Topic 6: Plant Nutrition
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Remember to watch the Investigations!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Define photosynthesis.
The process by which plants synthesize carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light.
State the word equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen in the presence of light and chlorophyll.
What is chlorophyll?
A green pigment that is found in chloroplasts within plant cells.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
It absorbs light energy; it transfers energy from light into chemical energy, for the synthesis of carbohydrates, such as glucose.
How do plants store the carbohydrates made in photosynthesis for future use?
They convert it into starch molecules which act as an effective energy store.
How can carbohydrates be used to strengthen the plant?
They can be converted into cellulose to build cell walls.
How can be carbohydrates be used to give the plant energy?
Glucose can be used in respiration to provide energy.
How can carbohydrates help transfer materials around the plant?
It can be converted to sucrose for transport in the phloem.
What is the role of carbohydrates in attracting insects to flowers?
It can be used as nectar to attract insects for pollination.
Why are nitrate ions important for plants?
They make amino acids, which make proteins. Proteins are needed to help the plant grow.
Why is magnesium ions important for plants?
They make chlorophyll.
What is the deficiency of nitrate ions for plants?
Plants will have stunted growth.
What is the deficiency of magnesium ions for plants?
Plants will get yellow leaves.
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis in different environmental conditions?
The rate of photosynthesis is affected by three main limiting factors: light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
In low light conditions, light is the limiting factor because less energy is available to drive the reactions in photosynthesis. In an environment with low carbon dioxide levels, the plant cannot make enough glucose, so carbon dioxide becomes the limiting factor. If the temperature is too low, enzyme activity is reduced, slowing the rate of photosynthesis. If the temperature is too high, enzymes can become denatured and photosynthesis will decrease.
What is the chemical equation of photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
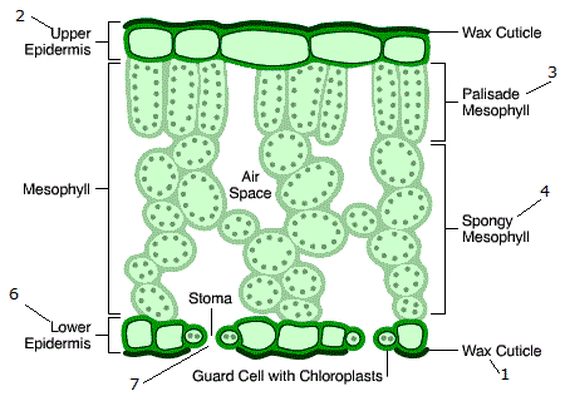
What are the two features of most leaves?
They have a large surface area and are thin.
How is a large surface area an adaptation for the leaf?
It increases the rate of diffusion of carbon dioxide from the leaf & into the air and allows more light to be absorbed for photosynthesis.
How is the leaf being thin an adaptation?
Carbon dioxide can diffuse quickly to the palisade mesophyll cells and light can reach all cells easily, allowing them to photosynthesize.
What are the 3 factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Light Intensity, Carbon Dioxide Concentration, Temperature
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Since light energy is converted into chemical energy, the more light a plant receives, the faster the rate of photosynthesis. This trend will continue until some other factor required for photosynthesis prevents the rate from increasing further because it is now in short supply..
How does carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide is one of the raw materials required for photosynthesis. So, the more carbon dioxide that is present, the faster the reaction can occur.
How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
As temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis increases as the reaction is controlled by enzymes. However, as the reaction is controlled by enzymes, this trend only continues up to a certain temperature beyond which the enzymes begin to denature and the rate of reaction decreases.
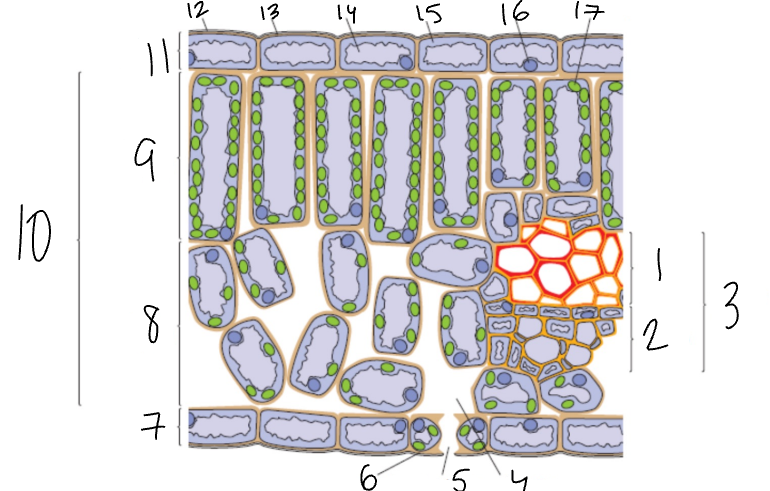
What is 1?
