3rd Quarter Vocabulary - Earth Science - 8th Grade
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms

cleavage
The way some minerals break along smooth, flat surfaces.
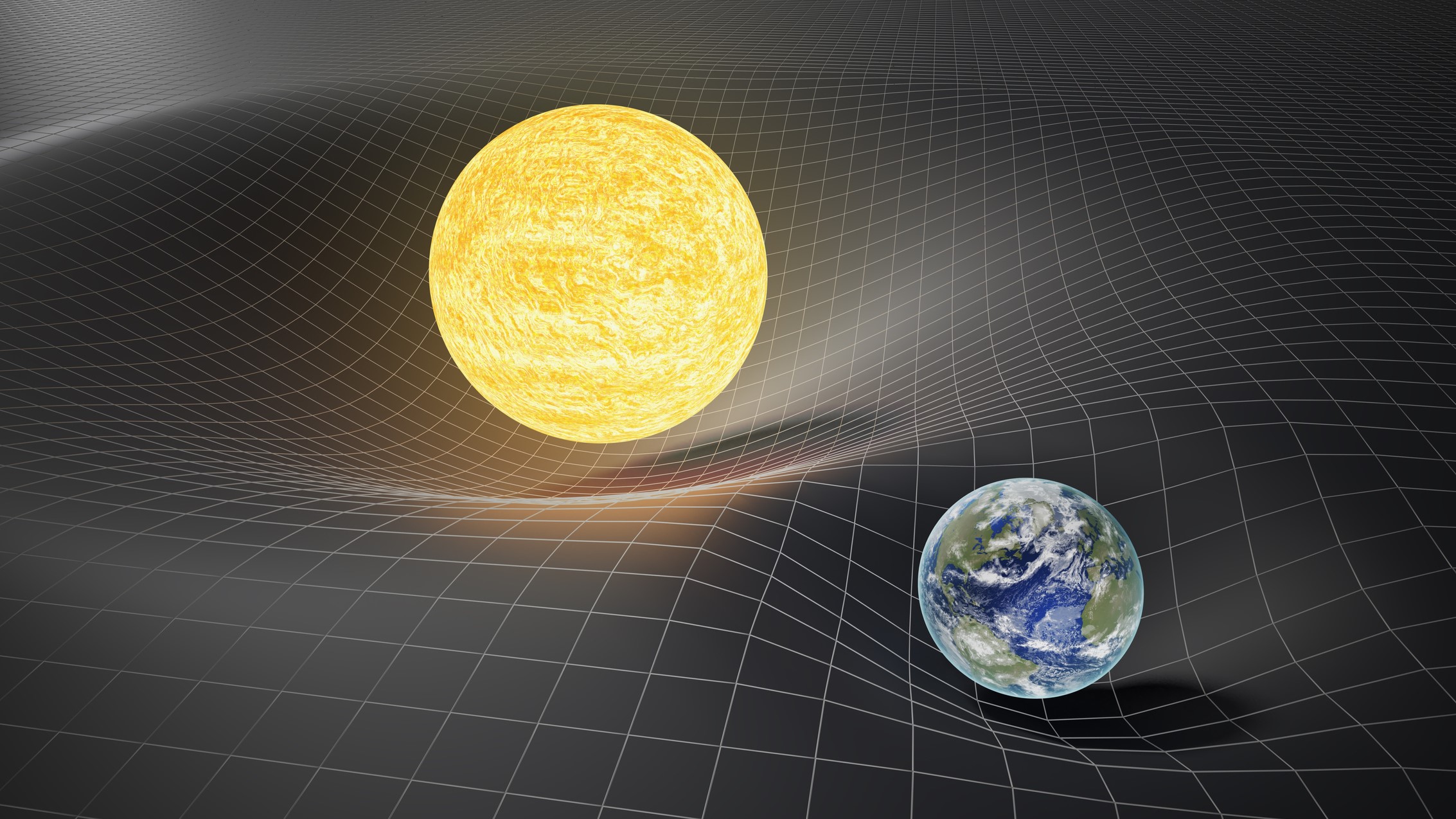
gravity
The force that pulls things toward each other, like how Earth pulls us down.
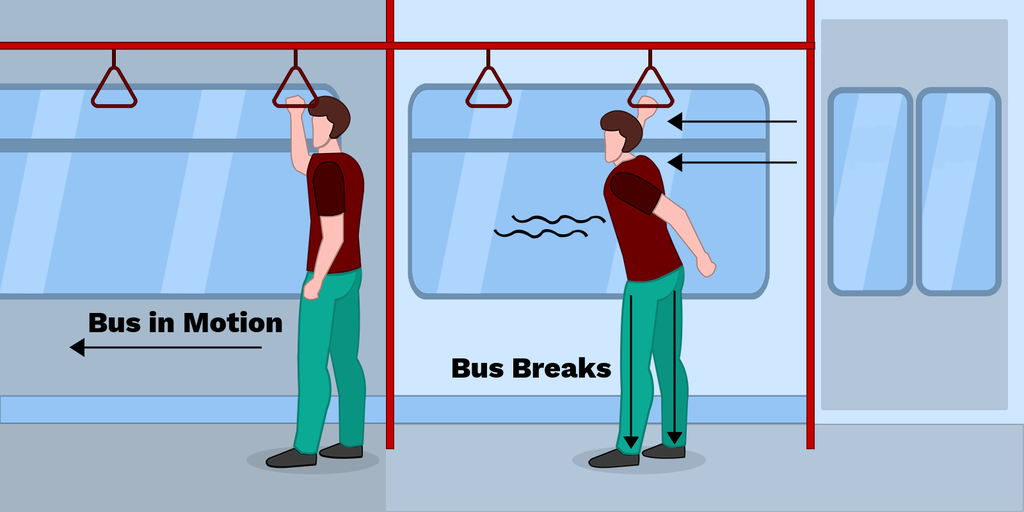
inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion.
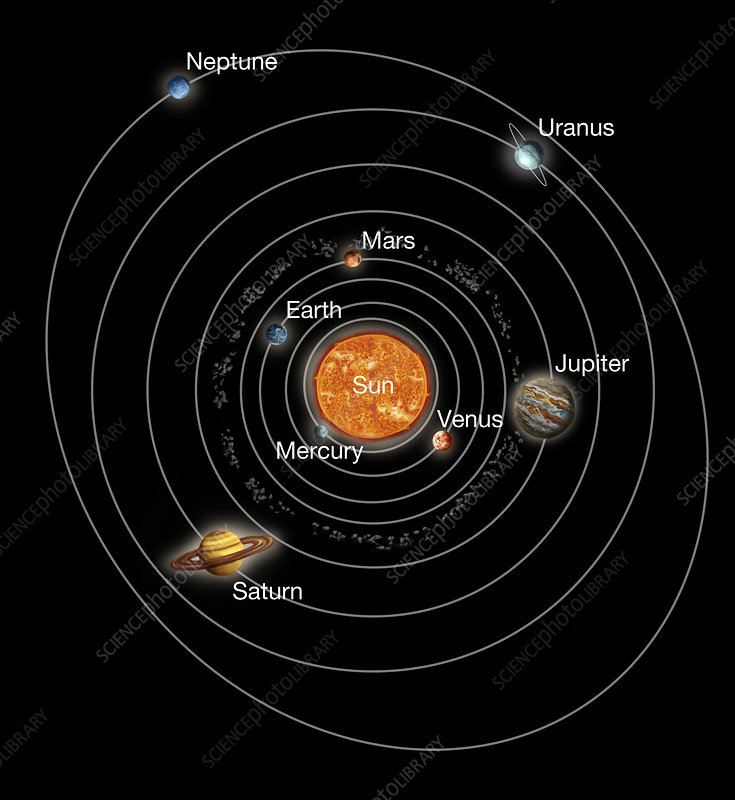
orbit
The path one object takes as it moves around another, like Earth going around the Sun.

ecosystem
A community of living and nonliving things that work together.
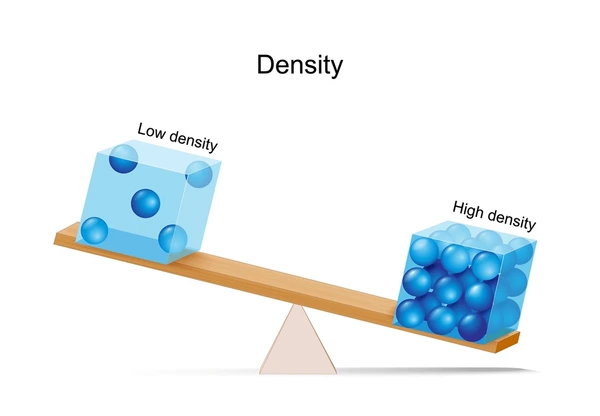
density
How tightly packed the matter in something is.
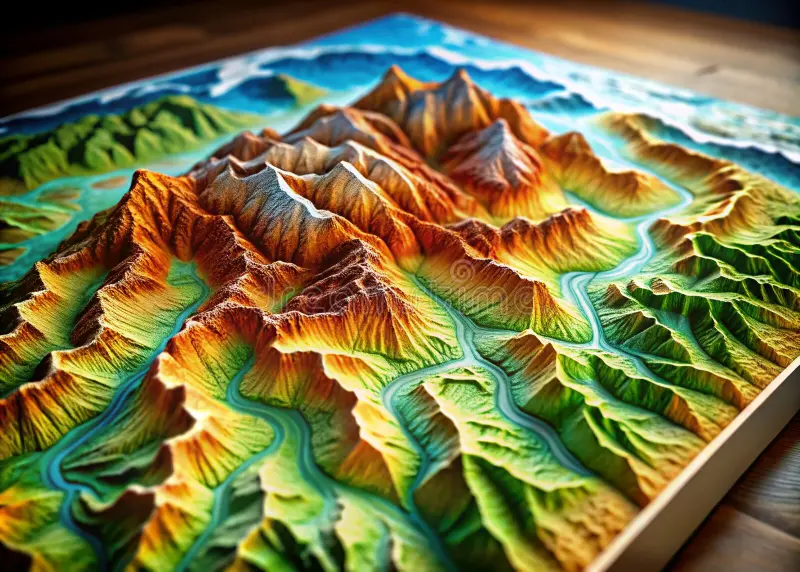

