Osmoregulation - Part 1 (11/12)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is Osmoregulation?
The process by which an animal controls the concentrations of both water and dissolved molecules in its body
What are electrolytes?
Substances that separate into ions when dissolved in water
What is Osmotic Stress?
When water or electrolyte imbalances disrupt the metabolic processes of the cell
Why can disturbances in water and electrolyte concentrations cause osmotic stress, cell damage, and death?
Hypotonic Environment
If the cell swells too much due to the intake of water, the cell will explode and die
Hypertonic Environment
If the cell shrivels up too much, it disrupts the metabolic processes of the cells and the cell dies
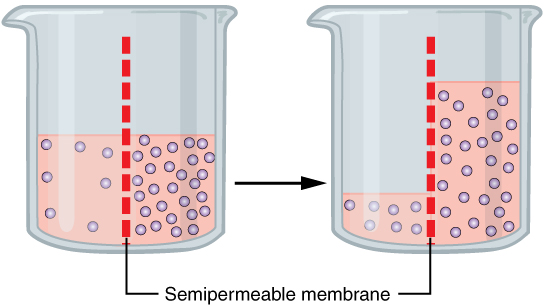
How does diffusion work?
What’s needed for Diffusion
A concentration gradient of an atom or molecule across a membrane
The membrane is permeable to that stom or molecule
THEN it will diffuse across the membrane until the concentration of the atom or molecule is equal on both sides

How does osmosis work?
Wherever there is a concentration gradient, osmosis will occur
Water flows from the side with high concentration to that of low concentration
“water follows salt”
What does ‘osmolarity’ mean?
The concentration of all dissolved solutes that can cause osmosis
What does ‘hypertonic’ mean?
The concentration of solutes (stuff dissolved in water) is higher on the outside of the cell
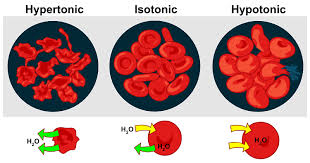
What does ‘hypotonic’ mean?
The concentration of solutes (stuff dissolved in water) is lower on the outside of the cell
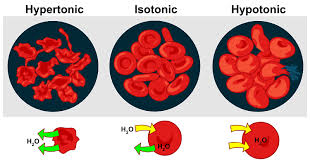
What does ‘isotonic’ mean?
The concentration of solutes (stuff dissolved in water) is the same on both sides
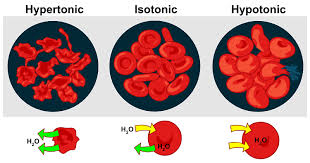
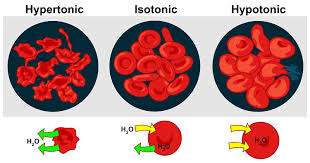
How does cell water and electrolyte concentrations change in hypertonic and hypotonic environments?
Hypertonic
Lose water by Osmosis
Gain excess electrolytes by diffusion
Hypotonic
Gain excess water by osmosis
Lose electrolytes by diffusion
What are osmoregulators?
Animals whose body cells have a different osmolarity than their environment

What are osmoconformers?
Animals whose body cells have the same osmolarity as their surroundings
Which animals fall into osmoregulators or osmoconformers?
Osmoregulators
All other marine fish that live in seawater aside from osmoconformers
Freshwater fish
Osmoconformers
Marine invertebrates and marine fish with cartilage-based skeletons

What are the different osmotic stresses and imbalances that happen in marine and freshwater fish?