Xylem
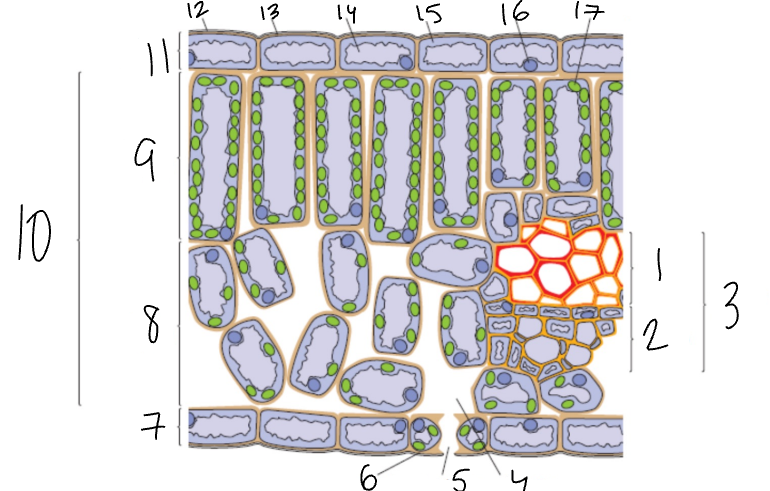
What is 2?
Phloem
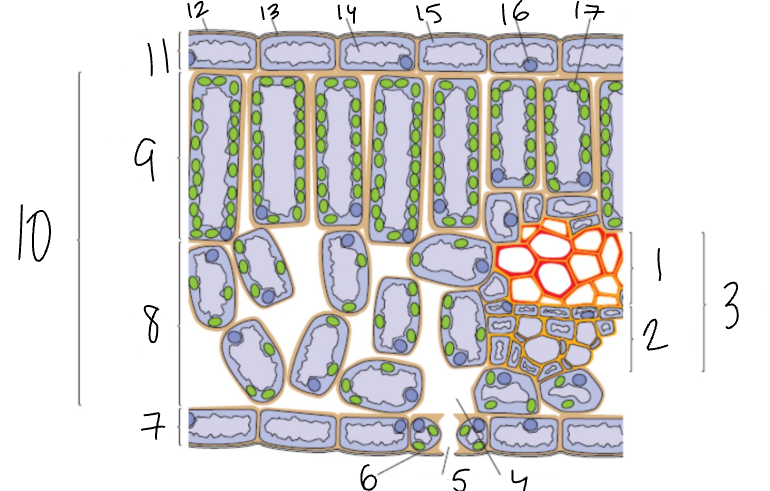
What is 3?
Vascular Bundle
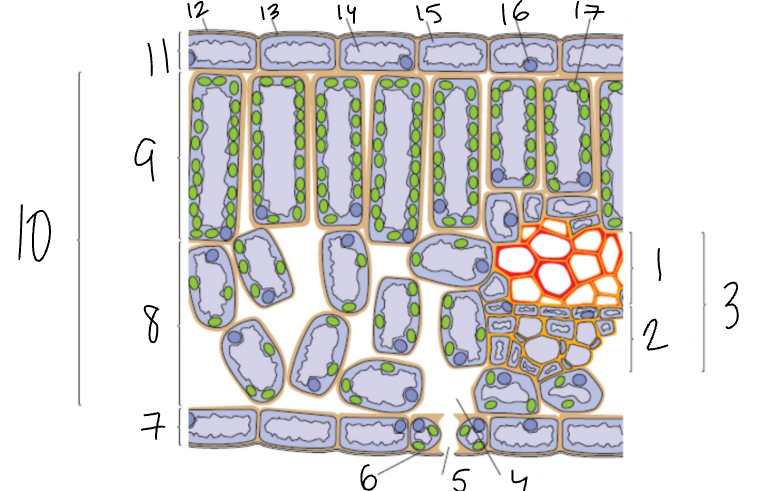
What is 4?
Air Space
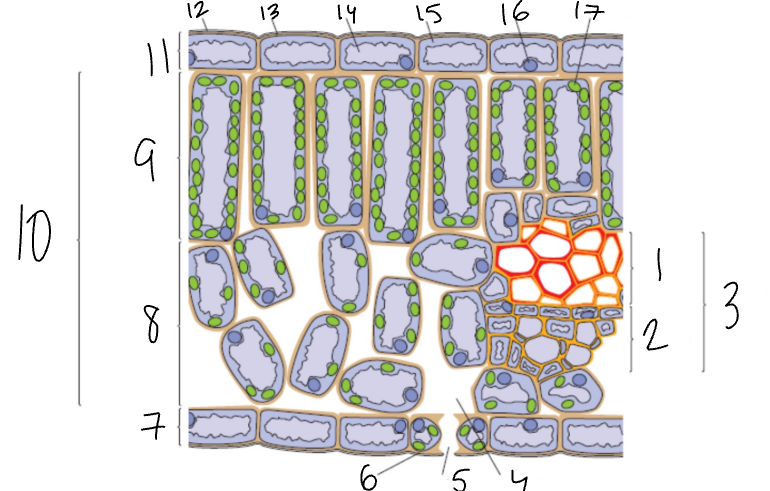
What is 5?