topography
The shape and features of Earth’s surface.
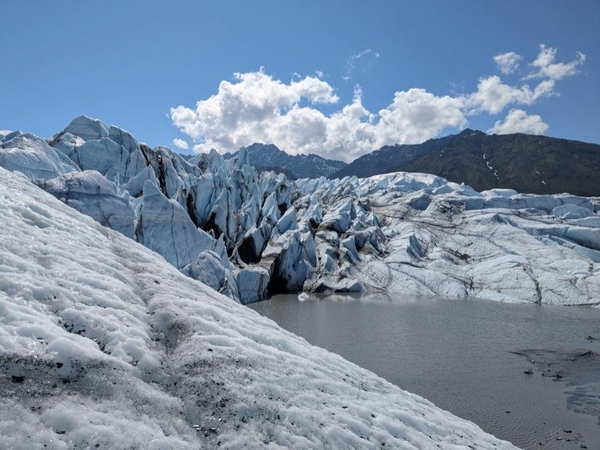

glacier
A large, slow-moving sheet of ice.

energy
The ability to make things move or change.
crust
The outermost solid layer of Earth.
mantle
The layer beneath the crust, made of hot, semi-solid rock.
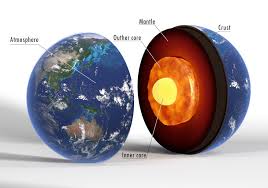
core
The innermost part of Earth, with a liquid outer core and solid inner core.

