Global systems Sections 1.1 and 2.2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Climate
the average weather conditions in a region measured over a period of several years
Weather
refers to specific atmospheric conditions at a particular location at a specific instant of time
What is climate determined by
Temperature and precipitation
The biosphere contains …
Atmosphere (air)
Hydrosphere(water)
Lithosphere(earth)
What is the source of all energy on earth
Sun
Insolation - Climate term
The amount of the sun’s energy that is actually received on the the Earth’s surface.
The higher latitudes receive slanting rays and more
at lower latitudes the sun rays are
the suns rays arrive
diffuse energy
more concentrated
parallel to the earth
Angle of incidence- Climate terms
The angle between the ray and a line that is drawn perpendicular to the Earth’s surface
How does insolation at the equator compare to the poles?
More insolation at the equator due to direct sunlight and less atmospheric filtering.
Less insolation at the poles due to low-angle sunlight and more atmosphere to pass through.
How would this impact climate and weather in those areas?
Equator: Hot, wet, stormy → tropical climates and frequent rain.
Poles: Cold, dry, calm → icy deserts with little precipitation.
These differences drive global climate zones, wind patterns, and weather systems that affect the entire planet.
what impacts the angle of incidence and insolation
Earth
Angle of inclination-Climate terms
The earth’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 from a line drawn perpendicular from its orbital plane.
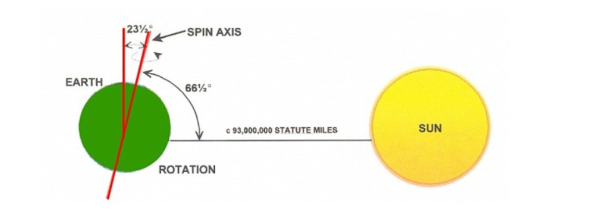
The only reason why we have seasons is because of this
angle of inclination. The earths tilt changes the insolation at different prats of the earth at different times of the year
Solstice-climate term
one of two points in earths orbit when the poles are most tiltes towards or away from the sun
June 22 summer solstice and winter solstice december 22
Equinox - climate term
When the number of daylight hours is exactly equal to the number of hours of might
Autumnal equinox september 23, vernal equinox is march 21
Absorption and reflection of solar radiation
When solar radiation (sunlight) reaches Earth, it is either absorbed or reflected by the atmosphere, clouds, and Earth's surface. Here's a breakdown:
In the lithmosphere and hydrosphere
The albedo of a surface is the percent of solar radiation that it relfects. THe average albedo of the Earth’s surface is about 30%
Are there ways we as humans could increase albedo?
Decrease albedo?
Can you think of an issue with decreasing albedo in terms of climate change?
Increase: painting roofs with with or reflective colors, creating reflective surfaces
Decreasing: Deforestation, urbanization, melting ice due to global warming, and agriculture changes
In terms of climate change: ice and snow are melting due to global warming
The types and amounts of radiation absorbed or reflects is affected by
The gases in the atmosphere: different layers contain different types and amounts of gases
Cloud cover and atmospheric dust
The natural greenhouse effect
When solar energy is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, some of it is re-emitted into the atmosphere in the form of radiation
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide,
Methane and water vapour prevent some of this longwave
radiation from leaving the atmosphere.
Without this natural greenhouse effect, our average atmospheric temperature would be below 0ºC.
Enhanced greenhouse effect
Human activities led to the build-up of extra greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, As a result, average surface temperatures are rising. Some of these examples are burning fossile fuels, deforestation, and landfills
Earths net radiation buget
Earth stays at a stable temperature (about 15°C) when the energy it receives from the Sun is equal to the energy it radiates back into space.
This balance is called radiative equilibrium.
The equation for Earth’s net radiation budget is:
Incoming Radiation – Outgoing Radiation = 0
As long as greenhouse gas levels stay constant and the Sun’s energy stays steady, this balance is maintained.
Affected by the enhanced greenhouse
Thermal energy
According to the second law of thermodynamics, thermal energy always moves from an area of high temperature to an area of low temperature
Radiation
is the emission of energy as particles or waves.
This energy, when absorbed by an object, will increase the kinetic energy and
Therefore, the temperature of the particles that make up the object
example earth taking in energy from the sun
Conduction
Heat moves from one particle to another within a solid. This happens when fast moving particles(hot particles) bump into slower (coolr) particles transferring energy
Convection
Heat travels through the movement of fluids such as liquids or gases. War fluids rise because its less dense and cooler fluids sink, creating a circular flow known as the CONVECTION CURRENT
wind
movement of air from areas of high pressure to low
pressure
Coriolis Effect-
bending of moving currents in response to
Earth’s rotation. The Coriolis effect causes winds in the two
hemispheres to move in opposite directions.
Jet streams
a narrow fast flowing "river" of air in the stratosphere. Changes
in Jet streams are important in predicting severe weather.