Stomata
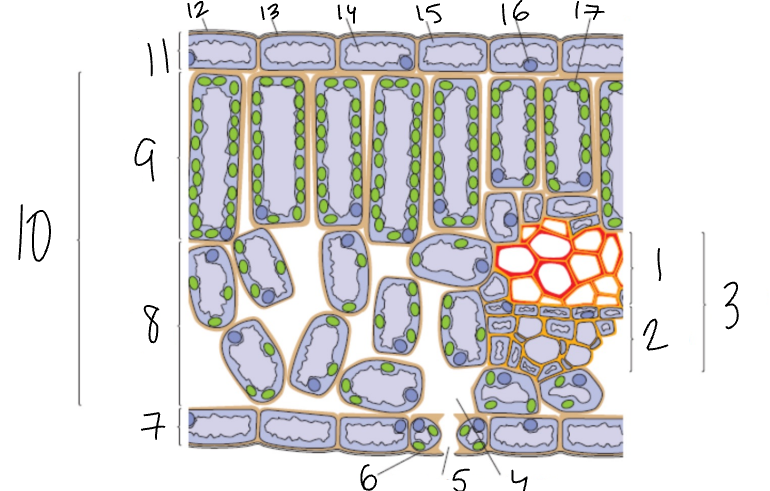
What is 6?
Guard Cell
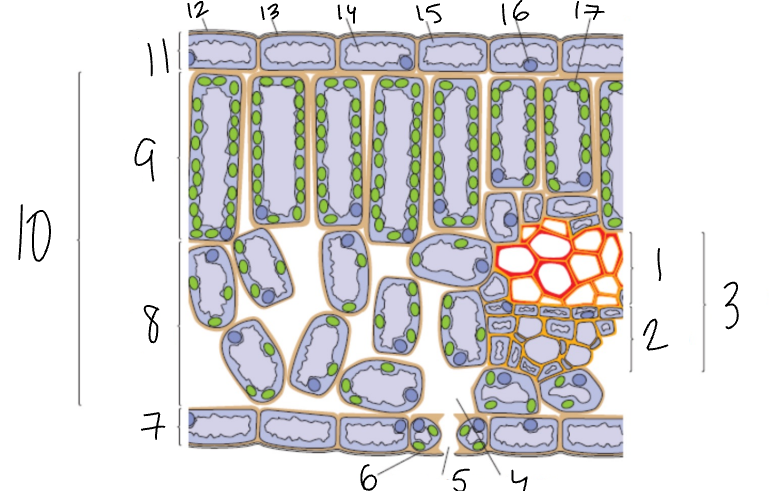
What is 7?
Lower Epidermis
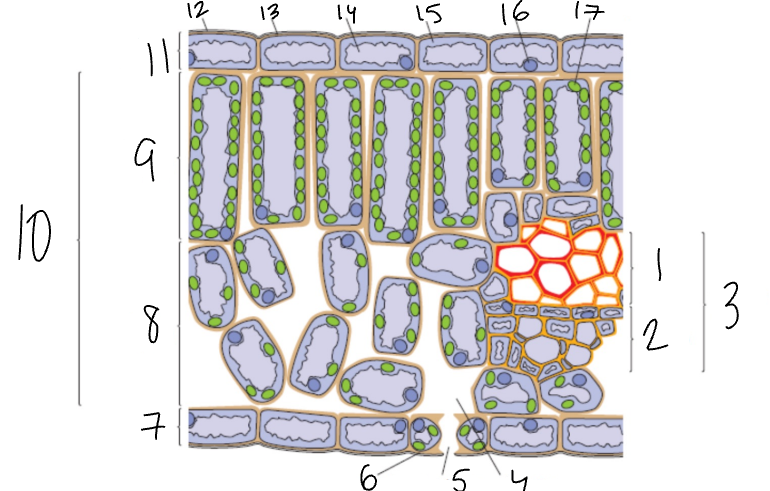
What is 8?
Spongy Mesophyll
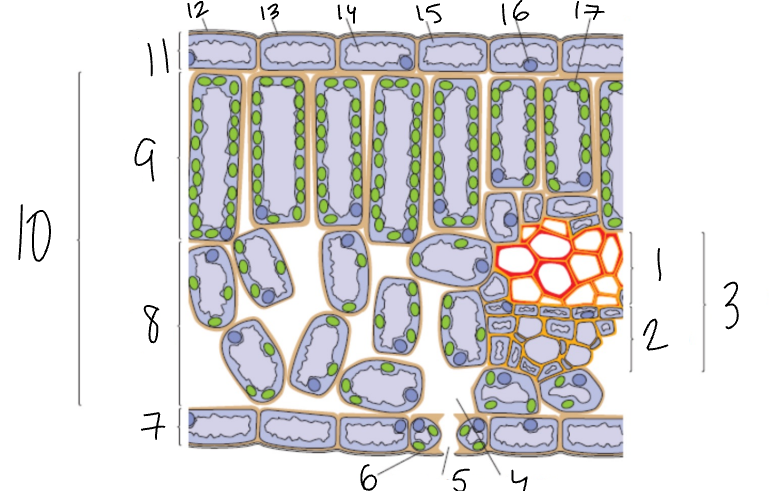
What is 9?