lithosphere
The rigid outer layer of Earth including crust and uppermost mantle.
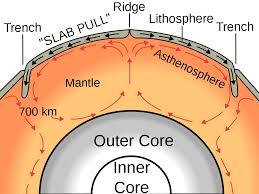
asthenosphere
The semi-fluid layer beneath the lithosphere that allows tectonic plates to move.
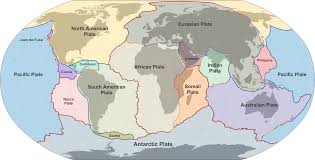
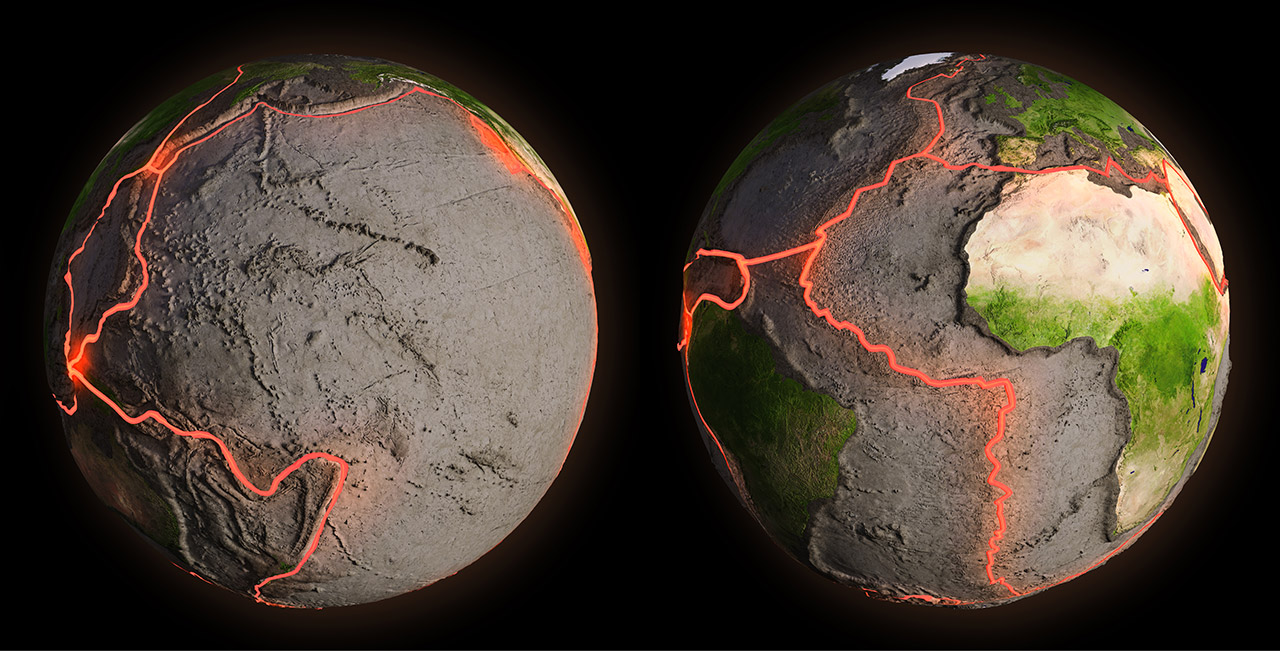
tectonic plate
A piece of Earth’s lithosphere that moves over the asthenosphere.
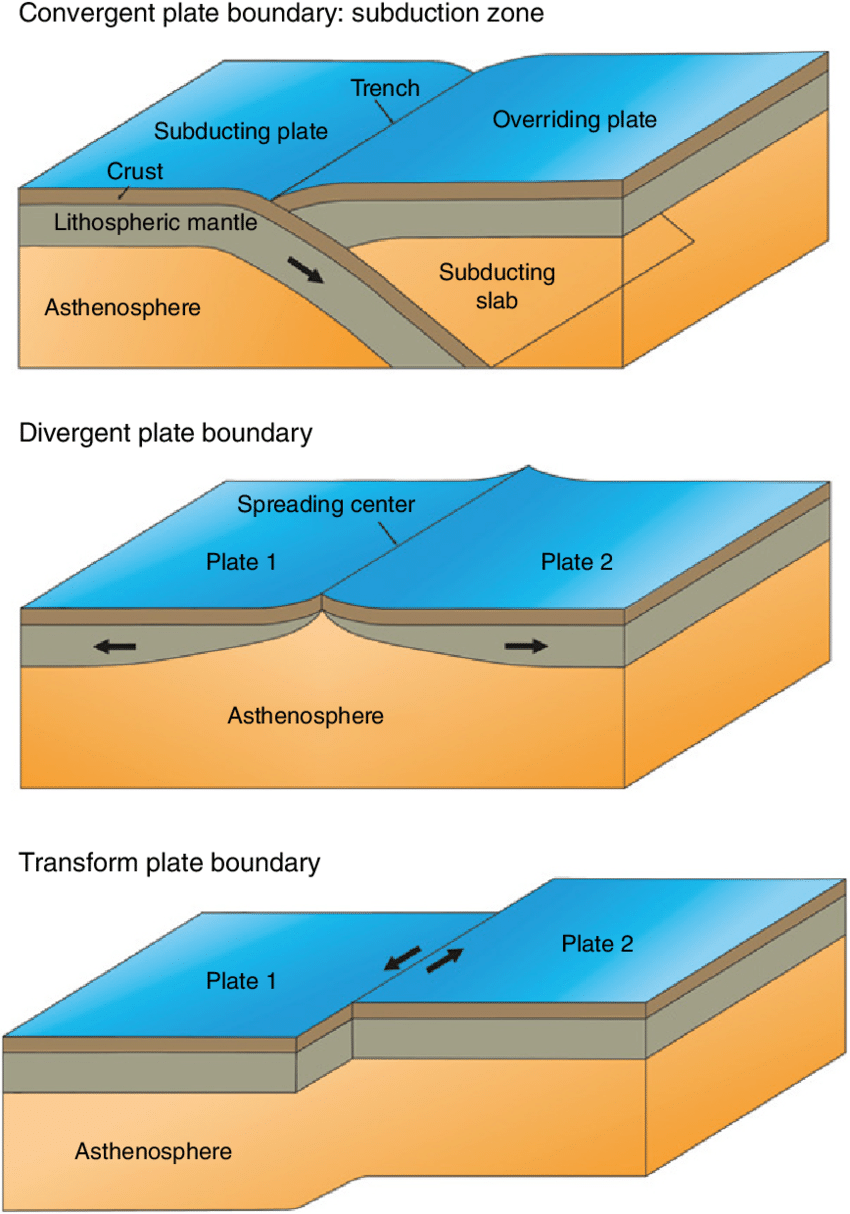
plate boundary
The edge where two tectonic plates meet.
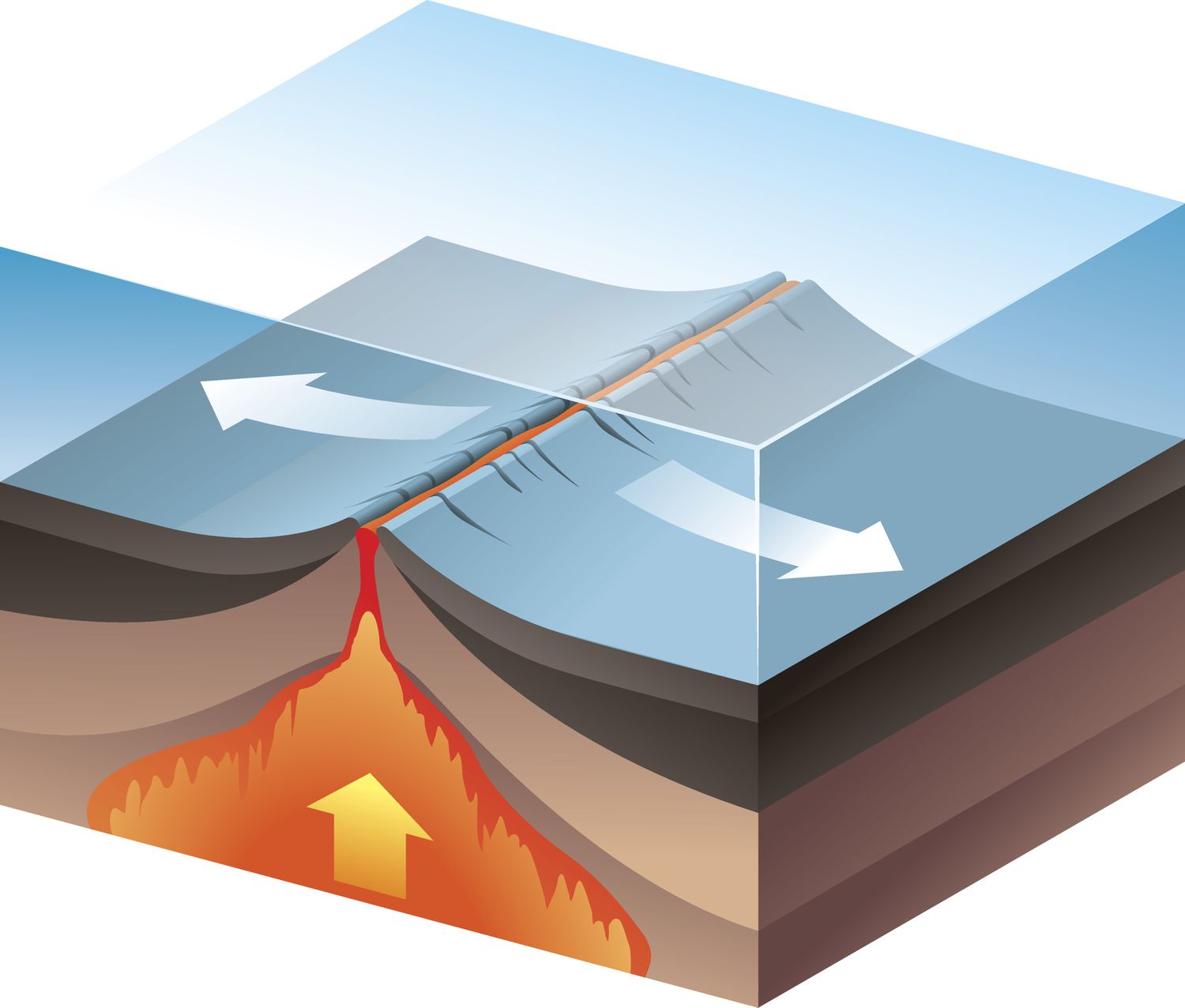
divergent boundary
Where two tectonic plates move apart.
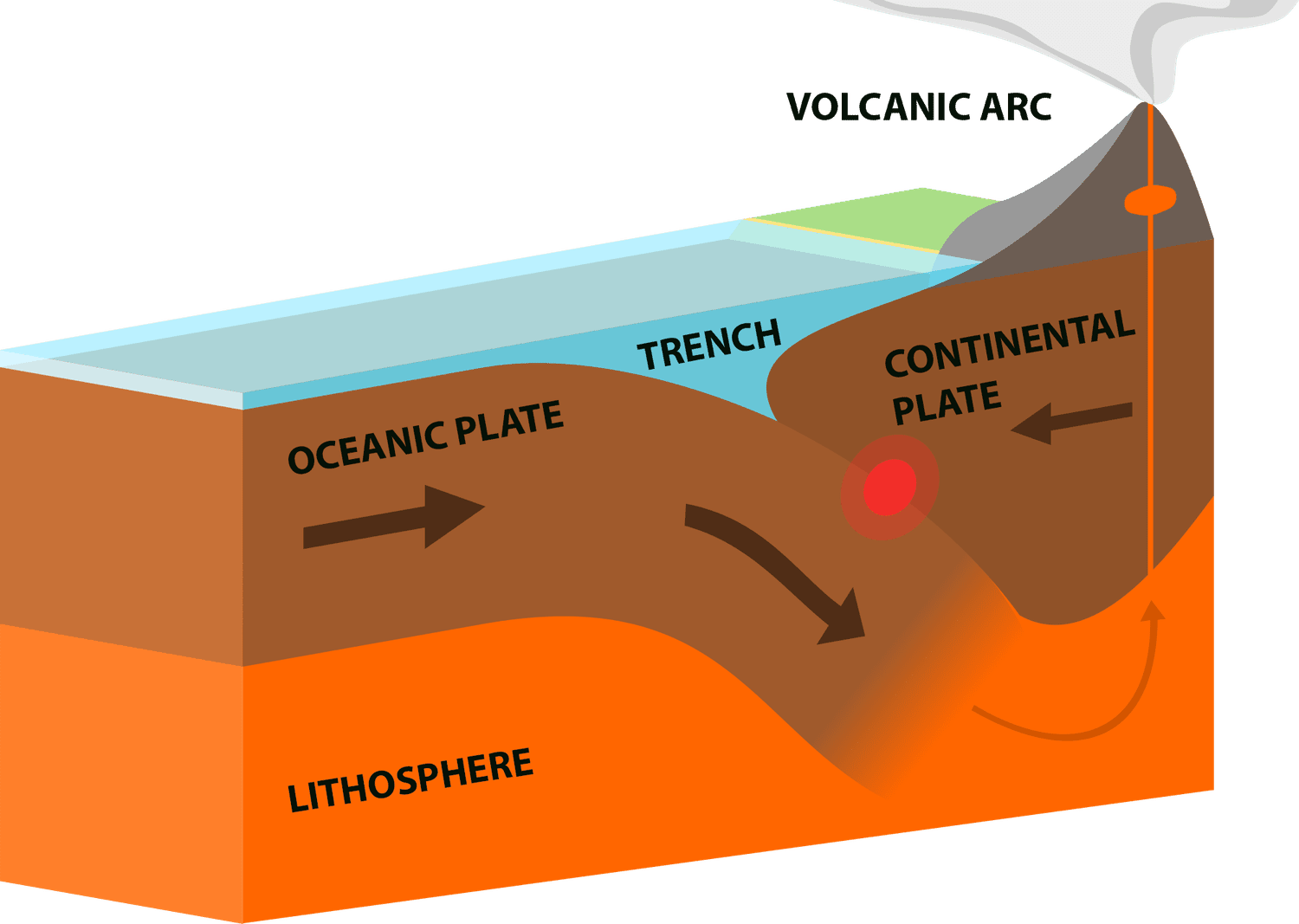
convergent boundary
Where two tectonic plates move toward each other.
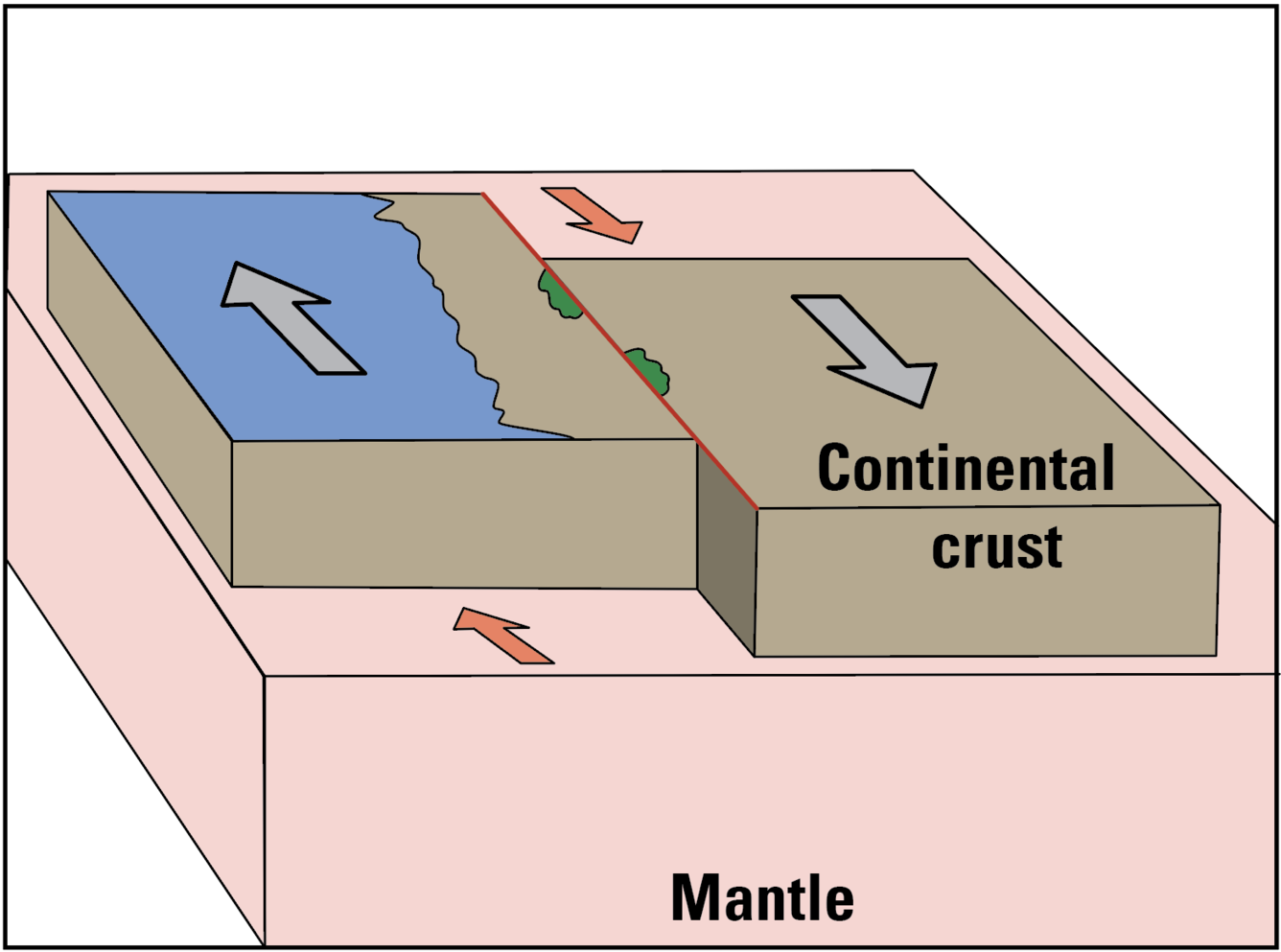
transform boundary
Where two tectonic plates slide past one another horizontally.
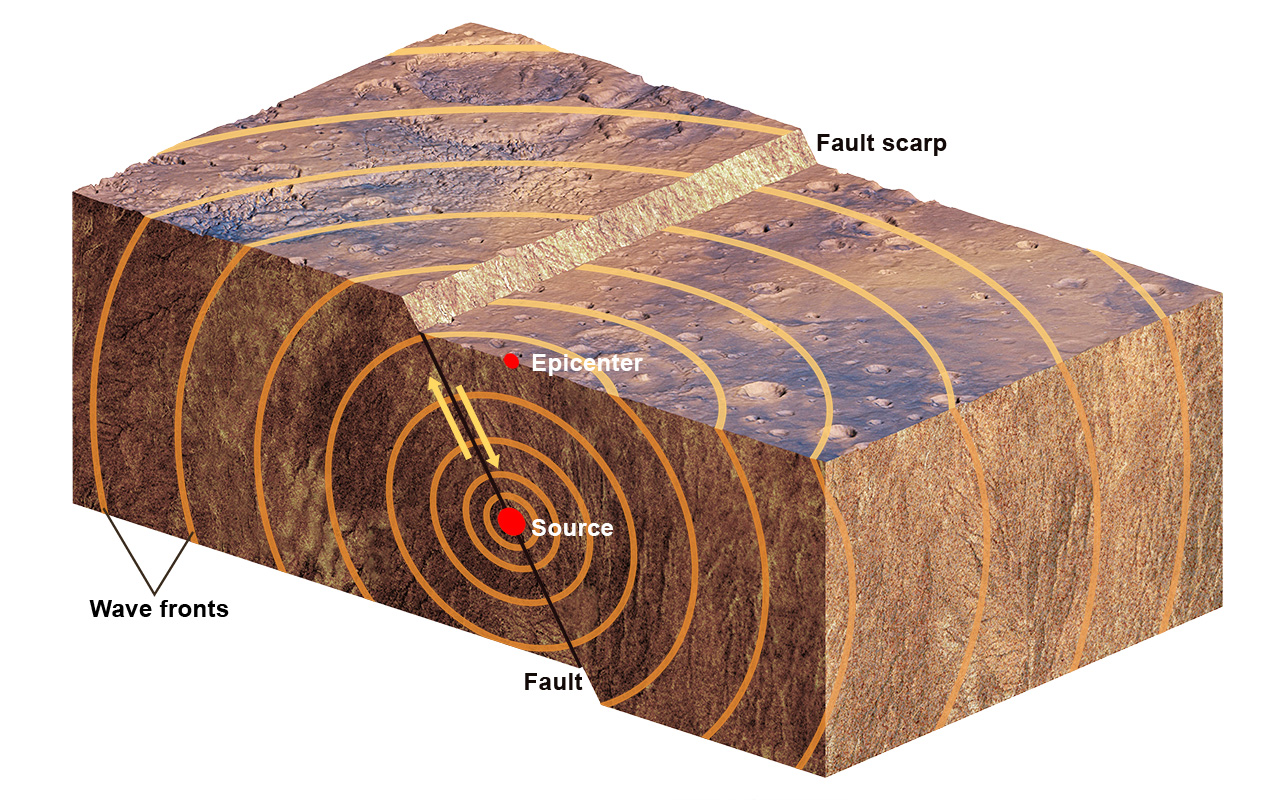
seismic wave
Energy waves that travel through Earth’s interior caused by earthquakes.
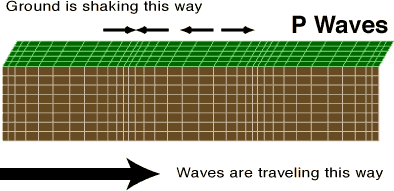
P-wave
Primary seismic wave that travels fastest through solids, liquids and gases.
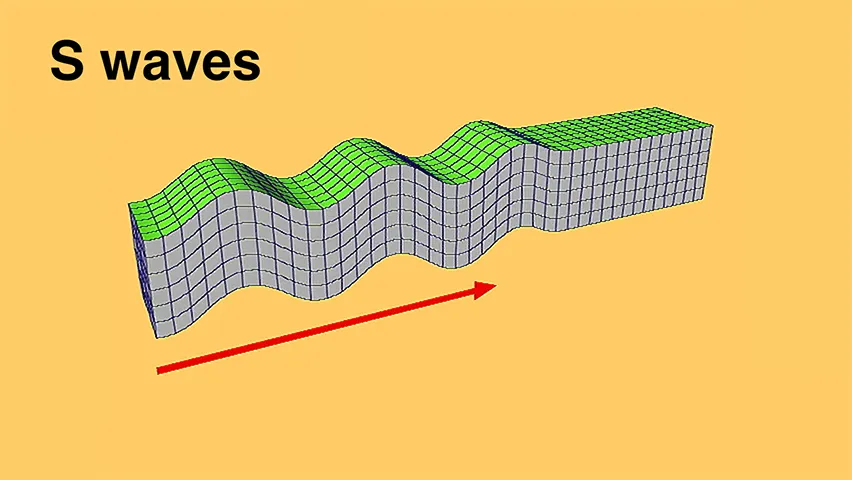
S-wave
Secondary seismic wave that travels slower and only through solids.

