-Belief that one cannot control the outcome of events.
-Showing resignation in the face of a situation over which you believe (based on past experience) you have no control. This can all lead to depression.
--Inescapable punishment
--Repeated failure
--Inability to overcome obstacles
-Studied by Martin Seligman
-Showing resignation in the face of a situation over which you believe (based on past experience) you have no control. This can all lead to depression.
--Inescapable punishment
--Repeated failure
--Inability to overcome obstacles
-Studied by Martin Seligman
89
New cards
Learned Helplessness Experiment
-What would happen if a person appraised a threatening situation as hopeless? Some of the first clues to answering this question came from studies carried out with dogs that were tested in a shuttle box. The dog was first placed in a harness (from which it could not escape) and then given several painful shocks that it was helpless to prevent. After having this experience, dogs that were placed in the shuttle box again reacted to the first shock by crouching, howling, and whining. None of them tried to escape. Instead, they seemed helplessly resigned to their fate because they had learned that there was nothing they could do about getting shocked.
--In the normal course of escape and avoidance learning, a light dims shortly before the floor is electrified
---(a). Because the light does not yet have meaning for the dog, the dog receives a shock (noninjurious, by the way) and leaps the barrier
---(b). Dogs soon learn to watch for the dimming of the light
---(c) and to jump before receiving a shock
---(d). Dogs made to feel “helpless” rarely even learn to escape shock, much less to avoid it.
--In the normal course of escape and avoidance learning, a light dims shortly before the floor is electrified
---(a). Because the light does not yet have meaning for the dog, the dog receives a shock (noninjurious, by the way) and leaps the barrier
---(b). Dogs soon learn to watch for the dimming of the light
---(c) and to jump before receiving a shock
---(d). Dogs made to feel “helpless” rarely even learn to escape shock, much less to avoid it.
90
New cards
Biofeedback
A process whereby electronic monitoring of a normally automatic bodily function is used to train someone to acquire voluntary control of that function.
91
New cards
Stress Management
The application of cognitive and behavioral strategies to reduce stress and improve coping skills.
92
New cards
NREM
Sleepwalking and night terrors occur during _____.
93
New cards
Sleep deprivation, REM deprivation, and prescription sedatives.
REM Rebound results from
94
New cards
False
True or false: Someone with a hardy personality has good communication skills.
95
New cards
Throughout life, in all cultures, and in some religious traditions.
Altered states of consciousness can be observed
96
New cards
Sedation of sub-cortical brain areas
Alcoholic/drug deaths are caused by
97
New cards
the first part of sleep.
The deepest stages of sleep occur in
98
New cards
Microsleep
The intrusion of sleep into consciousness is known as
99
New cards
NREM
Sleep sex and sleep talking occur during
100
New cards
narcolepsy/REM
A sudden, irresistible sleep attack is _____, characterized by _______.