Palisade Mesophyll
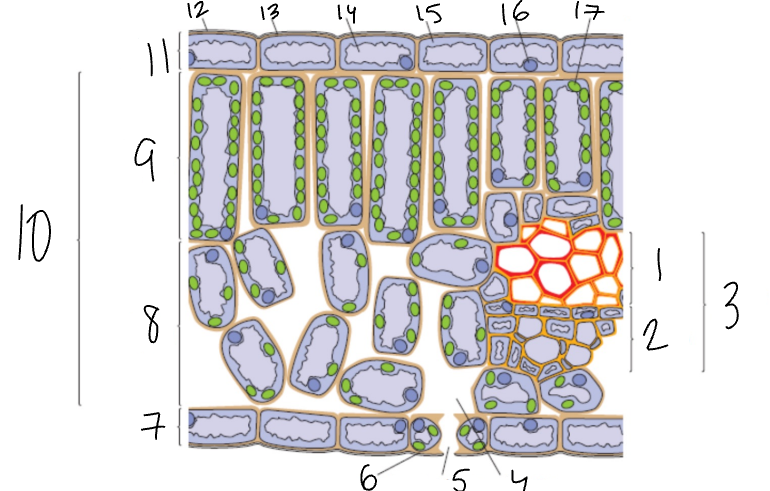
What is 11?
Upper Epidermis
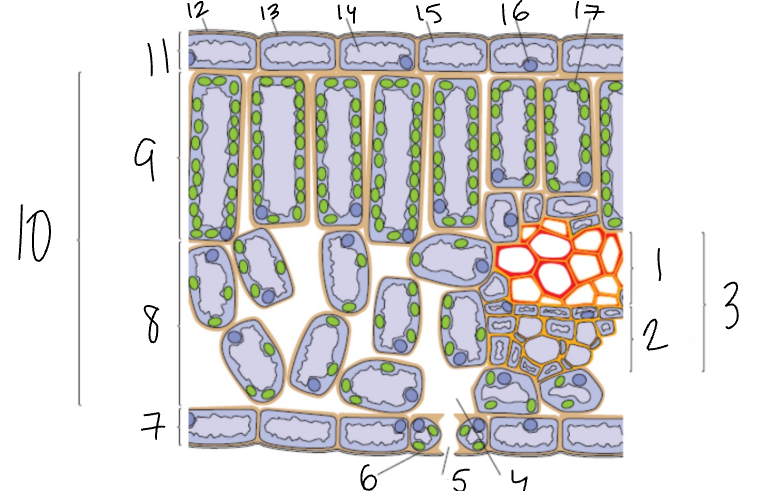
What is 12?
Wax Cuticle
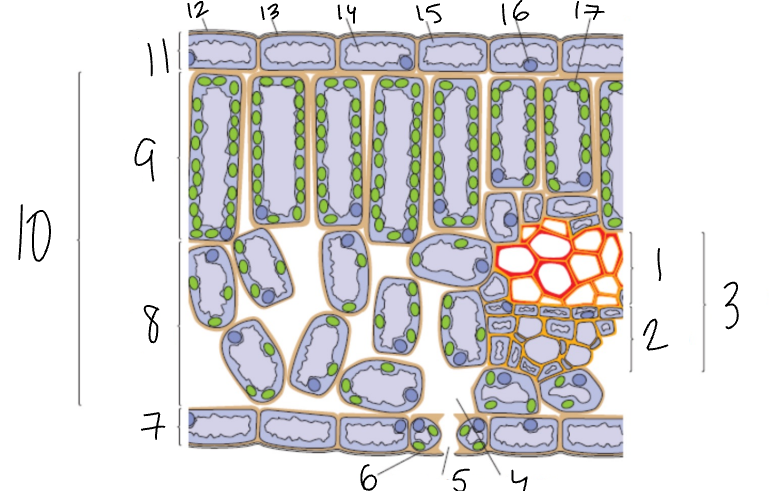
What is 17?