earthquake
A sudden release of energy in Earth's crust causing seismic waves.
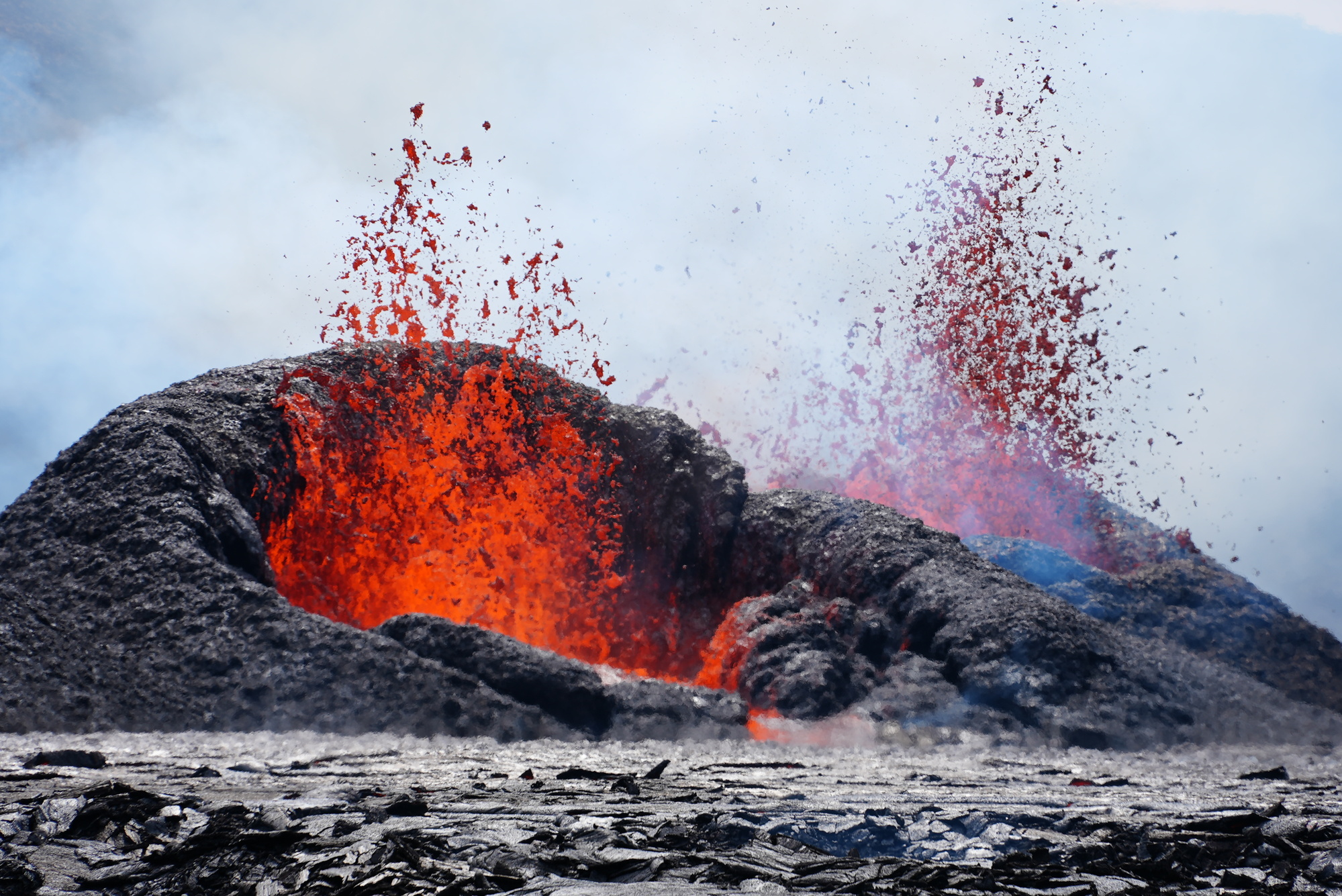