Marine
Live in a high osmolarity (hypertonic) environment
Lose water by osmosis
Gain excess electrolytes by diffusion
Freshwater
Live in a low osmolarity (hypotonic) environment
Gain excess water by osmosis
Lose electrolytes by diffusion
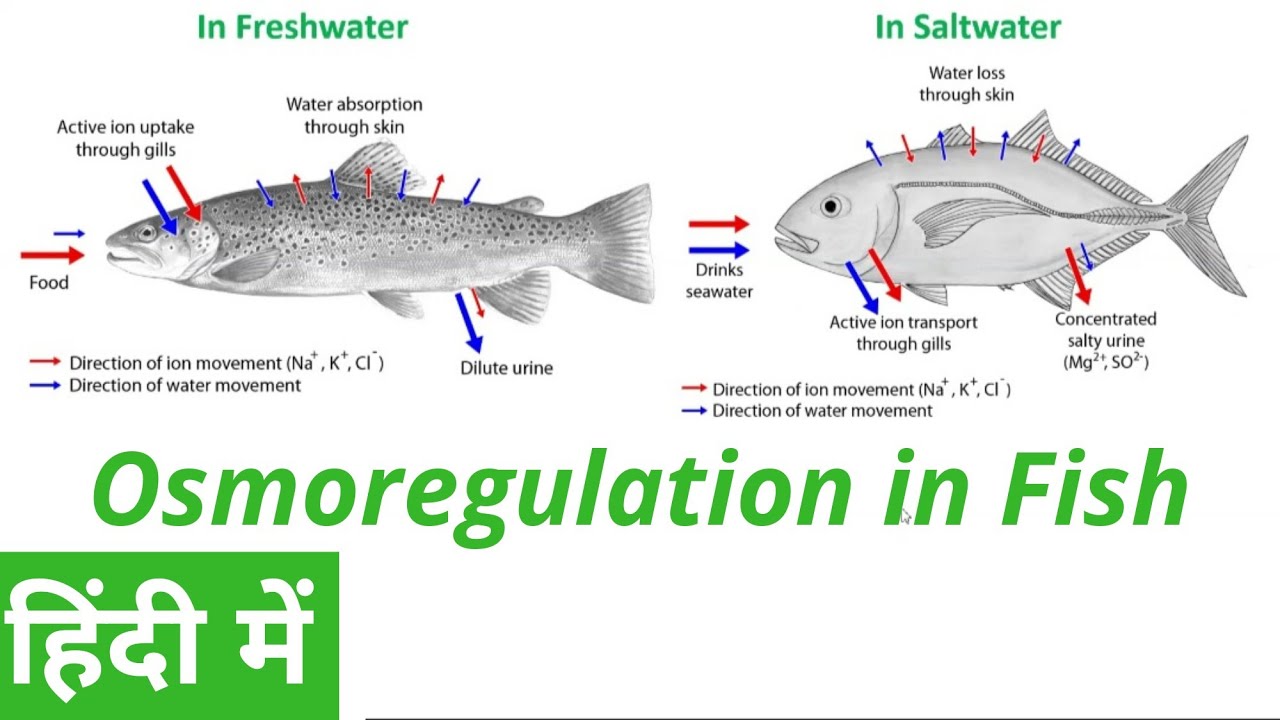
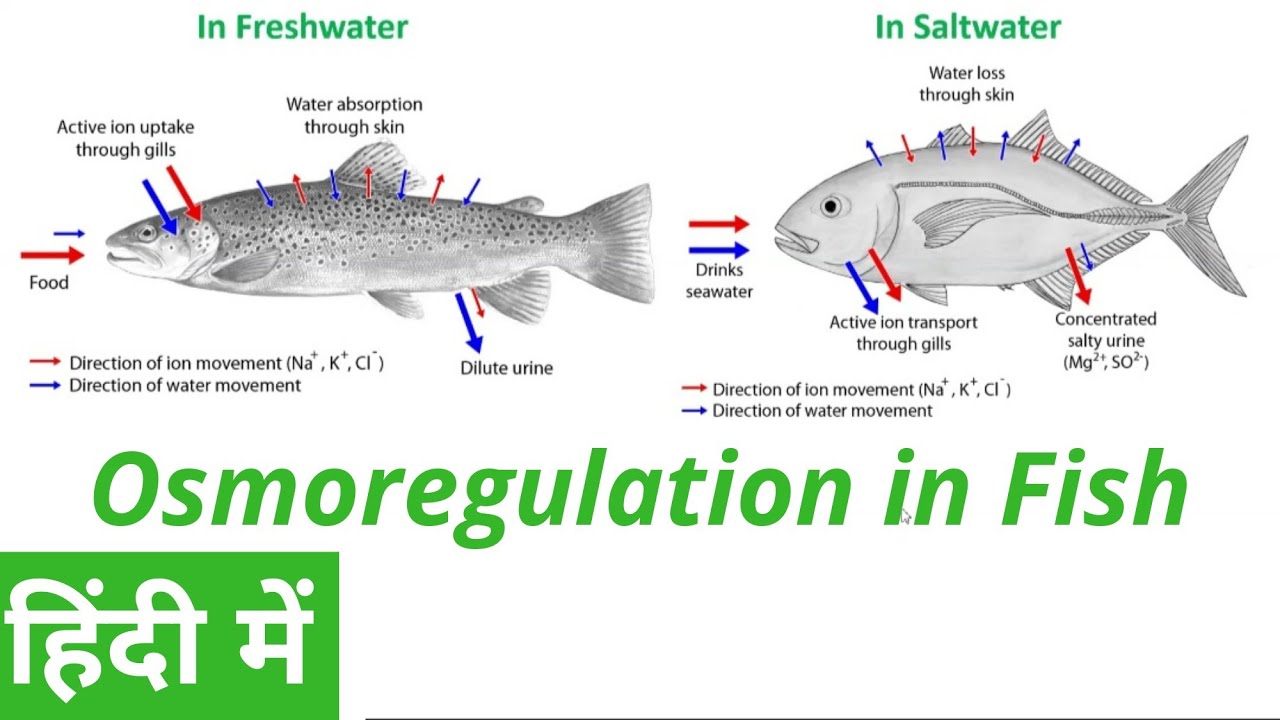
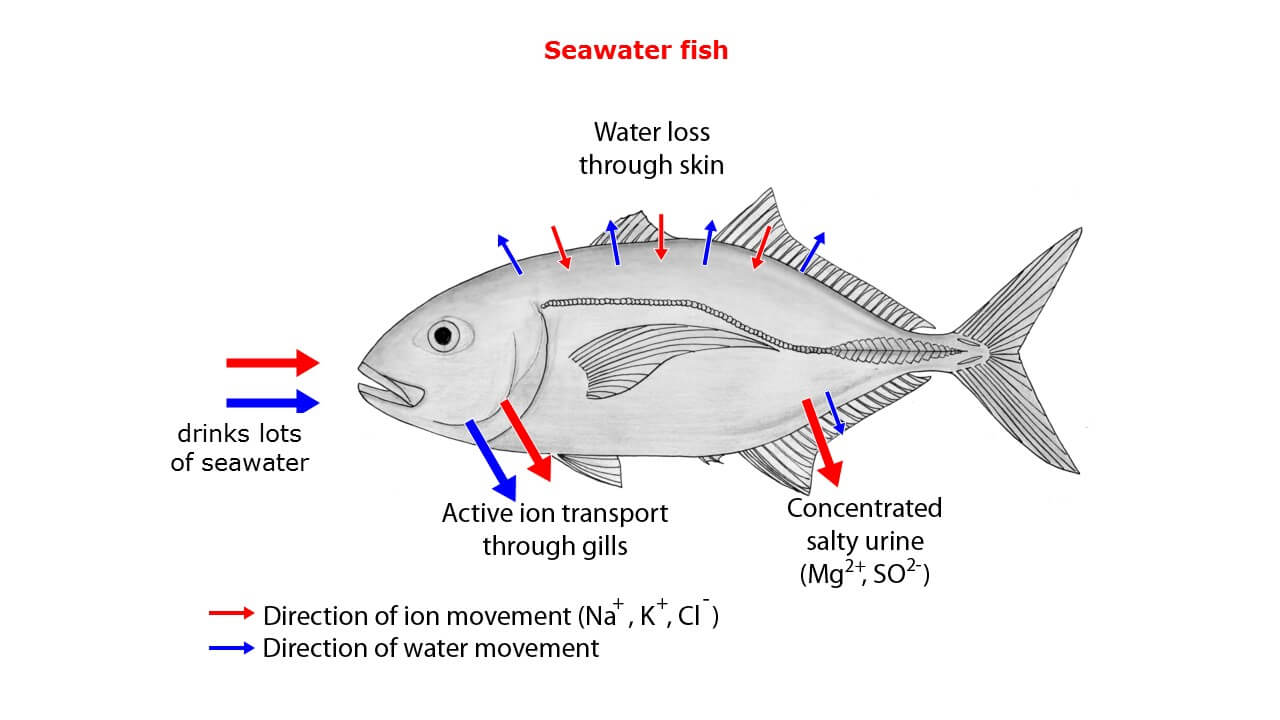
How do marine fish osmoregulate?