Chloroplast
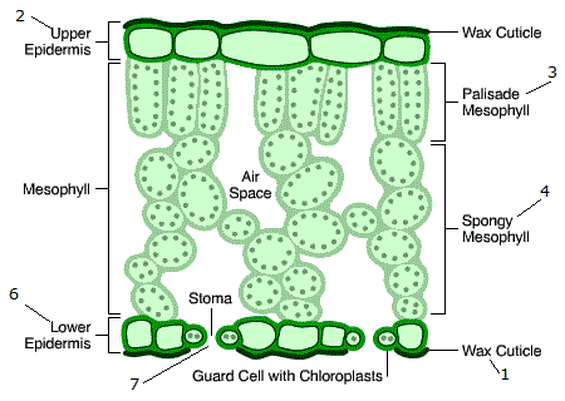
What is the structure of a wax cuticle?
It is a thin, transparent, waterproof, protective layer made of waxy substance on the top of the leaf. They prevent water from evaporating from the leaf.
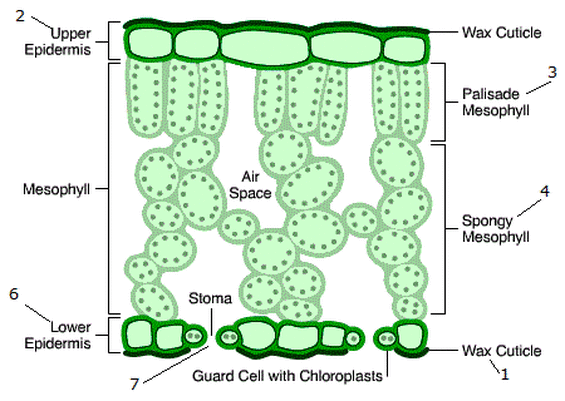
What is the structure of the upper epidermis?
It is a thin, single layer of flat, transparent cells found on the top surface of the leaf. It allows light to enter the palisade mesophyll cells.
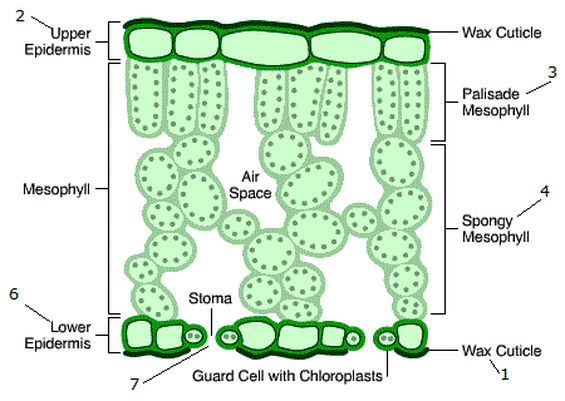
What is the structure of the palisade mesophyll cells?
They are tall, column shaped cells tightly packed with a huge amount of chloroplasts to absorb more light, maximizing photosynthesis.
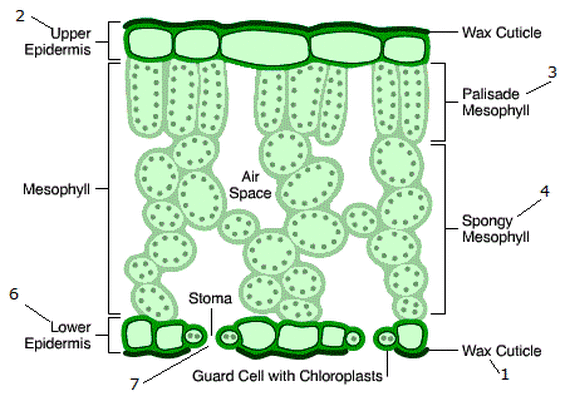
What is the structure of the spongy mesophyll cells?
They are are irregularly arranged mesophyll cells, containing internal air spaces that increases the surface area to volume ratio for the diffusion of gases, mainly carbon dioxide.
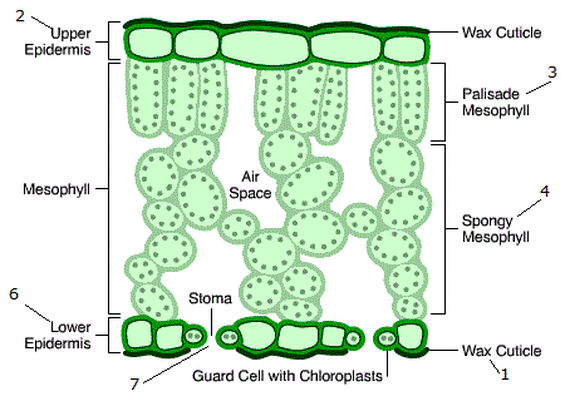
What is the structure of the lower epidermis?
It is a single layer of flat cells found on the underside of the leaf. It contains guard cells and the stomata.