volcano
A vent or opening in Earth’s surface through which magma and gases erupt.
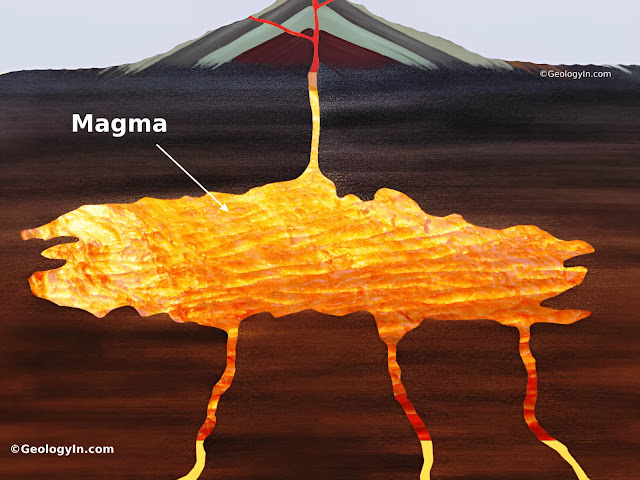
magma
Molten rock beneath Earth’s surface.
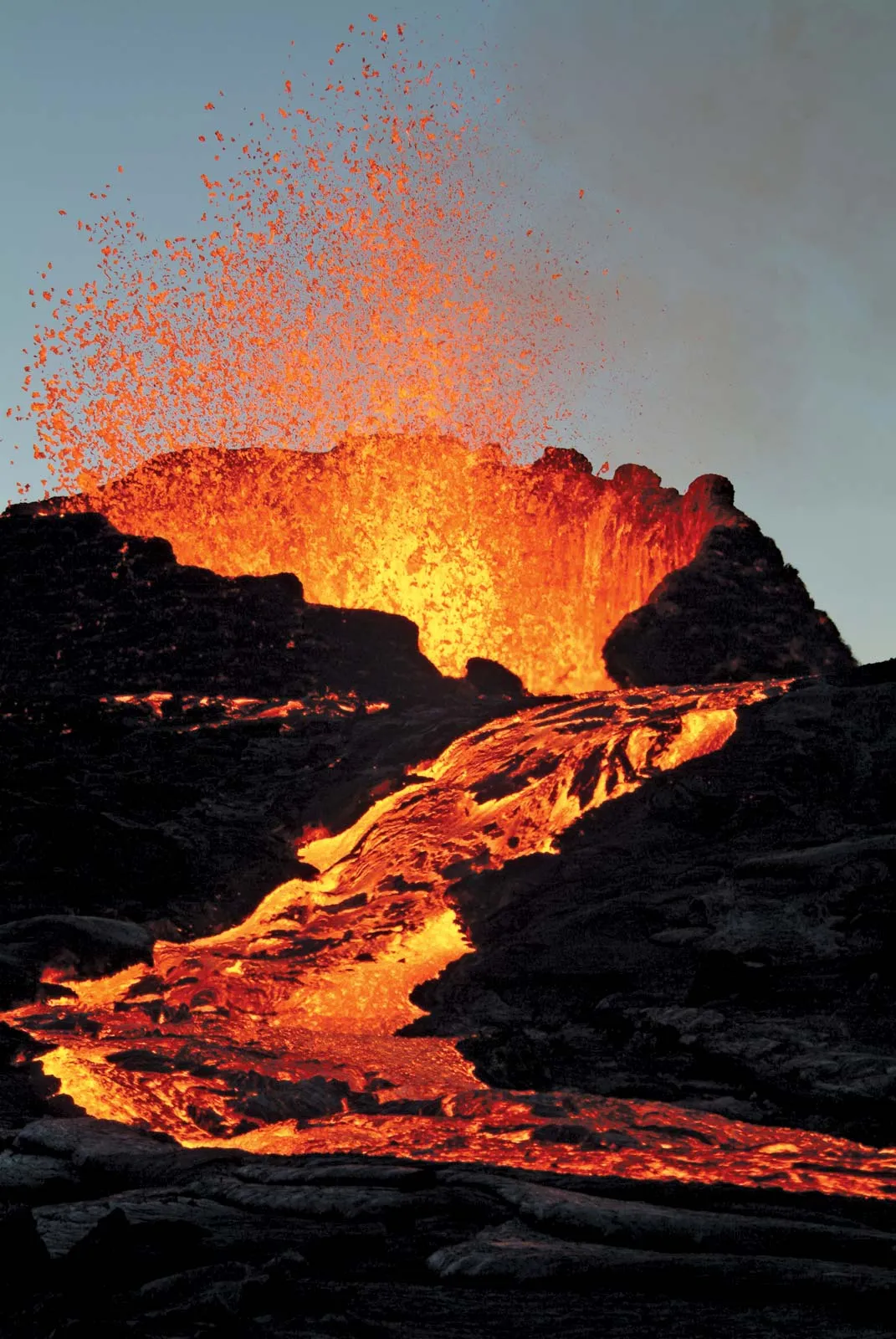

lava
Molten rock that has erupted onto Earth’s surface.
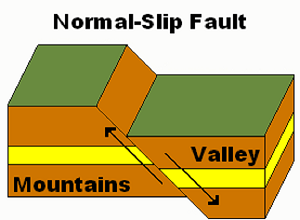
fault
A break or fracture in Earth’s crust along which movement has occurred.
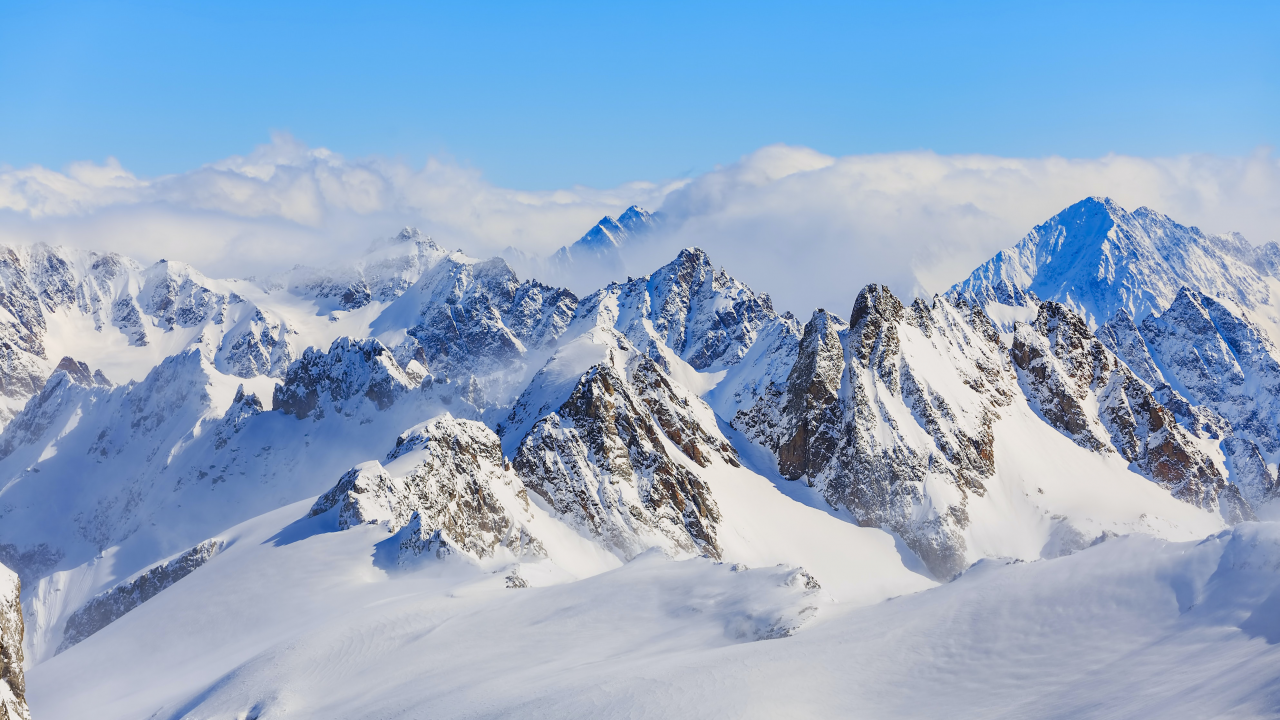

mountain range
A chain of mountains formed by tectonic forces.