Marine - High osmolarity (hypertonic) environment
Replace water by drinking seawater, produce little urine
Drinking adds extra excess electrolytes
Excess electrolytes go back to environment through gills
Gills have a protein that move salt by active transport
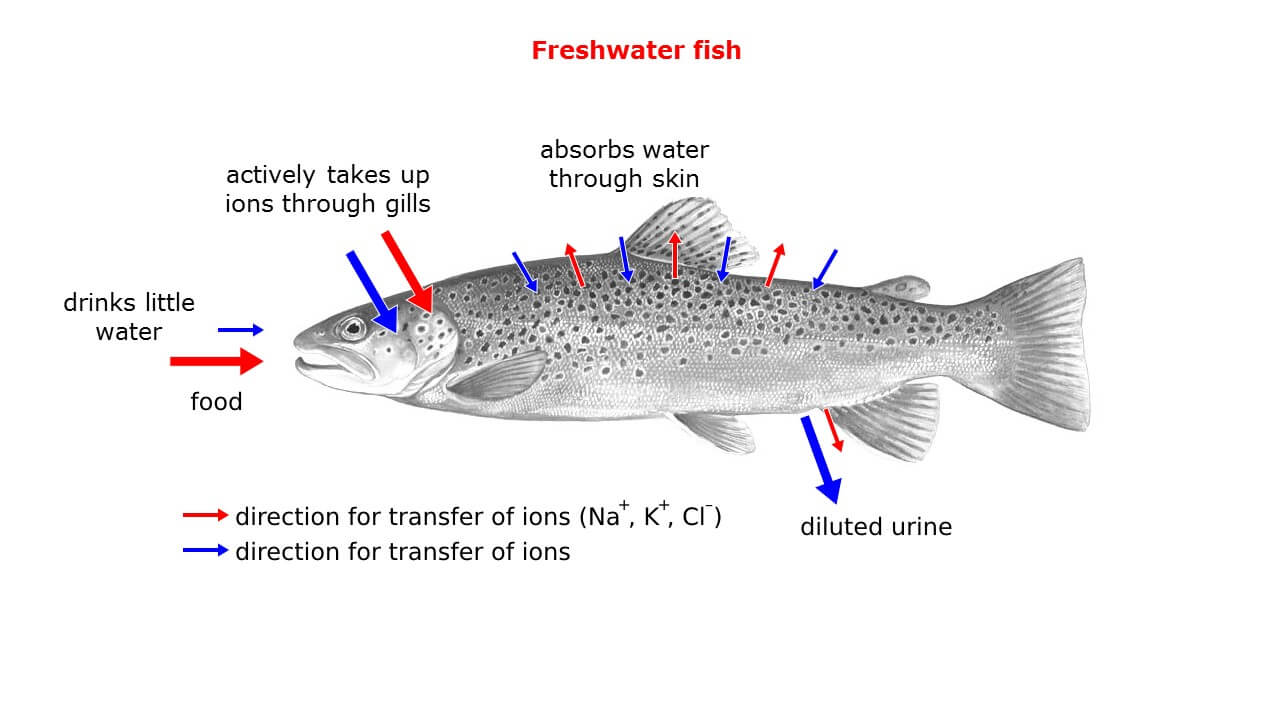
How do freshwater fish osmoregulate?