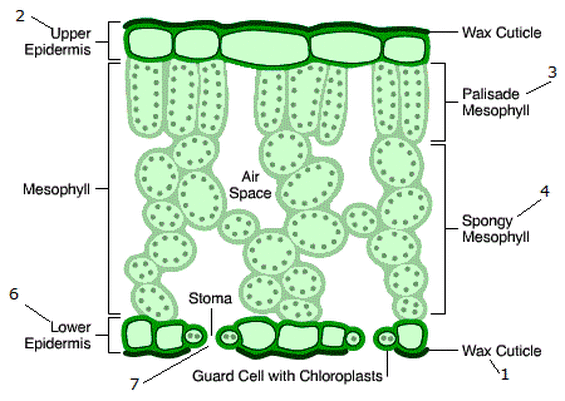
What is the structure of the guard cell?
They are specialized, curved cells found in pairs, surrounding each stoma on the surface of a leaf, mostly in the lower epidermis. It allows the stomata to open and close to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse in and oxygen to diffuse out.
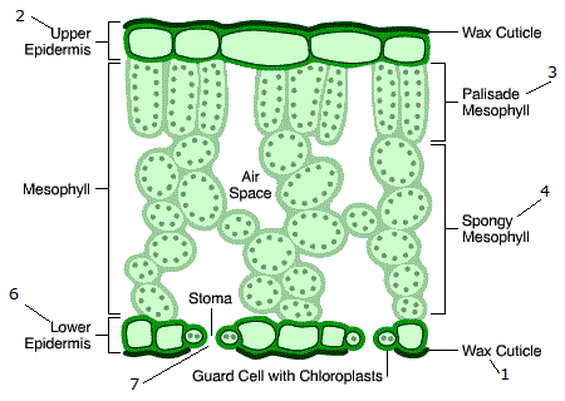
What is the structure of the stomata?
It is a tiny opening found mostly on the lower surface of the leaf, within the lower epidermis. It is where gas exchange takes place; opens during the day closes during the night. Water evaporation also happens here. They are in a greater concentration on the underside of the leaf to reduce water loss.
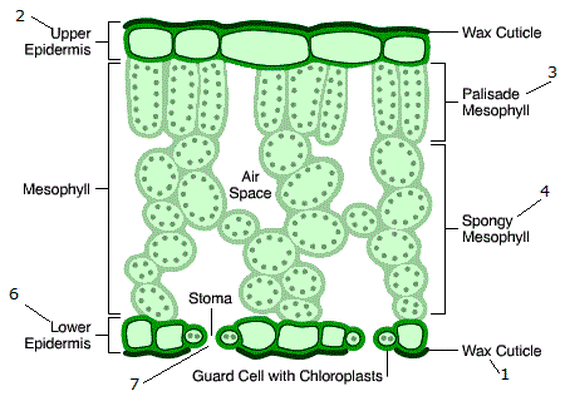
What is the structure of the vascular bundle?
It is a transport system found in the leaf veins and contains two main types of tissues: xylem and phloem. They transport substances to and from the leaf.
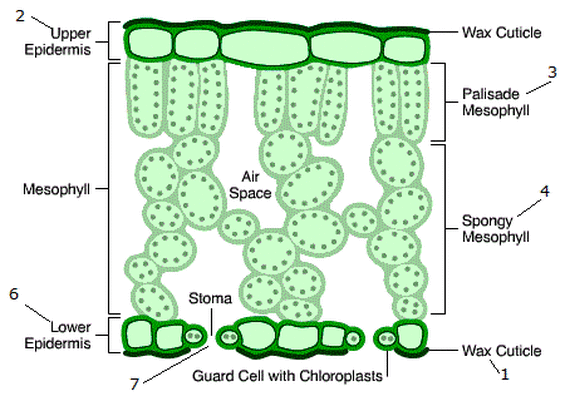
What is the structure of the xylem?
It is made up of dead, hollow cells that are joined end to end to form long, continuous tubes. The walls of xylem vessels are strengthened with a tough, waterproof substance called lignin. They transport water into the leaf for mesophyll cells to use in photosynthesis and for transpiration from the stomata.
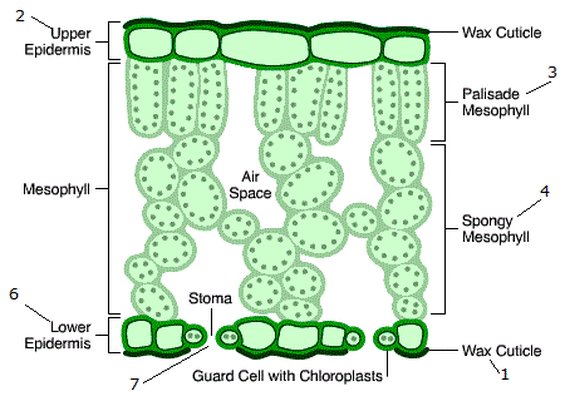
What is the structure of the phloem?
It is made up of living cells arranged in tubes. They transport sucrose and amino acids around the plant.
