Antigen processing and presentation
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Three sources of antigen to T cells and on which molecules they are presented on
cytosolic pathogen - degraded in cytosol - on MHC class I
Normal self proteins: Made by the cell’s own ribosomes as part of normal metabolism.
Viral proteins: Produced when a virus infects the cell and hijacks its ribosomes to make viral components.
Mutated or abnormal proteins: From cancerous transformation or defective ribosomal products (DRiPs).
These never “enter” from outside — they’re synthesized in the cytosol.
intravesicular pathogens - degraded in endocytic vesicle - on MHC class II (eg, tuberculosis)
extracellular pathogens and toxins - degraded in endocytic vesicle - on MHC class II
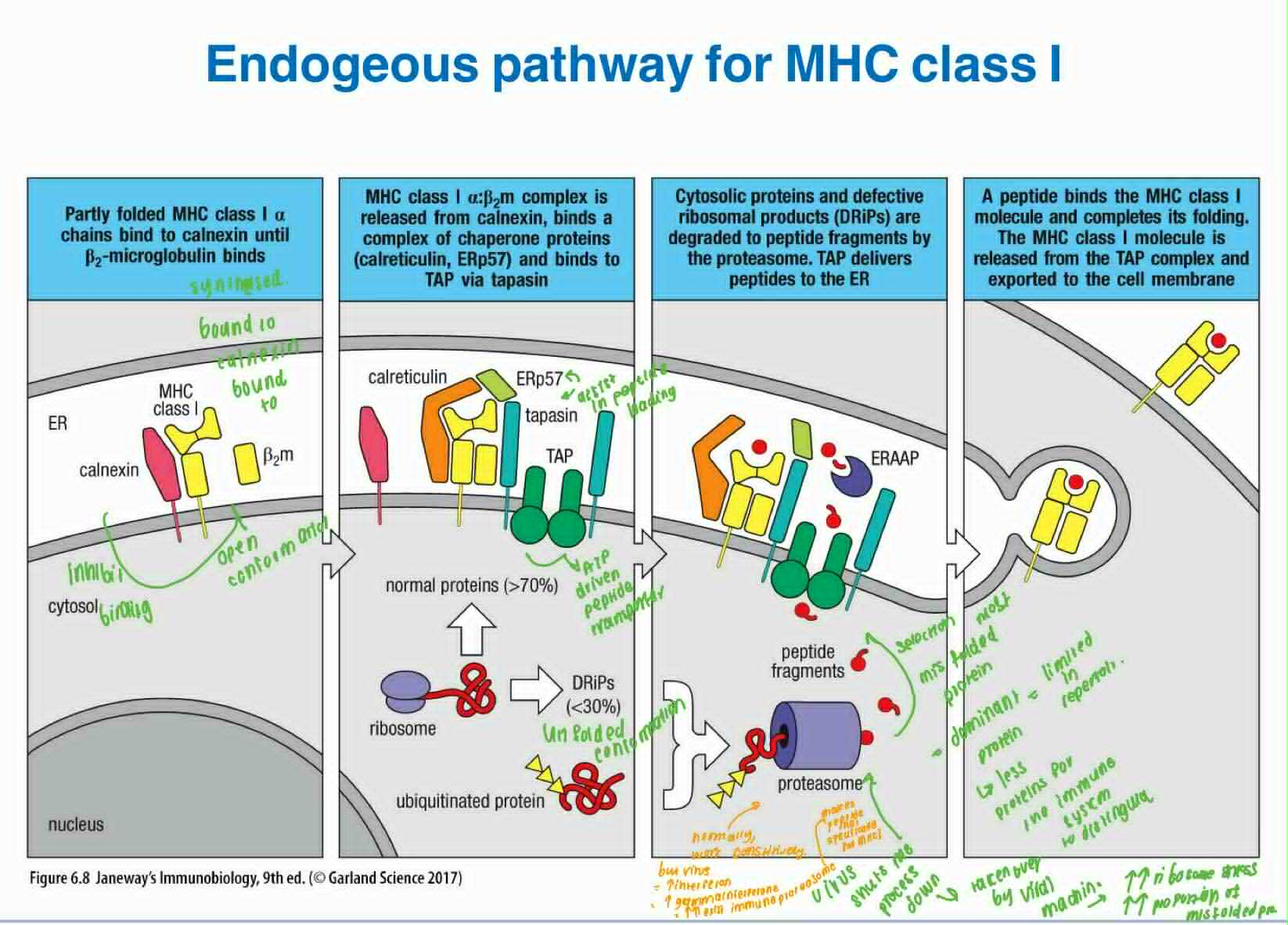
Steps of the endogenous pathway for MHC class I
How peptides sourced form nascent proteins inside the cells are ferried into the ER, where they are combined with the newly synthesized heavy chain of MHC class I and b2 microglobulin
Proteins are ubiquitinated by the UPS, which gets unfolded by the 19S subunit and degraded into the small peptides by the 20S subunit
Special proteosome: immunoproteosome
TAP1 and TAP2 which sits on the ER membrane ferry the peptides from the cytosol to the ER lumen
On the ER membrane:
Partly folded MHC class Ia chains bind to calnexin which inhibits b2m binding
b2m binding to mhc i leads to the release of calnexin and binds to a complex of chaperone proteins (calreticulin, ERp57) and binds to TAP via tapasin
TAP delivers peptide to the ER
The peptide binds MHC I and completes its folding, dissociate from the TAP complex and exported to the cell membrane
Immunoproteosome
gamma interferon (IFNy) induces alternative of the proteosome which alter the components, whilst also increasing the MHCI expression. The immunoproteosomes are very good at creating hydrophobic resides that are preferable for MHC I binding.