Freshwater - Low osmolarity (hypotonic) environment
Get rid of excess water by producing lots of urine, drink very little
Lost electrolytes from diffusion are absorbed back into the body through the gills
Gills have a protein that moves electrolytes by active transport
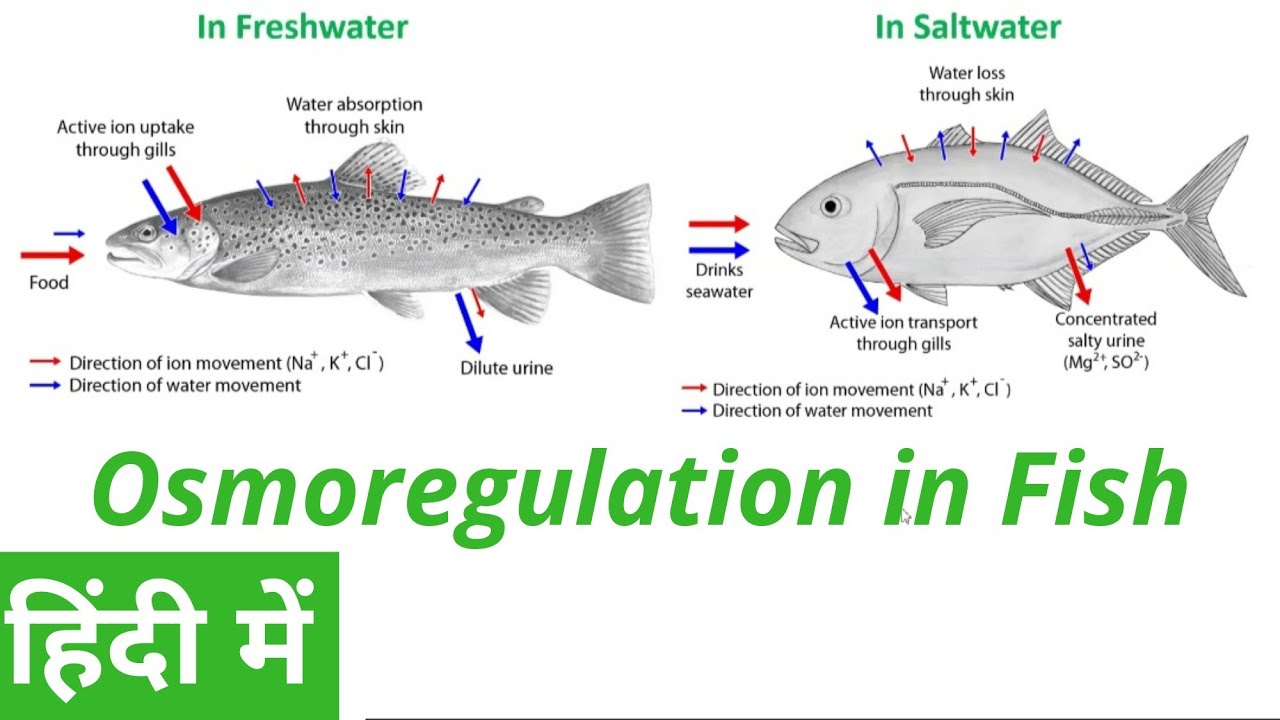
How are fish that are able to live in both marine and freshwater environments are able to osmoregulate in both types?
They are able to swap the location of their active transporter (what moves the electrolytes)
Marine is located on the inside of the gill cells
Electrolytes pushed out into water
Freshwater is located on the outside of the gill cells
Electrolytes pulled in from water
What are the different osmotic stresses and imbalances (water and electrolyte losses/gains) in terrestrial animals?
Water Loss
Evaporation from respiratory surfaces (ex. lungs) during breathing
Evaporation from body surface exposure to air
Electrolyte Loss
Freshwater sources are hypotonic, so electrolytes are lost in the gut by drinking
Electrolytes lost in urine
What is retention?
The act of absorbing a substance back into the body before it’s excreted
What is filtration?
Separating the water-based fluid of the body from cells and other large molecules
What is reabsorbtion?