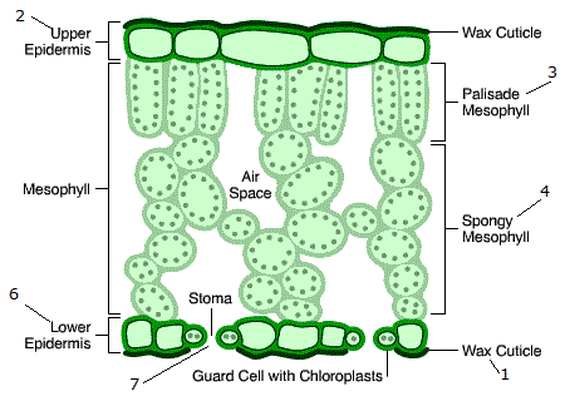
What is the structure of chloroplasts?
They are small green, oval-shaped structures inside palisade and some spongy mesophyll cells. They contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
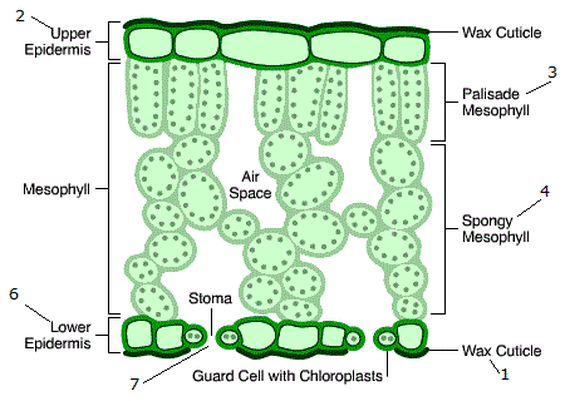
What is the structure of air spaces?
They are white or empty-looking gaps between spongy mesophyll cells. They allow for gas exchange (CO₂ in, O₂ out).
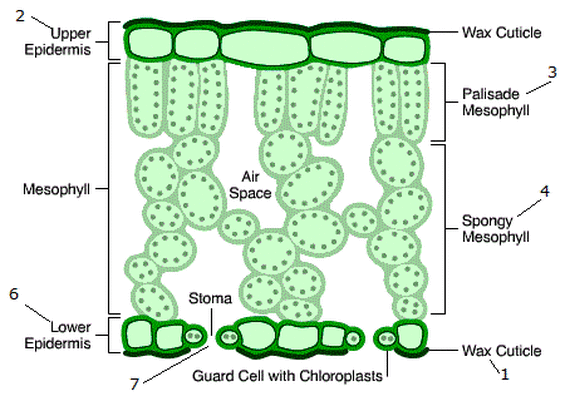
What are the structural adaptations of chloroplasts?
They contain chlorophyll, which captures light energy needed to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, allowing photosynthesis to take place.
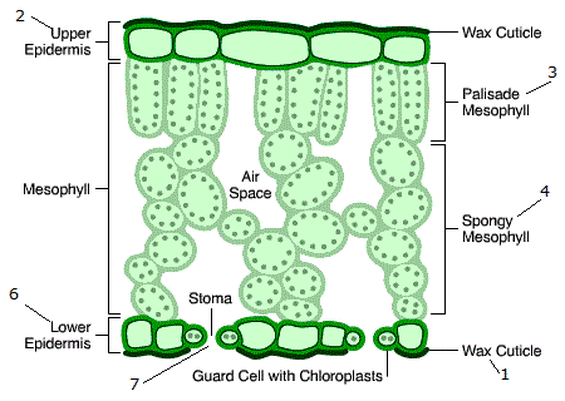
What are the structural adaptations of the cuticle?
Its waxy, waterproof layer that helps protect the leaf, preventing water loss without blocking light, allowing light to enter while keeping the leaf from drying out.
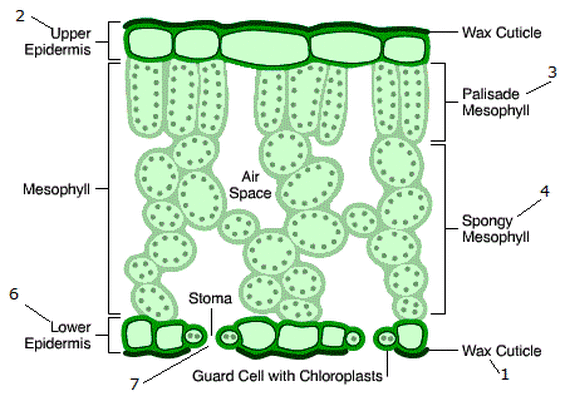
What are the structural adaptations of the guard cells?
They are bean-shaped and contain chloroplasts. Their shape changes to open or close the stoma, which helps regulate gas exchange and water loss. By controlling when stomata open, guard cells ensure that carbon dioxide enters when it is needed for photosynthesis, especially during daylight.