ocean trench
A deep, narrow depression in the ocean floor caused by subduction at convergent boundaries.
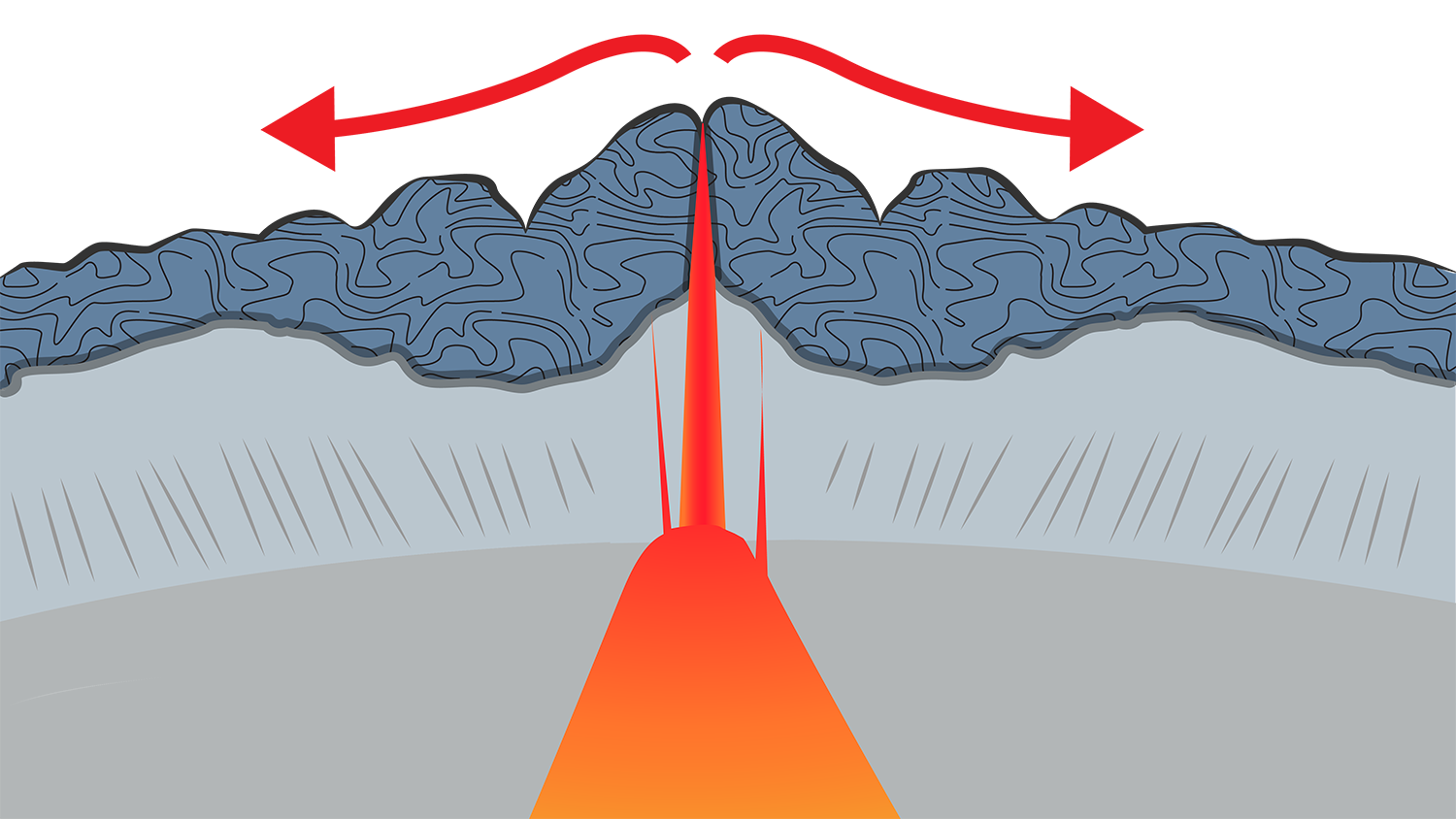
mid-ocean ridge
Underwater mountain ridge formed at divergent plate boundaries.

sedimentary rock
Rock formed by the accumulation and compaction of sediments.

igneous rock
Rock formed from the cooling of magma or lava.

metamorphic rock
Rock formed when existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical processes.

weathering
The breakdown of rocks and minerals at Earth’s surface.

erosion
The movement of weathered materials by wind, water, ice, or gravity.

deposition
The laying down of sediment carried by wind, water, or ice.

geologic time scale
A timeline that breaks up earth's 4.6 billion-year-history.
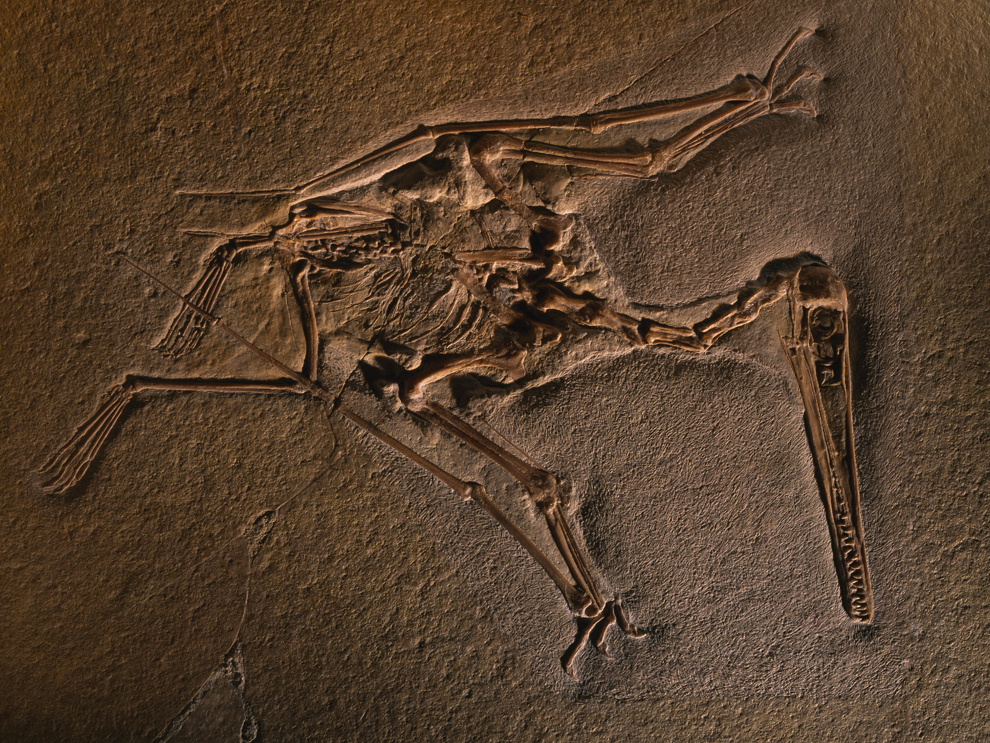

fossil
The preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms.
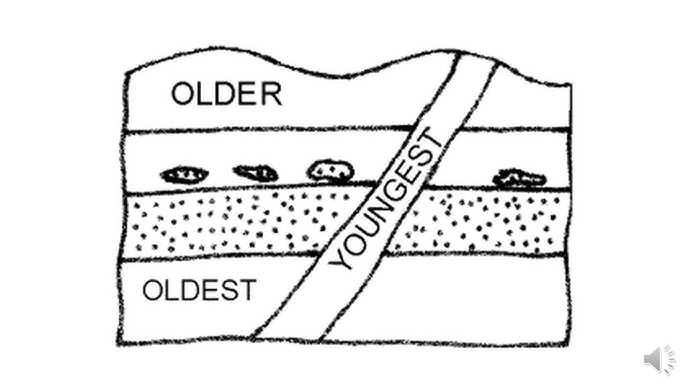
relative age
The age of a rock layer or fossil compared to others.

absolute age
The numerical age of a rock or fossil, often determined by radiometric dating.

