Unit 2: Population and Migration Patterns and Processes (copy)
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Demographic equation
A formula that uses birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration statistics to show population growth.
Crude birth rate (CBR)
The annual number of live births per 1,000 people in a population.
Crude death rate (CDR)
The annual number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population.
Green Revolution
Increased food and nutrition, access to sanitation, education, and healthcare.
Rate of natural increase (RNI) formula
Birth Rate - Death Rate / 10%.
Net Migration Rate (NMR)
The number of immigrants minus the number of emigrants for every thousand members of the population.
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The estimated average number of children born to each female of birthing age.
Dependency ratio
The number of people too young or too old to work compared to the number of people in the workforce.
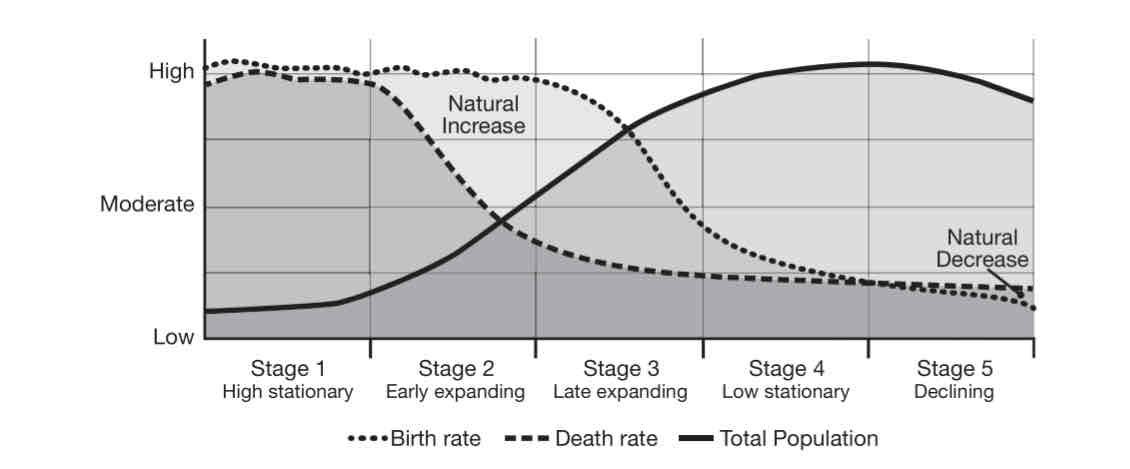
Demographic transition model (DTM)
A theory of how population changes over time, providing insights into migration, fertility, economic development, industrialization, urbanization, labor, politics, and the role of women.
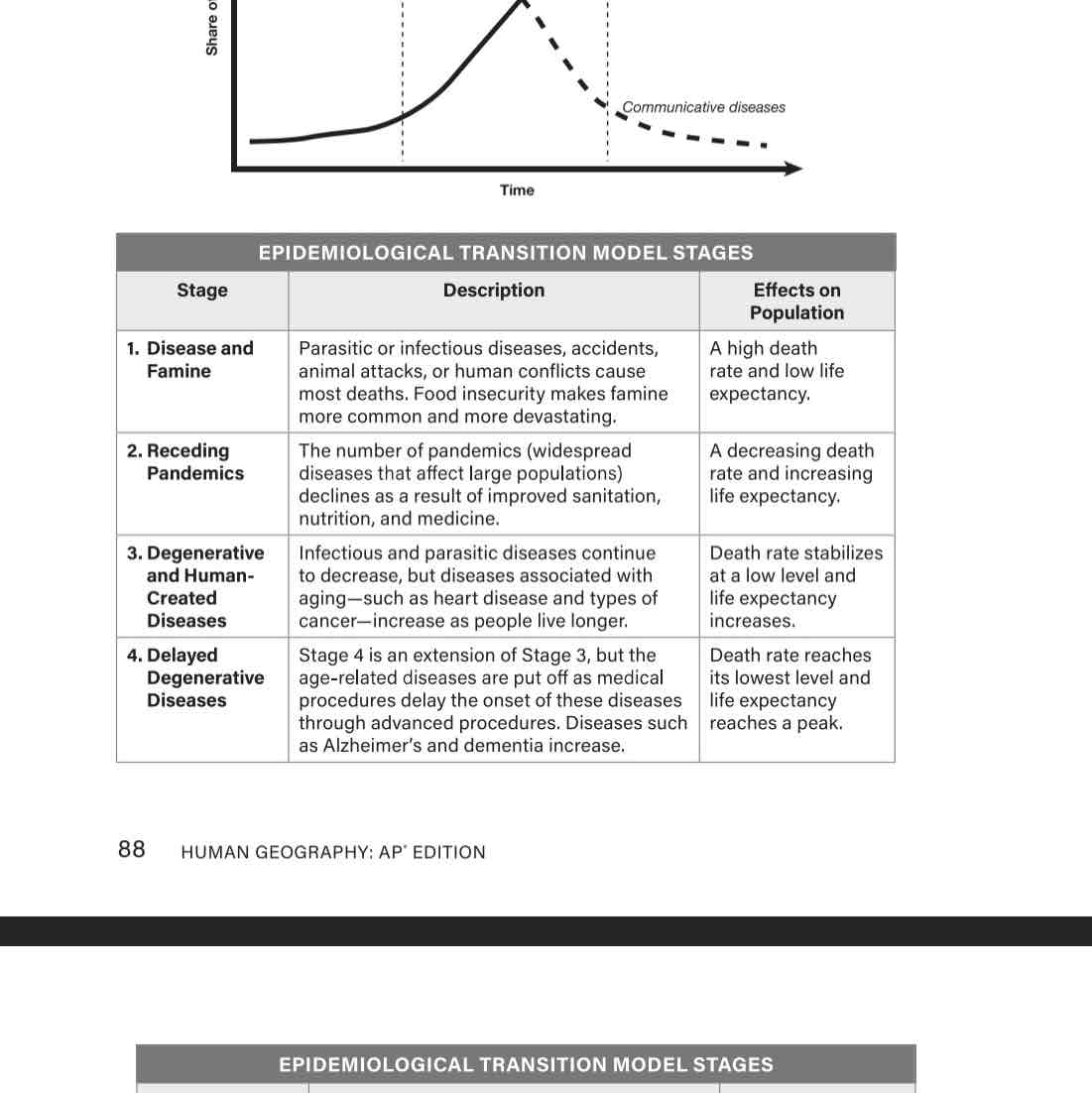
Epidemiological transition model (ETM)
A model that accounts for development due to increasing population growth rates caused by medical advances.
Stage One - DTM