Selectively absorbing the parts of the filtered material that we want to retain
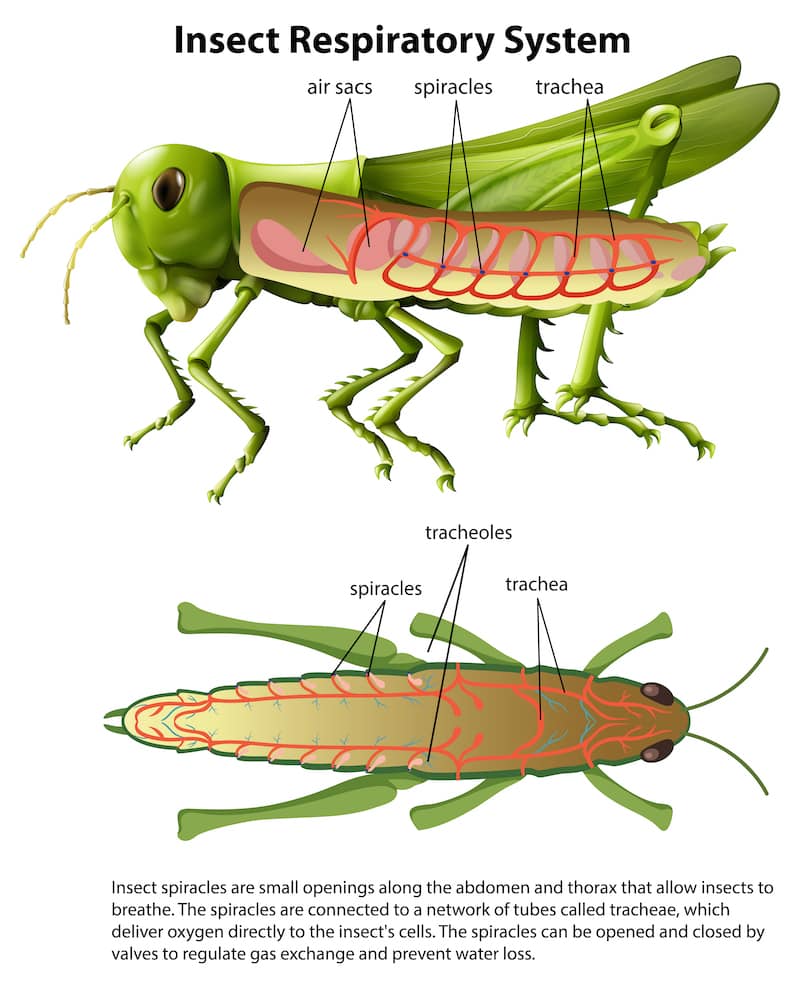
How do insects prevent water loss?
Minimize loss of water:
Insects have a thick exoskeleton that is coated in hydrophobic wax
Chitin minimizes diffusion
Wax layer blocks evaporation of water from the body
Respiratory system can be closed
Respiratory openings (spiracles) can be closed by small muscles
Minimizes water loss from the respiratory system
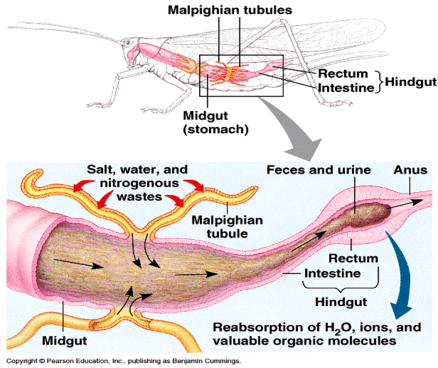
How do insects perform osmoregulation using the Malpighian tubules?
Malpighian tubules
“primitive kidneys”
Retention
In direct contact with the insects hemolymph (blood)
Removes only electrolytes, water, and waste products from the hemolymph by acting as a filter
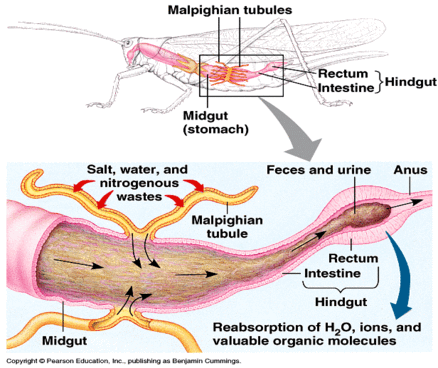
How do insects perform osmoregulation using the Hindgut?
Hindgut
Reabsorbs the amount of electrolytes and water that the insect must retain
Malpighian tubule is the filter, hindgut is the reabsorber
All waste products and any excess water or electrolytes are removed from the body in the feces