superposition
Where the oldest rocks are at the bottom and the youngest rocks are at the top.
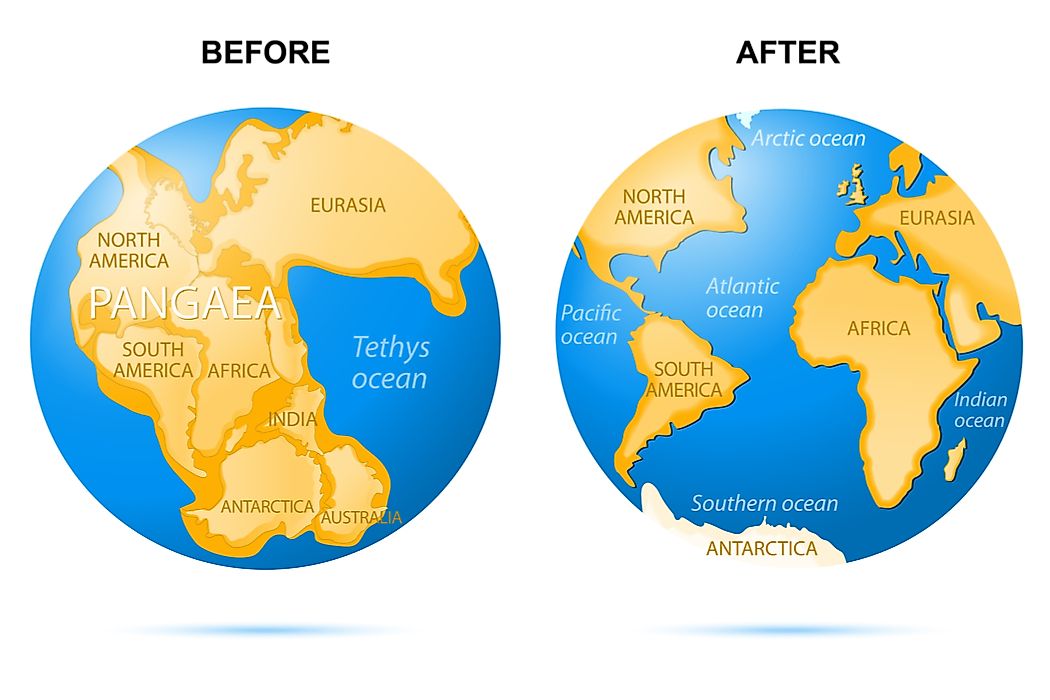
continental drift
The slow movement of continents over Earth’s surface.
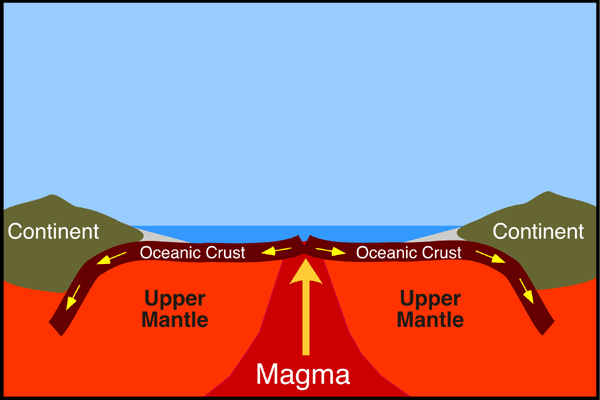
sea-floor spreading
When continents spread apart and new ocean floor is made.
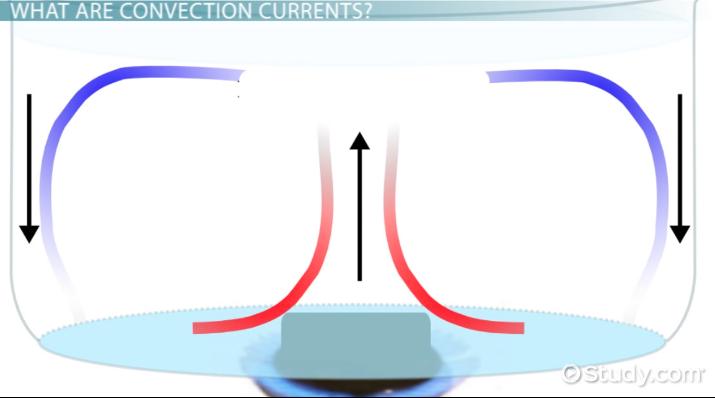
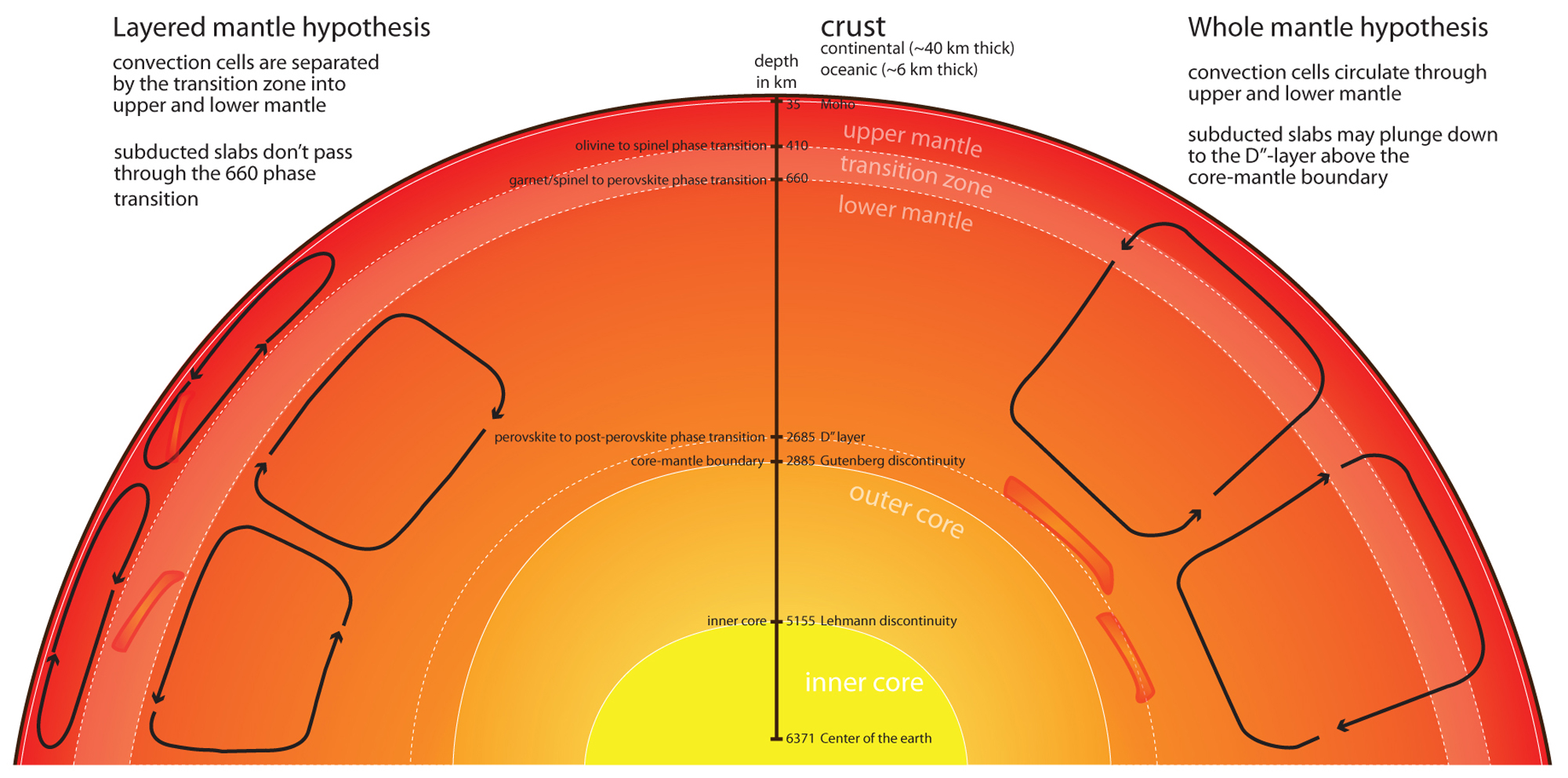
convection current
Movement within a fluid caused by differences in heat and density, driving plate motion.
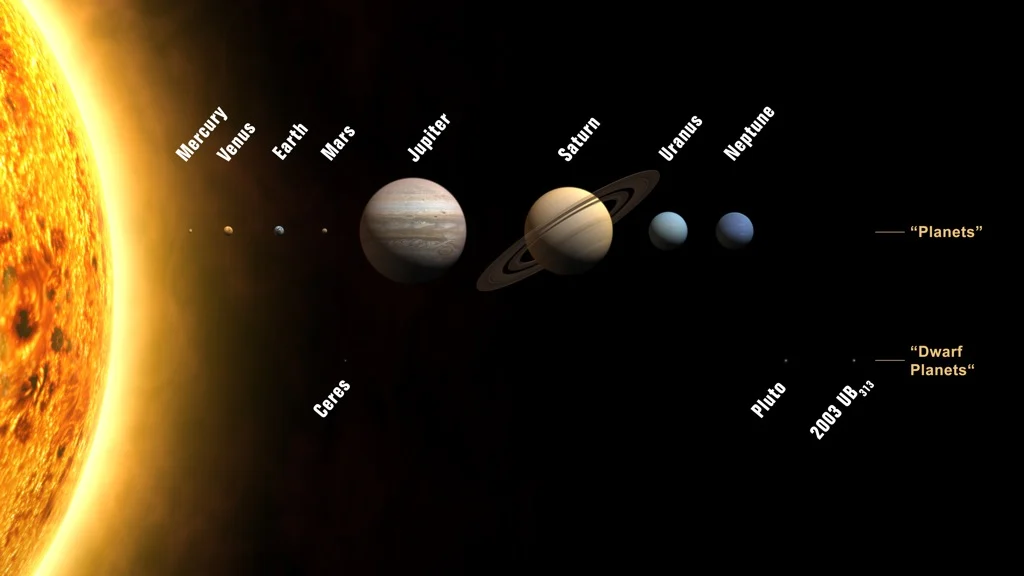
solar system
The Sun and all the objects orbiting it (planets, moons, asteroids, comets).
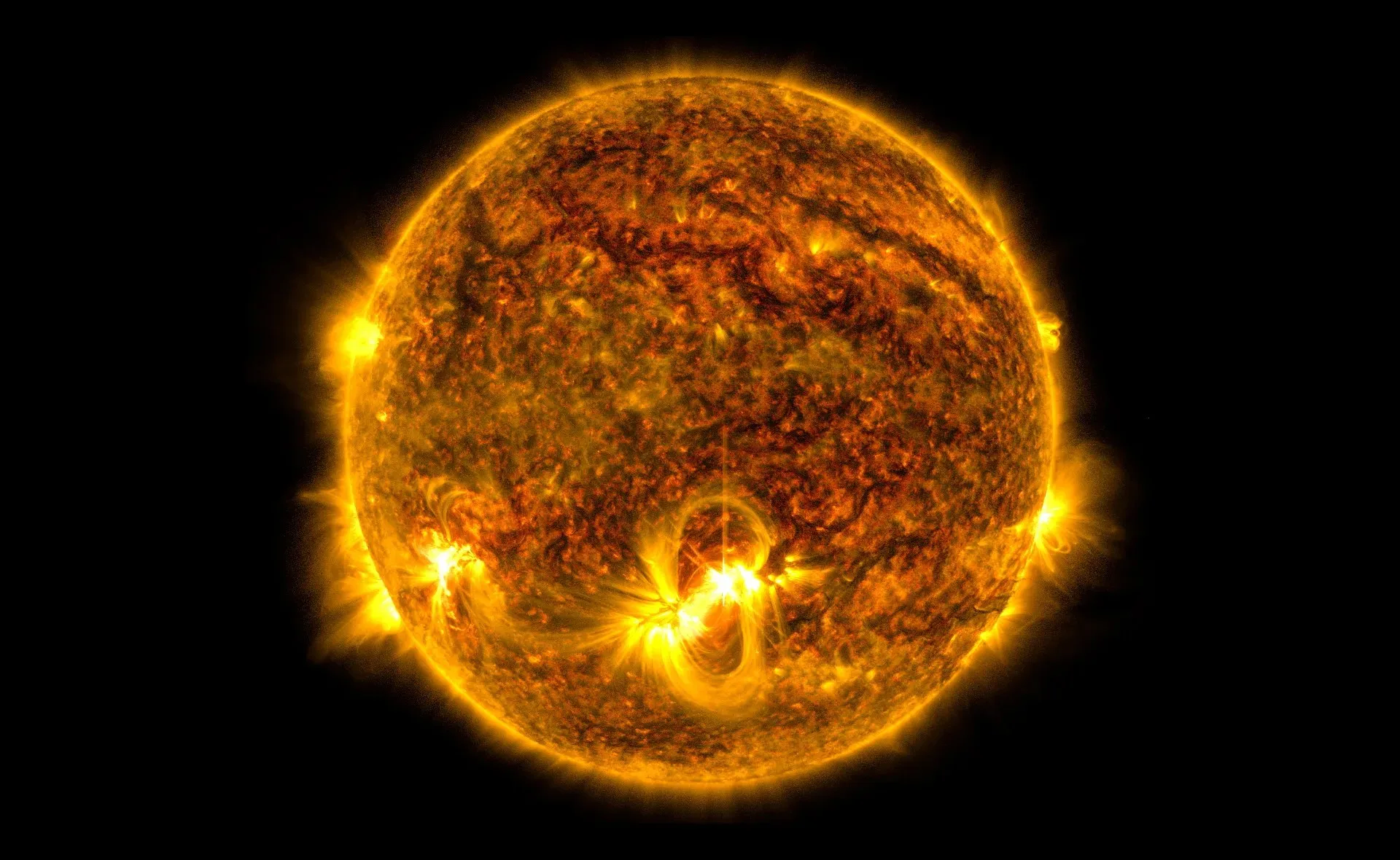