Historically characterized by pre-agricultural societies engaged in subsistence farming and transhumance, with high birth and death rates.
Stage Two - DTM
Typically agriculturally based economies with high birth rates, declining death rates, and rapid population growth.
Stage Three - DTM
Historically where most "industrialized" or manufacturing-based countries were found, with declining birth and death rates due to urbanization and fertility control.
Stages Four and Five - DTM
Converging birth and death rates resulting in limited population growth or decline, with service industries driving the economy.
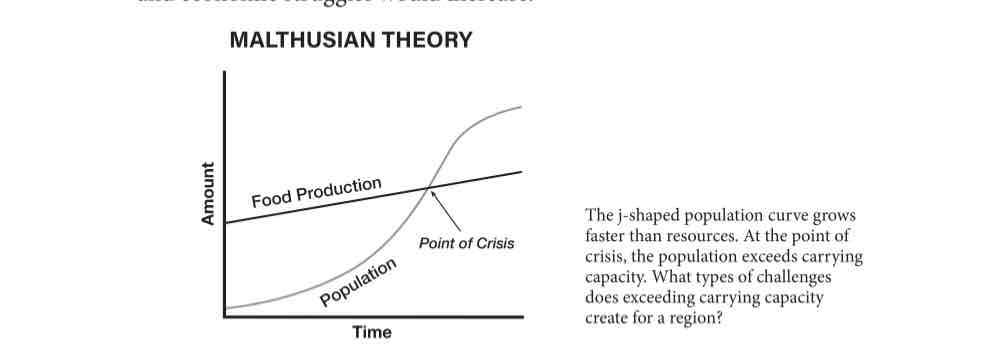
Malthusian Theory
The theory that global population would eventually outgrow the food supply, but food production has continued to stay ahead of population growth.
Sustainability
The ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Population Pyramids
Graphical representations of the population structure, gender, and age distribution of a country or place.
Arithmetic density
The number of people per square unit of land.
Physiologic density
The number of people per square unit of farmland.
Overpopulation
A major concern in resource-poor regions and globally. It leads to the depletion of nonrenewable energy sources and decreased personal space.
Migration
The movement of people from one location to another, usually voluntarily
Push factors
Specific factors commonly about the rural agricultural landscape and livelihood that force people to leave, such as armed conflict or environmental pollution.