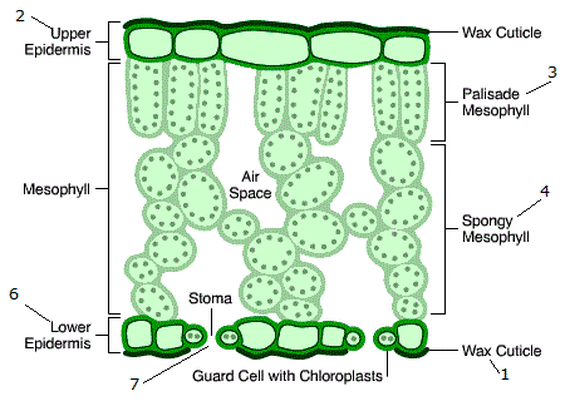
What are the structural adaptations of the stomata?
They’re tiny openings allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen to diffuse out.
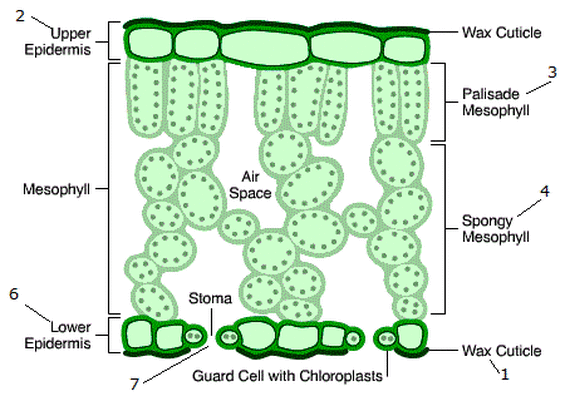
What are the structural adaptations of the epidermis?
They are thin and transparent to allow light to reach the palisade mesophyll cells.
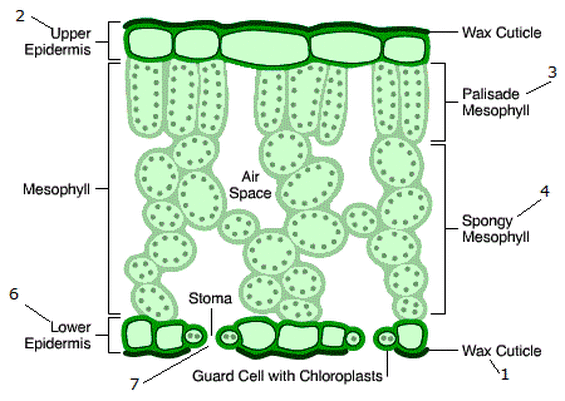
What are the structural adaptations of the palisade mesophyll cells?
They are at the top of the leaf, so they can absorb as much sunlight as possible for the chloroplasts.
They are tightly packed together to absorb as much light as possible.
They contain many chloroplasts, maximizing photosynthesis.
Their shape and arrangement help maximize light absorption, making them the main site of photosynthesis in the leaf
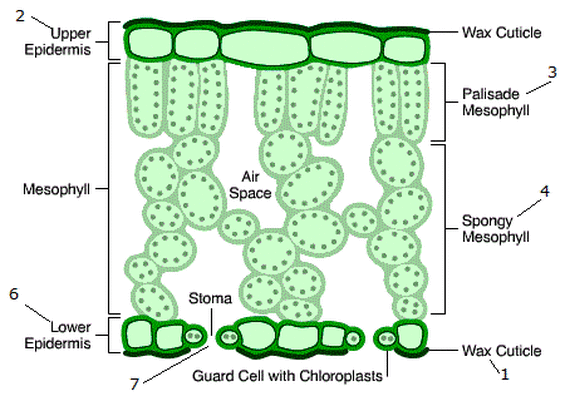
What are the structural adaptations of the spongy mesophyll cells?
They are irregularly shaped and are loosely packed with large air spaces between them. These cells are found beneath the palisade mesophyll. They contain fewer chloroplasts than palisade cells but can still carry out some photosynthesis. The air spaces allow for the easy diffusion of gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, in and out of the cells, increasing surface area.
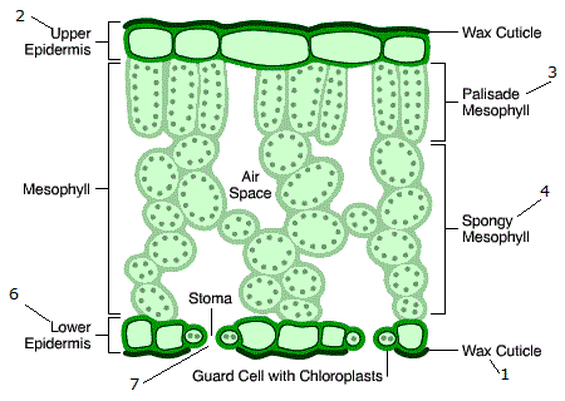
What are the structural adaptations of the vascular Bundle?
They have thick cell walls in the bundles to help support the leaf and stem.
What are the structural adaptations of the network of veins (vascular bundles)?
They allow water transport to the cells of the leaf and carbohydrates from the leaf for photosynthesis.