star
A big, bright ball of plasma held together by gravity (e.g., the Sun).
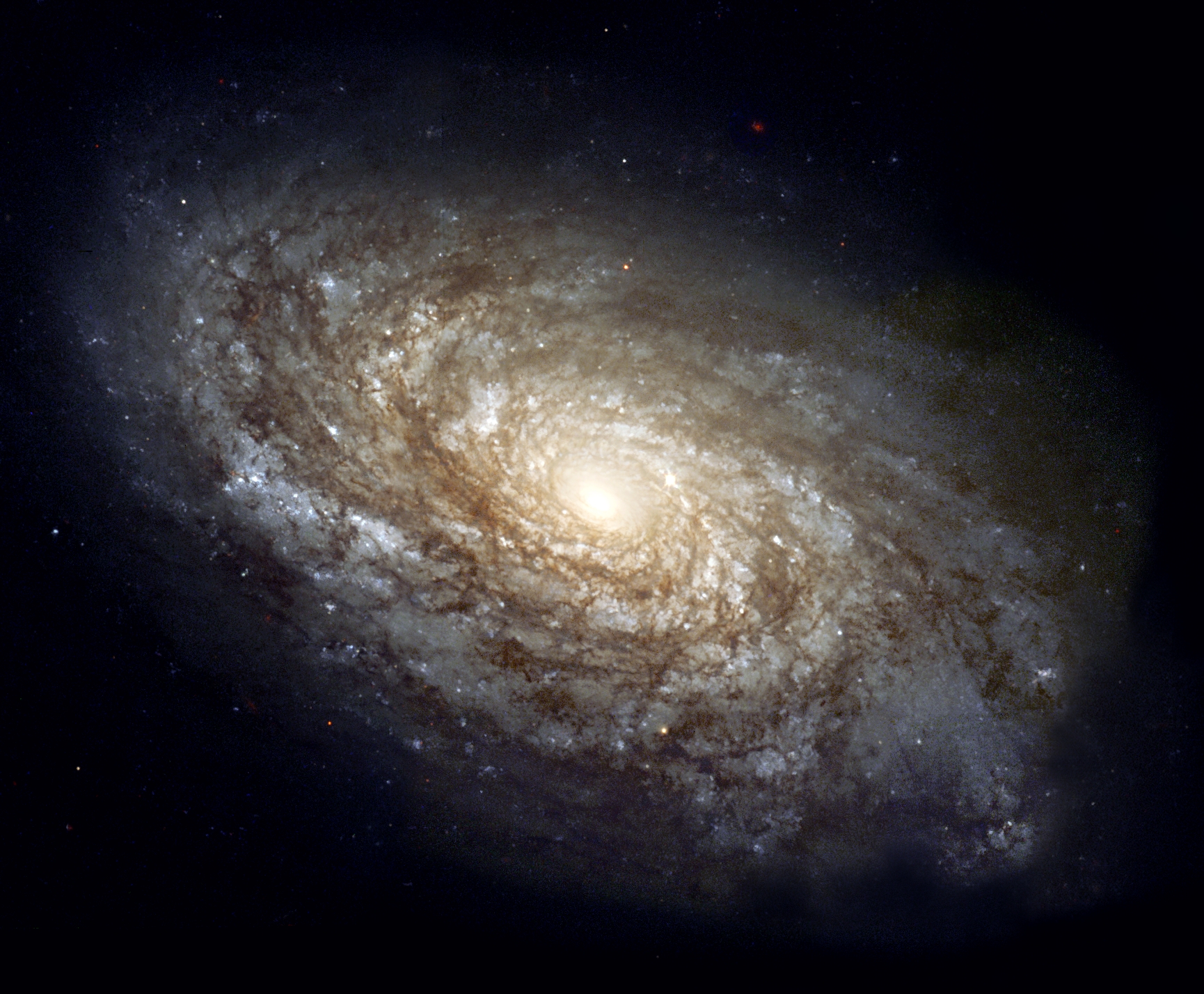

galaxy
A large system of stars, gas and dust held together by gravity.
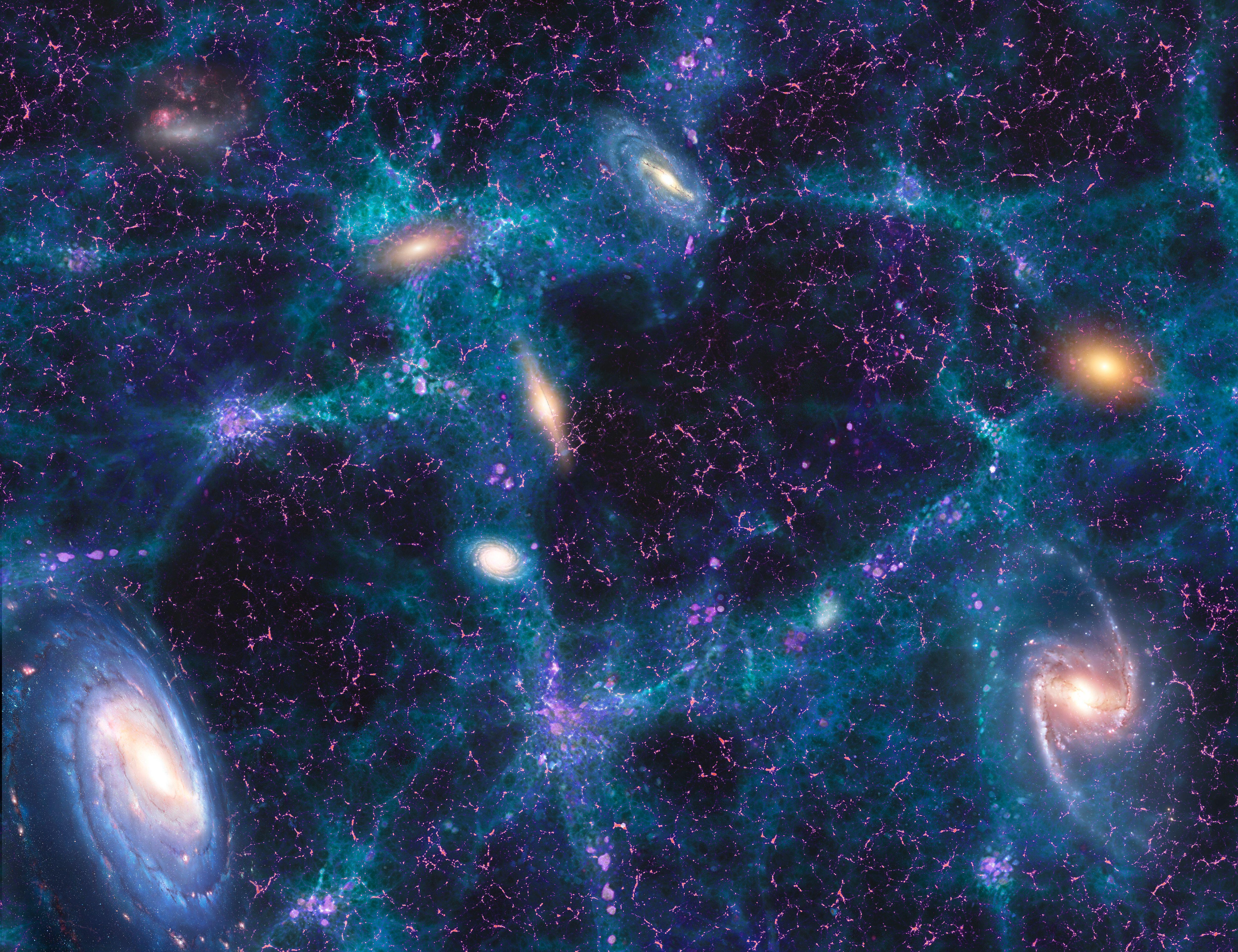

universe
All space, time, matter, and energy that exist.