Are TAPs ATP dependent?
Yes
What are Drips?
Product after ribosome translation - proteins that are in unfolded conformation, which gets ubiquitinated and cut into peptides that can be expressed on MHC - usually are the dominant and common proteins
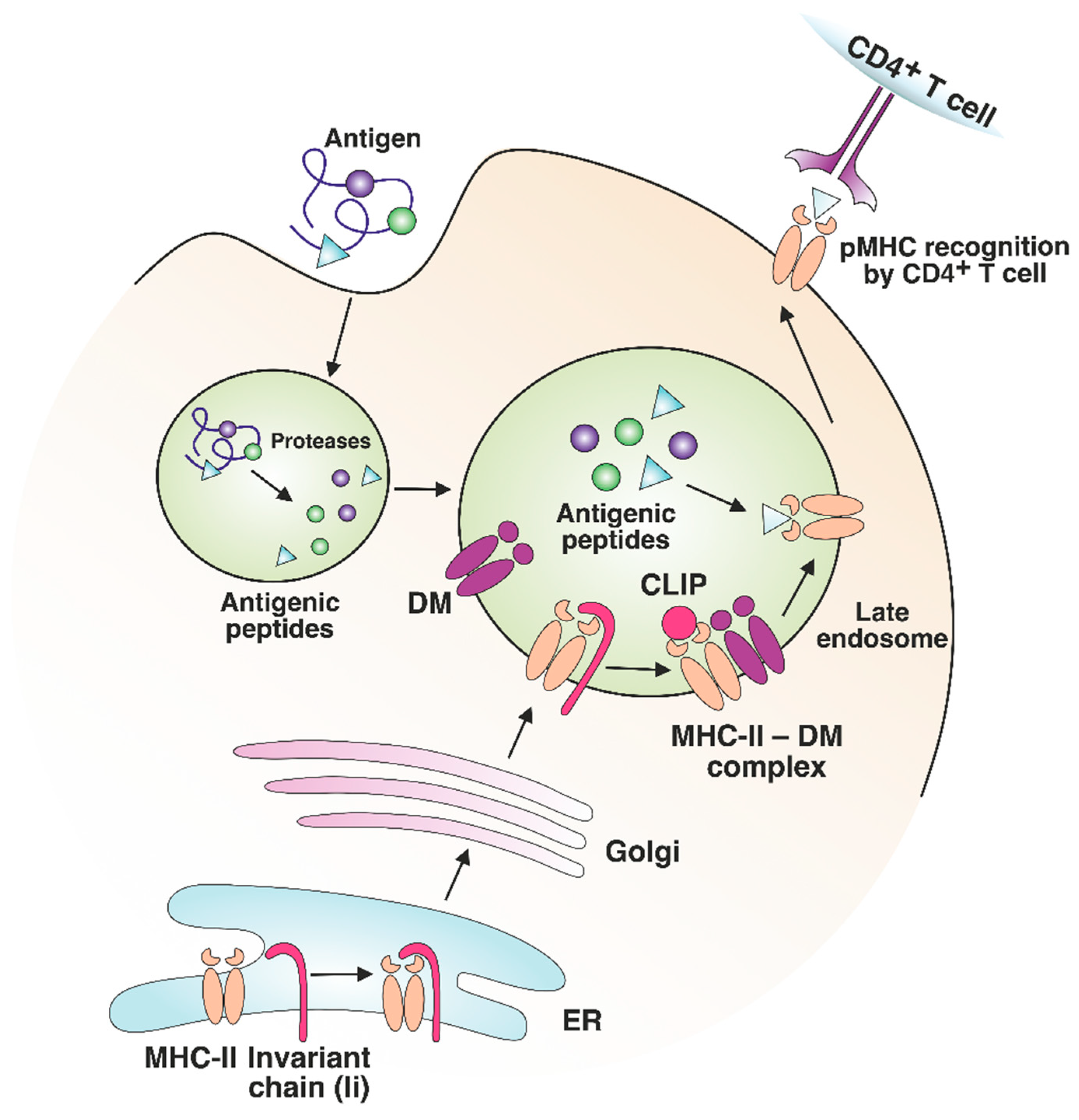
MHC class II peptide loading
Peptides sourced via endocytosis, phagocytosis or macrophagocytosis delivered to endosomes in pAPC - macrophage, DC, B cells
Acidification in the endosomes
Acidic cathepsin degrades proteins
MHC class II is first synthesized in the ER with the invariant chain (Ii). When it gets transported to the acidified endosome, Ii is progressively cleaved to a shorter chain (CLIP)
The peptide cannot bind to MHCII due to CLIP, but when HLA -DM /DO binds to MHC class I molecule, releasing CLIP and allow other peptides to bind. MHC II transported to the cell membrane
What is cross-presentation in DC and how it is important in CTL licensing
Certain subsets of DC are efficient in capturing exogenous proteins and allow them to be present on MHCI.
These proteins can enter the phagolysosome and gets degraded in the proteosome, or get directly transported from the phagolysosome into a vesicular loading compartment
Important for CTL to kill other virally infected cells