Pull factors
Specific factors commonly about cities that attract people somewhere, such as job opportunities or access to healthcare.
Interregional Migrants
People who move from one region to another within a country.
Transnational Migration
Movement of people across national borders, involving the relocation and settlement in a different country.
Forced Migration
Movement of individuals or groups who are compelled to leave their homes or countries due to factors such as conflict, persecution, or environmental disasters.
Undocumented Immigrants
Individuals residing in a country without legal authorization by the government of that country. Commonly seeking refuge or employment.
Amnesty Program
Government programs that allow undocumented immigrants the opportunity to apply for official legal status.
Step Migration
The gradual movement of people from rural areas to urban areas in a series of small steps driven by economic opportunities and better living conditions.
Chain Migration
The process where immigrants move to a new country because of existing connections with family or friends who have already settled there.
Life-course changes
The various transitions and transformations that occur throughout an individual's life and can cause people to migrate.
Synonym for Birth Rate
Natality
Synonym for Death Rate
Mortality Rate
Rate of Natural Increase
Difference between the birth rate and the death rate in a population.
Reduced Fecundity
When the majority of women are heavily engaged in business, they are far less likely to have children.
Doubling Time
How long it would take for a country to double in size.
Replacement Rate
2.1 TFR
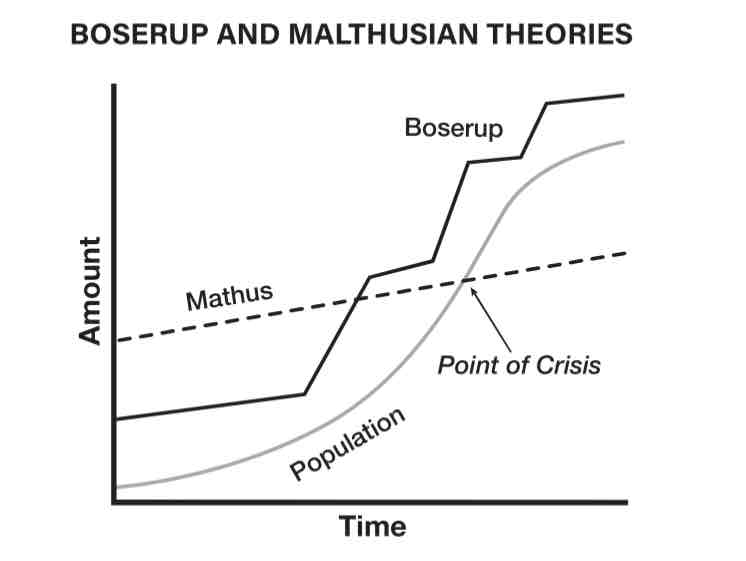
Boserup theory
the more people there are, the more people can work instead of more mouths to feed
as pop increases = more pressure on agriculture system = inspires invention = more food
antinatalist policies
policies that attempted to reduce the number of children born in a country
used by developing countries
China One Child Policy - 1979-2016
118 males:100 females
changes to 2 children in 2016
pronatalist policies
programs designed to increase fertility rates
paid time off, free childcare, government discounts
Denmark Singapore Italy Russia - promoted more children by national pride
What policies did Singapore have
both anti and pro
“Stop at Two” - 1966
“Have three or more if you can afford it “ - 1987
“Work Life Harmony” - 2000
paid leave, cash bonuses, tax rebates for working mothers
intervening obstacles
barriers that make migrants destination harder to reach
political - laws on immigration
environmental - deserts or oceans
walls and constructs
social - married to someone on route and settles in their community
economic - not enough money for destination
intervening opportunities
opportunities on route that disrupt their original migration plan
Ravensteins law of migration

Gravity model
as population of city increases = migration increases
distance to city grows = migration decreases
guest workers
transnational migrants who relocate to a new country to find labor that isn’t available locally
unskilled agricultural or manual labor
internally displaced person (IDP)
when migrants move to another part of the same country
refugee
people who migrate out of international borders
remittances
money sent from migrants to their families back in their home countries
brain drain
when migration out of a country is made of skilled people
ethnic enclaves
neighborhoods made of mostly the same ethnic group
little italy
chinatown
transhumance
process of herders moving with their animals to different pastures during different seasons
Italy, Greece, Turkey
Arithmetic population density
people divided by land
agricultural density
farmers divided/arable land
Physiological density
people/ arable land
Great Migration
large migration in the US that triggers after the end of world war I in 1917 where many in south cities migrated to the rest of the country